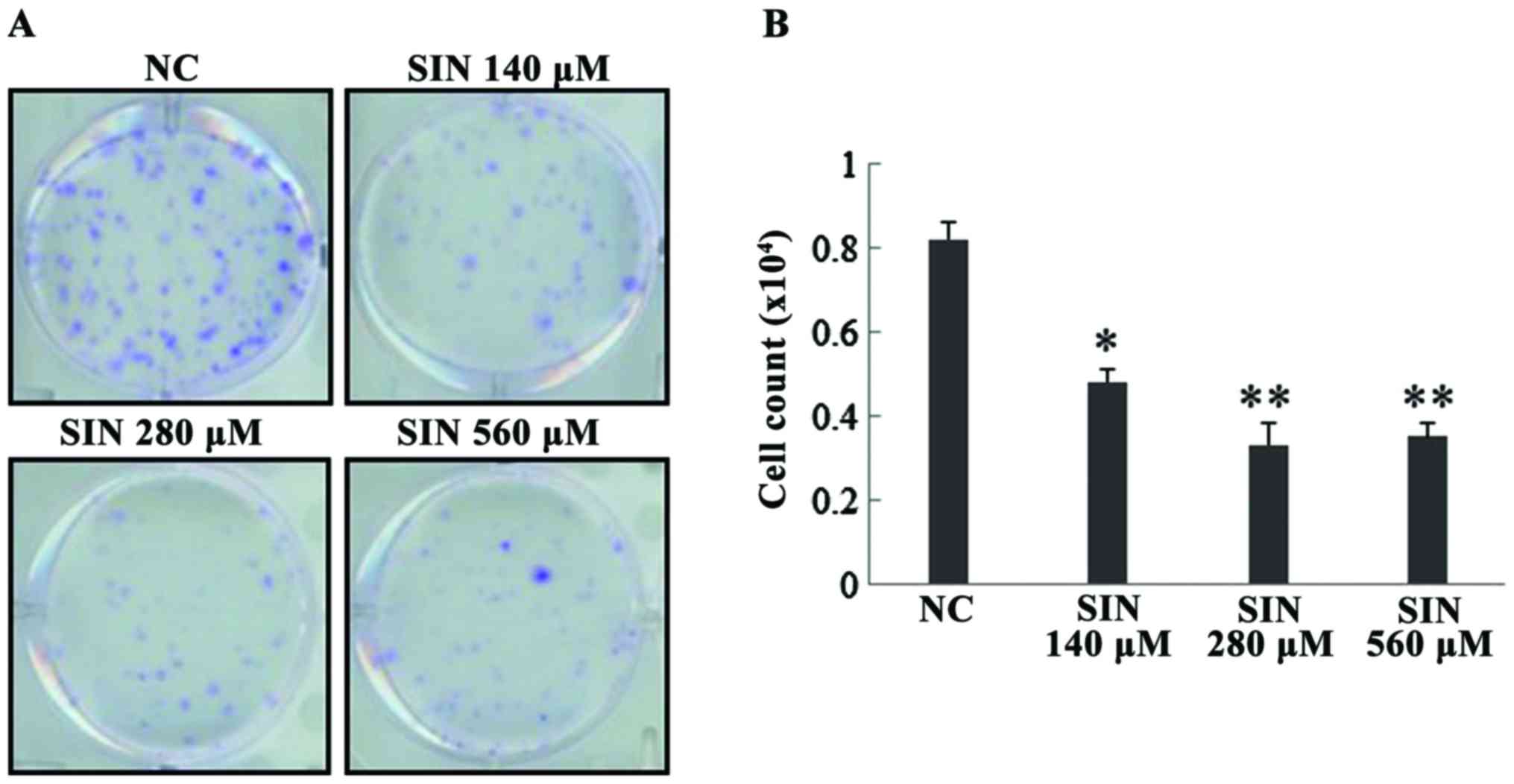
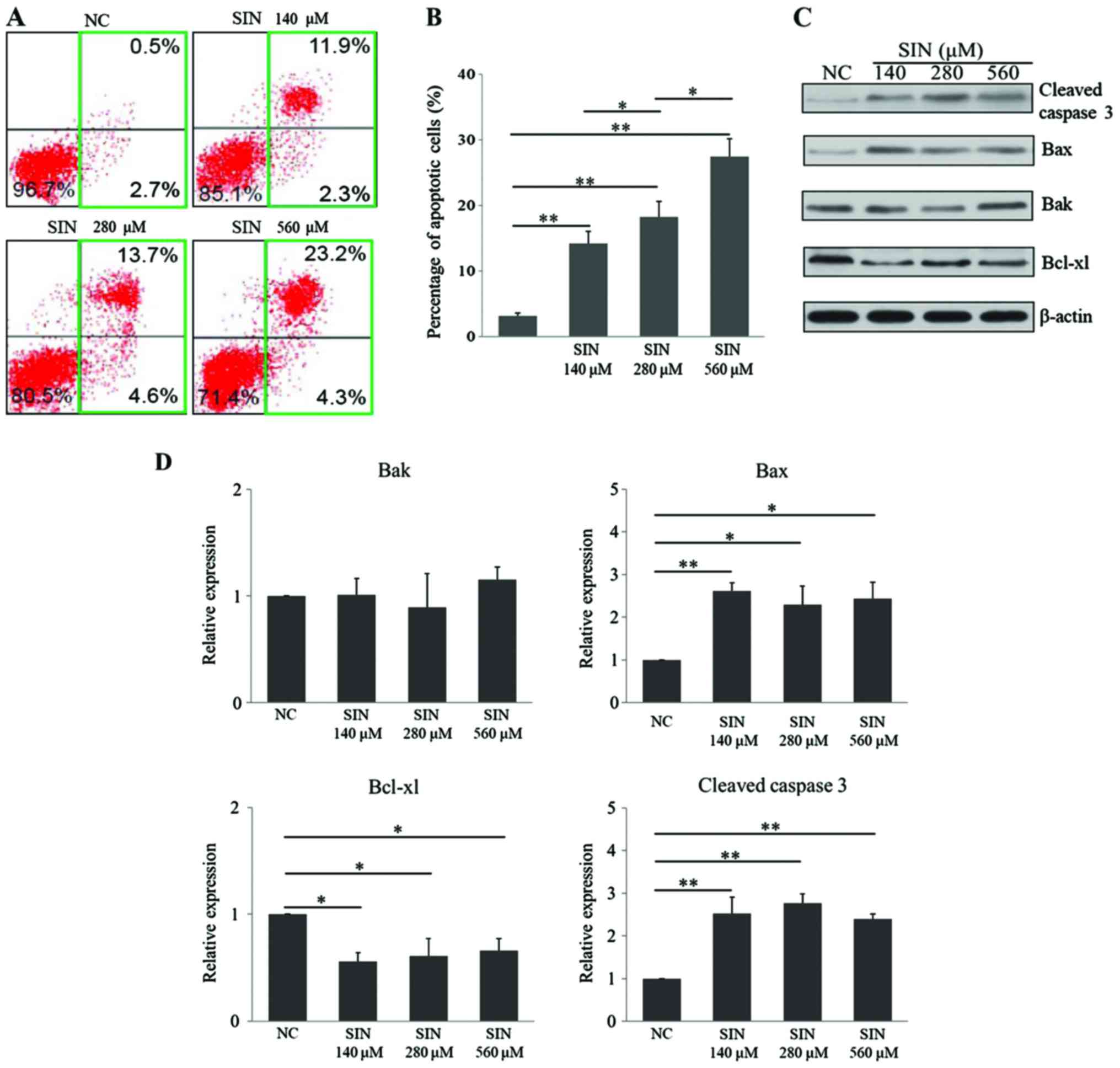
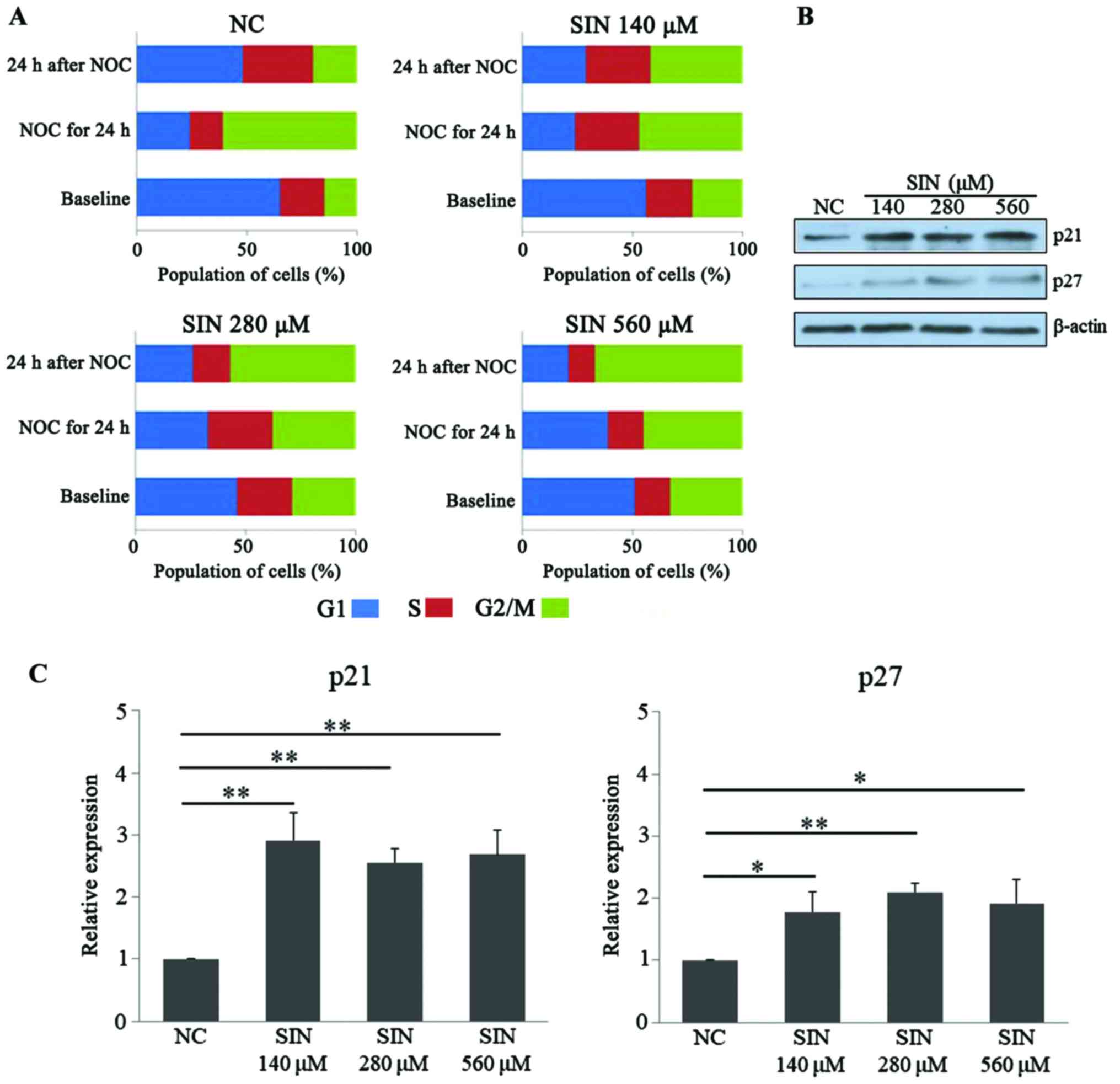
|
1
|
Daniels TR, Delgado T, Helguera G and
Penichet ML: The transferrin receptor part II: Targeted delivery of
therapeutic agents into cancer cells. Clin Immunol. 121:159–176.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Dutta R and Mahato RI: Recent advances in
hepatocellular carcinoma therapy. Pharmacol Ther. 173:106–117.
