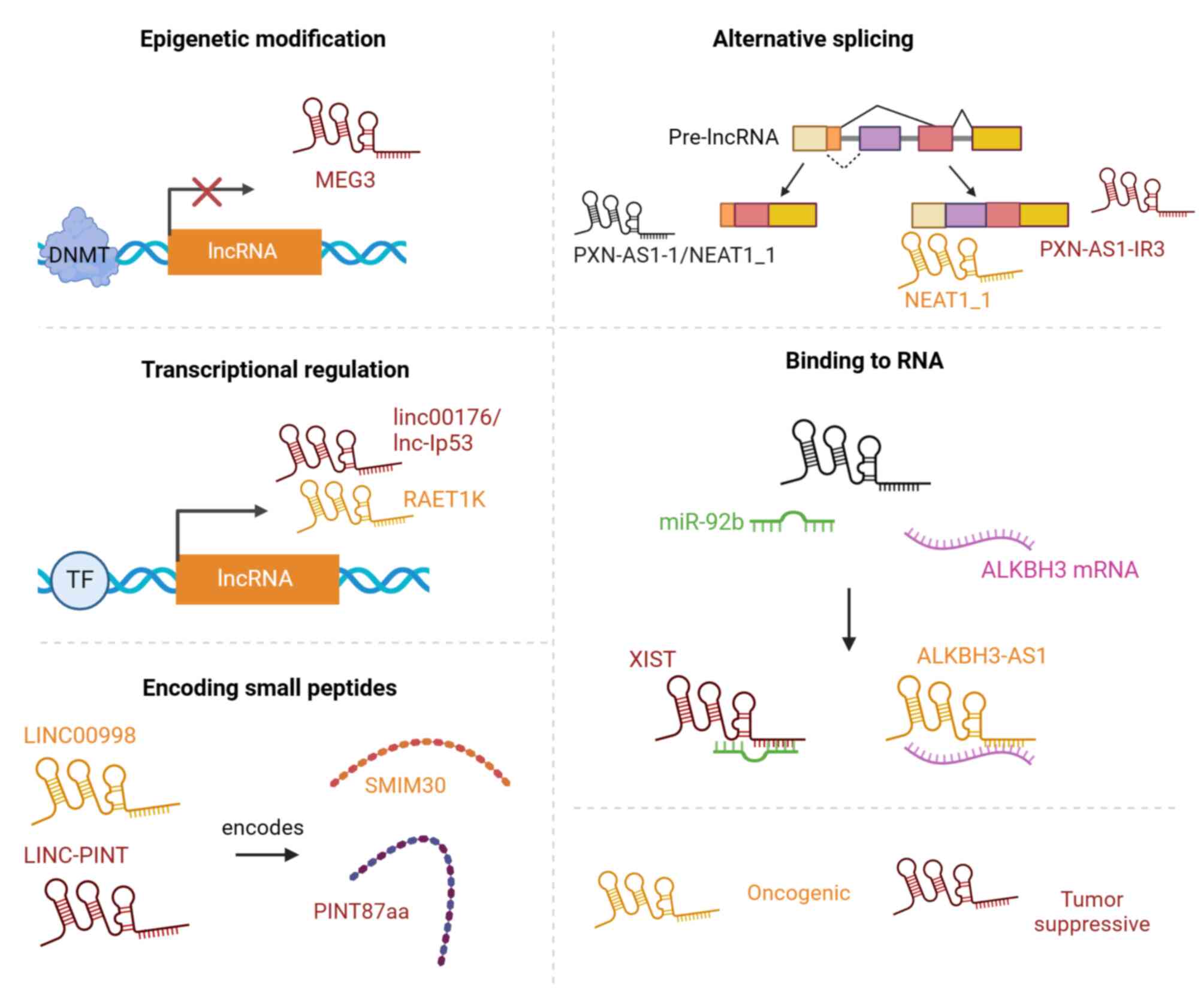
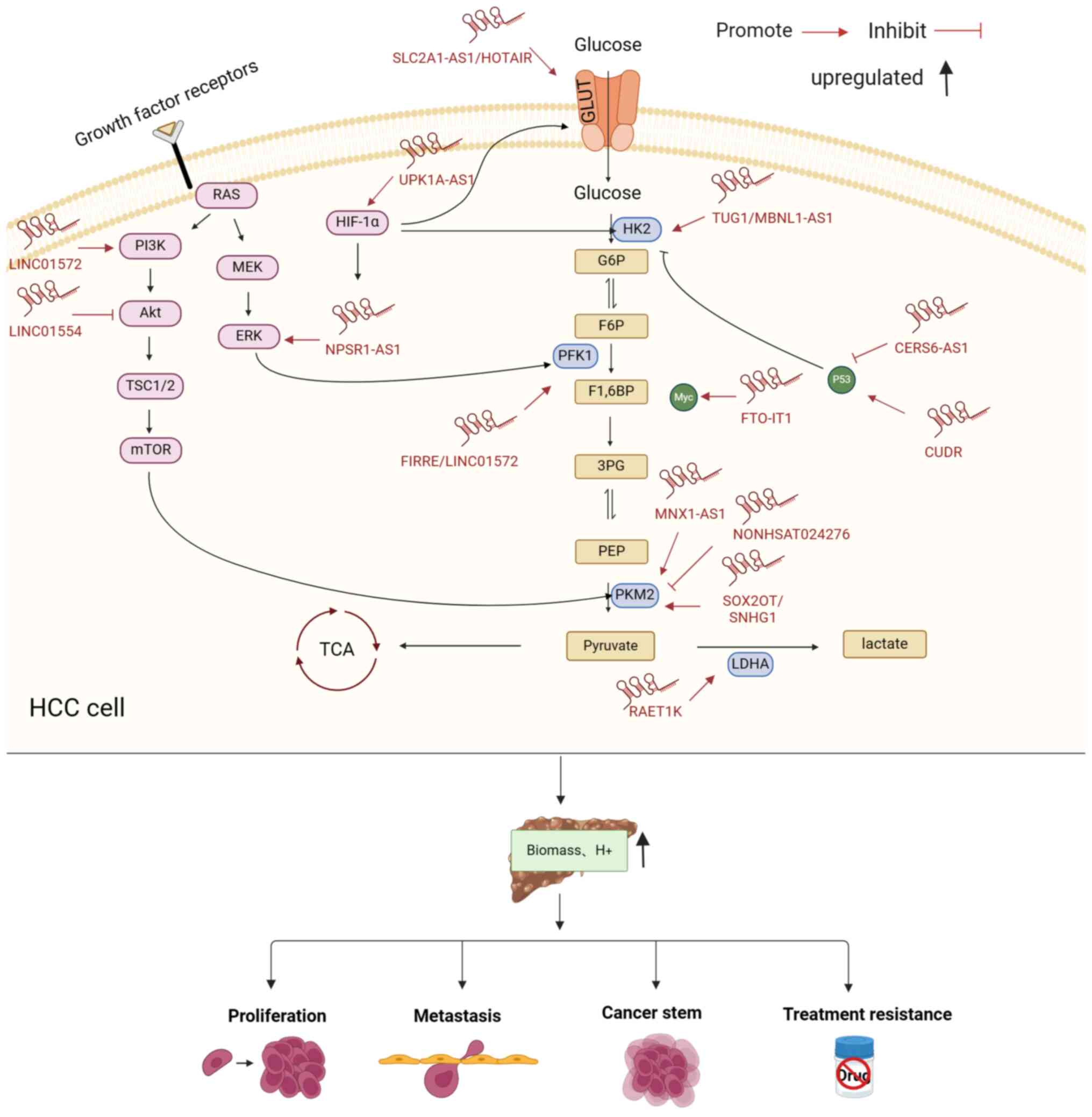
|
1
|
Bertuccio P, Turati F, Carioli G,
Rodriguez T, La Vecchia C, Malvezzi M and Negri E: Global trends
and predictions in hepatocellular carcinoma mortality. J Hepatol.
