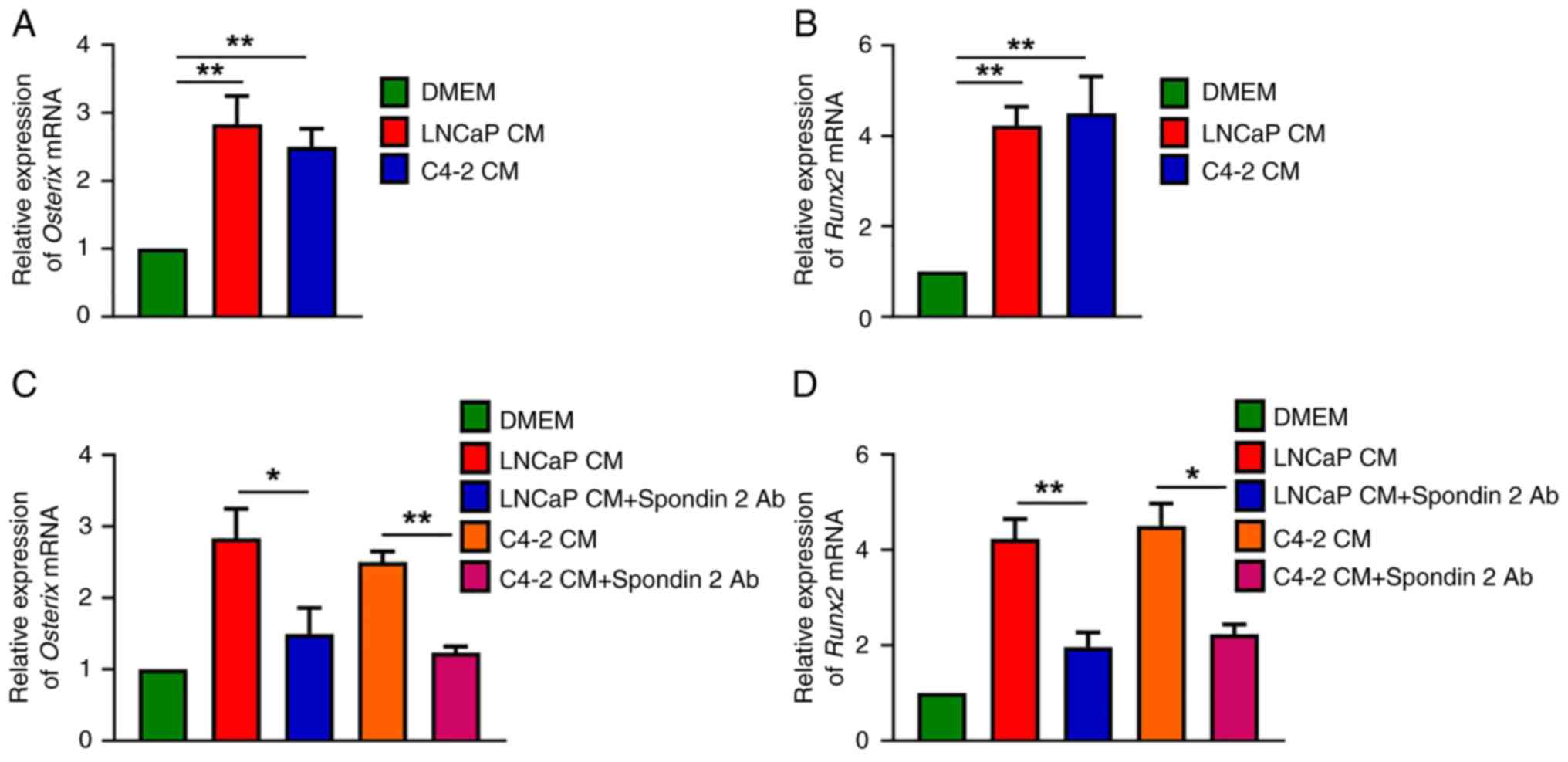
|
1
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Guise TA, Mohammad KS, Clines G, Stebbins
EG, Wong DH, Higgins LS, Vessella R, Corey E, Padalecki S, Suva L
and Chirgwin JM: Basic mechanisms responsible for osteolytic and
osteoblastic bone metastases. Clin Cancer Res. 12:6213s–6216s.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cornford P, van den Bergh RCN, Briers E,
Van den Broeck T, Cumberbatch MG, De Santis M, Fanti S, Fossati N,
Gandaglia G, Gillessen S, et al: EAU-EANM-ESTRO-ESUR-SIOG
guidelines on prostate cancer. Part II-2020 update: Treatment of
relapsing and metastatic prostate cancer. Eur Urol. 79:263–282.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Clezardin P, Coleman R, Puppo M, Ottewell
P, Bonnelye E, Paycha F, Confavreux CB and Holen I: Bone
metastasis: Mechanisms, therapies, and biomarkers. Physiol Rev.
