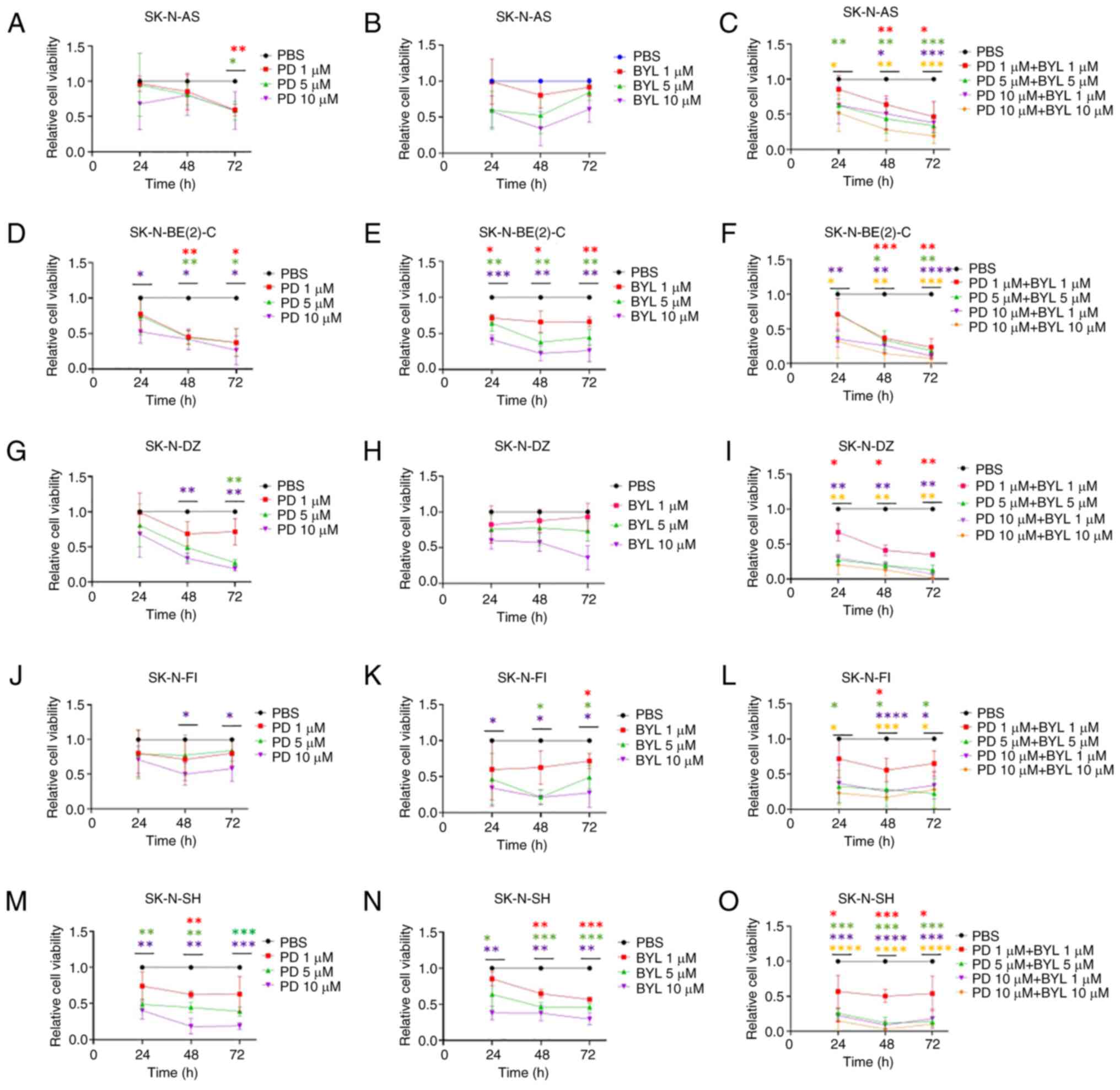
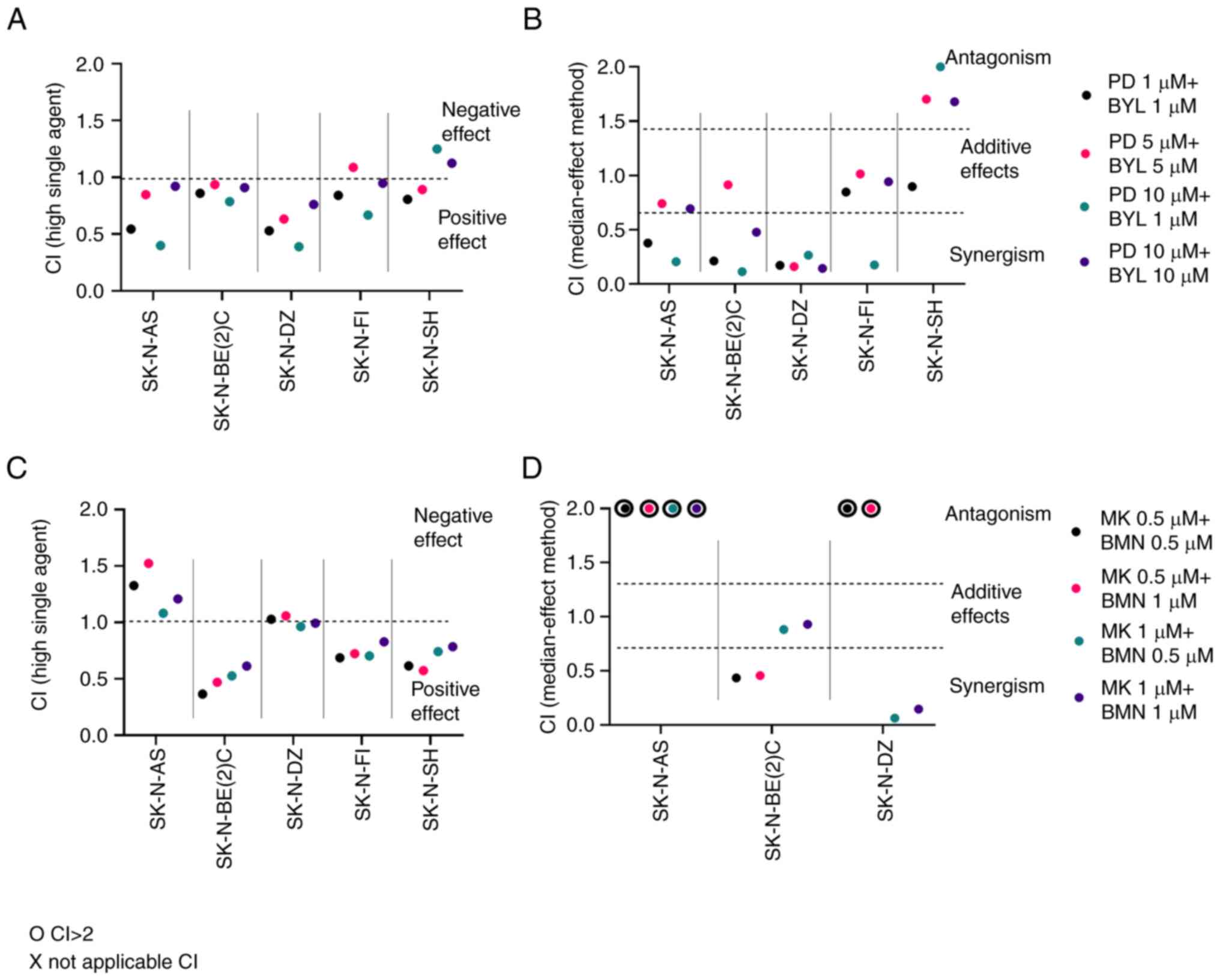
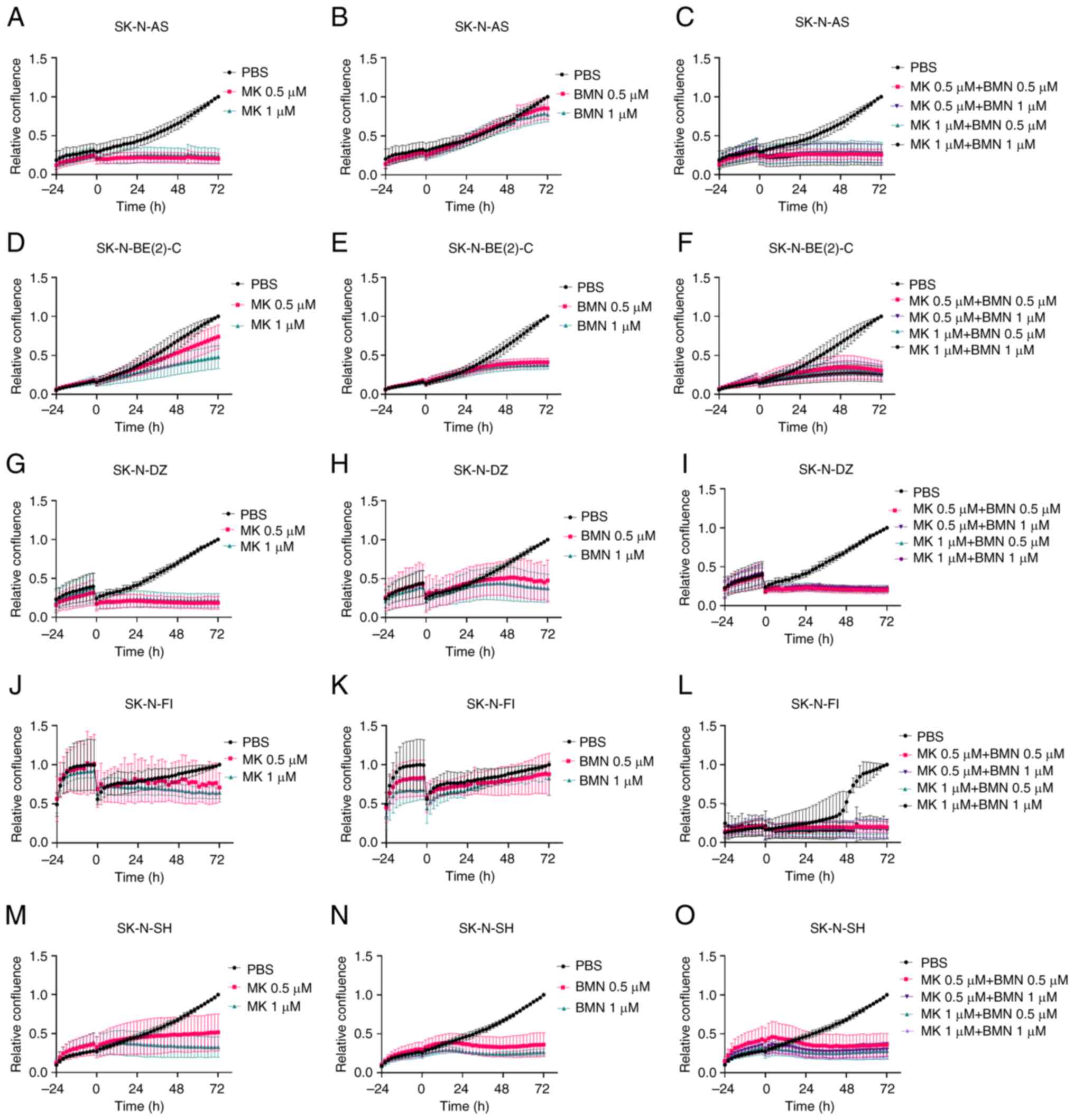
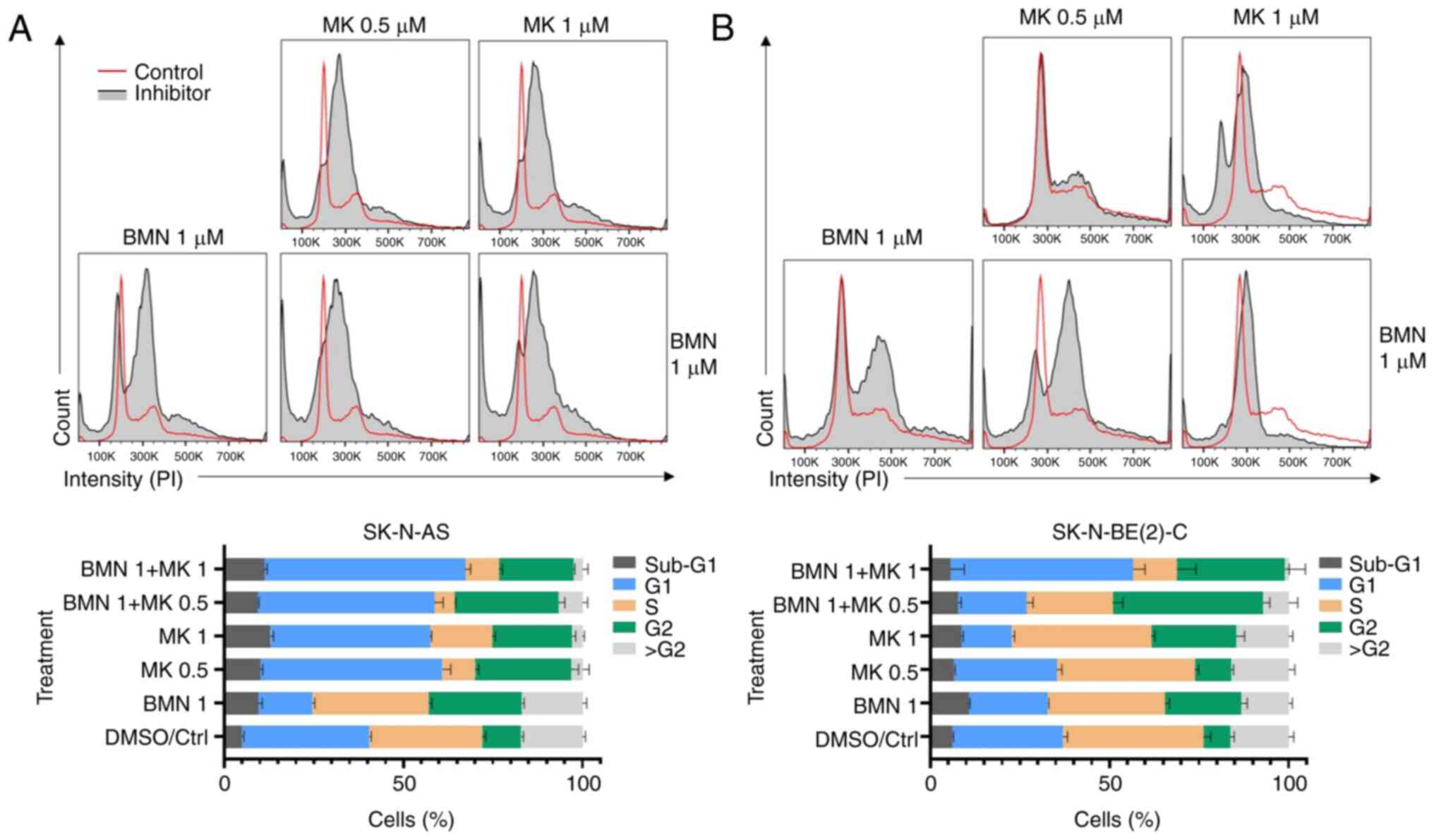
|
1
|
Ward E, DeSantis C, Robbins A, Kohler B
and Jemal A: Childhood and adolescent cancer statistics, 2014. CA
Cancer J Clin. 64:83–103. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
D'Angio GJ, Evans AE and Koop CE: Special
pattern of widespread neuroblastoma with a favourable prognosis.
Lancet. 1:1046–1049. 1971. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Nakagawara A, Li Y, Izumi H, Muramori K,
Inada H and Nishi M: Neuroblastoma. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1:214–241.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bo Q and Matthay KK: Advancing therapy for
neuroblastoma. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 19:515–533. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hero B, Simon T, Spitz R, Ernestus K,
Gnekow AK, Scheel-Walter HG, Schwabe D, Schilling FH, Benz-Bohm G
and Berthold F: Localized infant neuroblastomas often show
spontaneous regression: Results of the prospective trials NB95-S
and NB97. J Clin Oncol. 26:1504–1510. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Matthay KK, Maris JM, Schleiermacher G,
Nakagawara A, Mackall CL, Diller L and Weiss WA: Neuroblastoma. Nat
Rev Dis Prim. 2:160782016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
London WB, Bagatell R, Weigel BJ, Fox E,
Guo D, Van Ryn C, Naranjo A and Park JR: Historical time to disease
progression and progression-free survival in patients with
recurrent/refractory neuroblastoma treated in the modern era on
children's oncology group early-phase trials. Cancer.