67:302–309. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Yang JD, Hainaut P, Gores GJ, Amadou A,
Plymoth A and Roberts LR: A global view of hepatocellular
carcinoma: Trends, risk, prevention and management. Nat Rev
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:589–604. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Vander Heiden MG, Cantley LC and Thompson
CB: Understanding the Warburg effect: The metabolic requirements of
cell proliferation. Science. 324:1029–1033. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lunt SY and Vander Heiden MG: Aerobic
glycolysis: meeting the metabolic requirements of cell
proliferation. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol. 27:441–464. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shestov AA, Liu X, Ser Z, Cluntun AA, Hung
YP, Huang L, Kim D, Le A, Yellen G, Albeck JG, et al: Quantitative
determinants of aerobic glycolysis identify flux through the enzyme
GAPDH as a limiting step. Elife. 3:e033422014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guido C, Whitaker-Menezes D, Capparelli C,
Balliet R, Lin Z, Pestell RG, Howell A, Aquila S, Andò S,
Martinez-Outschoorn U, et al: Metabolic reprogramming of
cancer-associated fibroblasts by TGF-β drives tumor growth:
Connecting TGF-β signaling with ‘Warburg-like’ cancer metabolism
and L-lactate production. Cell Cycle. 11:3019–3035. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liberti MV and Locasale JW: The Warburg
effect: How does it benefit cancer cells? Trends Biochem Sci.
41:211–218. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Sattler UGA and Mueller-Klieser W: The
anti-oxidant capacity of tumour glycolysis. Int J Radiat Biol.
85:963–971. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Beyoğlu D, Imbeaud S, Maurhofer O,
Bioulac-Sage P, Zucman-Rossi J, Dufour JF and Idle JR: Tissue
metabolomics of hepatocellular carcinoma: Tumor energy metabolism
and the role of transcriptomic classification. Hepatology.
58:229–238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Bustamante E and Pedersen PL: High aerobic
glycolysis of rat hepatoma cells in culture: Role of mitochondrial
hexokinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 74:3735–3739. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Djebali S, Davis CA, Merkel A, Dobin A,
Lassmann T, Mortazavi A, Tanzer A, Lagarde J, Lin W, Schlesinger F,
et al: Landscape of transcription in human cells. Nature.
489:101–108. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
ENCODE Project Consortium, Birney E,
Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Dutta A, Guigó R, Gingeras TR, Margulies EH,
Weng Z, Snyder M, Dermitzakis ET, et al: Identification and
analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the
ENCODE pilot project. Nature. 447:799–816. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Deng H, Zhang J, Shi J, Guo Z, He C, Ding
L, Tang JH and Hou Y: Role of long non-coding RNA in tumor drug
resistance. Tumour Biol. 37:11623–11631. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Li J, Meng H, Bai Y and Wang K: Regulation
of lncRNA and its role in cancer metastasis. Oncol Res. 23:205–217.
2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shen XH, Qi P and Du X: Long non-coding
RNAs in cancer invasion and metastasis. Mod Pathol. 28:4–13. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Statello L, Guo CJ, Chen LL and Huarte M:
Gene regulation by long non-coding RNAs and its biological
functions. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 22:96–118. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yuan SX, Zhang J, Xu QG, Yang Y and Zhou
WP: Long noncoding RNA, the methylation of genomic elements and
their emerging crosstalk in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett.
379:239–244. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Tang J, Xie Y, Xu X, Yin Y, Jiang R, Deng
L, Tan Z, Gangarapu V, Tang J and Sun B: Bidirectional
transcription of Linc00441 and RB1 via H3K27 modification-dependent
way promotes hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 8:e26752017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Braconi C, Kogure T, Valeri N, Huang N,
Nuovo G, Costinean S, Negrini M, Miotto E, Croce CM and Patel T:
microRNA-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding RNA gene
MEG3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene. 30:4750–4756. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhou Y, Huan L, Wu Y, Bao C, Chen B, Wang
L, Huang S, Liang L and He X: LncRNA ID2-AS1 suppresses tumor
metastasis by activating the HDAC8/ID2 pathway in hepatocellular
carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 469:399–409. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yuan JH, Liu XN, Wang TT, Pan W, Tao QF,
Zhou WP, Wang F and Sun SH: The MBNL3 splicing factor promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma by increasing PXN expression through the
alternative splicing of lncRNA-PXN-AS1. Nat Cell Biol. 19:820–832.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Zhou HZ, Li F, Cheng ST, Xu Y, Deng HJ, Gu
DY, Wang J, Chen WX, Zhou YJ, Yang ML, et al: DDX17-regulated
alternative splicing that produced an oncogenic isoform of PXN-AS1
to promote HCC metastasis. Hepatology. 75:847–865. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang H, Su X, Burley SK and Zheng XFS:
mTOR regulates aerobic glycolysis through NEAT1 and nuclear
paraspeckle-mediated mechanism in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Theranostics. 12:3518–3533. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tran DDH, Kessler C, Niehus SE, Mahnkopf
M, Koch A and Tamura T: Myc target gene, long intergenic noncoding
RNA, Linc00176 in hepatocellular carcinoma regulates cell cycle and
cell survival by titrating tumor suppressor microRNAs. Oncogene.
