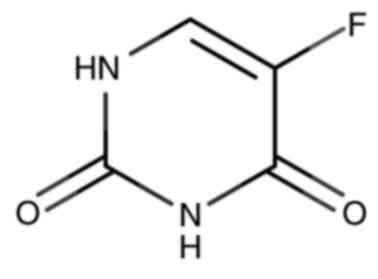
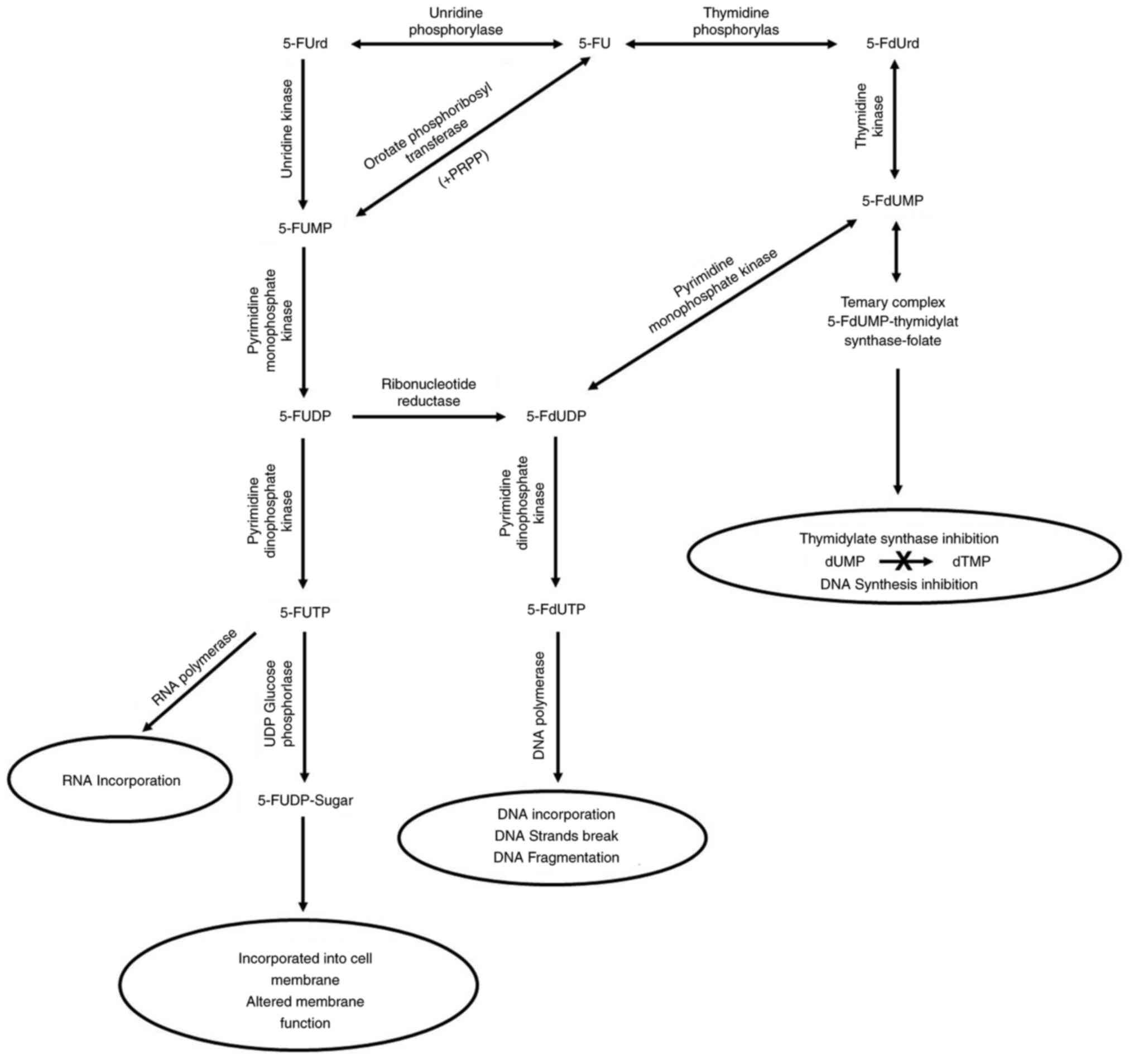
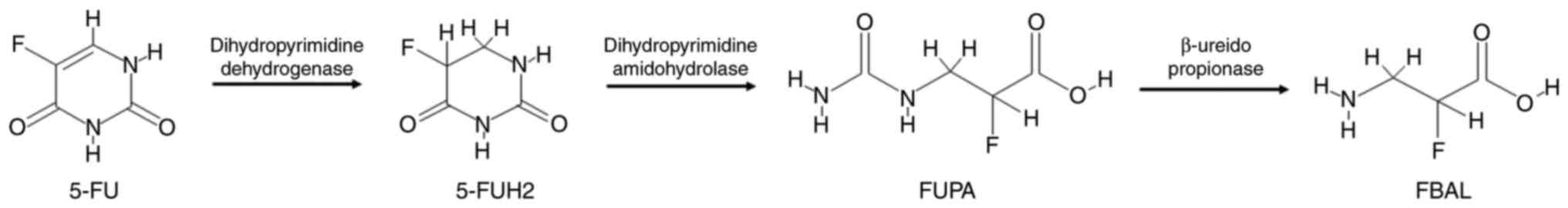
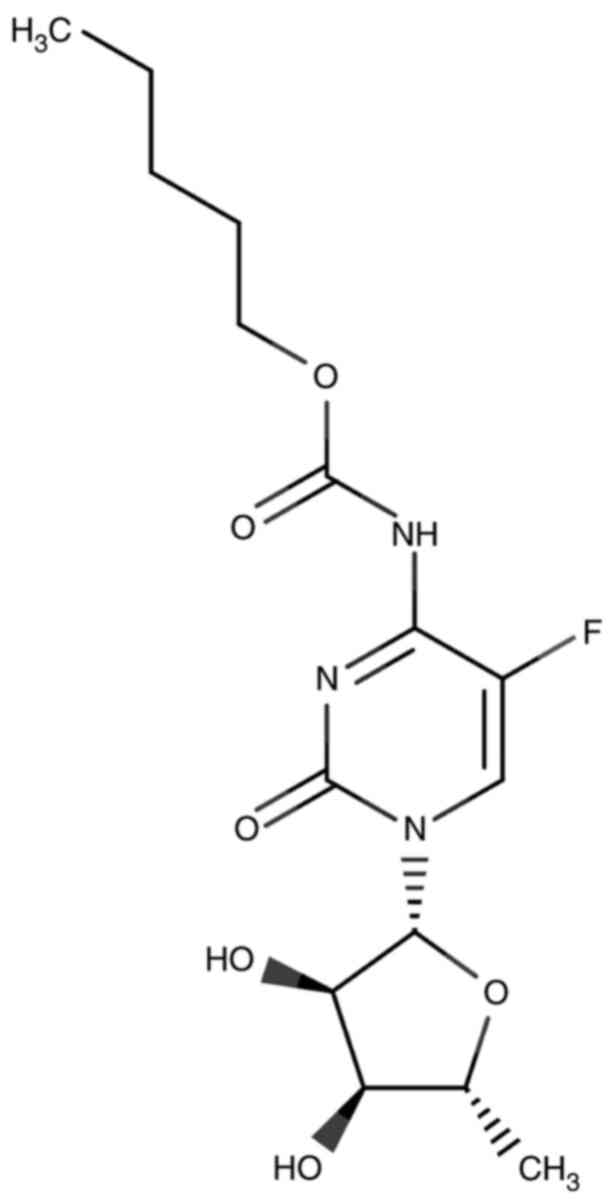
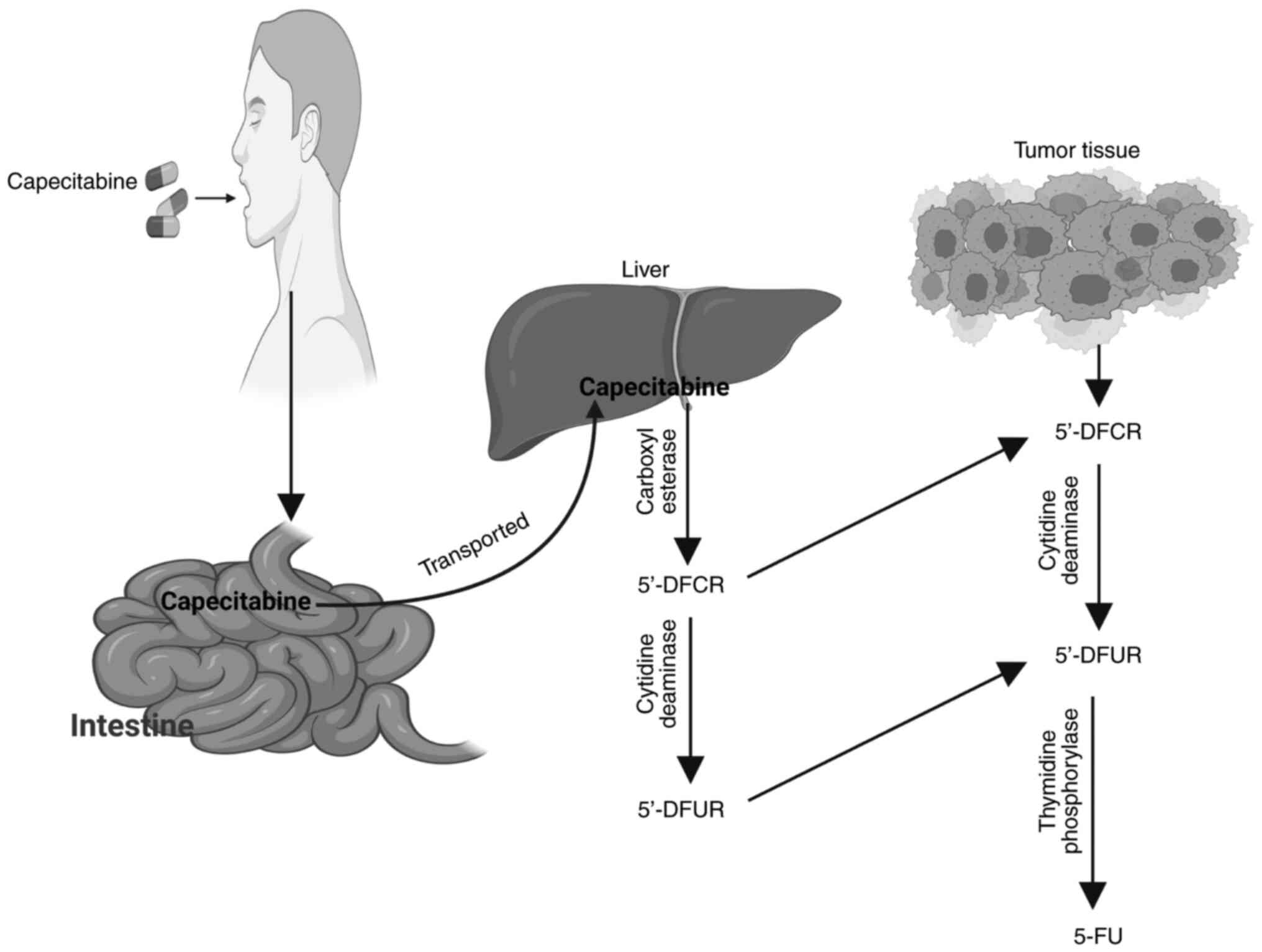
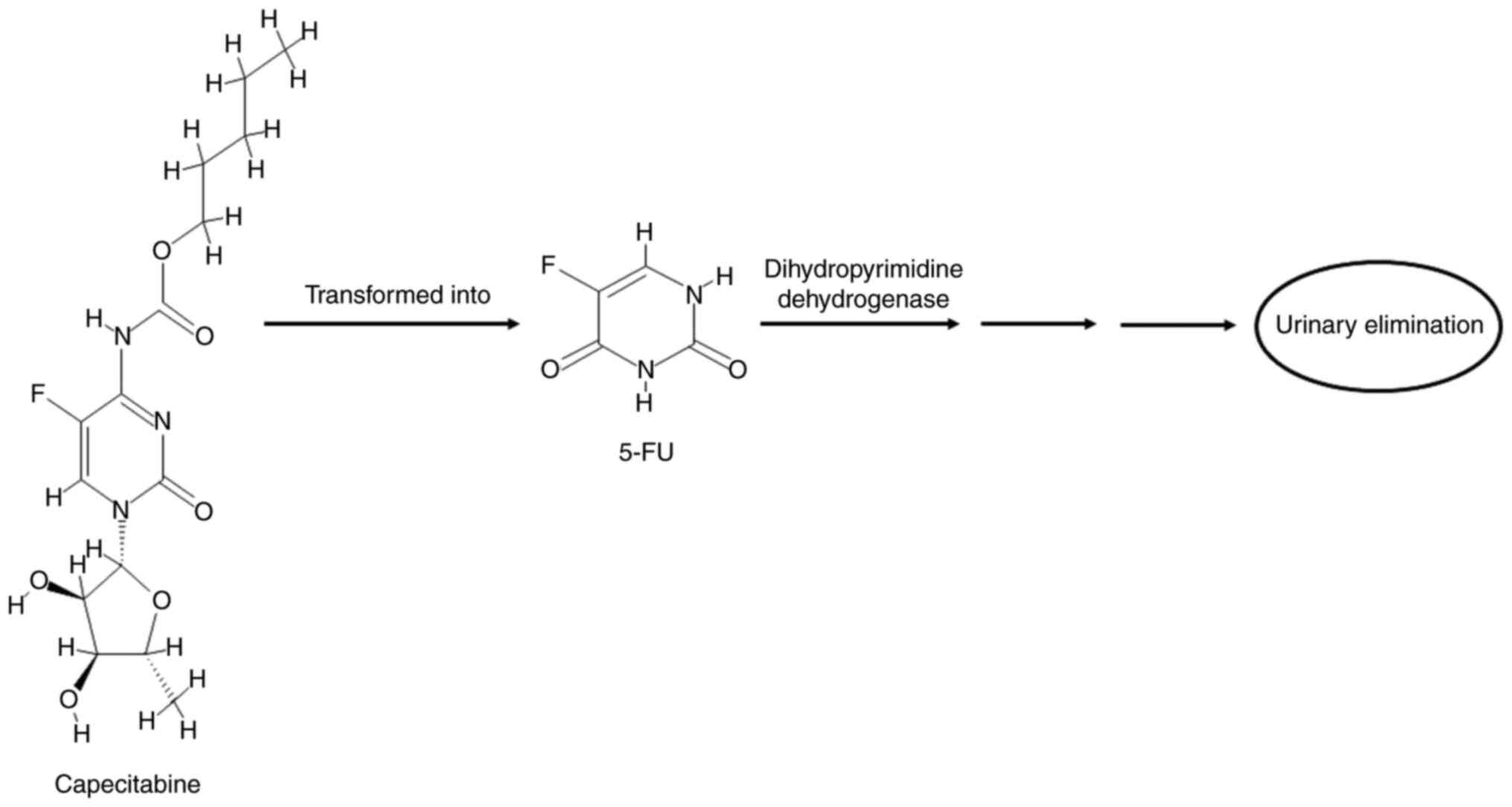
|
1
|
Seigel RL, Miller K and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 70:7–30. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Blecher E, Chaney-Graves K, DeSantis C,
Edwards B, Ferlay J, Forman D, Grey N, Harford J, Kramer J, McMikel
A and McNeal B: Global cancer facts and figures. American Cancer
Society; Atlanta, GA, USA: 2011
|
|
3
|
Bray F, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Siegel
RL, Torre LA and Jemal A: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN
estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in
185 countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 68:394–424. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Alzahrani SM, Al Doghaither HA and
Al-Ghafari AB: General insight into cancer: An overview of
colorectal cancer (review). Mol Clin Oncol. 15:2712021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Centelles JJ: General aspects of
colorectal cancer. ISRN Oncol. 2012:1392682012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Blagosklonny MV: Analysis of FDA approved
anticancer drugs reveals the future of cancer therapy. Cell Cycle.
