Introduction
Human acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of
hematopoietic stem/progenitor cells that causes rapid growth of
abnormal cells in the bone marrow and circulating blood,
interfering with normal blood cell production through the
accumulation of immature myeloblasts (1). According to the World Health
Organization classification system, there are >20 subtypes of
AML, which are classified based on genetic abnormalities (gene or
chromosome changes) in myeloblasts and the percentage of
myeloblasts in bone marrow and blood. This type of leukemia tends
to worsen quickly if not treated (2).
AML treatment consists of chemotherapy and
hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (3,4). In
general, leukemic cells and hematopoietic tissues are more
sensitive to external stress than other tissues (5), so they are removed with chemotherapy
or whole-body ionizing radiation (IR) before hematopoietic stem
cell transplantation. However, serious side effects such as
graft-vs.-host disease and infections caused by immunodeficiency
are possible (6). Furthermore,
leukemic cells exposed to IR can develop a radiation resistance
population, which reduces the therapeutic effects of radiotherapy.
To reduce damage to healthy tissues while effectively targeting
cancer cells, fractionated irradiation is commonly used in
radiotherapy. Furthermore, it is noninvasive and widely accepted,
even by patients with limited treatment options. According to the
radiotherapeutic guidelines for AML by the International Journal of
Radiation Oncology (7), the most
common total body irradiation schedules include twice-daily 2 Gy
fractions given over 3 days (total dose, 12 Gy); twice-daily 1.5 Gy
fractions over 4–4.5 days (total dose, 12–13.5 Gy); and
three-times-daily 1.2 Gy fractions over 4 days (total dose, 12 Gy).
It is known that fractionated radiation exposure of cancer cells
can result in radioresistant cells in rare cases (8). Our group previously established a
radioresistant leukemic cell model with HL60 and its
characteristics were determined (9–12).
However, the pharmacological effect of various already approved
chemicals in these cells has remained elusive.
Recently, arsenic trioxide (ATO) has been proposed
as a chemical drug with antitumor properties against acute
promyelocytic leukemia (APL), a type of AML. ATO was found to have
antitumor effects on lymphoma and liver carcinoma in China in the
1970s, and Niu et al (13)
described clinical trials on APL. Soignet et al (14) then confirmed its antitumor effect in
patients with APL. Furthermore, the antitumor effects of APL were
confirmed in clinical trials in Japan, and it has been approved by
pharmaceutical regulations in several countries (15). ATO easily binds to thiol groups, and
when it interacts with intracellular mitochondria, reactive oxygen
species (ROS) are produced, causing cell damage (16,17).
ROS activated by ATO inhibits cell proliferation and death via a
cascade of active caspase families in the mitochondrial pathway
(18). However, there have been no
reports on the antitumor effects of ATO on radioresistant leukemia
cells or when combined with radiation.
The present study sought to clarify the antitumor
effect of ATO on leukemia cells that have developed radiation
resistance, as well as to determine its efficacy when combined with
IR.
Materials and methods
Cell preparation and culture
The human leukemia cell line HL60 (native cells) was
purchased from the RIKEN BioResource Center. The
radiation-resistant HL60 (Res-HL60) cell line was generated by
exposing the cells to 4 Gy irradiation per week for 4 weeks. Native
cells and Res-HL60 cells were cultured in RPMI-1640 medium (Thermo
Fisher Scientific, Inc.) supplemented with 10% heat-inactivated
fetal bovine serum (Japan Bioserum) and 1% penicillin/streptomycin
(Thermo Fisher Scientific, Inc.) in a saturated humidified
atmosphere at 37°C with 95% air and 5% CO2. The
characteristics of Res-HL60 (a higher cell proliferative capacity
and smaller cell size) were reported in previous studies by our
group (9–12).
Irradiation
X-ray irradiation (150 kVp, 20 mA with 0.5-mm
aluminum and 0.3-mm copper filters) was performed with an X-ray
generator (MBR-1520R-3; Hitachi Medical Co., Ltd.) at a 45-cm
distance between the focus and target. The dose was monitored using
a thimble ionization chamber set next to the sample during
irradiation. The dose rate was 1 Gy/min. The exposure of cultured
cells to X-rays was performed in the same manner as previously
described (9–12).
Determination of the half maximal
inhibitory concentration (IC50) of ATO
Crystallized ATO (Kanto Chemical Co., Inc.) has a
low solubility in pure water. Thus, after dissolving ATO in a 20%
sodium hydroxide solution (Nacalai Tesque Inc.), hydrochloric acid
(Nacalai Tesque Inc.) was added to neutralize it. The ATO solution
(4.8 mM) was sterilized by passing it through a 0.45-µm filter to
then it was added to cell culture medium (RPMI1640) to reach final
concentrations of 0.39 to 25 µM. Native cells and Res-HL60 cells
were seeded in a 24-well plate (Corning, Inc.) with 0.5 ml of
culture medium at 1×105 cells/ml. The cultures were
incubated at 37°C in a humidified atmosphere with 95% air and 5%
CO2. ATO was added to the culture medium after 24 h and
the total number of viable cells was counted after 48 or 72 h using
the trypan blue dye exclusion method (Merck KGaA). ATO
concentrations that reduced the number of viable cells by 50%
(IC50) were calculated by plotting the cell viability
against the log concentration of ATO and fitting the concentration.
The statistics of the Boltzmann function were used to calculate the
IC50. The percentage of viable cells was calculated
using the trypan blue exclusion assay, and viable cells were
counted with a Burker-Turk hemocytometer.
Cell cycle distribution analysis
Native cells and Res-HL60 cells were seeded in a
60-mm culture dish with 4 ml of medium and 2×105
cells/ml. After being irradiated at 4 Gy and/or administered ATO,
the cells were incubated for 24 h (early phase) and 48 h (late
phase). The harvested cells (5×105 cells) were treated
with pre-cooled (−20°C) 70% ethanol for 10 min on ice, and RNase I
(5 µg/ml; Merck KGaA) was also added. These cells were stained with
propidium iodide (50 µg/ml) for 30 min in the dark at room
temperature. Cell cycle distribution analysis was performed with a
Cell Lab Quanta™ Sc MPL (Beckman Coulter, Inc.). To calculate the
proportion of cells in the sub-G1,
G0/G1, S and G2/M phases, the
Kaluza analysis software (version 2.1; Beckman Coulter, Inc.) was
used.
Measurement of intracellular ROS
levels
The ROS fluorescent probe
dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA; Dojindo
Laboratories, Inc.) was used to measure intracellular ROS levels.
The prepared cells (2×105 cells) were harvested from the
same dishes as those used for cell cycle measurements. The cells
were washed twice with Hanks' balanced salt solution (HBSS) and
then incubated with DCFH-DA working solution for 30 min at 37°C in
a humidified atmosphere of 95% air/5% CO2. The cells
were washed twice more with HBSS. The ROS levels were then measured
using a flow cytometer (Cell Lab Quanta™ Sc MPL). The excitation
and fluorescence wavelengths were set to 488 and 530 nm,
respectively.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was performed using OriginLab
software version 9.1 (OriginLab Corp.) and Office 365 (Microsoft
Corp.) with an add-in software (OMS Publishing, Inc.). The
Boltzmann function was used to calculate the IC50 and
the coefficient of determination (R2 value) was calculated.
Following the Kruskal-Wallis test to assess group differences, the
Steel test was performed as a non-parametric post-hoc test to
identify significant differences in the cell damage analysis
(surviving fraction, cell-cycle distribution and ROS detection).
All data in this study were nonparametric. P<0.05 was considered
to indicate statistical significance.