37:75–85. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhou Y, Huang Y, Hu K, Zhang Z, Yang J and
Wang Z: HIF1A activates the transcription of lncRNA RAET1K to
modulate hypoxia-induced glycolysis in hepatocellular carcinoma
cells via miR-100-5p. Cell Death Dis. 11:1762020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu J, Liu S, Ye F, Shen Y, Tie Y, Zhu J,
Wei L, Jin Y, Fu H, Wu Y and Zheng X: Long noncoding RNA MEG3
interacts with p53 protein and regulates partial p53 target genes
in hepatoma cells. PLoS One. 10:e1397902015.
|
|
27
|
Lu Q, Wang H, Lei X, Ma Q, Zhao J, Sun W,
Guo C, Huang D and Xu Q: LncRNA ALKBH3-AS1 enhances ALKBH3 mRNA
stability to promote hepatocellular carcinoma cell proliferation
and invasion. J Cell Mol Med. 26:5292–5302. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhuang LK, Yang YT, Ma X, Han B, Wang ZS,
Zhao QY, Wu LQ and Qu ZQ: MicroRNA-92b promotes hepatocellular
carcinoma progression by targeting Smad7 and is mediated by long
non-coding RNA XIST. Cell Death Dis. 7:e22032016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pang Y, Liu Z, Han H, Wang B, Li W, Mao C
and Liu S: Peptide SMIM30 promotes HCC development by inducing
SRC/YES1 membrane anchoring and MAPK pathway activation. J Hepatol.
73:1155–1169. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiang X, Fu Y, Zhao K, Miao R, Zhang X, Ma
X, Liu C, Zhang N and Qu K: Cellular senescence in hepatocellular
carcinoma induced by a long non-coding RNA-encoded peptide PINT87aa
by blocking FOXM1-mediated PHB2. Theranostics. 11:4929–4944. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xu W, Deng B, Lin P, Liu C, Li B, Huang Q,
Zhou H, Yang J and Qu L: Ribosome profiling analysis identified a
KRAS-interacting microprotein that represses oncogenic signaling in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Sci China Life Sci. 63:529–542.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Li S, Li J, Dai W, Zhang Q, Feng J, Wu L,
Liu T, Yu Q, Xu S, Wang W, et al: Genistein suppresses aerobic
glycolysis and induces hepatocellular carcinoma cell death. Br J
Cancer. 117:1518–1528. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Li Y, Lu Z, Liang Z, Ji D, Zhang P, Liu Q,
Zheng X and Yao Y: Metastasis-associated in colon cancer-1 is
associated with poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma, partly
by promoting proliferation through enhanced glucose metabolism. Mol
Med Rep. 12:426–434. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Pan L, Feng F, Wu J, Fan S, Han J, Wang S,
Yang L, Liu W, Wang C and Xu K: Demethylzeylasteral targets lactate
by inhibiting histone lactylation to suppress the tumorigenicity of
liver cancer stem cells. Pharmacol Res. 181:1062702022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Ganapathy-Kanniappan S: Linking tumor
glycolysis and immune evasion in cancer: Emerging concepts and
therapeutic opportunities. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer.
