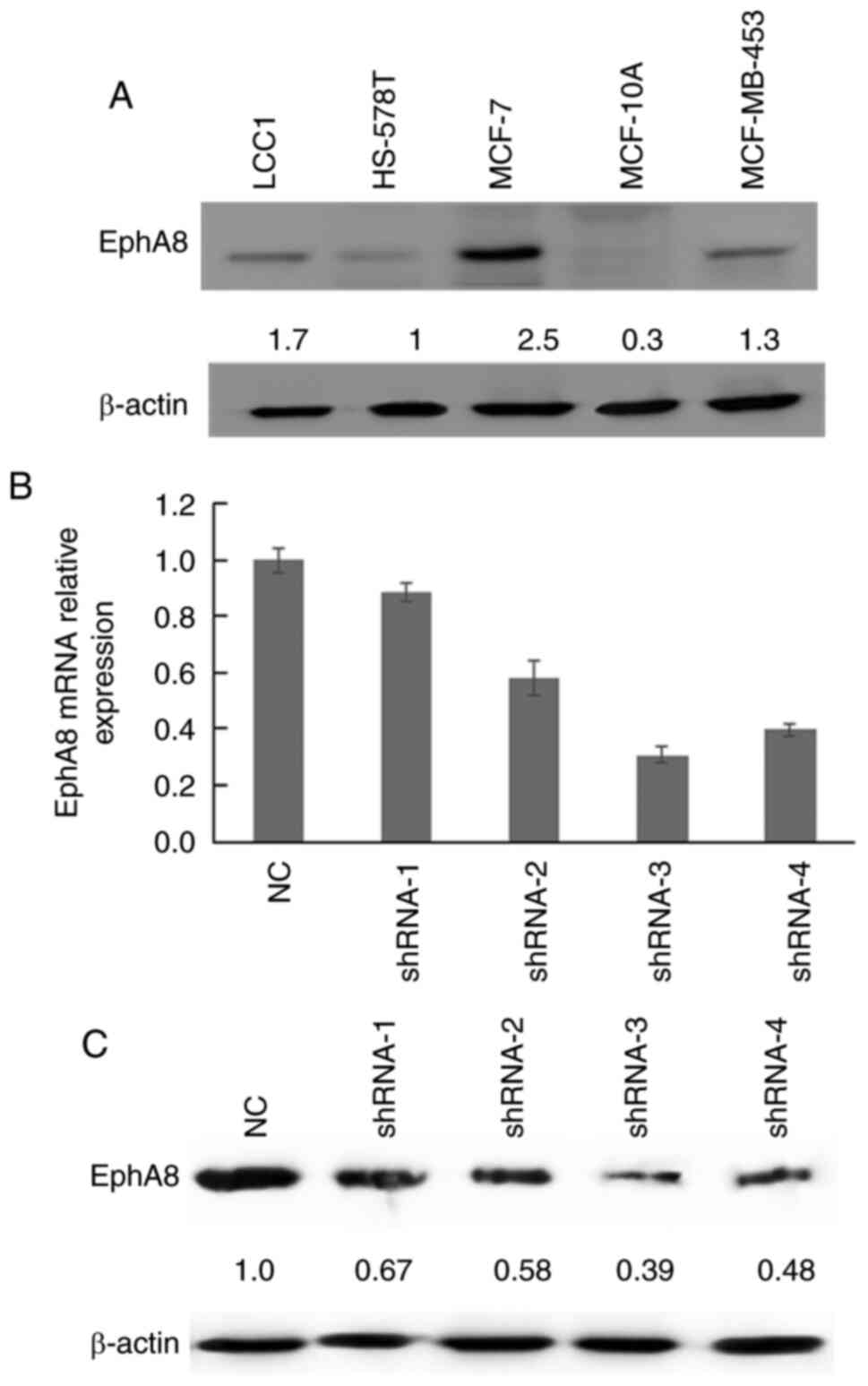
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. Feb 4–2021.(Epub ahead
of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Januškevičienė I and Petrikaite V:
Heterogeneity of breast cancer: The importance of interaction
between different tumor cell populations. Life Sci. 239:1170092019.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Koren S and Bentires-Alj M: Breast tumor
heterogeneity: Source of fitness, hurdle for therapy. Mol Cell.