Results
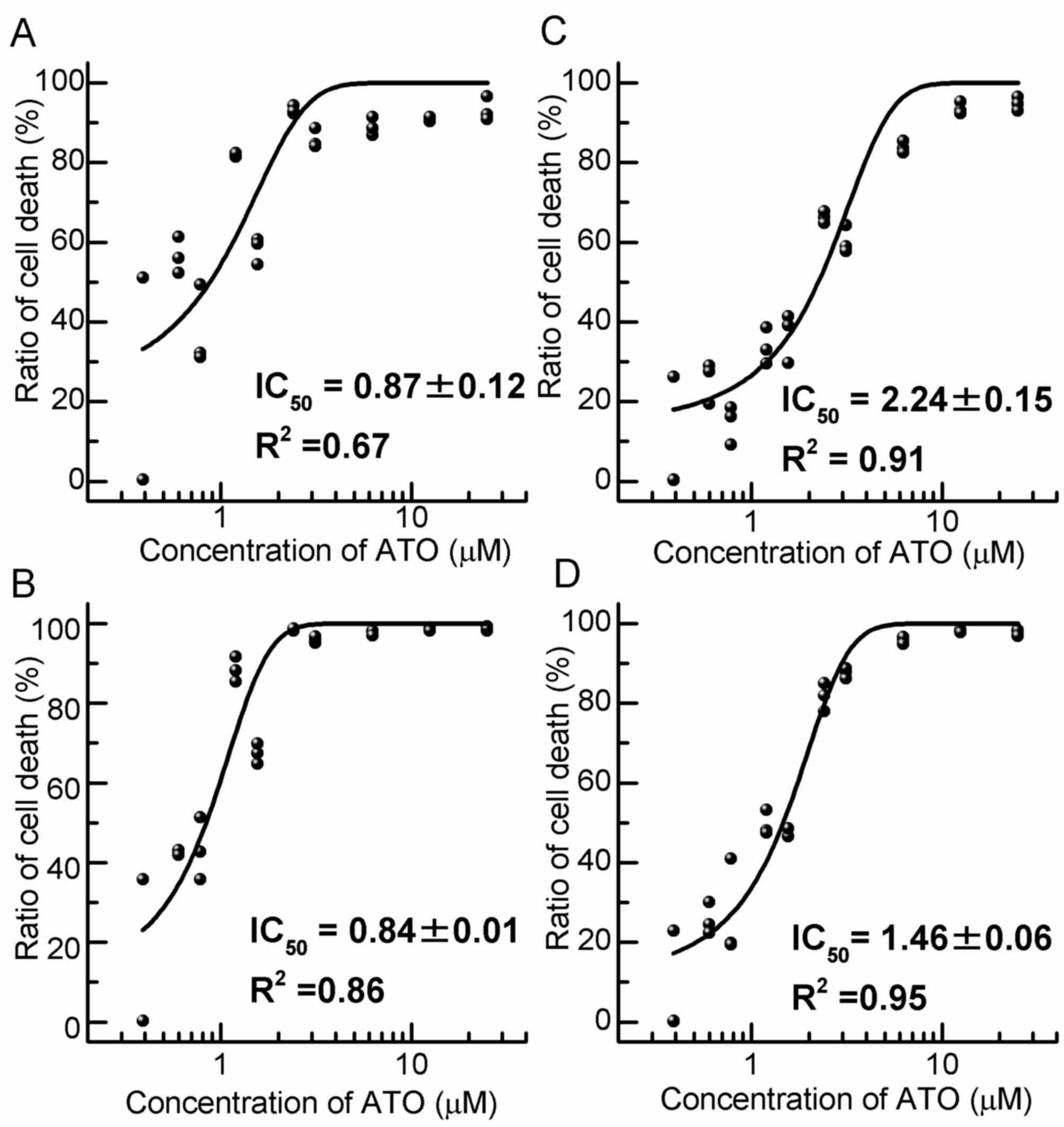
Cell toxicity of ATO
To determine the IC50 of ATO for HL60
cells, the number of viable cells after culture with various
concentrations of ATO was calculated (Fig. 1). The IC50 for native
cell was 0.87±0.12 µM after 48 h and 0.84±0.01 µM after 72 h of
incubation (Fig. 1A and B).
Furthermore, the IC50 for Res-HL60 was 2.24±0.15 µM
after 48 h and 1.46±0.06 µM after 72 h of incubation (Fig. 1C and D). Thereafter, the viable cell
count, cell cycle distribution analysis and intracellular ROS level
analysis were performed at the IC50 concentration of ATO
(native: 0.87±0.12 µM; Res: 2.24±0.15 µM).
Analysis of viable cells after
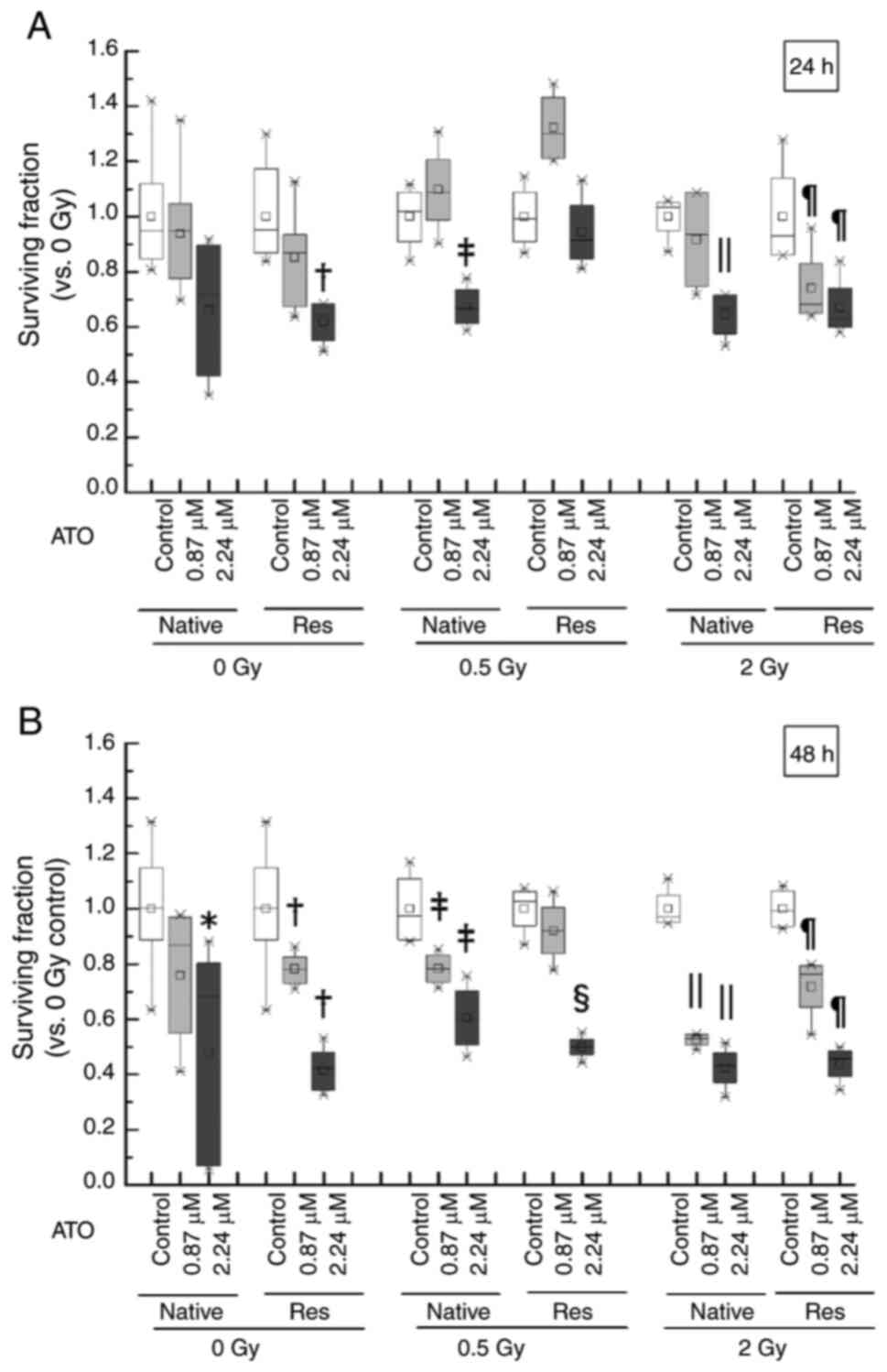
exposure to IR and/or ATO
As the combination of ATO and 4 Gy was found to be
too toxic, conditions similar to the clinical dose (0.5–2 Gy) were
used in the present study. The inhibition potency of cell
proliferation in HL-60 cells exposed to ATO and/or IR was assessed
in the early phase and late phase. The survival rate due to the
addition of ATO showed a significant decrease in the late phase in
native cells {native control: Median [interquartile range
(IQR)]=1.00 (0.89–1.15); 2.24 µM ATO: Median (IQR)=0.68
(0.07–0.80), P<0.05}, but the viability of Res-HL60 cells
started to decrease in early phase {control in early phase: Median
(IQR)=0.95 (0.87–1.18); 2.24 µM ATO in early phase: Median
