|
1
|
Mejia JC and Pasko J: Primary liver
cancers: Intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma and hepatocellular
carcinoma. Surg Clin North Am. 100:535–549. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chidambaranathan-Reghupaty S, Fisher PB
and Sarkar D: Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): Epidemiology,
etiology and molecular classification. Adv Cancer Res. 149:1–61.
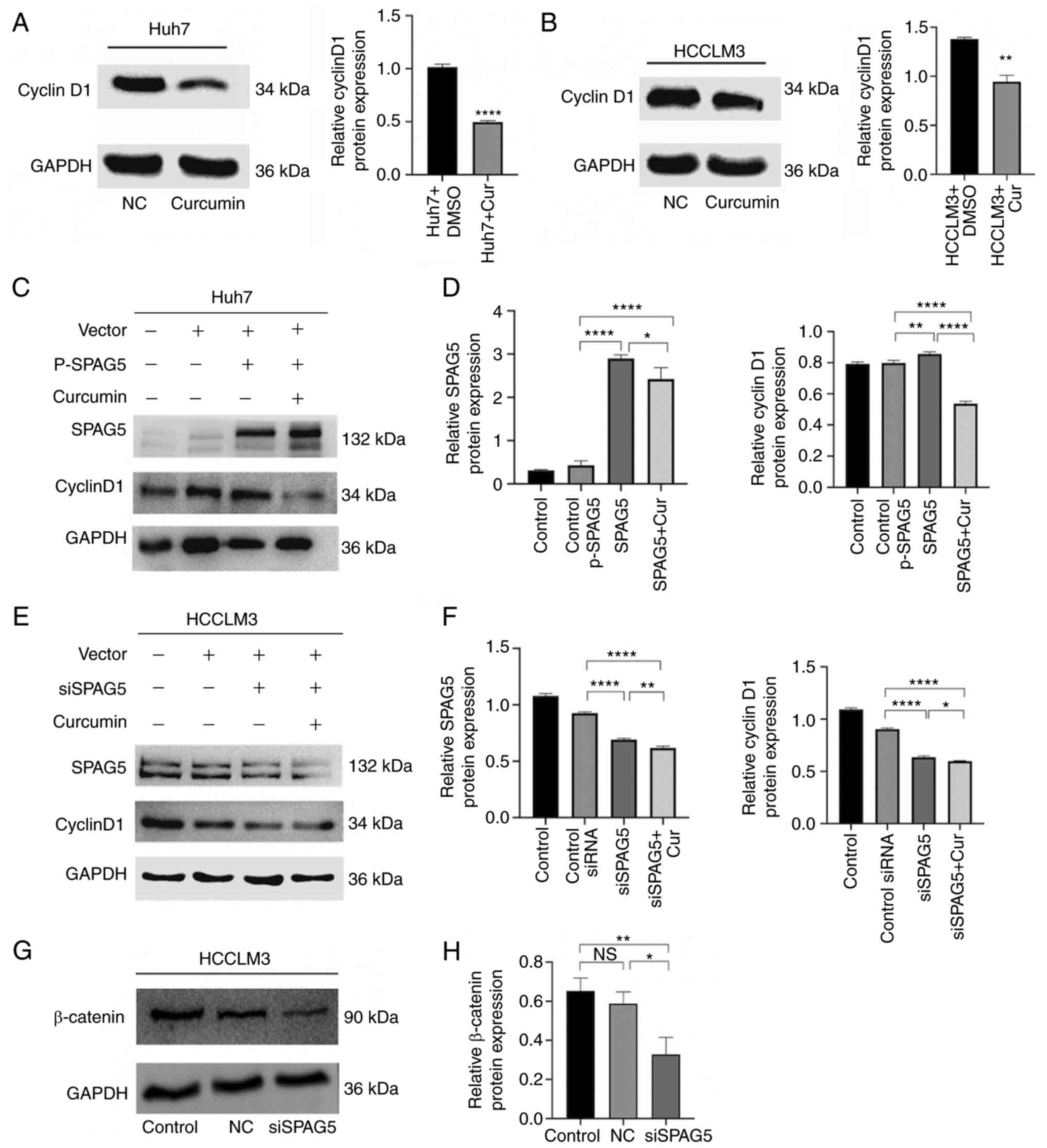
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Shi JF, Cao M, Wang Y, Bai FZ, Lei L, Peng
J, Feletto E, Canfell K, Qu C and Chen W: Is it possible to halve
the incidence of liver cancer in China by 2050? Int J Cancer.