2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yamasaki H: Pharmacology of sinomenine, an
anti-rheumatic alkaloid from Sinomenium acutum. Acta Med
Okayama. 30:1–20. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wang Y, Fang Y, Huang W, Zhou X, Wang M,
Zhong B and Peng D: Effect of sinomenine on cytokine expression of
macrophages and synoviocytes in adjuvant arthritis rats. J
Ethnopharmacol. 98:37–43. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhao ZJ, Zhao C, Xiao J and Wang JC:
Transdermal Permeation and Anti-Inflammation Activities of Novel
Sinomenine Derivatives. Molecules. 21:E15202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Q and Li XK: Immunosuppressive and
anti-inflammatory activities of sinomenine. Int Immunopharmacol.
11:373–376. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chen DP, Wong CK, Leung PC, Fung KP, Lau
CB, Lau CP, Li EK, Tam LS and Lam CW: Anti-inflammatory activities
of Chinese herbal medicine sinomenine and Liang Miao San on tumor
necrosis factor-α-activated human fibroblast-like synoviocytes in
rheumatoid arthritis. J Ethnopharmacol. 137:457–468. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lee JY, Yoon SY, Won J, Kim HB, Kang Y and
Oh SB: Sinomenine produces peripheral analgesic effects via
inhibition of voltage-gated sodium currents. Neuroscience.
358:28–36. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hong Y, Yang J, Shen X, Zhu H, Sun X, Wen
X, Bian J, Hu H, Yuan L, Tao J, et al: Sinomenine hydrochloride
enhancement of the inhibitory effects of anti-transferrin receptor
antibody-dependent on the COX-2 pathway in human hepatoma cells.
Cancer Immunol Immunother. 62:447–454. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lu XL, Zeng J, Chen YL, He PM, Wen MX, Ren
MD, Hu YN, Lu GF and He SΧ: Sinomenine hydrochloride inhibits human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell growth in vitro and in
vivo: Involvement of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis induction.
Int J Oncol. 42:229–238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li X, Wang K, Ren Y, Zhang L, Tang XJ,
Zhang HM, Zhao CQ, Liu PJ, Zhang JM and He JJ: MAPK signaling
mediates sinomenine hydrochloride-induced human breast cancer cell
death via both reactive oxygen species-dependent and -independent
pathways: An in vitro and in vivo study. Cell Death Dis.
5:e13562014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li X, Li P, Liu C, Ren Y, Tang X, Wang K
and He J: Sinomenine hydrochloride inhibits breast cancer
metastasis by attenuating inflammation-related
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness. Oncotarget.
8:13560–13574. 2017.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Zhou L, Luan H, Liu Q, Jiang T, Liang H,
Dong X and Shang H: Activation of PI3K/Akt and ERK signaling
pathways antagonized sinomenine-induced lung cancer cell apoptosis.
Mol Med Rep. 5:1256–1260. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jiang S, Gao Y, Hou W, Liu R, Qi X, Xu X,
Li J, Bao Y, Zheng H and Hua B: Sinomenine inhibits A549 human lung
cancer cell invasion by mediating the STAT3 signaling pathway.
Oncol Lett. 12:1380–1386. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu Z, Duan ZJ, Chang JY, Zhang ZF, Chu R,
Li YL, Dai KH, Mo GQ and Chang QY: Sinomenine sensitizes
multidrug-resistant colon cancer cells (Caco-2) to doxorubicin by
downregulation of MDR-1 expression. PLoS One. 9:e985602014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhao B, Liu L, Mao J, Liu K, Fan W, Liu J,
Zhang Z and Li Q: Sinomenine hydrochloride attenuates the
proliferation, migration, invasiveness, angiogenesis and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition of clear-cell renal cell
carcinoma cells via targeting Smad in vitro. Biomed Pharmacother.
96:1036–1044. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Deng F, Ma YX, Liang L, Zhang P and Feng
J: The pro-apoptosis effect of sinomenine in renal carcinoma via
inducing autophagy through inactivating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway.