3:1033–1040. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kinch MS: An analysis of FDA-approved
drugs for oncology. Drug Discov Today. 19:1831–1835. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sun J, Wei Q, Zhou Y, Wang J, Liu Q and Xu
H: A systematic analysis of FDA-approved anticancer drugs. BMC Syst
Biol. 11 (Suppl 5):S872017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Winkler GC, Barle EL, Galati G and Kluwe
WM: Functional differentiation of cytotoxic cancer drugs and
targeted cancer therapeutics. Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 70:46–53.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tseng HH and He B: Molecular markers as
therapeutic targets in lung cancer. Chin J Cancer. 32:59–62. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kinsella AR, Smith D and Pickard M:
Resistance to chemotherapeutic antimetabolites: A function of
salvage pathway involvement and cellular response to DNA damage. Br
J Cancer. 75:935–945. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Espinosa E, Zamora P, Feliu J and Barón
MG: Classification of anticancer drugs-a new system based on
therapeutic targets. Cancer Treat Rev. 29:515–523. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peters GJ: Novel developments in the use
of antimetabolites. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids.
33:358–374. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Peters GJ and Jansen G: Antimetabolites.
Souhami RL, Tannock I, Hohenberger P and Horiot JC: ‘Oxford
Textbook of Oncology’. Oxford University Press; pp. 663–713.
2001
|
|
15
|
Kaye SB: New antimetabolites in cancer
chemotherapy and their clinical impact. Br J Cancer. 78 (Suppl
3):S1–S7. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Peters GJ, Van der Wilt CL, Van Moorsel
CJ, Kroep JR, Bergman AM and Ackland SP: Basis for effective
combination cancer chemotherapy with antimetabolites. Pharmacol
Ther. 87:227–253. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pizzorno G, Diasio RB and Cheng YC:
Pyrimidine analogs. In Holland-Frei Cancer Medicine. 6th edition.
BC Decker; 2003, Available from:. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK13287/
|
|
18
|
Thorn CF, Marsh S, Carrillo MW, McLeod HL,
Klein TE and Altman RB: PharmGKB summary: Fluoropyrimidine
pathways. Pharmacogenet Genomics. 21:237–242. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Saif MW: Targeting cancers in the
gastrointestinal tract: Role of capecitabine. Onco Targets Ther.
2:29–41. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Walko CM and Lindley C: Capecitabine: A
review. Clin Ther. 27:23–44. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Fluorouracil: Uses, Interactions,
Mechanism of Action | DrugBank Online. (2022). Retrieved.
4–May;2022.from. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00544
|
|
22
|
Carrillo E, Navarro SA, Ramírez A, García
MÁ, Griñán-Lisón C, Perán M and Marchal JA: 5-Fluorouracil
derivatives: A patent review (2012–2014). Expert Opin Ther Pat.
25:1131–1144. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Adjei AA: A review of the pharmacology and
clinical activity of new chemotherapy agents for the treatment of
colorectal cancer. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 48:265–277. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hirsch BR and Zafar SY: Capecitabine in
the management of colorectal cancer. Cancer Manag Res. 3:79–89.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Malet-Martino M and Martino R: Clinical
studies of three oral prodrugs of 5-fluorouracil (capecitabine,
UFT, S-1): A review. Oncologist. 7:288–323. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
DrugBank Online, . 5-Fluorouracil.
https://go.drugbank.com/structures/DB00544/image.svgRetrieved.
September 29–2022.
|
|
27
|
EMBL's European Bioinformatics Institute
(EMBL-EBI), . 5-fluorouracil (CHEBI:46345). http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:46345Retrieved.
May 4–2022.
|
|
28
|
National Center for Biotechnology
Information, . FLUOROURACIL. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/3228Retrieved.
May 4–2022.
|
|
29
|
CAMEO Chemicals, . FLUOROURACIL.
https://cameochemicals.noaa.gov/chemical/5005Retrieved.
May 4–2022.
|
|
30
|
PubChem, . https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.govRetrieved. May
4–2022.
|
|
31
|
ChemAxon, . Calculators and Predictors.
https://chemaxon.com/products/calculators-and-predictors#topology_analysisRetrieved.
4–May;2022.
|
|
32
|
DrugBank Online, . DrugBank Release
Version 5.1.8. https://go.drugbank.com/releases/latestRetrieved. May
4–2022.
|
|
33
|
Wielińska J, Nowacki A and Liberek B:
5-Fluorouracil-complete insight into its neutral and ionised forms.
Molecules. 24:36832019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Privat EJ and Sowers LC: A proposed
mechanism for the mutagenicity of 5-formyluracil. Mutat Res.