123:4914–4923. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Johnsen JI, Dyberg C and Wickström M:
Neuroblastoma-A neural crest derived embryonal malignancy. Front
Mol Neurosci. 12:92019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hemmings BA and Restuccia DF: The
PI3K-PKB/Akt pathway. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol.
7:a0266092015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kostopoulou ON, Holzhauser S, Lange BKA,
Ohmayer A, Andonova T, Bersani C, Wickström M and Dalianis T:
Analyses of FGFR3 and PIK3CA mutations in neuroblastomas and the
effects of the corresponding inhibitors on neuroblastoma cell
lines. Int J Oncol. 55:1372–1384. 2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Holzhauser S, Lukoseviciute M, Andonova T,
Ursu RG, Dalianis T, Wickström M and Kostopoulou ON: Targeting
fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) and Phosphoinositide
3-kinase (PI3K) signaling pathways in medulloblastoma cell lines.
Anticancer Res. 40:53–66. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Holzhauser S, Lukoseviciute M,
Papachristofi C, Vasilopoulou C, Herold N, Wickström M, Kostopoulou
ON and Dalianis T: Effects of PI3K and FGFR inhibitors alone and in
combination, and with/without cytostatics in childhood
neuroblastoma cell lines. Int J Oncol. 58:211–225. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lukoseviciute M, Maier H,
Poulou-Sidiropoulou E, Rosendahl E, Holzhauser S, Dalianis T and
Kostopoulou ON: Targeting PI3K, FGFR, CDK4/6 signaling pathways
together with cytostatics and radiotherapy in two medulloblastoma
cell lines. Front Oncol. 11:7486572021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Katso R, Okkenhaug K, Ahmadi K, White S,
Timms J and Waterfield MD: Cellular function of phosphoinositide
3-kinases: Implications for development, homeostasis, and cancer.
Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 17:615–675. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Engelman JA, Luo J and Cantley LC: The
evolution of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases as regulators of growth
and metabolism. Nat Rev Genet. 7:606–619. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
King D, Yeomanson D and Bryant HE: PI3King
the lock: Targeting the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway as a novel
therapeutic strategy in neuroblastoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol.
37:245–251. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Khezri MR, Jafari R, Yousefi K and
Zolbanin NM: The PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in cancer: Molecular
mechanisms and possible therapeutic interventions. Exp Mol Pathol.
127:1047872022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zage PE: Novel therapies for relapsed and
refractory neuroblastoma. Children (Basel). 5:1482018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Creevey L, Ryan J, Harvey H, Bray IM,
Meehan M, Khan AR and Stallings RL: MicroRNA-497 increases
apoptosis in MYCN amplified neuroblastoma cells by targeting the
key cell cycle regulator WEE1. Mol Cancer. 12:232013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rader J, Russell MR, Hart LS, Nakazawa MS,
Belcastro LT, Martinez D, Li Y, Carpenter EL, Attiyeh EF, Diskin
SJ, et al: Dual CDK4/CDK6 inhibition induces cell-cycle arrest and
senescence in neuroblastoma. Clin Cancer Res. 19:6173–6182. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Knudsen ES, Pruitt SC, Hershberger PA,
Witkiewicz AK and Goodrich DW: Cell cycle and beyond: Exploiting
new RB1 controlled mechanisms for cancer therapy. Trends Cancer.
5:308–324. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Morgan DO: Cyclin-dependent kinases:
Engines, clocks, and microprocessors. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol.
13:261–291. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: Living with or
without cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev.
