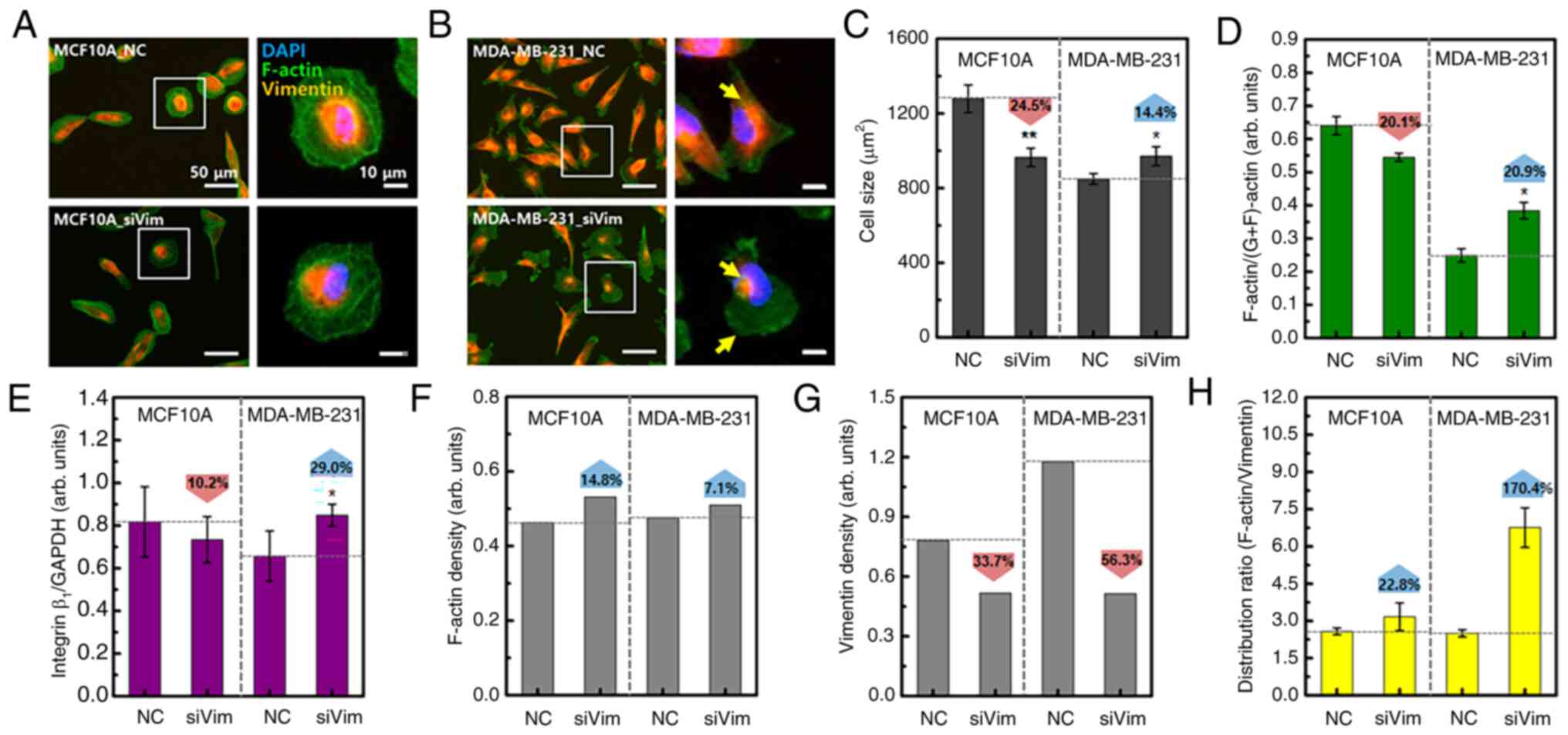
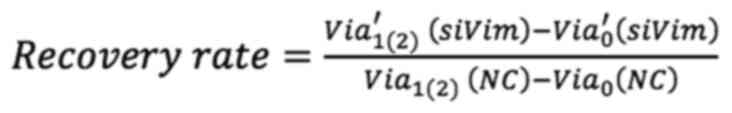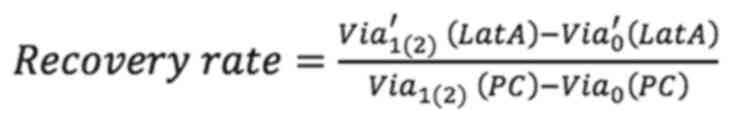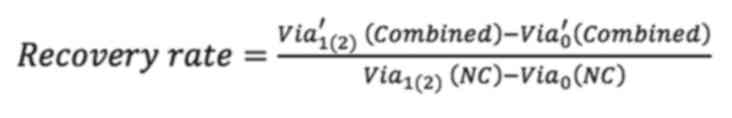|
1
|
Lin Z, Han Y, Wu B and Fang W: Altered
cytoskeletal structures in transformed cells exhibiting obviously
metastatic capabilities. Cell Res. 1:141–51. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Fletcher DA and Mullins RD: Cell mechanics
and the cytoskeleton. Nature. 463:485–492. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamaguchi H and Condeelis J: Regulation of
the actin cytoskeleton in cancer cell migration and invasion.