1868:212–220. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
He H, Chen T, Mo H, Chen S, Liu Q and Guo
C: Hypoxia-inducible long noncoding RNA NPSR1-AS1 promotes the
proliferation and glycolysis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
regulating the MAPK/ERK pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
533:886–892. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu C, Xu K, Liu J, He C, Liu P, Fu Q,
Zhang H and Qin T: LncRNA RP11-620J15.3 promotes HCC cell
proliferation and metastasis by targeting miR-326/GPI to enhance
glycolysis. Biol Direct. 18:152023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Zhang H, Zhao L, Ren P and Sun X: LncRNA
MBNL1-AS1 knockdown increases the sensitivity of hepatocellular
carcinoma to tripterine by regulating miR-708-5p-mediated
glycolysis. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 1–18. 2023.(Epub ahead of
print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lu L, Huang J, Mo J, Da X, Li Q, Fan M and
Lu H: Exosomal lncRNA TUG1 from cancer-associated fibroblasts
promotes liver cancer cell migration, invasion, and glycolysis by
regulating the miR-524-5p/SIX1 axis. Cell Mol Biol Lett. 27:172022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Lin YH, Wu MH, Huang YH, Yeh CT, Cheng ML,
Chi HC, Tsai CY, Chung IH, Chen CY and Lin KH: Taurine up-regulated
gene 1 functions as a master regulator to coordinate glycolysis and
metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 67:188–203.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Hu M, Fu Q, Jing C, Zhang X, Qin T and Pan
Y: LncRNA HOTAIR knockdown inhibits glycolysis by regulating
miR-130a-3p/HIF1A in hepatocellular carcinoma under hypoxia. Biomed
Pharmacother. 125:1097032020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Wei S, Fan Q, Yang L, Zhang X, Ma Y, Zong
Z, Hua X, Su D, Sun H, Li H and Liu Z: Promotion of glycolysis by
HOTAIR through GLUT1 upregulation via mTOR signaling. Oncol Rep.
38:1902–1908. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Malakar P, Stein I, Saragovi A, Winkler R,
Stern-Ginossar N, Berger M, Pikarsky E and Karni R: Long Noncoding
RNA MALAT1 regulates cancer glucose metabolism by enhancing
mTOR-mediated translation of TCF7L2. Cancer Res. 79:2480–2493.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Xu M, Zhou C, Weng J, Chen Z, Zhou Q, Gao
J, Shi G, Ke A, Ren N, Sun H and Shen Y: Tumor associated
macrophages-derived exosomes facilitate hepatocellular carcinoma
malignance by transferring lncMMPA to tumor cells and activating
glycolysis pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 41:2532022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li X, Zhao Q, Qi J, Wang W, Zhang D, Li Z
and Qin C: lncRNA Ftx promotes aerobic glycolysis and tumor
progression through the PPARγ pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Int J Oncol. 53:551–566. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Chen K, Wang X, Wei B, Sun R, Wu C and
Yang HJ: LncRNA SNHG6 promotes glycolysis reprogramming in
hepatocellular carcinoma by stabilizing the BOP1 protein. Anim
Cells Syst (Seoul). 26:369–379. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Wang F, Hu Y, Wang H, Hu P, Xiong H, Zeng
Z, Han S, Wang D, Wang J, Zhao Y, et al: LncRNA FTO-IT1 promotes
glycolysis and progression of hepatocellular carcinoma through
modulating FTO-mediated N6-methyladenosine modification on GLUT1
and PKM2. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 42:2672023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liang Y, Zhang D, Zheng T, Yang G, Wang J,
Meng F, Liu Y, Zhang G, Zhang L, Han J, et al: lncRNA-SOX2OT
promotes hepatocellular carcinoma invasion and metastasis through
miR-122-5p-mediated activation of PKM2. Oncogenesis. 9:542020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Ye Y, Wang M, Wang G, Mai Z, Zhou B, Han
Y, Zhuang J and Xia W: lncRNA miR4458HG modulates hepatocellular
carcinoma progression by activating m6A-dependent glycolysis and
promoting the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 80:992023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Li X, Li Y, Bai S, Zhang J, Liu Z and Yang
J: NR2F1-AS1/miR-140/HK2 axis regulates hypoxia-induced glycolysis
and migration in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res.