148:1051–1065. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M,
Soerjomataram I, Jemal A and Bray F: Global cancer statistics 2020:
GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36
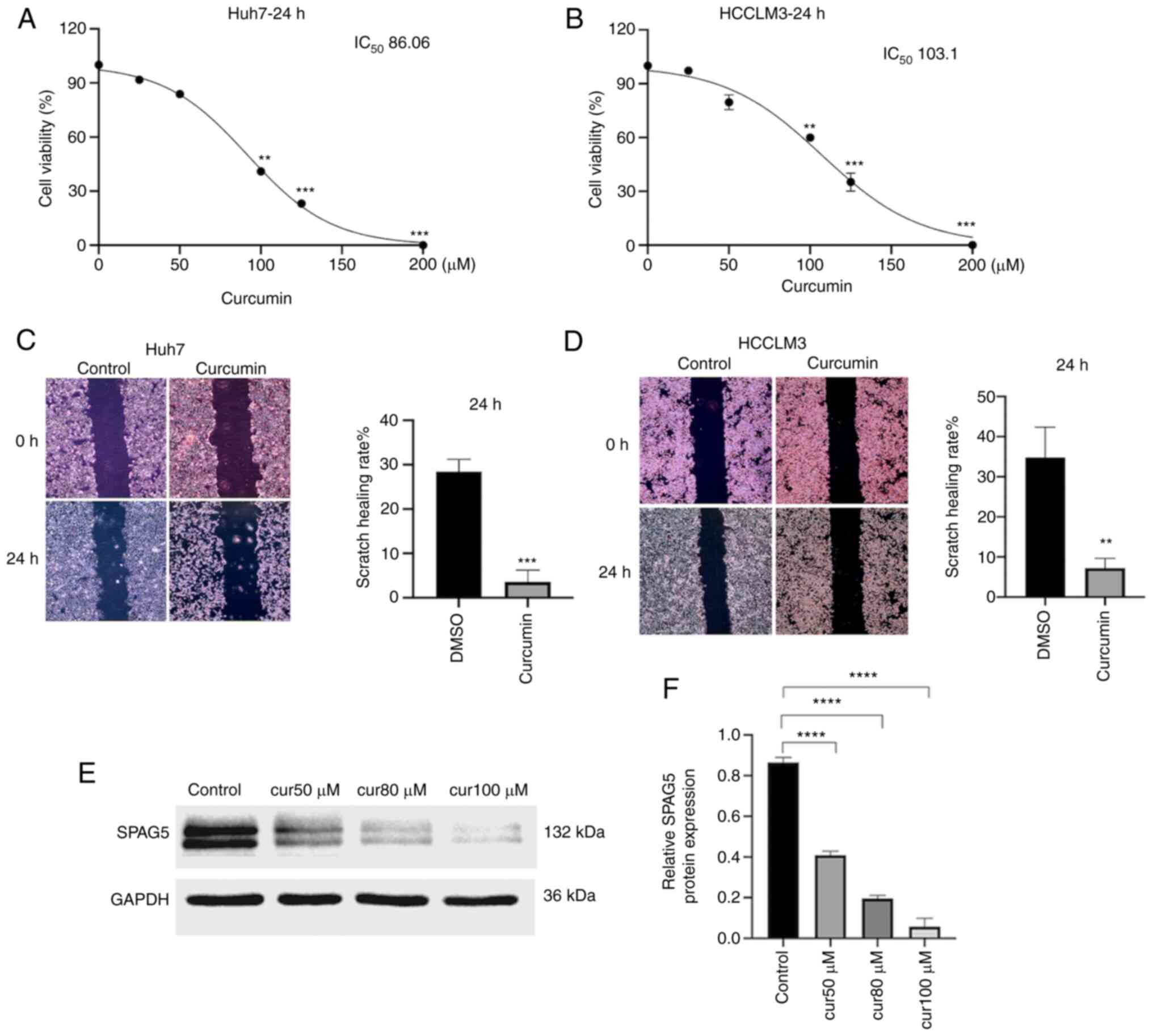
cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 71:209–249. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
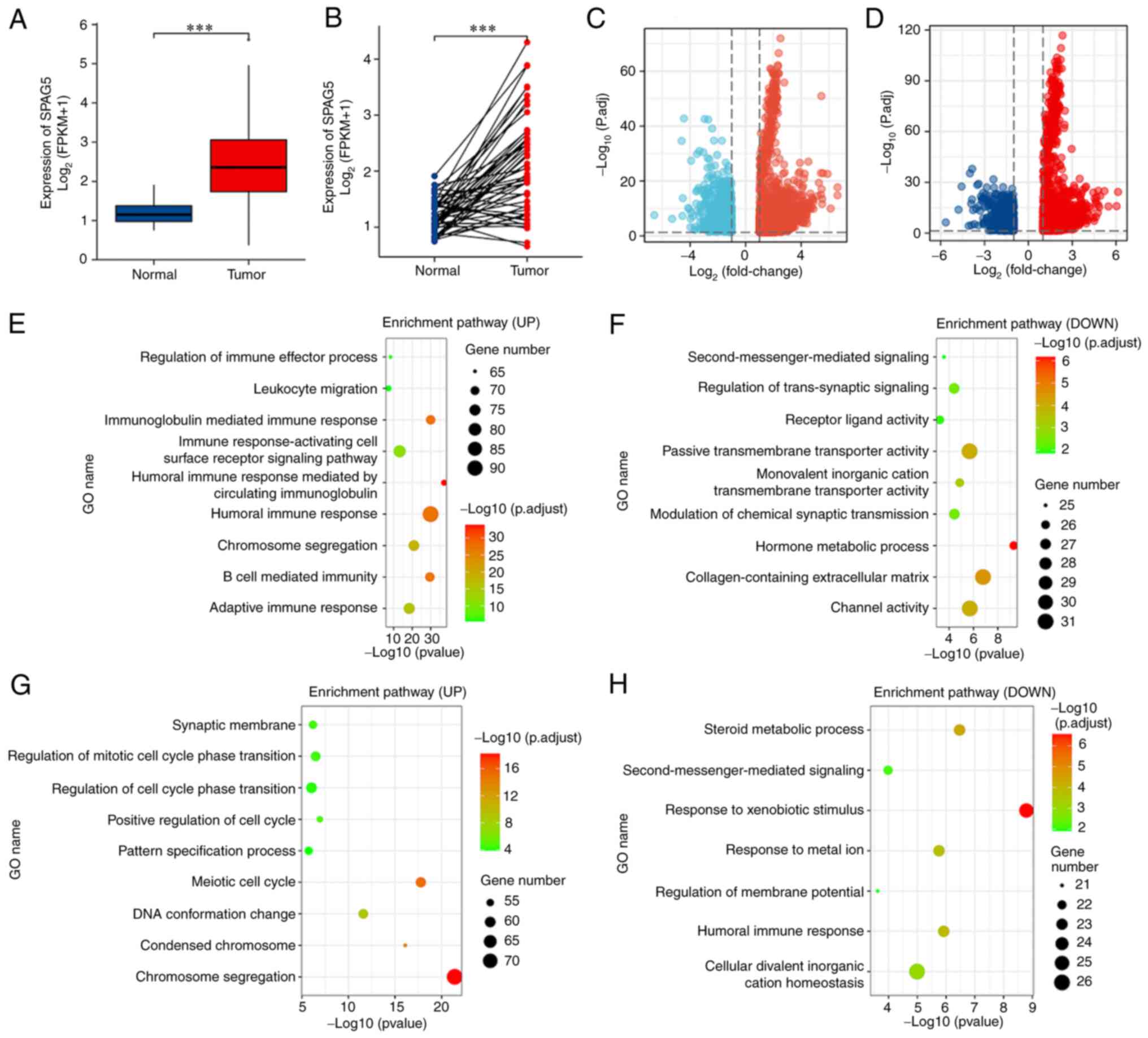
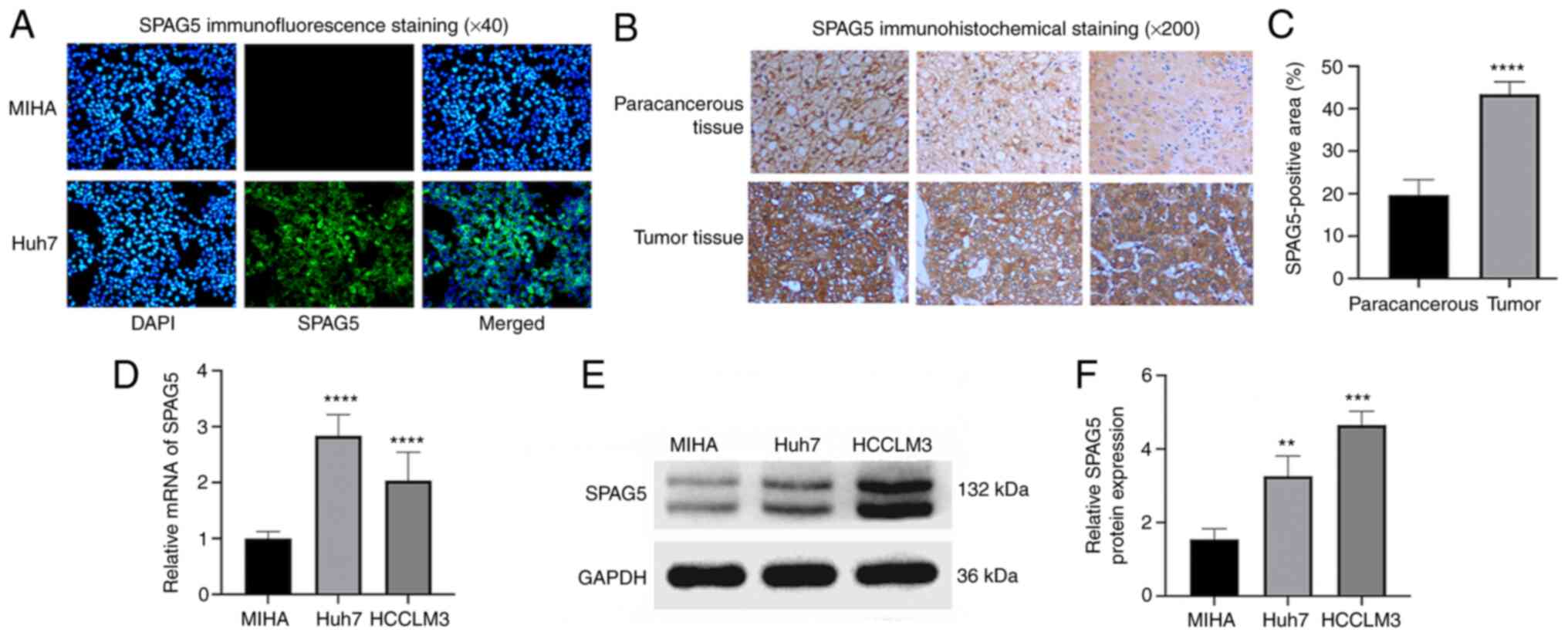
5
|
Thein KH, Kleylein-Sohn J, Nigg EA and
Gruneberg U: Astrin is required for the maintenance of sister
chromatid cohesion and centrosome integrity. J Cell Biol.
178:345–354. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Buechler S: Low expression of a few genes
indicates good prognosis in estrogen receptor positive breast
cancer. BMC Cancer. 9:2432009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Välk K, Vooder T, Kolde R, Reintam MA,
Petzold C, Vilo J and Metspalu A: Gene expression profiles of
non-small cell lung cancer: Survival prediction and new biomarkers.