354:151–156. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Şanli N, Şanli S and Alsancak G:
Determination of dissociation constants of folinic acid
(leucovorin), 5-fluorouracil, and irinotecan in hydro-organic media
by a spectrophotometric method. J Chem Eng Data. 55:2695–2699.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Phua LC, Mal M, Koh PK, Cheah PY, Chan EC
and Ho HK: Investigating the role of nucleoside transporters in the
resistance of colorectal cancer to 5-fluorouracil therapy. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 71:817–823. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Álvarez P, Marchal JA, Boulaiz H, Carrillo
E, Vélez C, Rodríguez-Serrano F, Melguizo C, Prados J, Madeddu R
and Aranega A: 5-Fluorouracil derivatives: A patent review. Expert
Opin Ther Pat. 22:107–23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Gustavsson B, Carlsson G, Machover D,
Petrelli N, Roth A, Schmoll HJ, Tveit KM and Gibson F: A review of
the evolution of systemic chemotherapy in the management of
colorectal cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer. 14:1–0. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Piedbois P, Buyse M, Blijham G, Glimelius
B, Herrmann RB, Valone F, Carlson R, Machiavelli M, Delfino C, Abad
A and Petrelli N: Meta-analysis of randomized trials testing the
biochemical modulation of fluorouracil by methotrexate in
metastatic colorectal cancer. In Database of Abstracts of Reviews
of Effects (DARE): Quality-assessed Reviews [Internet]. Centre for
Reviews and Dissemination (UK); 1994, Available from:. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK66225/
|
|
40
|
Mikhail SE, Sun JF and Marshall JL: Safety
of capecitabine: A review. Expert Opin Drug Saf. 9:831–841. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Van der Jeught K, Xu HC, Li YJ, Lu XB and
Ji G: Drug resistance and new therapies in colorectal cancer. World
J Gastroenterol. 24:3834–3848. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Di Costanzo F, Sdrobolini A and Gasperoni
S: Capecitabine, a new oral fluoropyrimidine for the treatment of
colorectal cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 35:101–108. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Mohammadian M, Zeynali S, Azarbaijani AF,
Ansari MH and Kheradmand F: Cytotoxic effects of the
newly-developed chemotherapeutic agents 17-AAG in combination with
oxaliplatin and capecitabine in colorectal cancer cell lines. Res
Pharm Sci. 12:517–525. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Sharma R, Adam E and Schumacher U: The
action of 5-fluorouracil on human HT29 colon cancer cells grown in
SCID mice: Mitosis, apoptosis and cell differentiation. Br J
Cancer. 76:1011–1016. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Swiss Institute of Bioinformatics, .
SwissADME. http://www.swissadme.ch/index.phpRetrieved. May
4–2022.
|
|
46
|
Elmore S: Apoptosis: A review of
programmed cell death. Toxicol Pathol. 35:495–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
D'Arcy MS: Cell death: A review of the
major forms of apoptosis, necrosis and autophagy. Cell Biol Int.
43:582–592. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Schafer KA: The cell cycle: A review. Vet
Pathol. 35:461–478. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Dickson MA and Schwartz GK: Development of
cell-cycle inhibitors for cancer therapy. Curr Oncol. 16:36–43.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Nigg EA: Cyclin-dependent protein kinases:
Key regulators of the eukaryotic cell cycle. Bioessays. 17:471–480.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Park MT and Lee SJ: Cell cycle and cancer.
J Biochem Mol Biol. 36:60–65. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M,
Roberts K and Walter P: Molecular biology of the cell. 4th edition.
New York: Garland Science; 2002, Available from:. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK21054/
|
|
53
|
Sagona AP and Stenmark H: Cytokinesis and
cancer. FEBS Lett. 584:2652–2661. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Green DR, McGahon A and Martin SJ:
Regulation of apoptosis by oncogenes. J Cell Biochem. 60:33–38.
1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Brown JM and Wouters BG: Apoptosis, p53,
and tumor cell sensitivity to anticancer agents. Cancer Res.
59:1391–1399. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Tiwari M: Antimetabolites: Established
cancer therapy. J Cancer Res Ther. 8:510–519. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Övey İS and Güler Y: Apoptotic efficiency
of capecitabine and 5-fluorouracil on human cancer cells through
TRPV1 channels. NISCAIR-CSIR. pp64–72. 2020.http://nopr.niscair.res.in/handle/123456789/54047
|
|
58
|
Shi H, Jiang J, Ji J, Shi M, Cai Q, Chen
X, Yu Y, Liu B, Zhu Z and Zhang J: Anti-angiogenesis participates
in antitumor effects of metronomic capecitabine on colon cancer.
Cancer Lett. 349:128–135. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
De Angelis PM, Svendsrud DH, Kravik KL and
Stokke T: Cellular response to 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) in
5-FU-resistant colon cancer cell lines during treatment and
recovery. Mol Cancer. 5:202006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Gao L, Shen L, Yu M, Ni J, Dong X, Zhou Y
and Wu S: Colon cancer cells treated with 5-fluorouracil exhibit
changes in polylactosamine-type N-glycans. Mol Med Rep.
9:1697–1702. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Afrin S, Giampieri F, Cianciosi D,
Alvarez-Suarez JM, Bullon B, Amici A, Quiles JL, Forbes-Hernández
TY and Battino M: Strawberry tree honey in combination with
5-fluorouracil enhances chemosensitivity in human colon
adenocarcinoma cells. Food Chem Toxicol. 156:1124842021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
DrugBank Online, . Capecitabine: Uses,
Interactions, Mechanism of Action. https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB01101Retrieved. May
4–2022.
|
|
63
|
DrugBank Online, . Capecitabine.
https://go.drugbank.com/structures/DB01101/image.svgRetrieved.