101:797–855. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dayyani F, Varkaris A, Araujo JC, Song JH,
Chatterji T, Trudel GC, Logothetis CJ and Gallick GE: Increased
serum insulin-like growth factor-1 levels are associated with
prolonged response to dasatinib-based regimens in metastatic
prostate cancer. Prostate. 73:979–985. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhang C, Long F, Wan J, Hu Y and He H:
MicroRNA-205 acts as a tumor suppressor in osteosarcoma via
targeting RUNX2. Oncol Rep. 35:3275–3284. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jagga S, Sharma AR, Kim EJ and Nam JS:
Isoflavone-enriched whole soy milk powder stimulates osteoblast
differentiation. J Food Sci Technol. 58:595–603. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Choi YH, Han Y, Jin SW, Lee GH, Kim GS,
Lee DY, Chung YC, Lee KY and Jeong HG: Pseudoshikonin I enhances
osteoblast differentiation by stimulating Runx2 and Osterix. J Cell
Biochem. 119:748–757. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li Y, Cao C, Jia W, Yu L, Mo M, Wang Q,
Huang Y, Lim JM, Ishihara M, Wells L, et al: Structure of the
F-spondin domain of mindin, an integrin ligand and pattern
recognition molecule. EMBO J. 28:286–297. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Parry R, Schneider D, Hudson D, Parkes D,
Xuan JA, Newton A, Toy P, Lin R, Harkins R, Alicke B, et al:
Identification of a novel prostate tumor target, mindin/RG-1, for
antibody-based radiotherapy of prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
65:8397–8405. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qian X, Li C, Pang B, Xue M, Wang J and
Zhou J: Spondin-2 (SPON2), a more prostate-cancer-specific
diagnostic biomarker. PLoS One. 7:e372252012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang Q, Wang XQ, Wang J, Cui SJ, Lou XM,
Yan B, Qiao J, Jiang YH, Zhang LJ, Yang PY and Liu F: Upregulation
of spondin-2 predicts poor survival of colorectal carcinoma
patients. Oncotarget. 6:15095–15110. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Feng Y, Hu Y, Mao Q, Guo Y, Liu Y, Xue W
and Cheng S: Upregulation of spondin-2 protein expression
correlates with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Int
Med Res. 47:569–579. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Schmid F, Wang Q, Huska MR,
Andrade-Navarro MA, Lemm M, Fichtner I, Dahlmann M, Kobelt D,
Walther W, Smith J, et al: SPON2, a newly identified target gene of
MACC1, drives colorectal cancer metastasis in mice and is
prognostic for colorectal cancer patient survival. Oncogene.
35:5942–5952. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang C, Ou R, Chen X, Zhang Y, Li J,
Liang Y, Zhu X, Liu L, Li M, Lin D, et al: Tumor cell-derived SPON2
promotes M2-polarized tumor-associated macrophage infiltration and
cancer progression by activating PYK2 in CRC. J Exp Clin Cancer
Res. 40:3042021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang RS, Lin WL, Chen YZ, Tang CH, Huang
TH, Lu BY and Fu WM: Regulation by ultrasound treatment on the
integrin expression and differentiation of osteoblasts. Bone.
36:276–283. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ylitalo EB, Thysell E, Jernberg E,
Lundholm M, Crnalic S, Egevad L, Stattin P, Widmark A, Bergh A and
Wikström P: Subgroups of castration-resistant prostate cancer bone
metastases defined through an inverse relationship between androgen
receptor activity and immune response. Eur Urol. 71:776–787. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Vo BT, Morton D Jr, Komaragiri S, Millena
AC, Leath C and Khan SA: TGF-β effects on prostate cancer cell
migration and invasion are mediated by PGE2 through activation of
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Endocrinology. 154:1768–1779. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tan M, Xu J, Siddiqui J, Feng F and Sun Y:
Depletion of SAG/RBX2 E3 ubiquitin ligase suppresses prostate
tumorigenesis via inactivation of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR axis. Mol
Cancer. 15:812016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhang YL, Li Q, Yang XM, Fang F, Li J,
Wang YH, Yang Q, Zhu L, Nie HZ, Zhang XL, et al: SPON2 Promotes
M1-like macrophage recruitment and inhibits hepatocellular
carcinoma metastasis by distinct integrin-Rho GTPase-hippo
pathways. Cancer Res. 78:2305–2317. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Jiang W, Takeshita N, Maeda T, Sogi C,
Oyanagi T, Kimura S, Yoshida M, Sasaki K, Ito A and Takano-Yamamoto
T: Connective tissue growth factor promotes chemotaxis of
preosteoblasts through integrin α5 and Ras during tensile
force-induced intramembranous osteogenesis. Sci Rep. 11:23682021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bai G, Cai Z, Zhai X, Xiong J, Zhang F and
Li H: A new nomogram for the prediction of bone metastasis in
patients with prostate cancer. J Int Med Res.