Biochim Biophys Acta. 1773:642–652. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Tang DD and Gerlach BD: The roles and
regulation of the actin cytoskeleton, intermediate filaments and
microtubules in smooth muscle cell migration. Respir Res.
18:542017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu CY, Lin HH, Tang MJ and Wang YK:
Vimentin contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition cancer
cell mechanics by mediating cytoskeletal organization and focal
adhesion maturation. Oncotarget. 6:15966–15983. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sun B, Fang Y, Li Z, Chen Z and Xiang J:
Role of cellular cytoskeleton in epithelial-mesenchymal transition
process during cancer progression. Biomed Rep. 3:603–610. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Battaglia RA, Delic S, Herrmann H and
Snider NT: Vimentin on the move: New developments in cell
migration. F1000Res. 7:17962018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Wu S, Du Y, Beckford J and Alachkar H:
Upregulation of the EMT marker vimentin is associated with poor
clinical outcome in acute myeloid leukemia. J Transl Med.
16:1702108. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Tadokoro A, Kanaji N, Liu D, Yokomise H,
Haba R, Ishii T, Takagi T, Watanabe N, Kita N, Kadowaki N and
Bandoh S: Vimentin regulates invasiveness and is a poor prognostic
marker in non-small cell lung cancer. Anticancer Res. 36:1545–1551.
2106.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kwon S, Yang W, Moon D and Kim KS:
Comparison of cancer cell elasticity by cell type. J Cancer.
11:5403–5412. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li X, Kierfeld J and Lipowsky R: Actin
polymerization and depolymerization coupled to cooperative
hydrolysis. Phys Rev Lett. 103:0481022009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Satelli A and Li S: Vimentin in cancer and
its potential as a molecular target for cancer therapy. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 68:3033–3046. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peng GE, Wilson SR and Weiner OD: A
pharmacological cocktail for arresting actin dynamics in living
cells. Mol Biol Cell. 22:3986–3994. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Stehn JR, Haass NK, Bonello T, Desouza M,
Kottyan G, Treutlein H, Zeng J, Nascimento PRBB, Sequeira VB,
Butler TL, et al: A novel class of anticancer compounds targets the
actin cytoskeleton in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 73:5169–5182. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Tang K, Xin Y, Li K, Chen X and Tan Y:
Cell cytoskeleton and stiffness are mechanical indicators of
organotropism in breast cancer. Biology (Basel).
10:2592021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gandalovičová A, Rosel D, Fernandes M,
Veselý P, Heneberg P, Čermák V, Petruželka L, Kumar S, Sanz-Moreno
V and Brábek J: Migrastatics-anti-metastatic and anti-invasion
drugs: Promises and challenges. Trends Cancer. 3:391–406. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fife CM, McCarroll JA and Kavallaris M:
Movers and shakers: Cell cytoskeleton in cancer metastasis. Brit J
Pharmacol. 171:5507–5523. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Atteeq M: Evaluating anticancer properties
of withaferin A-a potent phytochemical. Front Pharmacol.
13:9753202022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nagy Z, Cheung BB, Tsang W, Tan O, Herath
M, Ciampa OC, Shadma F, Carter DR and Marshall GM: Withaferin A
activates TRIM16 for its anti-cancer activity in melanoma. Sci Rep.
10:197242020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Burikhanov R, Sviripa VM, Hebbar N, Zhang
W, Layton WJ, Hamza A, Zhan CG, Watt DS, Liu C and Rangnekar VM:
Arylquins target vimentin to trigger Par-4 secretion for tumor cell
apoptosis. Nat Chem Biol. 10:924–926. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheratta AR, Thayyullathil F,
Pallichankandy S, Subburayan K, Alakkal A and Galadari S: Prostate
apoptosis response-4 and tumor suppression: It's not just about
apoptosis anymore. Cell Death Dis. 12:472021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Giganti A and Friederich E: The actin
cytoskeleton as a therapeutic target: State of the art and future
directions. Prog Cell Cycle Res. 5:511–525. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Cramer LP: Role of actin-filament
disassembly in lamellipodium protrusion in motile cells revealed
using the drug jasplakinolide. Curr Biol. 9:1095–1105. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Strouhalova K, Přechová M, Gandalovičová
A, Brábek J, Gregor M and Rosel D: Vimentin intermediate filaments
as potential target for cancer treatment. Cancers (Basel).
