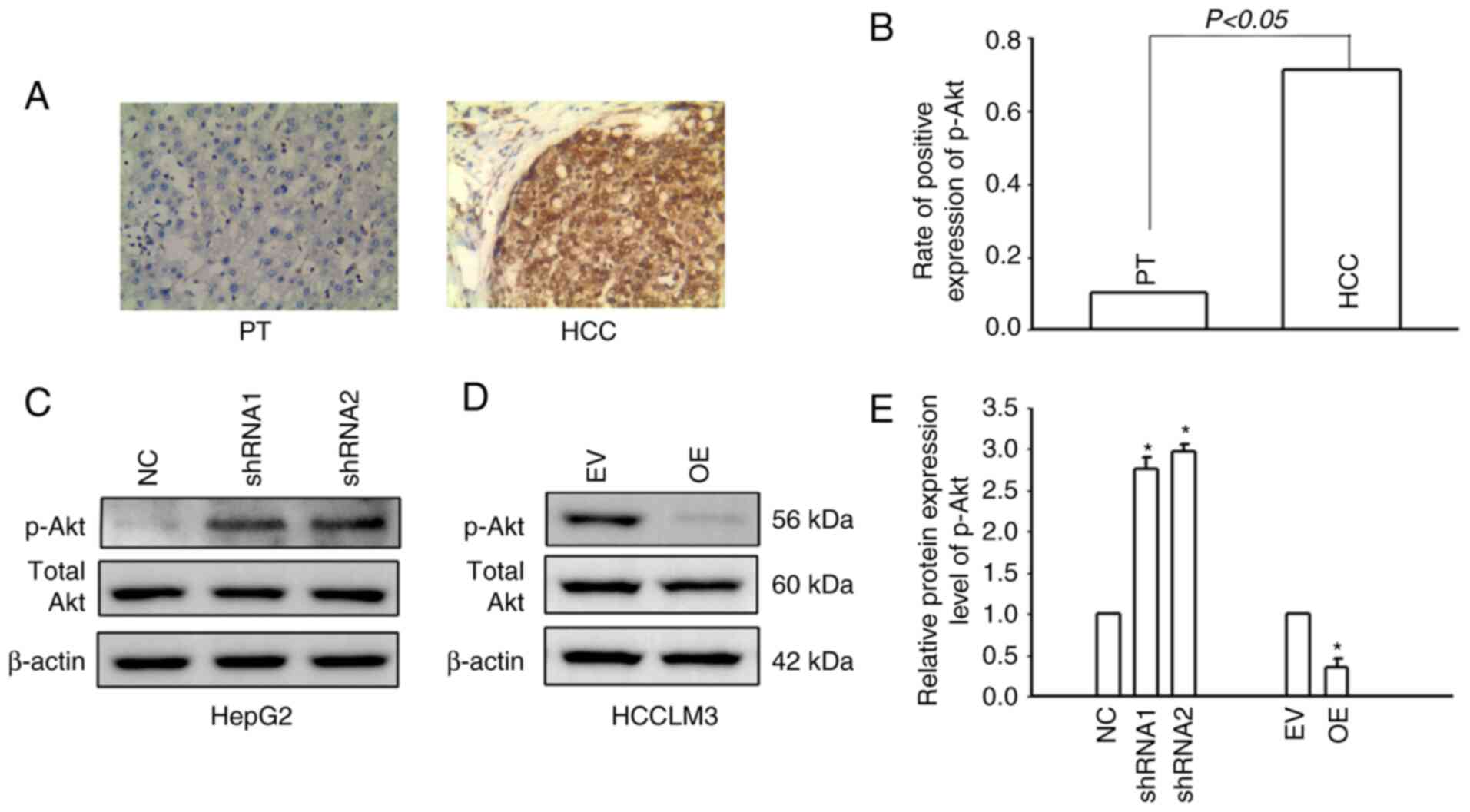
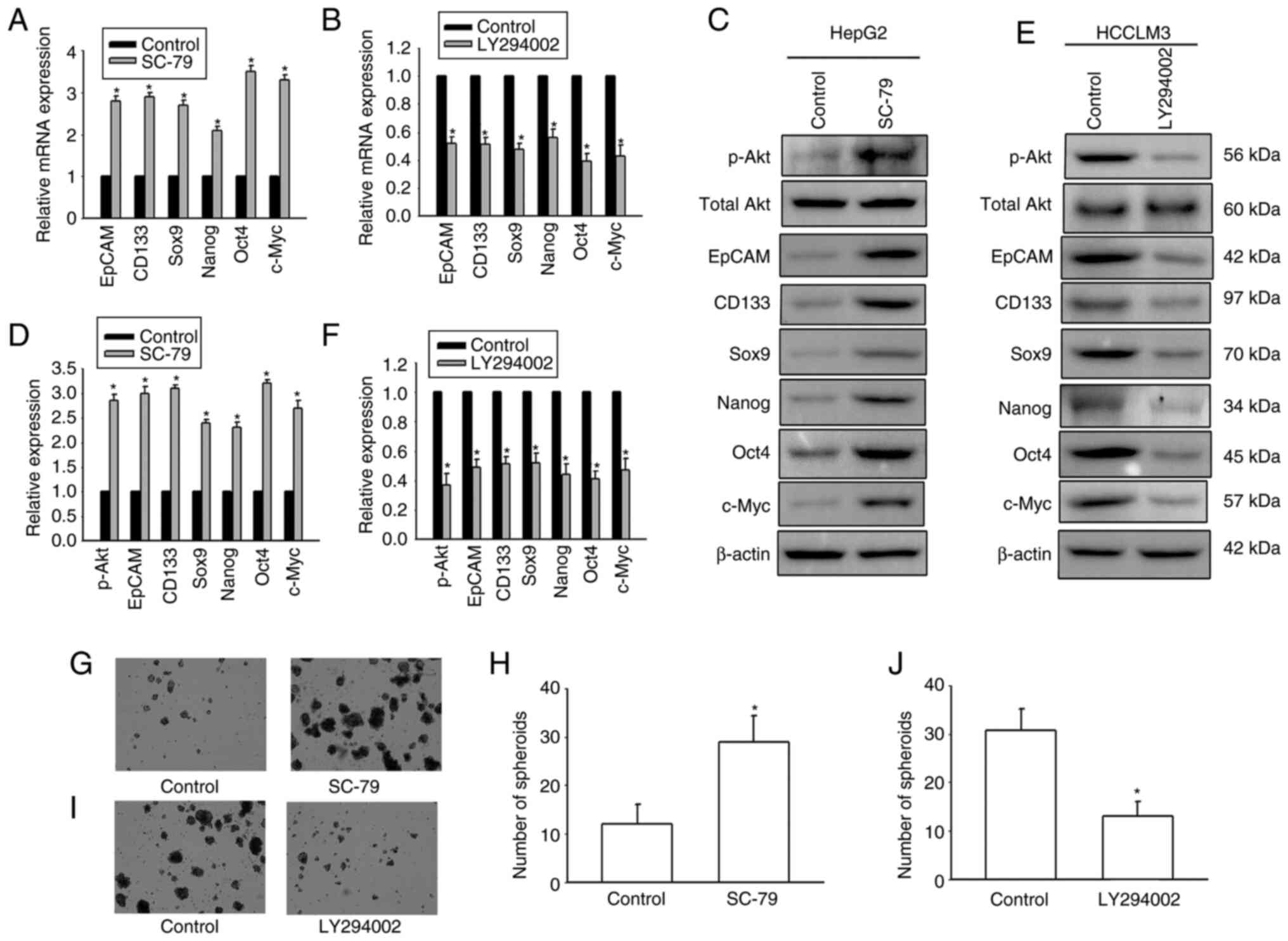
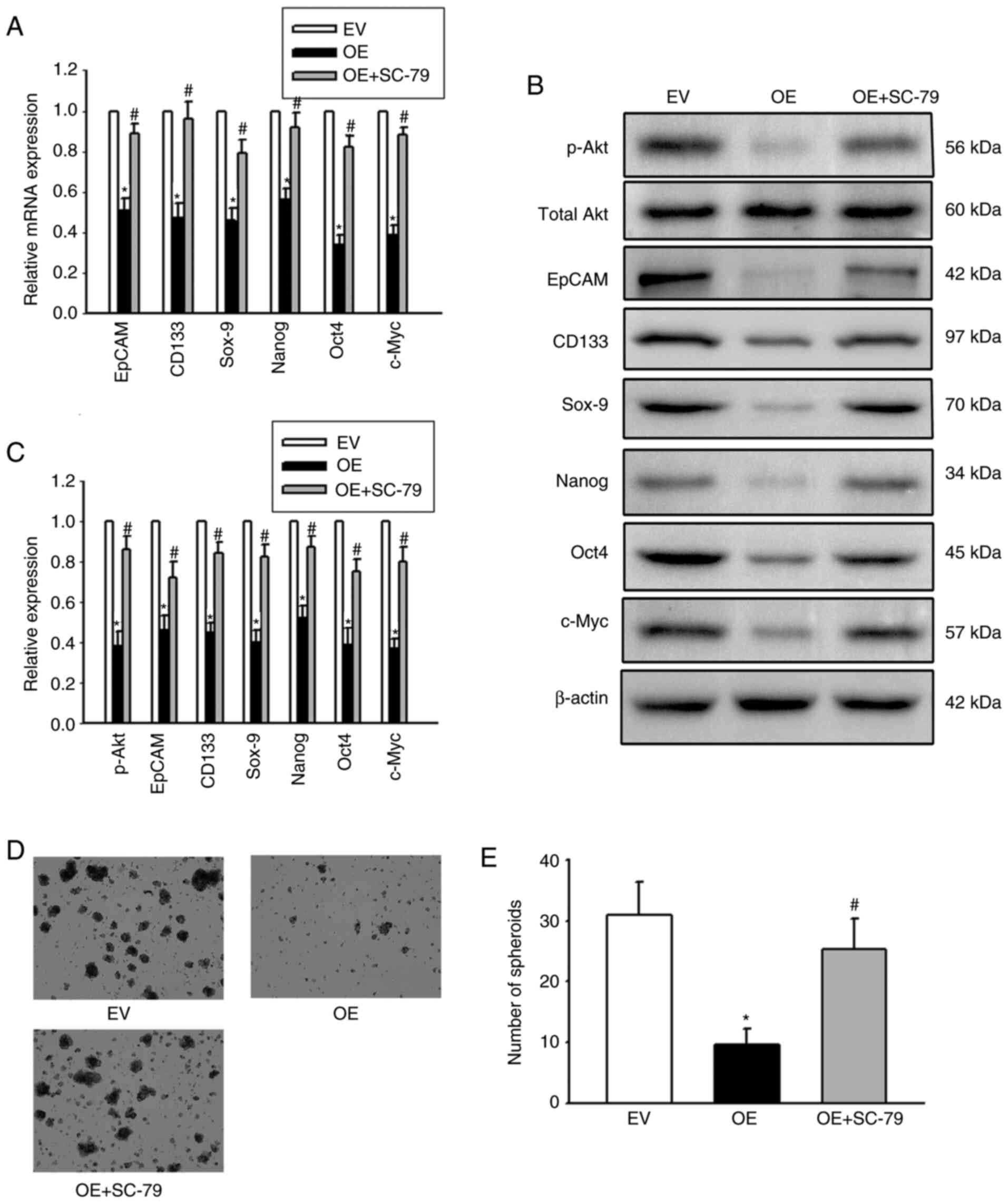
|
1
|
Llovet JM, Kelley RK, Villanueva A, Singal
AG, Pikarsky E, Roayaie S, Lencioni R, Koike K, Zucman-Rossi J and
Finn RS: Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 7:62021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
McGlynn KA, Petrick JL and El-Serag HB:
Epidemiology of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 73 (Suppl
1):S4–S13. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Liu YC, Yeh CT and Lin KH: Cancer stem
cell functions in hepatocellular carcinoma and comprehensive
therapeutic strategies. Cells. 9:13312020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pinheiro PS, Medina HN, Callahan KE, Jones
PD, Brown CP, Altekruse SF, McGlynn KA and Kobetz EN: The
association between etiology of hepatocellular carcinoma and
race-ethnicity in Florida. Liver Int. 40:1201–1210. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yang A, Ju W, Yuan X, Han M, Wang X, Guo
Z, Wei X, Wang D, Zhu X, Wu L and He X: Comparison between liver
resection and liver transplantation on outcomes in patients with
solitary hepatocellular carcinoma meeting UNOS criteria: A
population-based study of the SEER database. Oncotarget.