(IQR)=0.64 (0.55–0.68), P<0.05; control in late phase: Median
(IQR)=1.00 (0.89–1.15); 0.87 µM ATO in late phase: Median
(IQR)=0.78 (0.73–0.83), P<0.05; 2.24 µM ATO in late phase:
Median (IQR)=0.42 (0.34–0.48), P<0.05} (Fig. 2). After exposure of the native cells
to 0.5-Gy IR in the late phase, a significant decrease in the
surviving cell fraction in the ATO concentration dependency in
comparison with the nontreatment control was observed [control:
median (IQR)=0.97 (0.89–1.11); 0.87 µM ATO: Median (IQR)=0.78
(0.74–0.83), P<0.05; 2.24 µM ATO: Median (IQR)=0.60 (0.51–0.70),
P<0.05] and 2 Gy [control: Median (IQR)=0.97 (0.95–1.05); 0.87
µM ATO: Median (IQR)=0.53 (0.51–0.54), P<0.05; 2.24 µM ATO:
Median (IQR)=0.43 (0.37–0.48), P<0.05]. Furthermore, Res-HL60
cells with additional ATO at the IC50 concentration
(2.24 µM) and 2 Gy IR exposure in the early phase were
significantly decreased [median (IQR)=0.63 (0.60–0.74), P<0.05]
compared to the control cells (without ATO) [median (IQR)=0.93
(0.86–1.14)]. Native cells exposed to 2-Gy were also similarly
decreased in early phase [control: Median (IQR)=1.04 (0.95–1.05);
2.24 µM ATO: Median (IQR)=0.67 (0.57–0.72), P<0.05]. A similar
trend at 2-Gy was continued until the late phase [native control:
Median (IQR)=0.97 (0.95–1.05); native with 0.87 µM ATO: Median
(IQR)=0.53 (0.51–0.54), P<0.05; native with 2.27 µM ATO: Median