Biomed Pharmacother. 97:1269–1274. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jiang Y, Jiao Y, Wang Z, Li T, Liu Y, Li
Y, Zhao X and Wang D: sinomenine hydrochloride inhibits human
glioblastoma cell growth through reactive oxygen species generation
and autophagy-lysosome pathway activation: An in vitro and in vivo
study. Int J Mol Sci. 18:E19452017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang H, Ren Y, Tang X, Wang K, Liu Y,
Zhang L, Li X, Liu P, Zhao C and He J: Vascular normalization
induced by sinomenine hydrochloride results in suppressed mammary
tumor growth and metastasis. Sci Rep. 5:88882015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Wang J, Yang ZR, Dong WG, Zhang JX, Guo
XF, Song J and Qiu S: Cooperative inhibitory effect of sinomenine
combined with 5-fluorouracil on esophageal carcinoma. World J
Gastroenterol. 19:8292–8300. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Zieve GW, Turnbull D, Mullins JM and
McIntosh JR: Production of large numbers of mitotic mammalian cells
by use of the reversible microtubule inhibitor nocodazole.
Nocodazole accumulated mitotic cells. Exp Cell Res. 126:397–405.
1980. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Porter AG and Jänicke RU: Emerging roles
of caspase-3 in apoptosis. Cell Death Differ. 6:99–104. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wolter KG, Hsu YT, Smith CL, Nechushtan A,
Xi XG and Youle RJ: Movement of Bax from the cytosol to
mitochondria during apoptosis. J Cell Biol. 139:1281–1292. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chittenden T, Harrington EA, O'Connor R,
Flemington C, Lutz RJ, Evan GI and Guild BC: Induction of apoptosis
by the Bcl-2 homologue Bak. Nature. 374:733–736. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Korsmeyer SJ: Regulators of cell death.
Trends Genet. 11:101–105. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Finucane DM, Bossy-Wetzel E, Waterhouse
NJ, Cotter TG and Green DR: Bax-induced caspase activation and
apoptosis via cytochrome c release from mitochondria is inhibitable
by Bcl-xL. J Biol Chem. 274:2225–2233. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xiong Y, Hannon GJ, Zhang H, Casso D,
Kobayashi R and Beach D: p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin
kinases. Nature. 366:701–704. 1993. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K
and Elledge SJ: The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent
inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell. 75:805–816. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Polyak K, Kato JY, Solomon MJ, Sherr CJ,
Massague J, Roberts JM and Koff A: p27Kip1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor,
links transforming growth factor-beta and contact inhibition to
cell cycle arrest. Genes Dev. 8:9–22. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Polyak K, Lee MH, Erdjument-Bromage H,
Koff A, Roberts JM, Tempst P and Massagué J: Cloning of p27Kip1, a
cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of
extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell. 78:59–66. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Jiang T, Zhou L, Zhang W, Qu D, Xu X, Yang
Y and Li S: Effects of sinomenine on proliferation and apoptosis in
human lung cancer cell line NCI-H460 in vitro. Mol Med Rep.
3:51–56. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Xie T, Ren HY, Lin HQ, Mao JP, Zhu T, Wang
SD and Ye ZM: Sinomenine prevents metastasis of human osteosarcoma
cells via S phase arrest and suppression of tumor-related
neovascularization and osteolysis through the CXCR4-STAT3 pathway.
Int J Oncol. 48:2098–2112. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wyllie AH: Apoptosis: Cell death in tissue
regulation. J Pathol. 153:313–316. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Williams GT: Programmed cell death:
Apoptosis and oncogenesis. Cell. 65:1097–1098. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Salvesen GS: Caspases: Opening the boxes
and interpreting the arrows. Cell Death Differ. 9:3–5. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Slee EA, Adrain C and Martin SJ:
Executioner caspase-3, −6, and −7 perform distinct, non-redundant
roles during the demolition phase of apoptosis. J Biol Chem.
276:7320–7326. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Hall PA: Cell proliferation. J Pathol.
165:349–354. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Deng C, Zhang P, Harper JW, Elledge SJ and
Leder P: Mice lacking p21CIP1/WAF1 undergo normal development, but
are defective in G1 checkpoint control. Cell. 82:675–684. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|