60:537–546. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bratton MR, Duong BN, Elliott S, Weldon
CB, Beckman BS, McLachlan JA and Burow ME: Regulation of
ERalpha-mediated transcription of Bcl-2 by PI3K-AKT crosstalk:
Implications for breast cancer cell survival. Int J Oncol.
37:541–550. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lisabeth EM, Falivelli G and Pasquale EB:
Eph receptor signaling and ephrins. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
5:a0091592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Boyd AW, Bartlett PF and Lackmann M:
Therapeutic targeting of EPH receptors and their ligands. Nat Rev
Drug Discov. 13:39–62. 2014. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nikolov DB, Xu K and Himanen JP:
Eph/ephrin recognition and the role of Eph/ephrin clusters in
signaling initiation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1834:2160–2165. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Shiuan E and Chen J: Eph receptor tyrosine
kinases in tumor immunity. Cancer Res. 76:6452–6457. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Pasquale EB: Eph receptors and ephrins in
cancer: Bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer.
10:165–180. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hafner C, Schmitz G, Meyer S, Bataille F,
Hau P, Langmann T, Dietmaier W, Landthaler M and Vogt T:
Differential gene expression of Eph receptors and ephrins in benign
human tissues and cancers. Clin Chem. 50:490–499. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Nagano K, Maeda Y, Kanasaki S, Watanabe T,
Yamashita T, Inoue M, Higashisaka K, Yoshioka Y, Abe Y, Mukai Y, et
al: Ephrin receptor A10 is a promising drug target potentially
useful for breast cancers including triple negative breast cancers.
J Control Release. 189:72–79. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park S, Frisen J and Barbacid M: Aberrant
axonal projections in mice lacking EphA8 (Eek) tyrosine protein
kinase receptors. EMBO J. 16:3106–3114. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kandouz M: The Eph/Ephrin family in cancer
metastasis: Communication at the service of invasion. Cancer
Metastasis Rev. 31:353–373. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gu C and Park S: The EphA8 receptor
regulates integrin activity through p110gamma
phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase in a tyrosine kinase
activity-independent manner. Mol Cell Biol. 21:4579–4597. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kim Y, Park E, Noh H and Park S:
Expression of EphA8-Fc in transgenic mouse embryos induces
apoptosis of neural epithelial cells during brain development. Dev
Neurobiol. 73:702–712. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gu C, Shim S, Shin J, Kim J, Park J, Han K
and Park S: The EphA8 receptor induces sustained MAP kinase
activation to promote neurite outgrowth in neuronal cells.
Oncogene. 24:4243–4256. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Liu X, Xu Y, Jin Q, Wang W, Zhang S, Wang
X, Zhang Y, Xu X and Huang J: EphA8 is a prognostic marker for
epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncotarget. 7:20801–20809. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Murray S, Briasoulis E, Linardou H,
Bafaloukos D and Papadimitriou C: Taxane resistance in breast
cancer: Mechanisms, predictive biomarkers and circumvention
strategies. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:890–903. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Coradini D, Biganzoli E, Ardoino I,
Ambrogi F, Boracchi P, Demicheli R, Daidone MG and Moliterni A: p53
status identifies triple-negative breast cancer patients who do not
respond to adjuvant chemotherapy. Breast. 24:294–297. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Youngblood VM, Kim LC, Edwards DN, Hwang
Y, Santapuram PR, Stirdivant SM, Lu P, Ye F, Brantley-Sieders DM
and Chen J: The Ephrin-A1/EPHA2 signaling axis regulates glutamine
metabolism in HER2-positive breast cancer. Cancer Res.