(IQR)=0.43 (0.37–0.48), P<0.05; Res control: Median (IQR)=0.99
(0.94–1.06), Res with 0.87 µM ATO: Median (IQR)=0.76 (0.64–0.79),
P<0.05; Res with 2.24 µM ATO: Median (IQR)=0.46 (0.39–0.49),
P<0.05].
Alteration of cell-cycle distribution
by IR with or without ATO
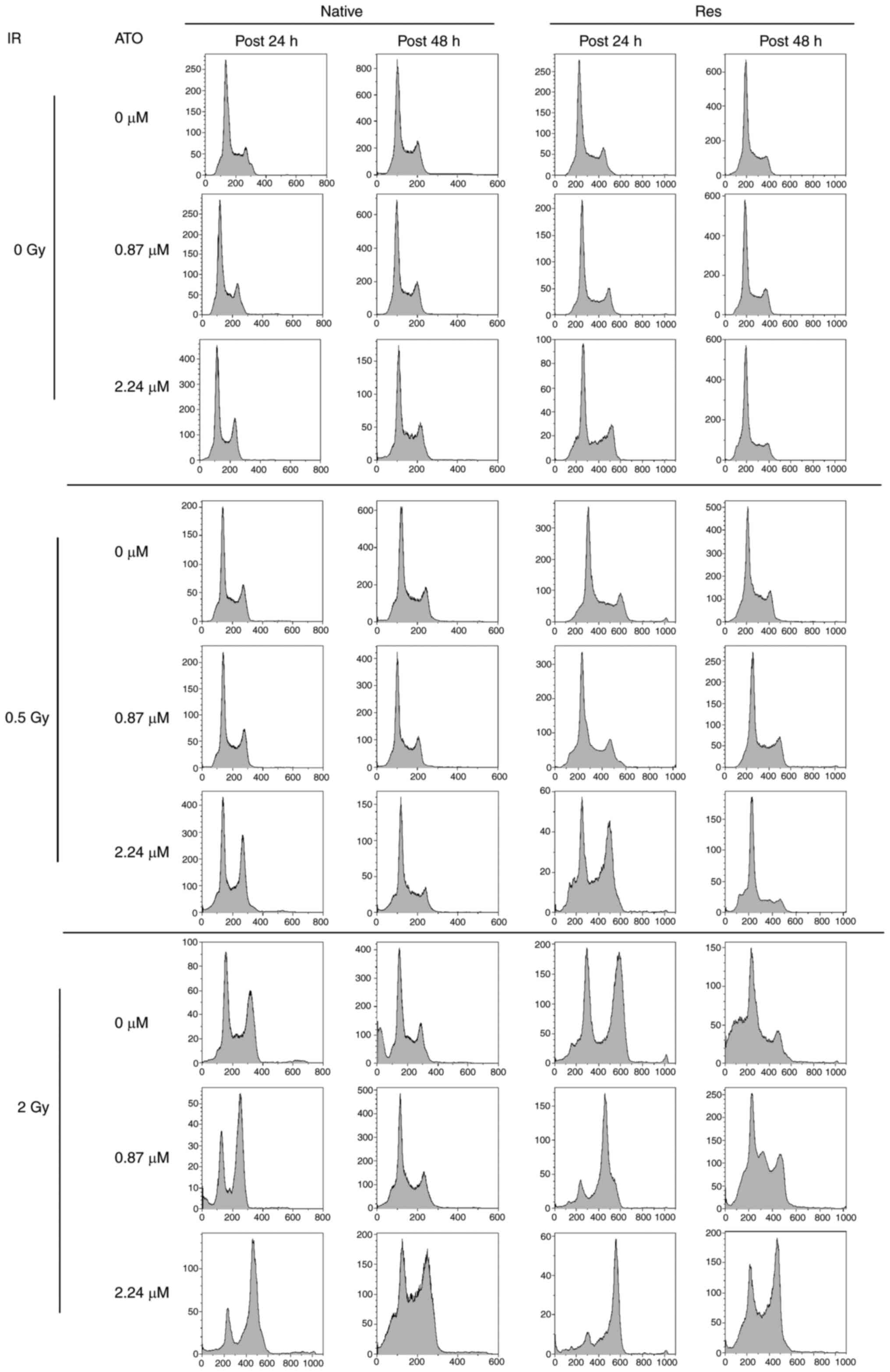
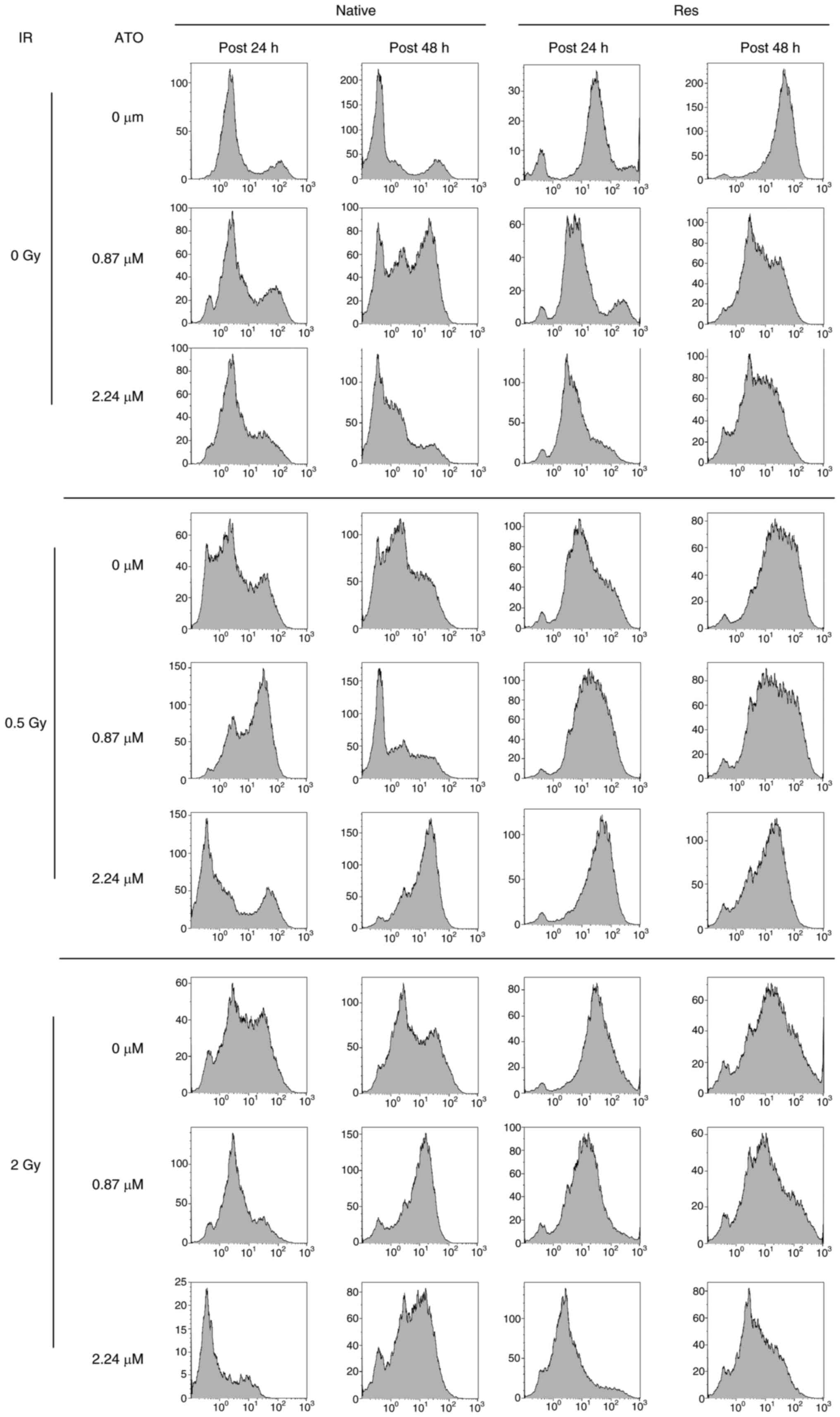
Analysis of the cell-cycle distribution of native
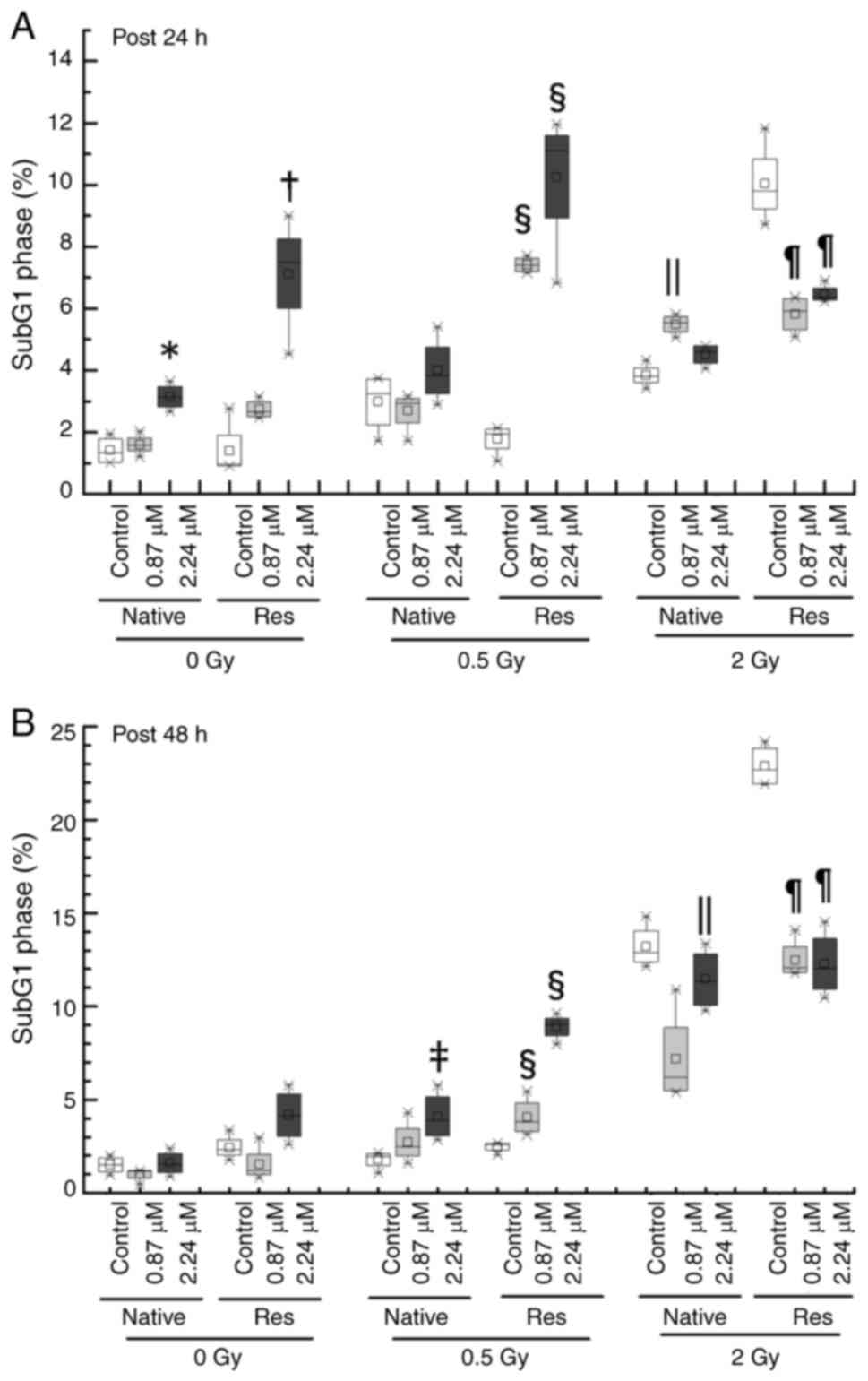
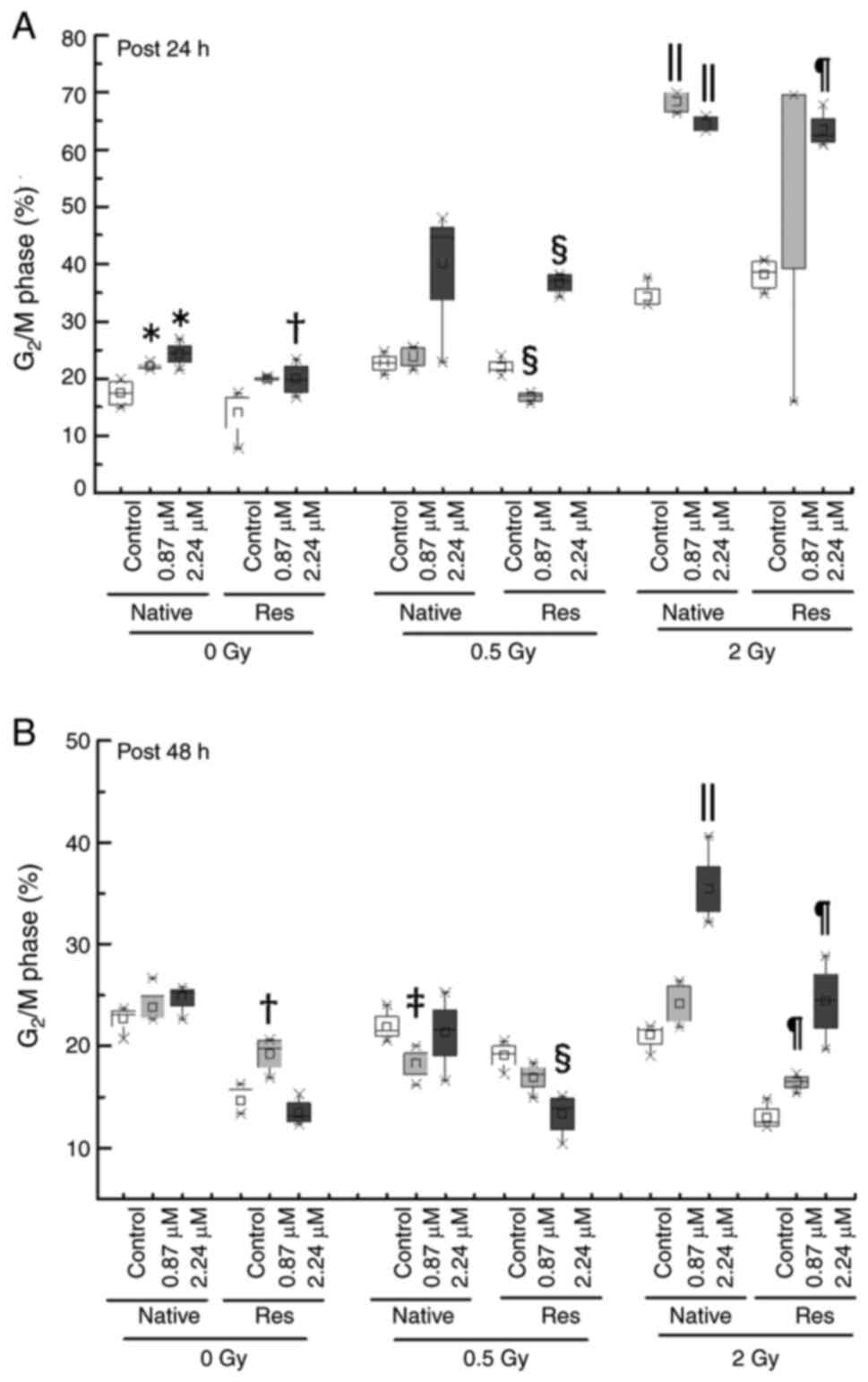
and Res HL60 cells was conducted using flow cytometry (Fig. 3). Exposure to IR increased the ratio
of the sub-G1 phase and G2/M phase in both cell lines in comparison
to the non-irradiated control (Fig.
4). Furthermore, the addition of ATO resulted in a larger
G2/M-phase population at early phase in comparison to the group
with no additional ATO. To provide a detailed cell cycle population
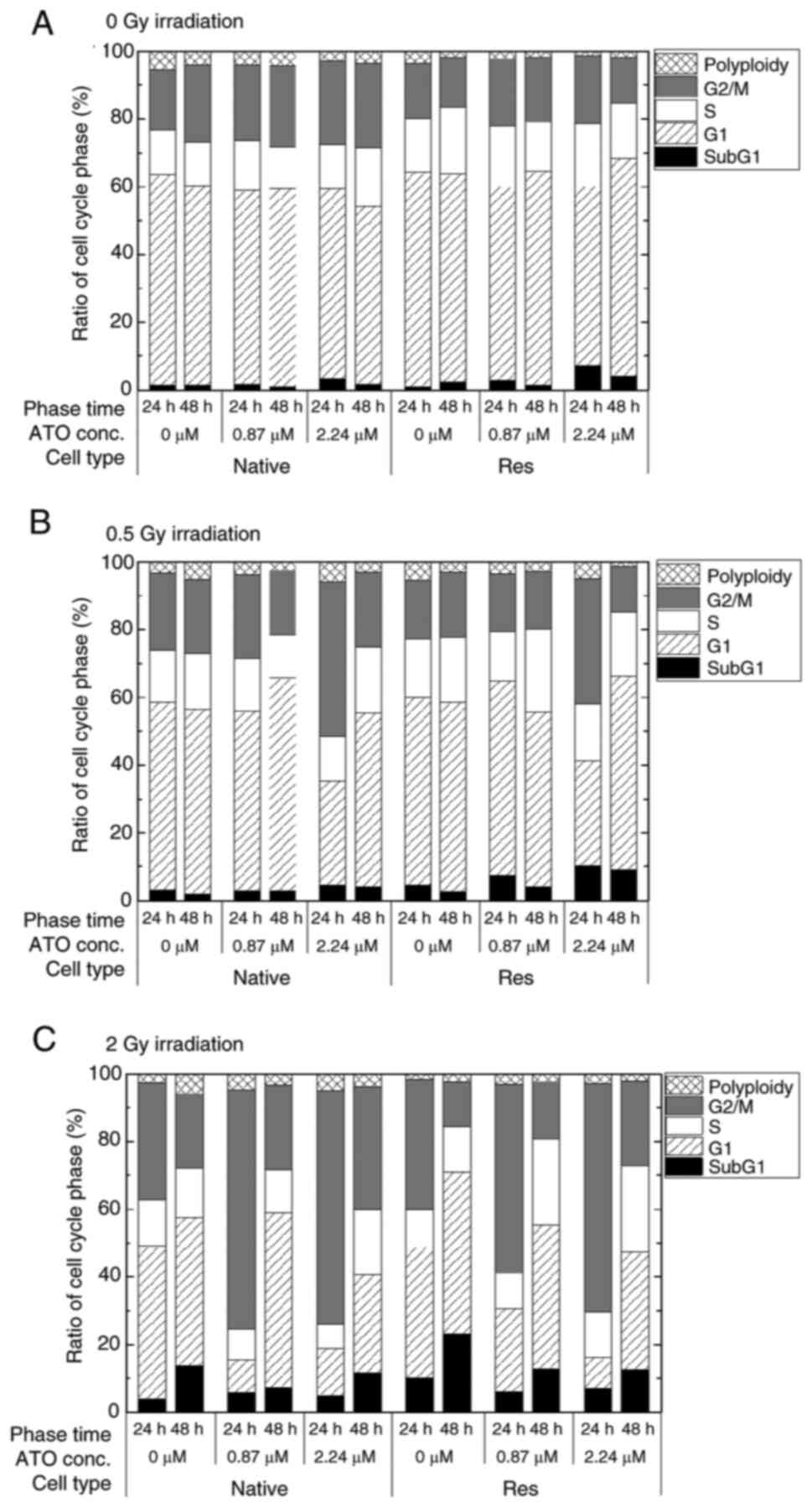
analysis, statistical analysis was performed. When the rate of the
change in the sub-G1 phase population was examined in greater
detail, the subG1 phase population in both control cells without
ATO was significantly increased by exposure to IR, but only the
conditions of 2-Gy in late phase exhibited a marked increase
{native in early phase [0 Gy, 1.32 (1.01–1.78)%; 0.5 Gy, 3.24
(2.24–3.72)%, P<0.05 vs. 0 Gy; 2 Gy, 3.82 (3.60–4.18)%,