September 29–2022.
|
|
64
|
Team, E. Capecitabine (CHEBI:31348),
2022b, . Retrieved. 4–May;2022.from. http://www.ebi.ac.uk/chebi/searchId.do?chebiId=CHEBI:31348
|
|
65
|
Twelves C, Boyer M, Findlay M, Cassidy J,
Weitzel C, Barker C, Osterwalder B, Jamieson C and Hieke K; Xeloda
Colorectal Cancer Study Group, : Capecitabine (Xeloda) improves
medical resource use compared with 5-fluorouracil plus leucovorin
in a phase III trial conducted in patients with advanced colorectal
carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 37:597–604. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Budman DR, Meropol NJ, Reigner B, Creaven
PJ, Lichtman SM, Berghorn E, Behr J, Gordon RJ, Osterwalder B and
Griffin T: Preliminary studies of a novel oral fluoropyrimidine
carbamate: Capecitabine. J Clin Oncol. 16:1795–1802. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
National Center for Biotechnology
Information, . CAPECITABINE. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/source/hsdb/7656Retrieved.
May 4–2022.
|
|
68
|
O'Neil MJ: The merck index-an encyclopedia
of chemicals, drugs and biologicals. Merck and Co. Inc.; Whitehouse
Station, NJ: pp. pp17232006
|
|
69
|
Loo WT, Chow LW, Suzuki T, Ono K, Ishida
T, Hirakawa H, Ohuchi N and Sasano H: Expression of thymidine
phosphorylase and dihydropyrimidine dehydrogenase in human breast
carcinoma cells and tissues. Anticancer Res. 29:2525–2530.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Schüller J, Cassidy J, Dumont E, Roos B,
Durston S, Banken L, Utoh M, Mori K, Weidekamm E and Reigner B:
Preferential activation of capecitabine in tumor following oral
administration to colorectal cancer patients. Cancer Chemother
Pharmacol. 45:291–297. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Brito RA, Medgyesy D, Zukowski TH, Royce
ME, Ravandi-Kashani F, Hoff PM and Pazdur R: Fluoropyrimidines: A
critical evaluation. Oncology. 57 (Suppl 1):S2–S8. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Li M, Zhang N and Li M: Capecitabine
treatment of HCT-15 colon cancer cells induces apoptosis via
mitochondrial pathway. Trop J Pharm Res. 16:1529–1536. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Ciccolini J, Fina F, Bezulier K,
Giacometti S, Roussel M, Evrard A, Cuq P, Romain S, Martin PM and
Aubert C: Transmission of apoptosis in human colorectal tumor cells
exposed to capecitabine, Xeloda, is mediated via Fas. Mol Cancer
Ther. 1:923–927. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Prasad S, Yadav VR, Sung B, Reuter S,
Kannappan R, Deorukhkar A, Diagaradjane P, Wei C,
Baladandayuthapani V, Krishnan S, et al: Ursolic acid inhibits
growth and metastasis of human colorectal cancer in an orthotopic
nude mouse model by targeting multiple cell signaling pathways:
Chemosensitization with capecitabine. Clin Cancer Res.
18:4942–4953. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Namvaran A, Fazeli M, Farajnia S, Hamidian
G and Rezazadeh H: Apoptosis and caspase 3 pathway role on
anti-proliferative effects of scrophulariaoxy sepala methanolic
extract on caco-2 cells. Drug Res (Stuttg). 67:547–552. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Loo WT, Sasano H and Chow LW: Evaluation
of therapeutic efficacy of capecitabine on human breast carcinoma
tissues and cell lines in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother. 61:553–557.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Nazari-Vanani R, Karimian K, Azarpira N
and Heli H: Capecitabine-loaded nanoniosomes and evaluation of
anticancer efficacy. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 47:420–426.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Kang YK, Lee SS, Yoon DH, Lee SY, Chun YJ,
Kim MS, Ryu MH, Chang HM, Lee JL and Kim TW: Pyridoxine is not
effective to prevent hand-foot syndrome associated with
capecitabine therapy: Results of a randomized, double-blind,
placebo-controlled study. J Clin Oncol. 28:3824–3829. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Satoh T and Hosokawa M: The mammalian
carboxylesterases: From molecules to functions. Annu Rev Pharmacol
Toxicol. 38:257–288. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Sanghani SP, Quinney SK, Fredenburg TB,
Sun Z, Davis WI, Murry DJ, Cummings OW, Seitz DE and Bosron WF:
Carboxylesterases expressed in human colon tumor tissue and their
role in CPT-11 hydrolysis. Clin Cancer Res. 9:4983–4991.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Satoh T and Hosokawa M: Structure,
function and regulation of carboxylesterases. Chem Biol Interact.
