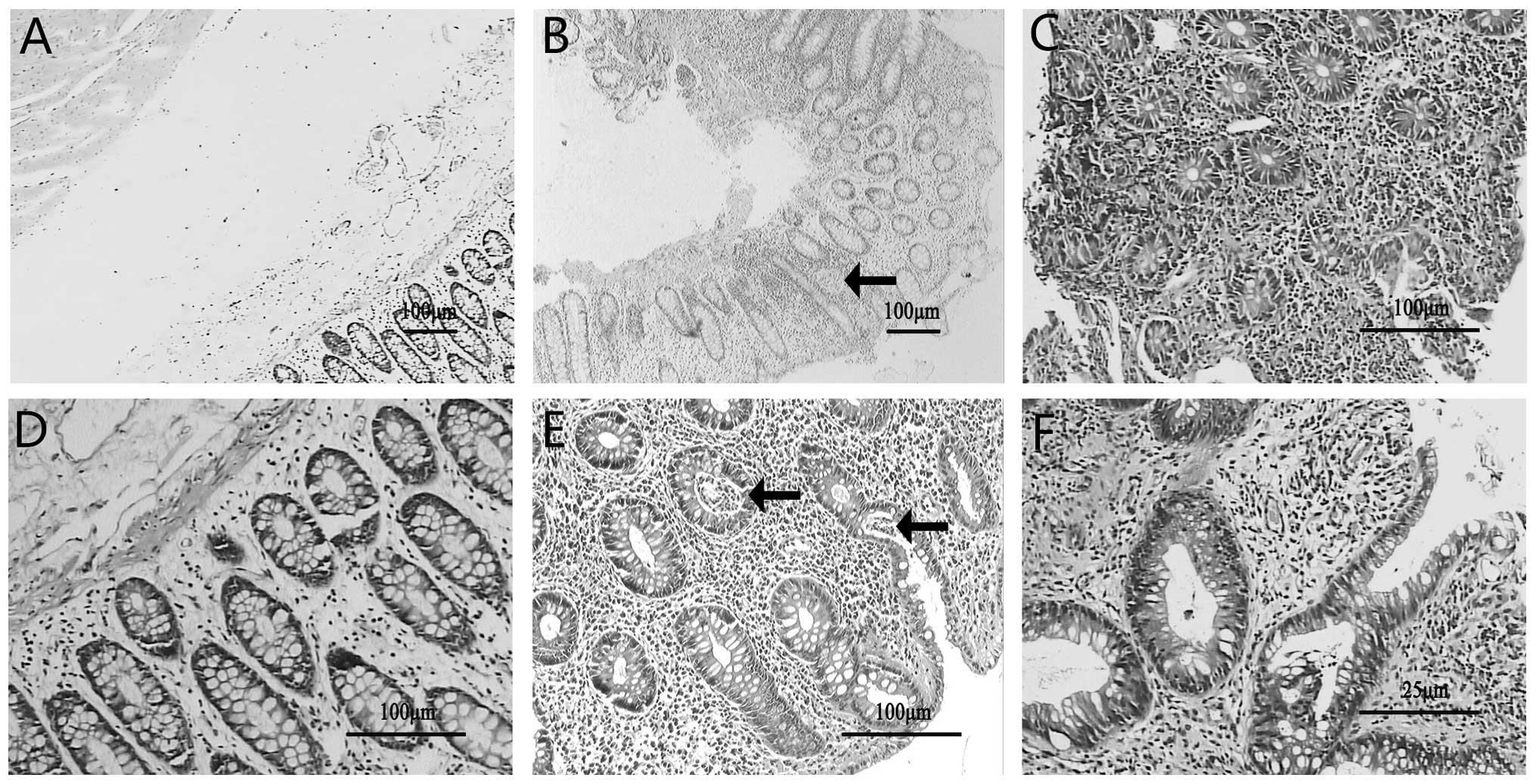
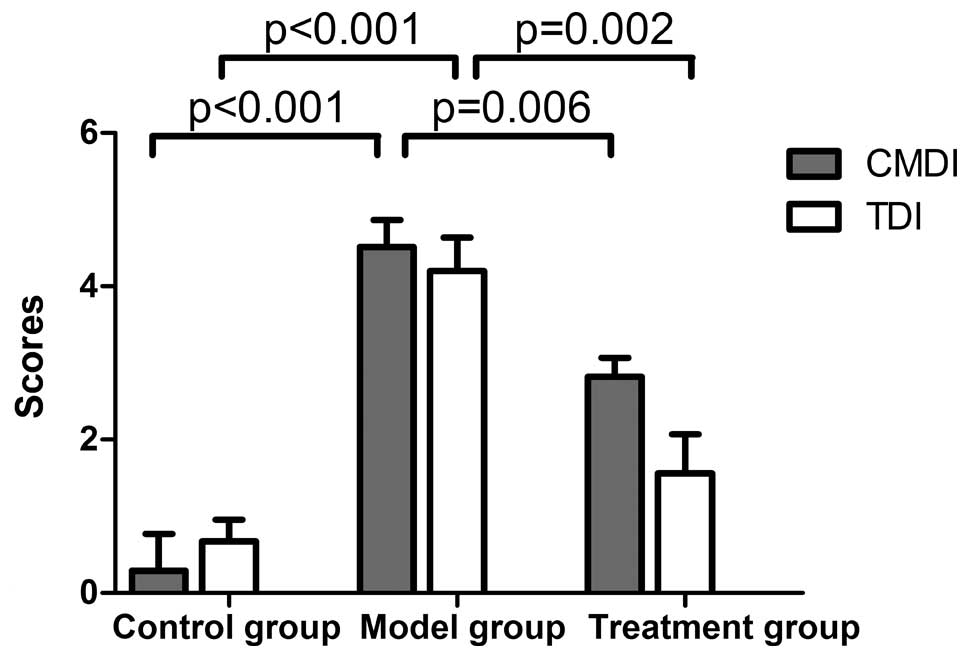