P<0.05 vs. 0 Gy], Res in early phase [0 Gy, 0.95 (0.90–1.90)%;
0.5 Gy, 1.95 (1.48–2.10)%, P<0.05 vs. 0 Gy; 2 Gy, 9.80
(9.21–10.84)%, P<0.05 vs. 0 Gy], native in late phase [0 Gy,
1.50 (1.10–1.89)%; 0.5 Gy, 1.95 (1.48–2.10)%; 2 Gy, 12.90
(12.38–14.05)%, P<0.05 vs. 0 Gy], Res in late phase [0 Gy, 2.32
(2.03–2.84)%; 0.5 Gy, 2.60 (2.29–2.65)%; 2 Gy, 22.70
(21.92–23.85)%, P<0.05 vs. 0 Gy]} (Fig. 5). Res-HL60 supplemented with 2.24-µM
ATO showed a higher rate of change in the median (IQR)% [0 Gy, 7.50
(6.02–8.25)%; 0.5-Gy, 11.1 (8.91–11.58)%; 2 Gy, 6.36 (6.28–6.65)%]
than the native cells [0 Gy, 3.15 (2.82–3.48)%; 0.5 Gy, 3.84
(3.22–4.78)%; 2 Gy, 4.59 (4.22–4.80)%] in the early phase
(P<0.05) (Fig. 5A). However,
2-Gy irradiation with 0.87- and 2.24 µM ATO resulted in
downregulation compared with the control (P<0.05) (Fig. 5B). By contrast, a significant
increase in the ratio of the G2/M phase in both cell lines was
observed after the early phase with ATO [native with 0.87 µM ATO,
21.97 (21.81–22.28)%; native with 2.24 µM ATO, 24.30 (22.82–25.85);
Res with 2.24 µM ATO, 19.74 (17.87–22.11)%] in comparison to the
control [native, 17.50 (15.40–19.50)%; Res, 15.20 (11.11–16.81)%)]
(P<0.05), and exposure to 0.5 and 2 Gy irradiation with 2.24 µM
ATO induced a further increase in the median (IQR) [native with 0.5
Gy, 44.63 (33.80–44.80)%; Res with 0.5 Gy, 37.11 (35.22–38.10)%;
native with 2 Gy, 68.44 (66.76–69.95)%; Res with 2 Gy, 62.47