8:97428–97438. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou G, Latchoumanin O, Bagdesar M,
Hebbard L, Duan W, Liddle C, George J and Qiao L: Aptamer-based
therapeutic approaches to target cancer stem cells. Theranostics.
7:3948–3961. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lan X, Wu YZ, Wang Y, Wu FR, Zang CB, Tang
C, Cao S and Li SL: CD133 silencing inhibits stemness properties
and enhances chemoradiosensitivity in CD133-positive liver cancer
stem cells. Int J Mol Med. 31:315–324. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Karagonlar ZF, Akbari S, Karabicici M,
Sahin E, Avci ST, Ersoy N, Ates KE, Balli T, Karacicek B, Kaplan
KN, et al: A novel function for KLF4 in modulating the
de-differentiation of EpCAM−/CD133-nonStem Cells into
EpCAM+/CD133+ liver cancer stem cells in HCC
cell line HuH7. Cells. 9:11982020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ma XL, Hu B, Tang WG, Xie SH, Ren N, Guo L
and Lu RQ: CD73 sustained cancer-stem-cell traits by promoting SOX9
expression and stability in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hematol
Oncol. 13:112020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Jang JW, Song Y, Kim SH, Kim JS, Kim KM,
Choi EK, Kim J and Seo HR: CD133 confers cancer stem-like cell
properties by stabilizing EGFR-AKT signaling in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 389:1–10. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Deng Y, Li M, Zhuo M, Guo P, Chen Q, Mo P,
Li W and Yu C: Histone demethylase JMJD2D promotes the self-renewal
of liver cancer stem-like cells by enhancing EpCAM and Sox9
expression. J Biol Chem. 296:1001212021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Huang B, Yan X and Li Y: Cancer stem cell
for tumor therapy. Cancers (Basel). 13:48142021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu JI and Wang LH: Emerging roles of gap
junction proteins connexins in cancer metastasis, chemoresistance
and clinical application. J Biomed Sci. 26:82019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nakashima Y, Ono T, Yamanoi A, El-Assal
ON, Kohno H and Nagasue N: Expression of gap junction protein
connexin32 in chronic hepatitis, liver cirrhosis, and
hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 39:763–768. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yu M, Han G, Qi B and Wu X: Cx32 reverses
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in doxorubicin-resistant
hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep. 37:2121–2128. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu M, Zou Q, Wu X, Han G and Tong X:
Connexin 32 affects doxorubicin resistance in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells mediated by Src/FAK signaling pathway. Biomed
Pharmacother. 95:1844–1852. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Trosko JE: Cancer prevention and therapy
of two types of gap junctional intercellular
communication-deficient ‘cancer stem cell’. Cancers (Basel).
11:872019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang J, Nie J, Ma X, Wei Y, Peng Y and Wei
X: Targeting PI3K in cancer: Mechanisms and advances in clinical
trials. Mol Cancer. 18:262019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sun S, Xue D, Chen Z, Ou-Yang Y, Zhang J,
Mai J, Gu J, Lu W, Liu X, Liu W, et al: R406 elicits anti-Warburg
effect via Syk-dependent and -independent mechanisms to trigger
apoptosis in glioma stem cells. Cell Death Dis. 10:3582019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mangiapane LR, Nicotra A, Turdo A,
Gaggianesi M, Bianca P, Di Franco S, Sardina DS, Veschi V, Signore
M, Beyes S, et al: PI3K-driven HER2 expression is a potential
therapeutic target in colorectal cancer stem cells. Gut.