49:30006052110583642021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Lee Y, Schwarz E, Davies M, Jo M, Gates J,
Wu J, Zhang X and Lieberman JR: Differences in the cytokine
profiles associated with prostate cancer cell induced osteoblastic
and osteolytic lesions in bone. J Orthop Res. 21:62–72. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boucher J, Balandre AC, Debant M, Vix J,
Harnois T, Bourmeyster N, Péraudeau E, Chépied A, Clarhaut J,
Debiais F, et al: Cx43 present at the leading edge membrane governs
promigratory effects of osteoblast-conditioned medium on human
prostate cancer cells in the context of bone metastasis. Cancers
(Basel). 12:30132020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rubin J, Fan X, Rahnert J, Sen B, Hsieh
CL, Murphy TC, Nanes MS, Horton LG, Beamer WG and Rosen CJ: IGF-I
secretion by prostate carcinoma cells does not alter tumor-bone
cell interactions in vitro or in vivo. Prostate. 66:789–800. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Tucci M, Mosca A, Lamanna G, Porpiglia F,
Terzolo M, Vana F, Cracco C, Russo L, Gorzegno G, Tampellini M, et
al: Prognostic significance of disordered calcium metabolism in
hormone-refractory prostate cancer patients with metastatic bone
disease. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis. 12:94–99. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Marie PJ: Targeting integrins to promote
bone formation and repair. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 9:288–295. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xu X, Zhang C, Trotter TN, Gowda PS, Lu Y,
Ponnazhagan S, Javed A, Li J and Yang Y: Runx2 deficiency in
osteoblasts promotes myeloma progression by altering the bone
microenvironment at new bone sites. Cancer Res. 80:1036–1048. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Liu Q, Li M, Wang S, Xiao Z, Xiong Y and
Wang G: Recent advances of osterix transcription factor in
osteoblast differentiation and bone formation. Front Cell Dev Biol.
8:6012242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Yuan G, Lian Z, Liu Q, Lin X, Xie D, Song
F, Wang X, Shao S, Zhou B, Li C, et al: Phosphatidyl inositol
3-kinase (PI3K)-mTOR inhibitor PKI-402 inhibits breast cancer
induced osteolysis. Cancer Lett. 443:135–144. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Zhu WB, Xiao N and Liu XJ: Dietary
flavonoid tangeretin induces reprogramming of epithelial to
mesenchymal transition in prostate cancer cells by targeting the
PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Oncol Lett. 15:433–440.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Le B, Powers GL, Tam YT, Schumacher N,
Malinowski RL, Steinke L, Kwon G and Marker PC: Multi-drug loaded
micelles delivering chemotherapy and targeted therapies directed
against HSP90 and the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in prostate cancer.
PLoS One. 12:e01746582017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
LoRusso PM: Inhibition of the
PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 34:3803–3815.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Liu H, Li X, Lin J and Lin M: Morroniside
promotes the osteogenesis by activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling.
Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 85:332–339. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Chang L, Graham PH, Hao J, Ni J, Bucci J,
Cozzi PJ, Kearsley JH and Li Y: PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway inhibitors
enhance radiosensitivity in radioresistant prostate cancer cells
through inducing apoptosis, reducing autophagy, suppressing NHEJ
and HR repair pathways. Cell Death Dis. 5:e14372014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Berrak O, Arisan ED, Obakan-Yerlikaya P,
Coker-Gürkan A and Palavan-Unsal N: mTOR is a fine tuning molecule
in CDK inhibitors-induced distinct cell death mechanisms via
PI3K/AKT/mTOR signaling axis in prostate cancer cells. Apoptosis.
21:1158–1178. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|