162:195–211. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Sanghani SP, Sanghani PC, Schiel MA and
Bosron WF: Human carboxylesterases: An update on CES1, CES2 and
CES3. Protein Pept Lett. 16:1207–1214. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Wang D, Zou L, Jin Q, Hou J, Ge G and Yang
L: Human carboxylesterases: A comprehensive review. Acta Pharm Sin
B. 8:699–712. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Pindel EV, Kedishvili NY, Abraham TL,
Brzezinski MR, Zhang J, Dean RA and Bosron WF: Purification and
cloning of a broad substrate specificity human liver
carboxylesterase that catalyzes the hydrolysis of cocaine and
heroin. J Biol Chem. 272:14769–14775. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Oakeshott JG, Claudianos C, Russell RJ and
Robin GC: Carboxyl/cholinesterases: A case study of the evolution
of a successful multigene family. Bioessays. 21:1031–1042. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Kim KK, Song HK, Shin DH, Hwang KY, Choe
S, Yoo OJ and Suh SW: Crystal structure of carboxylesterase from
Pseudomonas fluorescens, an alpha/beta hydrolase with broad
substrate specificity. Structure. 5:1571–1584. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Fleming CD, Edwards CC, Kirby SD, Maxwell
DM, Potter PM, Cerasoli DM and Redinbo MR: Crystal structures of
human carboxylesterase 1 in covalent complexes with the chemical
warfare agents soman and tabun. Biochemistry. 46:5063–5071. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Hosokawa M: Structure and catalytic
properties of carboxylesterase isozymes involved in metabolic
activation of prodrugs. Molecules. 13:412–431. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Taketani M, Shii M, Ohura K, Ninomiya S
and Imai T: Carboxylesterase in the liver and small intestine of
experimental animals and human. Life Sci. 81:924–932. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yano H, Kayukawa S, Iida S, Nakagawa C,
Oguri T, Sanda T, Ding J, Mori F, Ito A, Ri M, et al:
Overexpression of carboxylesterase-2 results in enhanced efficacy
of topoisomerase I inhibitor, irinotecan (CPT-11), for multiple
myeloma. Cancer Sci. 99:2309–2314. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Xie M, Yang D, Liu L, Xue B and Yan B:
Human and rodent carboxylesterases: Immunorelatedness, overlapping
substrate specificity, differential sensitivity to serine enzyme
inhibitors, and tumor-related expression. Drug Metab Dispos.
30:541–547. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Frances A and Cordelier P: The emerging
role of cytidine deaminase in human diseases: A new opportunity for
therapy? Mol Ther. 28:357–366. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Micozzi D, Carpi FM, Pucciarelli S,
Polzonetti V, Polidori P, Vilar S, Williams B, Costanzi S and
Vincenzetti S: Human cytidine deaminase: A biochemical
characterization of its naturally occurring variants. Int J Biol
Macromol. 63:64–74. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Vincenzetti S, Quadrini B, Mariani P, De
Sanctis G, Cammertoni N, Polzonetti V, Pucciarelli S, Natalini P
and Vita A: Modulation of human cytidine deaminase by specific
aminoacids involved in the intersubunit interactions. Proteins.
70:144–156. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Micozzi D, Pucciarelli S, Carpi FM,
Costanzi S, De Sanctis G, Polzonetti V, Natalini P, Santarelli IF,
Vita A and Vincenzetti S: Role of tyrosine 33 residue for the
stabilization of the tetrameric structure of human cytidine
deaminase. Int J Biol Macromol. 47:471–482. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Vincenzetti S, Pucciarelli S, Carpi FM,
Micozzi D, Polzonetti V, Natalini P, Santarelli I, Polidori P and
Vita A: Site directed mutagenesis as a tool to understand the
catalytic mechanism of human cytidine deaminase. Protein Pept Lett.
20:538–549. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Ho DH: Distribution of kinase and
deaminase of 1-beta-D-arabinofuranosylcytosine in tissues of man
and mouse. Cancer Res. 33:2816–2820. 1973.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Ishikawa T, Sawada N, Sekiguchi F, Fukase
Y and Ishitsuka H: Xeloda™ (capecitabine), a new oral
fluoropyrimidine carbamate with an improved efficacy profile over
other fluoropyrimidines. Proc Am Soc Clin Oncol. 16:226a1997.
|
|
99
|
Hessmann E, Patzak MS, Klein L, Chen N,
Kari V, Ramu I, Bapiro TE, Frese KK, Gopinathan A, Richards FM, et
al: Fibroblast drug scavenging increases intratumoural gemcitabine
accumulation in murine pancreas cancer. Gut. 67:497–507. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Elamin YY, Rafee S, Osman N, O Byrne KJ
and Gately K: Thymidine phosphorylase in cancer; enemy or friend?
Cancer Microenviron. 9:33–43. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Mitsiki E, Papageorgiou AC, Iyer S,
Thiyagarajan N, Prior SH, Sleep D, Finnis C and Acharya KR:
Structures of native human thymidine phosphorylase and in complex
with 5-iodouracil. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 386:666–670. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Li W and Yue H: Thymidine phosphorylase: A
potential new target for treating cardiovascular disease. Trends
Cardiovasc Med. 28:157–171. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
103
|
Bijnsdorp IV, Capriotti F, Kruyt FA,
Losekoot N, Fukushima M, Griffioen AW, Thijssen VL and Peters GJ:
Thymidine phosphorylase in cancer cells stimulates human
endothelial cell migration and invasion by the secretion of
angiogenic factors. Br J Cancer. 104:1185–1192. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Ishikawa F, Miyazono K, Hellman U, Drexler
H, Wernstedt C, Hagiwara K, Usuki K, Takaku F, Risau W and Heldin
CH: Identification of angiogenic activity and the cloning and
expression of platelet-derived endothelial cell growth factor.