(61.40–65.21)%] in comparison to control cells [native with 0.5 Gy,
22.70 (21.81–23.90)%; Res with 0.5 Gy, 21.40 (20.90–22.83)%; native
with 2 Gy, 33.20 (32.90–35.60)%; Res with 2 Gy, 38.65
(35.90–40.50)%] (P<0.05) (Fig.
6A). In addition, Res-HL60 cells exposed to 2-Gy irradiation
and 2.24-µM ATO maintained a higher G2/M phase population even in
the late phase than the control group however it was comparatively
lower than early phase [control of native, 21.80 (20.02–21.90)%;
native with 2.24 µM ATO, 34.51 (33.20–37.51)%; control of
Res, 12.54 (12.24–13.38)%; Res with 2.24 µM ATO, 24.54
(21.86–27.19)%] (P<0.05) (Fig.
6B).
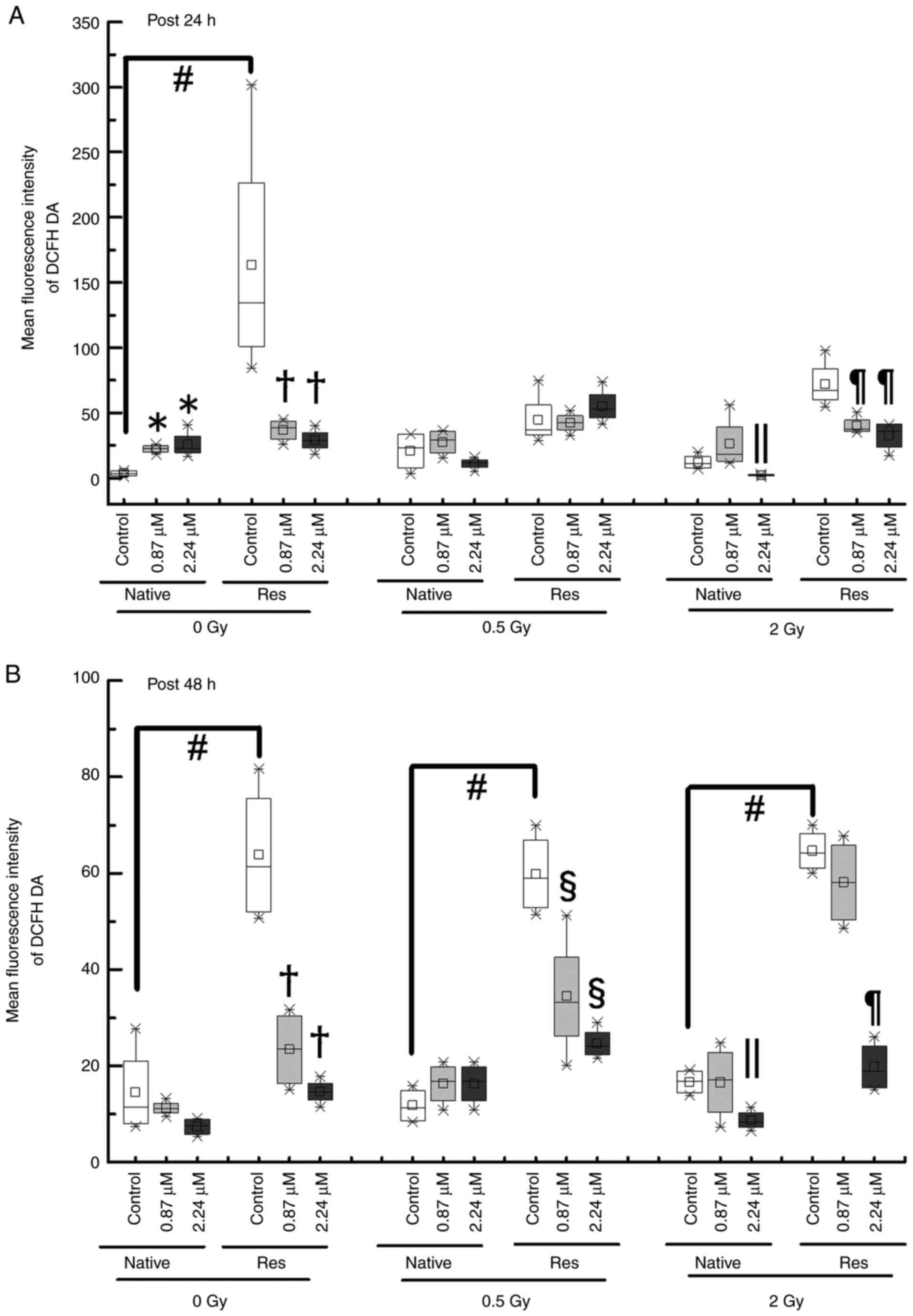
Intracellular ROS
To determine whether the inhibition of cell
proliferation and cell cycle disruption is related to ROS activity,
the intracellular DCFH-DA reaction, a ROS marker, was measured the
fluorescence intensity using a flow cytometer (Fig. 7). Although the ROS levels of
Res-HL60 were significantly higher than those of native cells under
nonirradiation conditions without ATO [median (IQR) at the early
phase, 3.5 (1.75–5.25) for native vs. 134.56 (101.31–227.24) for
Res; median (IQR) at the late phase, 11.38 (7.70–20.71) for native
vs. 61.39 (52.01–75.62) for Res)] (P<0.05), they did not
significantly differ or change after exposure to 0.5 or 2 Gy
irradiation at the early phase (Fig.