71:119–128. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kahraman DC, Kahraman T and Cetin-Atalay
R: Targeting PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway identifies differential
expression and functional role of IL8 in liver cancer stem cell
enrichment. Mol Cancer Ther. 18:2146–2157. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang N, Wang S, Li MY, Hu BG, Liu LP, Yang
SL, Yang S, Gong Z, Lai PBS and Chen GG: Cancer stem cells in
hepatocellular carcinoma: An overview and promising therapeutic
strategies. Ther Adv Med Oncol. 10:17588359188162872018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Shibue T and Weinberg RA: EMT, CSCs, and
drug resistance: The mechanistic link and clinical implications.
Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 14:611–629. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tanabe S, Quader S, Cabral H and Ono R:
Interplay of EMT and CSC in cancer and the potential therapeutic
strategies. Front Pharmacol. 11:9042020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Weidenfeld K, Schif-Zuck S, Abu-Tayeh H,
Kang K, Kessler O, Weissmann M, Neufeld G and Barkan D: Dormant
tumor cells expressing LOXL2 acquire a stem-like phenotype
mediating their transition to proliferative growth. Oncotarget.
7:71362–71377. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kawasaki Y, Omori Y, Li Q, Nishikawa Y,
Yoshioka T, Yoshida M, Ishikawa K and Enomoto K: Cytoplasmic
accumulation of connexin32 expands cancer stem cell population in
human HuH7 hepatoma cells by enhancing its self-renewal. Int J
Cancer. 128:51–62. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Totland MZ, Rasmussen NL, Knudsen LM and
Leithe E: Regulation of gap junction intercellular communication by
connexin ubiquitination: Physiological and pathophysiological
implications. Cell Mol Life Sci. 77:573–591. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Jiang JX and Penuela S: Connexin and
pannexin channels in cancer. BMC Cell Biol. 17 (Suppl 1):S122016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Alaei SR, Abrams CK, Bulinski JC,
Hertzberg EL and Freidin MM: Acetylation of C-terminal lysines
modulates protein turnover and stability of Connexin-32. BMC Cell
Biol. 19:222018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bamodu OA, Chang HL, Ong JR, Lee WH, Yeh
CT and Tsai JT: Elevated PDK1 expression drives PI3K/AKT/mTOR
signaling promotes radiation-resistant and dedifferentiated
phenotype of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cells. 9:7462020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Deng J, Bai X, Feng X, Ni J, Beretov J,
Graham P and Li Y: Inhibition of PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway
alleviates ovarian cancer chemoresistance through reversing
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and decreasing cancer stem cell
marker expression. BMC Cancer. 19:6182019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu Y, Zhang J, Zhang X, Zhou H, Liu G and
Li Q: Cancer Stem Cells: A potential breakthrough in HCC-targeted
therapy. Front Pharmacol. 11:1982020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Xia P and Xu XY: PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling
pathway in cancer stem cells: From basic research to clinical
application. Am J Cancer Res. 5:1602–1609. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Erdogan S, Doganlar O, Doganlar ZB,
Serttas R, Turkekul K, Dibirdik I and Bilir A: The flavonoid
apigenin reduces prostate cancer CD44(+) stem cell survival and
migration through PI3K/Akt/NF-κB signaling. Life Sci. 162:77–86.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Park JH, Kim YH, Shim S, Kim A, Jang H,
Lee SJ, Park S, Seo S, Jang WI, Lee SB and Kim MJ:
Radiation-activated PI3K/AKT pathway promotes the induction of
cancer stem-like cells via the upregulation of SOX2 in colorectal
cancer. Cells. 10:1352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|