13:427–437. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Ma X, Mao Z, Zhu J, Liu H and Chen F:
lncRNA PANTR1 upregulates BCL2A1 expression to promote
tumorigenesis and warburg effect of hepatocellular carcinoma
through restraining miR-587. J Immunol Res. 2021:17368192021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Shang R, Wang M, Dai B, Du J, Wang J, Liu
Z, Qu S, Yang X, Liu J, Xia C, et al: Long noncoding RNA SLC2A1-AS1
regulates aerobic glycolysis and progression in hepatocellular
carcinoma via inhibiting the STAT3/FOXM1/GLUT1 pathway. Mol Oncol.
14:1381–1396. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Shen C, Ding L, Mo H, Liu R, Xu Q and Tu
K: Long noncoding RNA FIRRE contributes to the proliferation and
glycolysis of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by enhancing PFKFB4
expression. J Cancer. 12:4099–4108. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Lai S, Quan Z, Hao Y, Liu J, Wang Z, Dai
L, Dai H, He S and Tang B: Long non-coding RNA LINC01572 promotes
hepatocellular carcinoma progression via sponging miR-195-5p to
enhance PFKFB4-mediated glycolysis and PI3K/AKT activation. Front
Cell Dev Biol. 9:7830882021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Ji W, Bai J and Ke Y: Exosomal ZFPM2-AS1
contributes to tumorigenesis, metastasis, stemness, macrophage
polarization, and infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma through
PKM mediated glycolysis. Environ Toxicol. 38:1332–1346. 2023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Wang Y, Yang F, Peng Q, Mei K, He H and
Yang Q: Long non-coding RNA SNHG1 activates glycolysis to promote
hepatocellular cancer progression through the miR-326/PKM2 axis. J
Gene Med. 24:e34402022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Xu B, Wei Y, Liu F, Li L, Zhou S, Peng Y
and Li B: Long noncoding RNA CERS6-AS1 modulates glucose metabolism
and tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting the
MDM2/p53 signaling pathway. Cell Death Discov. 8:3482022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wu Y, Wang Y, Yao H, Li H, Meng F, Li Q,
Lin X and Liu L: MNX1-AS1, a c-Myc induced lncRNA, promotes the
Warburg effect by regulating PKM2 nuclear translocation. J Exp Clin
Cancer Res. 41:3372022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Zhang D, Zou X, Song Y and Wu D: Long
non-coding RNA UPK1A-AS1 promotes glycolysis in hepatocellular
carcinoma cells via stabilization of HIF-1α. Nan Fang Yi Ke Da Xue
Xue Bao. 41:193–199. 2021.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Chen B, Xu X, Wu W, Zheng K and Yu Y:
LINC00659 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma malignant progression
by blocking aerobic glycolysis through FUS recruitment and SLC10A1
modulation. Anal Cell Pathol (Amst). 2023:58529632023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Zheng YL, Li L, Jia YX, Zhang BZ, Li JC,
Zhu YH, Li MQ, He JZ, Zeng TT, Ban XJ, et al: LINC01554-mediated
glucose metabolism reprogramming suppresses tumorigenicity in
hepatocellular carcinoma via downregulating PKM2 expression and
inhibiting Akt/mTOR signaling pathway. Theranostics. 9:796–810.
2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Guan YF, Huang QL, Ai YL, Chen QT, Zhao
WX, Wang XM, Wu Q and Chen HZ: Nur77-activated lncRNA WFDC21P
attenuates hepatocarcinogenesis via modulating glycolysis.
Oncogene. 39:2408–2423. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Li Y, Chen X, Huang H, Liao L, Chong H, Li
G, Yuan T, Lu W, Deng S and Huang Q: A feedback loop between
NONHSAT024276 and PTBP1 inhibits tumor progression and glycolysis
in HCC by increasing the PKM1/PKM2 ratio. Cancer Sci.