12:1842020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Han R and Chen J: A modified Sneddon model
for the contact between conical indenters and spherical samples. J
Mater Res. 36:1762–1771. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hou S, Isaji T, Hang Q, Im S, Fukada T and
Gu J: Distinct effects of integrin β1 on cell
proliferation and cellular signaling in MDA-MB-231 breast cancer
cells. Sci Rep. 6:184302016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Vinckier A and Semenza G: Measuring
elasticity of biological materials by atomic force microscopy. FEBS
Lett. 430:12–16. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ridley AJ: Life at the leading edge. Cell.
145:1012–1022. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gagliardi PA, Puliafito A, Blasio L,
Chianale F, Somale D, Seano G, Bussolino F and Primo L: Real-time
monitoring of cell protrusion dynamics by impedance responses. Sci
Rep. 5:102062015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Wilson K, Lewalle A, Fritzsche M,
Thorogate R, Duke T and Charras G: Mechanisms of leading-edge
protrusion in interstitial migration. Nat Commun. 4:28962013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Duarte S, Viedma-Poyatos Á,
Navarro-Carrasco E, Martínez AE, Pajares MA and Pérez-Sala D:
Vimentin filaments interact with the actin cortex in mitosis
allowing normal cell division. Nat Commun. 10:42002019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mezu-Ndubuisi OJ and Maheshwari A: The
role of integrins in inflammation and angiogenesis. Pediatr Res.
89:1619–1626. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Alberts B, Johnson A, Lewis J, Raff M,
Roberts K and Walter P: Molecular biology of the cell. 4th edition.
New York: Garland Science; 2002
|
|
34
|
Luo M and Guan JL: Focal adhesion kinase:
A prominent determinant in breast cancer initiation, progression
and metastasis. Cancer Lett. 289:127–139. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gemperle J, Dibus M, Koudelková L, Rosel D
and Brábek J: The interaction of p130Cas with PKN3 promotes
malignant growth. Mol Oncol. 13:264–289. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Madan R, Smolkin MB, Cocker R, Fayyad R
and Oktay MH: Focal adhesion proteins as markers of malignant
transformation and prognostic indicators in breast carcinoma. Hum
Pathol. 37:9–15. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Guan JL and Shalloway D: Regulation of
focal adhesion-associated protein tyrosine kinase by both cellular
adhesion and oncogenic transformation. Nature. 358:690–692. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Guan JL: Integrin signaling through FAK in
the regulation of mammary stem cells and breast cancer. IUBMB Life.
62:268–276. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hahm ER, Mathan SV, Singh RP and Singh SV:
Breast cancer selective disruption of actin cytoskeleton by diallyl
trisulfide. J Cancer Prev. 27:101–111. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Meng Z, Li Z, Xie M, Yu H, Jiang L and Yao
X: TM9SF4 is an F-actin disassembly factor that promotes tumor
progression and metastasis. Nat Commun. 13:57282022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Mierke CT: Mechanical cues affect
migration and invasion of cells from three different directions.
Front Cell Dev Biol. 8:5832262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Jonietz E: Mechanics: The forces of
cancer. Nature. 491:S56–S57. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Alibert C, Goud B and Manneville JB: Are
cancer cells really softer than normal cells? Biol Cell.
109:167–189. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu W, Mezencev R, Kim B, Wang L, McDonald
J and Sulchek T: Cell stiffness is a biomarker of the metastatic
potential of ovarian cancer cells. PLoS One. 7:e466092012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Kim TH, Gill NK, Nyberg KD, Nguyen AV,
Hohlbauch SV, Geisse NA, Nowell CJ, Sloan EK and Rowat AC: Cancer
cells become less deformable and more invasive with activation of
β-adrenergic signaling. J Cell Sci. 129:4563–4575. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sahai E: Illuminating the metastatic
process. Nat Rev Cancer. 7:737–749. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Pachmayr E, Treese C and Stein U:
Underlying mechanisms for distant metastasis-molecular biology.
Visc Med. 33:11–20. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|