8A). However, there were similar responses in ROS levels after
exposure to 0.5 or 2 Gy irradiation at the late phase in comparison
to non-irradiated conditions (in other words, Res-HL60 cells were
detected to have higher levels of ROS than native cells) (Fig. 8B). Furthermore, adding ATO at the
IC50 concentration to Res-HL60 reduced intracellular ROS
levels and the differences were more pronounced in the late
phase.
Discussion
An in vitro cell culture model was used in
the present study to clarify the antitumor effect of ATO on
radiation-resistant leukemia cells and/or to determine its efficacy
when combined with IR. In our established model (Res-HL60), the
IC50 of ATO was higher than that of native cells, and a
higher percentage of G2/M phase was observed after exposure to 2 Gy
with ATO in the early phase compared to a single 2 Gy IR. This
combination (exposure to 2 Gy with ATO) also showed a significantly
decrease of surviving fraction (~60%). These effects may be the
result of additive effects between ATO and IR.
Exposure to IR causes apoptosis in cells by
targeting DNA (19). Flow cytometry
can identify the sub-G1, G1, S and G2/M phases of the cell cycle,
with apoptotic cells included in the sub-G1 phase (20). A higher population in the sub-G1
phase in ResHL60 and native cells was also determined following
administration of ATO and/or IR. Furthermore, in Res-HL60 cells
supplemented with ATO, the effect on the sub-G1 phase, which is
induced by IR, was increased, implying that ATO promotes apoptosis
when exposed to IR. However, the production of intracellular ROS in
Res-HL60 cells differed from previous reports on leukemia cells. A
previous study by Ho et al (17) found that ATO induces apoptosis via
the mitochondria-mediated caspase 3 pathway by producing
intracellular ROS. In native cells, ROS production responses were
similar to previous reports following the addition of ATO; however,
in Res-HL60 cells, the concentration of ATO and ROS production had
no relationship and instead decreased ROS production when compared
to native cells. Mitochondrial metabolism contributes to ROS
production, which activates the downstream caspase pathway and
causes apoptosis (21).
When cells become radioresistant, glutathione
activity often increases, resulting in increased antioxidant
capacity (22,23). Furthermore, as ResHL60 cells have an
active potency of ATM/ATR and DNA-dependent protein kinase than
native cells for radiation resistance capacity (9), these combined abilities may suppress
ROS-mediated apoptosis. Jambrovics et al (24,25)
discovered that lacking intracellular transglutaminase 2, a
multifunctional enzyme, increases ATO-induced ROS production and
cell death. Our identification of IC50 concentrations
(0.78 µM for native, 2.24 µM for Res) and weaker toxic effect of
the ATO concentration in Res-HL60 cells compared to native cells
suggest that the antitoxic environment in Res cells is altered in
intracellular enzymes, leading to radio- and ATO resistance.
According to numerous reports, the antitumor effect
of leukemia cells ranges from 1 to 15 µM (17,26–30)
and has a similar ATO concentration to the IC50 of
Res-HL60, which is noteworthy. In many drug discovery fields, low
concentrations are essential for avoiding effects on normal tissue.
The concentration of ATO is expected to decrease even further when
combined with radiotherapy. From this perspective, it is very
significant that in the present study, an additive antitumor effect
was produced by combining low concentrations of ATO with radiation
on radioresistant cells. Heinke (31) reported that mitochondrial ROS drives
cell cycle progression. If ATO causes cell cycle arrest and then
cell death, ATO stimuli may be reduced in the production of
intracellular ROS. However, determining the cause of the decline in
ROS will necessitate a detailed analysis of the intracellular redox
state of various types of leukemic cells, including clinical
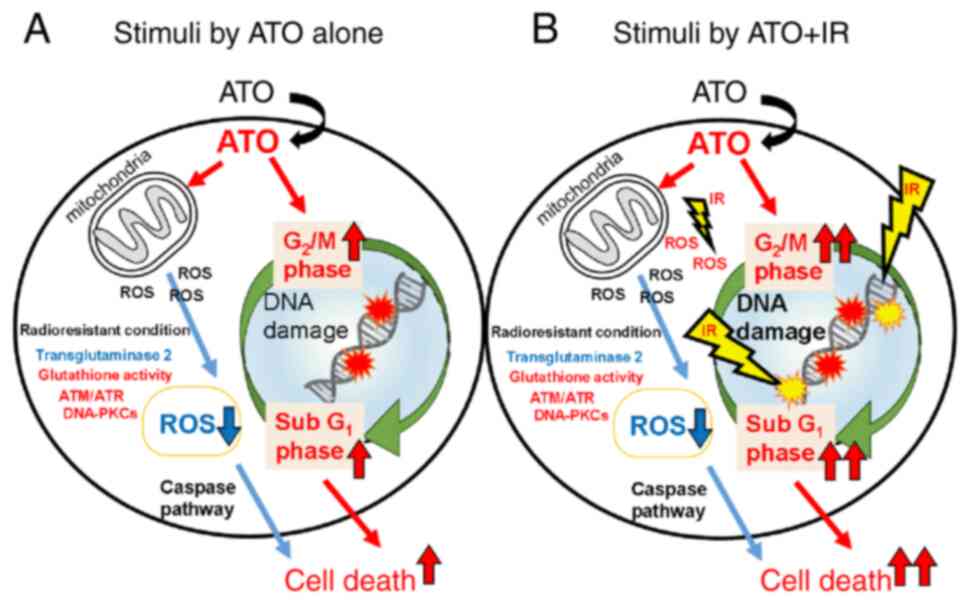
specimens, in the future. These findings (Fig. 9) reveal important information that
radioresistant leukemia cells respond differently to the antitumor
effect of ATO and the combined effect of IR.
In conclusion, these findings suggest that
radioresistant leukemia has distinct redox and cell death signals
involving ATO and IR.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Professor Yoichiro
Hosokawa (Department of Radiation Science, Hirosaki University
Graduate School of Health Sciences) for his kind assistance with
the establishment of Res-HL60.
Funding
This work was supported by JSPS KAKENHI, Grants-in-Aid for
Scientific Research (B) (grant no. 21H02861 to SM), Fund for the
Promotion of Joint International Research (Fostering Joint
International Research; grant no. 17KK0181 to SM), and Grant-in-Aid
for Challenging Research (Exploratory) (grant no. 19K22731 to SM).
The Takeda Science Foundation (2022, to SM) also provided support.
The funders had no involvement in the study design, data collection
and analysis, decision to publish or manuscript preparation.
Availability of data and materials
The data generated in the present study may be
requested from the corresponding author.
Authors' contributions
YM and SM designed the study, drafted the manuscript
and contributed significantly to its revision. YM, HS, KY, MK, TY
KH, and SM examined biological data. YM and SM checked and
confirmed the authenticity of the raw data. SM oversaw the study,
critically reviewed the manuscript and gave final approval for the
version to be submitted and published. All authors have read and
approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to
participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing
interests.