114:1519–1540. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Huang MD, Chen WM, Qi FZ, Sun M, Xu TP, Ma
P and Shu YQ: Long non-coding RNA TUG1 is up-regulated in
hepatocellular carcinoma and promotes cell growth and apoptosis by
epigenetically silencing of KLF2. Mol Cancer. 14:1652015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Chen K, Wei H, Pan J, Chen Z, Pan D, Gao
T, Huang J, Huang M, Ou M and Zhong W: Six1 is negatively
correlated with poor prognosis and reduces 5-fluorouracil
sensitivity via attenuating the stemness of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 861:1725992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Raju G, Pavitra E, Bandaru SS, Varaprasad
GL, Nagaraju GP, Malla RR, Huh YS and Han YK: HOTAIR: A potential
metastatic, drug-resistant and prognostic regulator of breast
cancer. Mol Cancer. 22:652023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Zhang J, Zhang P, Wang L, Piao HL and Ma
L: Long non-coding RNA HOTAIR in carcinogenesis and metastasis.
Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai). 46:1–5. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Li T, Sun X and Jiang X: UCA1 involved in
the metformin-regulated bladder cancer cell proliferation and
glycolysis. Tumour Biol. 39:10104283177108232017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Lou CH, Shao A, Shum EY, Espinoza JL,
Huang L, Karam R and Wilkinson MF: Posttranscriptional control of
the stem cell and neurogenic programs by the nonsense-mediated RNA
decay pathway. Cell Rep. 6:748–764. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
70
|
Zhou Y, Li Y, Wang N, Li X, Zheng J and Ge
L: UPF1 inhibits the hepatocellular carcinoma progression by
targeting long non-coding RNA UCA1. Sci Rep. 9:66522019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Grant SFA, Thorleifsson G, Reynisdottir I,
Benediktsson R, Manolescu A, Sainz J, Helgason A, Stefansson H,
Emilsson V, Helgadottir A, et al: Variant of transcription factor
7-like 2 (TCF7L2) gene confers risk of type 2 diabetes. Nat Genet.
38:320–323. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
72
|
Li GZ, Meng GX, Pan GQ, Zhang X, Yan LJ,
Li RZ, Ding ZN, Tan SY, Wang DX, Tian BW, et al: MALAT1/mir-1-3p
mediated BRF2 expression promotes HCC progression via inhibiting
the LKB1/AMPK signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 23:1882023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
73
|
Döring B, Lütteke T, Geyer J and Petzinger
E: The SLC10 carrier family: Transport functions and molecular
structure. Curr Top Membr. 70:105–168. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Tran QH, Nguyen VG, Tran CM and Nguyen MN:
Down-regulation of solute carrier family 10 member 1 is associated
with early recurrence and poorer prognosis of hepatocellular
carcinoma. Heliyon. 7:e064632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Lu C, Fang S, Weng Q, Lv X, Meng M, Zhu J,
Zheng L, Hu Y, Gao Y, Wu X, et al: Integrated analysis reveals
critical glycolytic regulators in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cell
Commun Signal. 18:972020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Zhang B, Xie Z and Li B: The
clinicopathologic impacts and prognostic significance of GLUT1
expression in patients with lung cancer: A meta-analysis. Gene.
689:76–83. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Kuai XY, Lei ZY, Liu XS and Shao XY: The
interaction of GLUT1 and FOXM1 leads to a poor prognosis in
colorectal cancer. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 20:941–950. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Xiao H, Wang J, Yan W, Cui Y, Chen Z, Gao
X, Wen X and Chen J: GLUT1 regulates cell glycolysis and
proliferation in prostate cancer. Prostate. 78:86–94. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Sun HW, Yu XJ, Wu WC, Chen J, Shi M, Zheng
L and Xu J: GLUT1 and ASCT2 as predictors for prognosis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 11:e01689072016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Barbosa AM and Martel F: Targeting glucose
transporters for breast cancer therapy: The effect of natural and
synthetic compounds. Cancers (Basel). 12:1542020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
DeWaal D, Nogueira V, Terry AR, Patra KC,
Jeon SM, Guzman G, Au J, Long CP, Antoniewicz MR and Hay N:
Hexokinase-2 depletion inhibits glycolysis and induces oxidative
phosphorylation in hepatocellular carcinoma and sensitizes to
metformin. Nat Commun. 9:4462018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Wu Q, Wang SP, Sun XX, Tao YF, Yuan XQ,
Chen QM, Dai L, Li CL, Zhang JY and Yang AL: HuaChanSu suppresses
tumor growth and interferes with glucose metabolism in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by restraining Hexokinase-2. Int J
Biochem Cell Biol. 142:1061232022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Ros S and Schulze A: Glycolysis back in
the limelight: Systemic targeting of HK2 blocks tumor growth.