76:1825–1836. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lodola A, Giorgio C, Incerti M, Zanotti I
and Tognolini M: Targeting Eph/ephrin system in cancer therapy. Eur
J Med Chem. 142:152–162. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gu C and Park S: The p110 gamma PI-3
kinase is required for EphA8-stimulated cell migration. FEBS Lett.
540:65–70. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chen J, Song W and Amato K: Eph receptor
tyrosine kinases in cancer stem cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
26:1–6. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Vaught D, Brantley-Sieders DM and Chen J:
Eph receptors in breast cancer: Roles in tumor promotion and tumor
suppression. Breast Cancer Res. 10:2172008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Mathot L, Kundu S, Ljungstrom V, Svedlund
J, Moens L, Adlerteg T, Falk-Sörqvist E, Rendo V, Bellomo C,
Mayrhofer M, et al: Somatic ephrin receptor mutations are
associated with metastasis in primary colorectal cancer. Cancer
Res. 77:1730–1740. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhuang G, Brantley-Sieders DM, Vaught D,
Yu J, Xie L, Wells S, Jackson D, Muraoka-Cook R, Arteaga C and Chen
J: Elevation of receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 mediates resistance
to trastuzumab therapy. Cancer Res. 70:299–308. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kumar SR, Singh J, Xia G, Krasnoperov V,
Hassanieh L, Ley EJ, Scehnet J, Kumar NG, Hawes D, Press MF, et al:
Receptor tyrosine kinase EphB4 is a survival factor in breast
cancer. Am J Pathol. 169:279–293. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Noren NK, Foos G, Hauser CA and Pasquale
EB: The EphB4 receptor suppresses breast cancer cell tumorigenicity
through an Abl-Crk pathway. Nat Cell Biol. 8:815–825. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Choudhary GS, Al-Harbi S, Mazumder S, Hill
BT, Smith MR, Bodo J, His ED and Almasan A: MCL-1 and
BCL-xL-dependent resistance to the BCL-2 inhibitor ABT-199 can be
overcome by preventing PI3K/AKT/mTOR activation in lymphoid
malignancies. Cell Death Dis. 6:e15932015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bernardi MP, Ngan SY, Michael M, Lynch AC,
Heriot AG, Ramsay RG and Phillips WA: Molecular biology of anal
squamous cell carcinoma: Implications for future research and
clinical intervention. Lancet Oncol. 16:e611–e621. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dey N, De P and Leyland-Jones B:
PI3K-AKT-mTOR inhibitors in breast cancers: From tumor cell
signaling to clinical trials. Pharmacol Ther. 175:91–106. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li JY, Xiao T, Yi HM, Yi H, Feng J, Zhu
JF, Huang W, Lu SS, Zhou YH, Li XH and Xiao ZQ: S897
phosphorylation of EphA2 is indispensable for EphA2-dependent
nasopharyngeal carcinoma cell invasion, metastasis and stem
properties. Cancer Lett. 444:162–174. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Lucero M, Thind J, Sandoval J, Senaati S,
Jimenez B and Kandpal RP: Stem-like cells from invasive breast
carcinoma cell line MDA-MB-231 express a distinct set of Eph
receptors and ephrin ligands. Cancer Genomics Proteomics.
17:729–738. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Camblin AJ, Pace EA, Adams S, Curley MD,
Rimkunas V, Nie L, Tan G, Bloom T, Iadevaia S, Baum J, et al: Dual
inhibition of IGF-1R and ErbB3 enhances the activity of gemcitabine
and nab-paclitaxel in preclinical models of pancreatic cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 24:2873–2885. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Lin YF, Tseng IJ, Kuo CJ, Lin HY, Chiu IJ
and Chiu HW: High-level expression of ARID1A predicts a favourable
outcome in triple-negative breast cancer patients receiving
paclitaxel-based chemotherapy. J Cell Mol Med. 22:2458–2468. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|