Nature. 338:557–562. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Bronckaers A, Gago F, Balzarini J and
Liekens S: The dual role of thymidine phosphorylase in cancer
development and chemotherapy. Med Res Rev. 29:903–953. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Kamatani N, Jinnah HA, Hennekam RC and van
Kuilenburg AB: Purine and pyrimidine metabolism. In Emery and
Rimoin's Principles and Practice of Medical Genetics. Academic
Press. 1–38. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
107
|
Harris AL and Generali D: Inhibitors of
tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Drug Design and Discovery. 275–306.
2008.
|
|
108
|
Temmink OH, de Bruin M, Turksma AW, Cricca
S, Laan AC and Peters GJ: Activity and substrate specificity of
pyrimidine phosphorylases and their role in fluoropyrimidine
sensitivity in colon cancer cell lines. Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
39:565–575. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
109
|
Sivridis E, Giatromanolaki A, Anastasiadis
P, Georgiou L, Gatter KC, Harris AL, Bicknell R and Koukourakis MI;
Tumour Angiogenesis Research Group, : Angiogenic co-operation of
VEGF and stromal cell TP in endometrial carcinomas. J Pathol.
196:416–422. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
110
|
Xiao X, Wang T, Li L, Zhu Z, Zhang W, Cui
G and Li W: Co-delivery of cisplatin(IV) and capecitabine as an
effective and non-toxic cancer treatment. Front Pharmacol.
10:1102019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
111
|
Huo X, Li J, Zhao F, Ren D, Ahmad R, Yuan
X, Du F and Zhao J: The role of capecitabine-based neoadjuvant and
adjuvant chemotherapy in early-stage triple-negative breast cancer:
A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMC Cancer. 21:782021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
112
|
Voegeli M and Wicki A: Neoadjuvant,
adjuvant and palliative systemic therapy of colorectal cancer. Ther
Umsch. 75:622–626. 2018.(In German). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
113
|
Zhou H, Wang Y, Lin Y, Cai W, Li X and He
X: Preliminary efficacy and safety of camrelizumab in combination
with XELOX plus bevacizumab or regorafenib in patients with
metastatic colorectal cancer: A retrospective study. Front Oncol.
11:7744452021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
114
|
Sabeti Aghabozorgi A, Moradi Sarabi M,
Jafarzadeh-Esfehani R, Koochakkhani S, Hassanzadeh M, Kavousipour S
and Eftekhar E: Molecular determinants of response to
5-fluorouracil-based chemotherapy in colorectal cancer: The
undisputable role of micro-ribonucleic acids. World J Gastrointest
Oncol. 12:942–956. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
115
|
Oneda E and Zaniboni A: Adjuvant treatment
of colon cancer with microsatellite instability-the state of the
art. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 169:1035372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
116
|
Cura Y, Pérez-Ramírez C, Sánchez-Martín A,
Membrive-Jimenez C, Valverde-Merino MI, González-Flores E and
Morales AJ: Influence of single-nucleotide polymorphisms on
clinical outcomes of capecitabine-based chemotherapy in colorectal
cancer patients: A systematic review. Cancers (Basel). 15:18212023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
117
|
Michel M, Kaps L, Maderer A, Galle PR and
Moehler M: The role of p53 dysfunction in colorectal cancer and its
implication for therapy. Cancers (Basel). 13:22962021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
118
|
Jung G, Hernández-Illán E, Moreira L,
Balaguer F and Goel A: Epigenetics of colorectal cancer: Biomarker
and therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
17:111–130. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
119
|
Marin JJG, Macias RIR, Monte MJ, Herraez
E, Peleteiro-Vigil A, Blas BS, Sanchon-Sanchez P, Temprano AG,
Espinosa-Escudero RA, Lozano E, et al: Cellular mechanisms
accounting for the refractoriness of colorectal carcinoma to
pharmacological treatment. Cancers (Basel). 12:26052020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
120
|
Zhang Y, Geng L, Talmon G and Wang J:
MicroRNA-520g confers drug resistance by regulating p21 expression
in colorectal cancer. J Biol Chem. 290:6215–6225. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
121
|
Boige V, Mollevi C, Gourgou S, Azria D,
Seitz JF, Vincent M, Bigot L, Juzyna B, Miran I, Gerard JP and
Laurent-Puig P: Impact of single-nucleotide polymorphisms in DNA
repair pathway genes on response to chemoradiotherapy in rectal
cancer patients: Results from ACCORD-12/PRODIGE-2 phase III trial.
Int J Cancer. 145:3163–3172. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
122
|
Leguisamo NM, Gloria HC, Kalil AN, Martins
TV, Azambuja DB, Meira LB and Saffi J: Base excision repair
imbalance in colorectal cancer has prognostic value and modulates
response to chemotherapy. Oncotarget. 8:54199–54214. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
123
|
Brown RE, Short SP and Williams CS:
Colorectal cancer and metabolism. Curr Colorectal Cancer Rep.
14:226–241. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
124
|
Chen Q, Meng F, Wang L, Mao Y, Zhou H, Hua
D, Zhang H and Wang W: A polymorphism in ABCC4 is related to
efficacy of 5-FU/capecitabine-based chemotherapy in colorectal
cancer patients. Sci Rep. 7:70592017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
125
|
Cao H, Xu E, Liu H, Wan L and Lai M:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in colorectal cancer metastasis:
A system review. Pathol Res Pract. 211:557–569. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|