Cancer Discov. 3:1105–1107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Zhang R, Su J, Xue SL, Yang H, Ju LL, Ji
Y, Wu KH, Zhang YW, Zhang YX, Hu JF and Yu M: HPV E6/p53 mediated
down-regulation of miR-34a inhibits Warburg effect through
targeting LDHA in cervical cancer. Am J Cancer Res. 6:312–320.
2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Zhang K, Zhang T, Yang Y, Tu W, Huang H,
Wang Y, Chen Y, Pan K and Chen Z:
N6-methyladenosine-mediated LDHA induction potentiates
chemoresistance of colorectal cancer cells through metabolic
reprogramming. Theranostics. 12:4802–4817. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
86
|
Christofk HR, Vander Heiden MG, Harris MH,
Ramanathan A, Gerszten RE, Wei R, Fleming MD, Schreiber SL and
Cantley LC: The M2 splice isoform of pyruvate kinase is important
for cancer metabolism and tumour growth. Nature. 452:230–233. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Kotowski K, Rosik J, Machaj F, Supplitt S,
Wiczew D, Jabłońska K, Wiechec E, Ghavami S and Dzięgiel P: Role of
PFKFB3 and PFKFB4 in cancer: Genetic basis, impact on disease
development/progression, and potential as therapeutic targets.
Cancers (Basel). 13:9092021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Wu M, An J, Zheng Q, Xin X, Lin Z, Li X,
Li H and Lu D: Double mutant P53 (N340Q/L344R) promotes
hepatocarcinogenesis through upregulation of Pim1 mediated by PKM2
and LncRNA CUDR. Oncotarget. 7:66525–66539. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Tang J, Yan T, Bao Y, Shen C, Yu C, Zhu X,
Tian X, Guo F, Liang Q, Liu Q, et al: LncRNA GLCC1 promotes
colorectal carcinogenesis and glucose metabolism by stabilizing
c-Myc. Nat Commun. 10:34992019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Yu Z, Wang Y, Deng J, Liu D, Zhang L, Shao
H, Wang Z, Zhu W, Zhao C and Ke Q: Long non-coding RNA COL4A2-AS1
facilitates cell proliferation and glycolysis of colorectal cancer
cells via miR-20b-5p/hypoxia inducible factor 1 alpha subunit axis.
Bioengineered. 12:6251–6263. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Badoiu SC, Greabu M, Miricescu D,
Stanescu-Spinu II, Ilinca R, Balan DG, Balcangiu-Stroescu AE, Mihai
DA, Vacaroiu IA, Stefani C and Jinga V: PI3K/AKT/mTOR dysregulation
and reprogramming metabolic pathways in renal cancer: Crosstalk
with the VHL/HIF axis. Int J Mol Sci. 24:83912023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
92
|
Zhu YJ, Zheng B, Wang HY and Chen L: New
knowledge of the mechanisms of sorafenib resistance in liver
cancer. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 38:614–622. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Zhang H, Wang Q, Liu J and Cao H:
Inhibition of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway reverses
sorafenib-derived chemo-resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Oncol Lett. 15:9377–9384. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Li J, Xing J, Yang Y, Liu J, Wang W, Xia
Y, Yan Z, Wang K, Wu D, Wu L, et al: Adjuvant
131I-metuximab for hepatocellular carcinoma after liver
resection: A randomised, controlled, multicentre, open-label, phase
2 trial. Lancet Gastroenterol Hepatol. 5:548–560. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Elgendy M, Cirò M, Hosseini A, Weiszmann
J, Mazzarella L, Ferrari E, Cazzoli R, Curigliano G, DeCensi A,
Bonanni B, et al: Combination of hypoglycemia and metformin impairs
tumor metabolic plasticity and growth by modulating the
PP2A-GSK3β-MCL-1 axis. Cancer Cell. 35:798–815. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Sasaki R, Kanda T, Yokosuka O, Kato N,
Matsuoka S and Moriyama M: Exosomes and hepatocellular carcinoma:
From bench to bedside. Int J Mol Sci. 20:14062019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|