References
|
1
|
Mishra SK, Millman SE and Zhang L:
Metabolism in acute myeloid leukemia: Mechanistic insights and
therapeutic targets. Blood. 141:1119–1135. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Russell JA, Irish W, Balogh A, Chaudhry
MA, Savoie ML, Turner AR, Larratt L, Storek J, Bahlis NJ, Brown CB,
et al: The addition of 400 cGY total body irradiation to a regimen
incorporating once-daily intravenous busulfan, fludarabine, and
antithymocyte globulin reduces relapse without affecting nonrelapse
mortality in acute myelogenous leukemia. Biol Blood Marrow
Transplant. 16:509–514. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Khoury JD, Solary E, Abla O, Akkari Y,
Alaggio R, Apperley JF, Bejar R, Berti E, Busque L, Chan JKC, et
al: The 5th edition of the World Health Organization classification
of haematolymphoid tumours: Myeloid and histiocytic/dendritic
neoplasms. Leukemia. 36:1703–1719. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Termuhlen AM, Klopfenstein K, Olshefski R,
Rosselet R, Yeager ND, Soni S and Gross TG: Mobilization of
PML-RARA negative blood stem cells and salvage with autologous
peripheral blood stem cell transplantation in children with
relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia. Pediatr Blood Cancer.
51:521–524. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Monzen S, Yoshino H, Kasai-Eguchi K and
Kashiwakura I: Characteristics of myeloid differentiation and
maturation pathway derived from human hematopoietic stem cells
exposed to different linear energy transfer radiation types. PLoS
One. 8:e593852013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kanda Y, Izutsu K, Hirai H, Sakamaki H,
Iseki T, Kodera Y, Okamoto S, Mitsui H, Iwato K, Hirabayashi N, et
al: Effect of graft-versus-host disease on the outcome of bone
marrow transplantation from an HLA-identical sibling donor using
GVHD prophylaxis with cyclosporine A and methotrexate. Leukemia.
18:1013–1019. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wong JYC, Filippi AR, Dabaja BS, Yahalom J
and Specht L: Total body irradiation: Guidelines from the
international lymphoma radiation oncology group (ILROG). Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 101:521–529. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Alfonso JCL and Berk L: Modeling the
effect of intratumoral heterogeneity of radiosensitivity on tumor
response over the course of fractionated radiation therapy. Radiat
Oncol. 14:882019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hazawa M, Hosokawa Y, Monzen S, Yoshino H
and Kashiwakura I: Regulation of DNA damage response and cell cycle
in radiation-resistant HL60 myeloid leukemia cells. Oncol Rep.
28:55–61. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Monzen S, Takimura K, Kashiwakura I and
Hosokawa Y: Acute promyelocytic leukemia mutated to radioresistance
suppressed monocyte lineage differentiation by phorbol 12-myristate
13-acetate. Leuk Res. 37:1162–1169. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Monzen S, Chiba M and Hosokawa Y: Genetic
network profiles associated with established resistance to ionizing
radiation in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells and their
extracellular vesicles. Oncol Rep. 35:749–756. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Monzen S, Chiba M, Ueno T, Morino Y,
Terada K, Yamaya H and Hosokawa Y: A radioresistant fraction of
acute promyelocytic leukemia cells exhibit CD38 cell-surface
antigen and mRNA expression. Oncol Lett. 15:6709–6714.
2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Niu C, Yan H, Yu T, Sun HP, Liu JX, Li XS,
Wu W, Zhang FQ, Chen Y, Zhou L, et al: Studies on treatment of
acute promyelocytic leukemia with arsenic trioxide: remission
induction, follow-up, and molecular monitoring in 11 newly
diagnosed and 47 relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia patients.
Blood. 94:3315–3324. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Soignet SL, Frankel SR, Douer D, Tallman
MS, Kantarjian H, Calleja E, Stone RM, Kalaycio M, Scheinberg DA,
Steinherz P, et al: United States multicenter study of arsenic
trioxide in relapsed acute promyelocytic leukemia. J Clin Oncol.
19:3852–3860. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Shigeno K, Naito K, Sahara N, Kobayashi M,
Nakamura S, Fujisawa S, Shinjo K, Takeshita A, Ohno R and Ohnishi
K: Arsenic trioxide therapy in relapsed or refractory Japanese
patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia: Updated outcomes of the
phase II study and postremission therapies. Int J Hematol.
82:224–229. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhou P, Kalakonda N and Comenzo RL:
Changes in gene expression profiles of multiple myeloma cells
induced by arsenic trioxide (ATO): Possible mechanisms to explain
ATO resistance in vivo. Br J Haematol. 128:636–644. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ho SY, Wu WJ, Chiu HW, Chen YA, Ho YS, Guo
HR and Wang YJ: Arsenic trioxide and radiation enhance apoptotic
effects in HL-60 cells through increased ROS generation and
regulation of JNK and p38 MAPK signaling pathways. Chem Biol
Interact. 193:162–171. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yousefnia S: Mechanistic effects of
arsenic trioxide on acute promyelocytic leukemia and other types of
leukemias. Cell Biol Int. 45:1148–1157. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Matt S and Hofmann TG: The DNA
damage-induced cell death response: A roadmap to kill cancer cells.
Cell Mol Life Sci. 73:2829–2850. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Faramarzian Azimi Maragheh B, Fatourachi
P, Mohammadi SM, Valipour B, Behtari M, Dehnad A and Nozad
Charoudeh H: Streptomyces Levis ABRIINW111 inhibits SW480
cells growth by apoptosis induction. Adv Pharm Bull. 8:675–682.
2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheung EC and Vousden KH: The role of ROS
in tumour development and progression. Nat Rev Cancer. 22:280–297.
2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bai X, Ni J, Beretov J, Wasinger VC, Wang
S, Zhu Y, Graham P and Li Y: Activation of the eIF2α/ATF4 axis
drives triple-negative breast cancer radioresistance by promoting
glutathione biosynthesis. Redox Biol. 43:1019932021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ning S, Zhang T, Lyu M, Lam JWY, Zhu D,
Huang Q and Tang BZ: A type I AIE photosensitiser-loaded biomimetic
nanosystem allowing precise depletion of cancer stem cells and
prevention of cancer recurrence after radiotherapy. Biomaterials.
295:1220342023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jambrovics K, Uray IP, Keillor JW, Fésüs L
and Balajthy Z: Benefits of combined all-trans retinoic acid and
arsenic trioxide treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia cells
and further enhancement by inhibition of atypically expressed
transglutaminase 2. Cancers (Basel). 12:6482020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Jambrovics K, Botó P, Pap A, Sarang Z,
Kolostyák Z, Czimmerer Z, Szatmari I, Fésüs L, Uray IP and Balajthy
Z: Transglutaminase 2 associated with PI3K and PTEN in a
membrane-bound signalosome platform blunts cell death. Cell Death
Dis. 14:2172023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu J, Koken MH, Quignon F, Chelbi-Alix
MK, Degos L, Wang ZY, Chen Z and de Thé H: Arsenic-induced PML
targeting onto nuclear bodies: implications for the treatment of
acute promyelocytic leukemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 94:3978–3983.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jing Y, Dai J, Chalmers-Redman RM, Tatton
WG and Waxman S: Arsenic trioxide selectively induces acute
promyelocytic leukemia cell apoptosis via a hydrogen
peroxide-dependent pathway. Blood. 94:2102–2111. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Davison K, Côté S, Mader S and Miller WH:
Glutathione depletion overcomes resistance to arsenic trioxide in
arsenic-resistant cell lines. Leukemia. 17:931–940. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Sumi D, Shinkai Y and Kumagai Y: Signal
transduction pathways and transcription factors triggered by
arsenic trioxide in leukemia cells Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
244:385–392. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li J: Downregulation of ROS1 enhances the
therapeutic efficacy of arsenic trioxide in acute myeloid leukemia
cell lines. Oncol Lett. 15:9392–9396. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Heinke L: Mitochondrial ROS drive cell
cycle progression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 23:5812022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|