Oncology. 79:283–292. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Yang YF, Zhang MF, Tian QH, Fu J, Yang X,
Zhang CZ and Yang H: SPAG5 interacts with CEP55 and exerts
oncogenic activities via PI3K/AKT pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Mol Cancer. 17:1172018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang H, Li S, Yang X, Qiao B, Zhang Z and
Xu Y: miR-539 inhibits prostate cancer progression by directly
targeting SPAG5. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 35:602016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li M, Li A, Zhou S, Lv H and Yang W: SPAG5
upregulation contributes to enhanced c-MYC transcriptional activity
via interaction with c-MYC binding protein in triple-negative
breast cancer. J Hematol Oncol. 12:142019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Abdel-Fatah TMA, Agarwal D, Liu DX,
Russell R, Rueda OM, Liu K, Xu B, Moseley PM, Green AR, Pockley AG,
et al: SPAG5 as a prognostic biomarker and chemotherapy sensitivity
predictor in breast cancer: A retrospective, integrated genomic,
transcriptomic, and protein analysis. Lancet Oncol. 17:1004–1018.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yuan LJ, Li JD, Zhang L, Wang JH, Wan T,
Zhou Y, Tu H, Yun JP, Luo RZ, Jia WH and Zheng M: SPAG5
upregulation predicts poor prognosis in cervical cancer patients
and alters sensitivity to taxol treatment via the mTOR signaling
pathway. Cell Death Dis. 5:e12472014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu H, Hu J, Wei R, Zhou L, Pan H, Zhu H,
Huang M, Luo J and Xu W: SPAG5 promotes hepatocellular carcinoma
progression by downregulating SCARA5 through modifying β-catenin
degradation. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 37:2292018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang J, Wang J, He X, Ma W, Sun L, Zhou
Q, Li M and Yu S: High expression of SPAG5 sustains the malignant
growth and invasion of breast cancer cells through the activation
of Wnt/β-catenin signalling. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol.