18:2699–2711. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hamilton E and Infante JR: Targeting
CDK4/6 in patients with cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 45:129–138. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ortega S, Malumbres M and Barbacid M:
Cyclin D-dependent kinases, INK4 inhibitors and cancer. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1602:73–87. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Braal CL, Jongbloed EM, Wilting SM,
Mathijssen RHJ, Koolen SLW and Jager A: Inhibiting CDK4/6 in breast
cancer with palbociclib, ribociclib, and abemaciclib: Similarities
and differences. Drugs. 81:317–331. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Schmidt EE, Ichimura K, Reifenberger G and
Collins VP: CDKN2 (p16/MTS1) gene deletion or CDK4 amplification
occurs in the majority of glioblastomas. Cancer Res. 15:6321–6324.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Muranen T, Meric-Bernstam F and Mills GB:
Promising rationally derived combination therapy with PI3K and
CDK4/6 inhibitors. Cancer Cell. 26:7–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Bonelli MA, Digiacomo G, Fumarola C,
Alfieri R, Quaini F, Falco A, Madeddu D, Monica SL, Cretella D,
Ravelli A, et al: Combined inhibition of CDK4/6 and PI3K/AKT/mTOR
pathways induces a synergistic anti-tumor effect in malignant
pleural mesothelioma cells. Neoplasia. 19:637–648. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Loibl S and Furlanetto J: Integrating
CDK4/6 inhibitors in the treatment of patients with early breast
cancer. Breast. 62:S70–S79. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Vora SR, Juric D, Kim N, Mino-Kenudson M,
Huynh T, Costa C, Lockerman EL, Pollack SF, Liu M, Li X, et al: CDK
4/6 inhibitors sensitize PIK3CA mutant breast cancer to PI3K
inhibitors. Cancer Cell. 26:136–149. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Paik J: Olaparib: A review as first-line
maintenance therapy in advanced ovarian cancer. Target Oncol.
16:847–856. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brown TJ and Reiss KA: PARP inhibitors in
pancreatic cancer. Cancer J. 27:465–475. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
De Bono J, Mateo J, Fizazi K, Saad F,
Shore N, Sandhu S, Chi KN, Sartor O, Agarwal N, Olmos D, et al:
Olaparib for metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. N
Engl J Med. 382:2091–2102. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Banerjee S, Moore KN, Colombo N, Scambia
G, Kim BG, Oaknin A, Friedlander M, Lisyanskaya A, Floquet A, Leary
A, et al: Maintenance olaparib for patients with newly diagnosed
advanced ovarian cancer and a BRCA mutation (SOLO1/GOG 3004):
5-year follow-up of a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled,
phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 22:1721–1731. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Fang Y, McGrail DJ, Sun C, Labrie M, Chen
X, Zhang D, Ju Z, Vellano CP, Lu Y, LI Y, et al: Sequential therapy
with PARP and WEE1 inhibitors minimizes toxicity while maintaining
efficacy. Cancer Cell. 35:851–867.e857. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
di Rorà AG, Cerchione C, Martinelli G and
Simonetti G: A WEE1 family business: Regulation of mitosis, cancer
progression, and therapeutic target. J Hematol Oncol. 13:1262020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Foucquier J and Guedj M: Analysis of drug
combinations: Current methodological landscape. Pharmacol Res
Perspect. 3:e001492015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Chou TC: Drug combination studies and
their synergy quantification using the Chou-Talalay method. Cancer
Res. 70:440–446. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kostopoulou ON, Zupancic M, Pont M, Papin
E, Lukoseviciute M, Mikelarena BA, Holzhauser S and Dalianis T:
Targeted therapy of HPV positive and negative tonsillar squamous
cell carcinoma cell lines reveals synergy between CDK4/6, PI3K and
sometimes FGFR inhibitors, but rarely between PARP and WEE1
inhibitors. Viruses. 14:13722022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Agostinetto E, Debien V, Marta GN,
Lambertini M, Piccart-Gebhart M and de Azambuja E: CDK4/6 and PI3K
inhibitors: A new promise for patients with HER2-positive breast
cancer. Eur J Clin Invest. 51:e135352021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Holzhauser S, Wild N, Zupancic M, Ursu RG,
Bersani C, Näsman A, Kostopoulou Ourania N and Dalianis T: Targeted
therapy with PI3K and FGFR inhibitors on human papillomavirus
positive and negative tonsillar and base of tongue cancer lines
with and without corresponding mutations. Front Oncol.
11:6404902021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Rihani A, Vandesompele J, Speleman F and
Van Maerken T: Inhibition of CDK4/6 as a novel therapeutic option
for neuroblastoma. Cancer Cell Int. 15:762015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Fry DW, Harvey PJ, Keller PR, Elliott WL,
Meade M, Trachet E, Albassam M, Zheng X, Leopold WR, Pryer NK and
Toogood PL: Specific inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 by
PD 0332991 and associated antitumor activity in human tumor
xenografts. Mol Cancer Ther. 3:1427–1438. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Challa S and Kraus WL: Two birds, one
stone: Non-canonical therapeutic effects of the PARP inhibitor
Talazoparib. Cell Chem Biol. 29:171–173. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|