46:597–606. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu JY, Zeng QH, Cao PG, Xie D, Yang F, He
LY, Dai YB, Li JJ, Liu XM, Zeng HL, et al: SPAG5 promotes
proliferation and suppresses apoptosis in bladder urothelial
carcinoma by upregulating Wnt3 via activating the AKT/mTOR pathway
and predicts poorer survival. Oncogene. 37:3937–3952. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rebouissou S, Franconi A, Calderaro J,
Letouzé E, Imbeaud S, Pilati C, Nault JC, Couchy G, Laurent A,
Balabaud C, et al: Genotype-phenotype correlation of CTNNB1
mutations reveals different ß-catenin activity associated with
liver tumor progression. Hepatology. 64:2047–2061. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hayat R, Manzoor M and Hussain A: Wnt
signaling pathway: A comprehensive review. Cell Biol Int.
46:863–877. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Clevers H and Nusse R: Wnt/β-catenin
signaling and disease. Cell. 149:1192–1205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
De A: Wnt/Ca2+ signaling pathway: A brief
overview. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 43:745–756. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhan T, Rindtorff N and Boutros M: Wnt
signaling in cancer. Oncogene. 36:1461–1473. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kahn M: Can we safely target the WNT
pathway? Nat Rev Drug Discov. 13:513–532. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Duchartre Y, Kim YM and Kahn M: The Wnt
signaling pathway in cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 99:141–149.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Steinhart Z and Angers S: Wnt signaling in
development and tissue homeostasis. Development. 145:dev1465892018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tafrihi M and Nakhaei Sistani R:
E-Cadherin/β-Catenin Complex: A target for anticancer and
antimetastasis plants/plant-derived compounds. Nutr Cancer.
69:702–722. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gupta SC, Patchva S and Aggarwal BB:
Therapeutic roles of curcumin: Lessons learned from clinical
trials. AAPS J. 15:195–218. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Udagawa T and Wood M: Tumor-stromal cell
interactions and opportunities for therapeutic intervention. Curr
Opin Pharmacol. 10:369–374. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Al-Ejeh F, Kumar R, Wiegmans A, Lakhani
SR, Brown MP and Khanna KK: Harnessing the complexity of DNA-damage
response pathways to improve cancer treatment outcomes. Oncogene.
29:6085–6098. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Jin H, Lian N, Zhang F, Chen L, Chen Q, Lu
C, Bian M, Shao J, Wu L and Zheng S: Activation of PPARγ/P53
signaling is required for curcumin to induce hepatic stellate cell
senescence. Cell Death Dis. 7:e21892016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ashrafizadeh M, Ahmadi Z, Mohamamdinejad
R, Yaribeygi H, Serban MC, Orafai HM and Sahebkar A: Curcumin
therapeutic modulation of the wnt signaling pathway. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 21:1006–1015. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Vallée A, Lecarpentier Y and Vallée JN:
Curcumin: A therapeutic strategy in cancers by inhibiting the
canonical WNT/β-catenin pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 38:3232019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Patel SS, Acharya A, Ray RS, Agrawal R,
Raghuwanshi R and Jain P: Cellular and molecular mechanisms of
curcumin in prevention and treatment of disease. Crit Rev Food Sci
Nutr. 60:887–939. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Ghasemi F, Shafiee M, Banikazemi Z,
Pourhanifeh MH, Khanbabaei H, Shamshirian A, Amiri Moghadam S,
ArefNezhad R, Sahebkar A, Avan A and Mirzaei H: Curcumin inhibits
NF-kB and Wnt/β-catenin pathways in cervical cancer cells. Pathol
Res Pract. 215:1525562019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Chen W, Chen X, Li S and Ren B:
Expression, immune infiltration and clinical significance of SPAG5
in hepatocellular carcinoma: A gene expression-based study. J Gene
Med. 22:e31552020. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15:5502014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhou M, Zhao K, Yao Y, Yuan Y, Pei R, Wang
Y, Chen J, Hu X, Zhou Y, Chen X and Wu C: Productive HBV infection
of well-differentiated, hNTCP-expressing human hepatoma-derived
(Huh7) cells. Virol Sin. 32:465–475. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Li B, Zhang Y, Wu W, Du G, Cai L, Shi H
and Chen S: Neovascularization of hepatocellular carcinoma in a
nude mouse orthotopic liver cancer model: A morphological study
using X-ray in-line phase-contrast imaging. BMC Cancer. 17:732017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ram S, Vizcarra P, Whalen P, Deng S,
Painter CL, Jackson-Fisher A, Pirie-Shepherd S, Xia X and Powell
EL: Pixelwise H-score: A novel digital image analysis-based metric
to quantify membrane biomarker expression from immunohistochemistry
images. PLoS One. 16:e02456382021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|