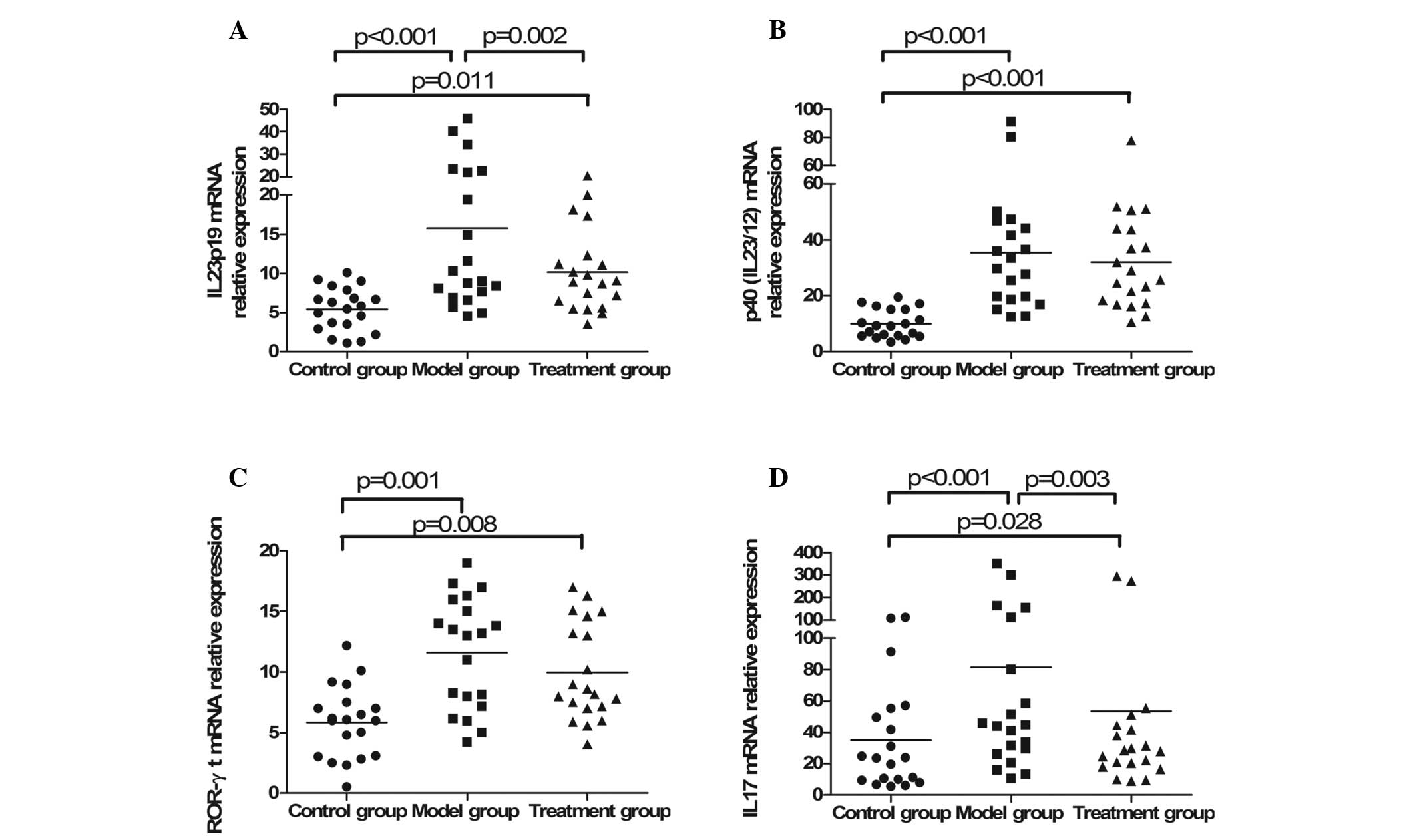
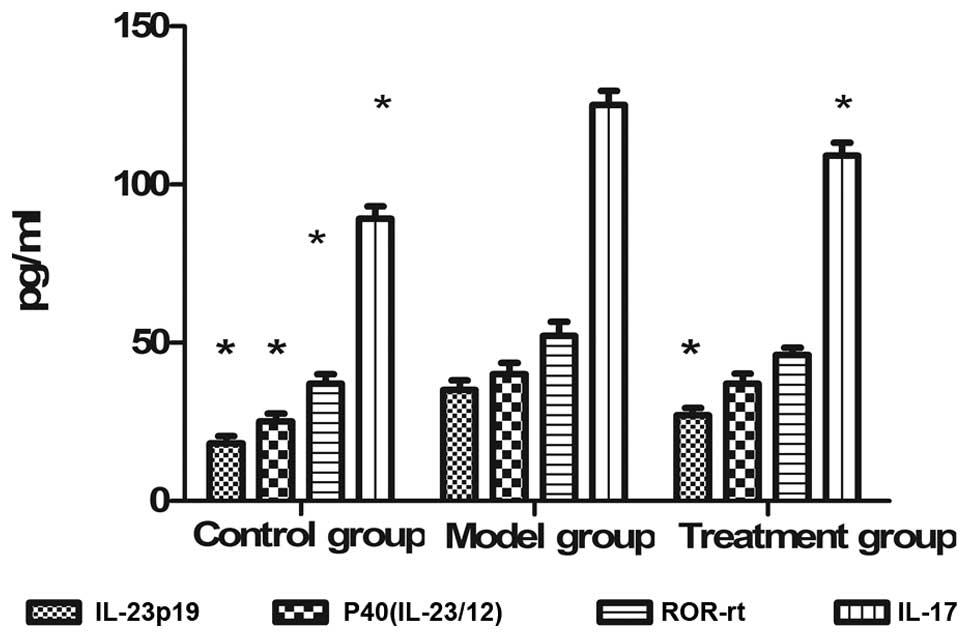
|
1
|
Geremia A, Biancheri P, Allan P, Corazza
GR and Di Sabatino A: Innate and adaptive immunity in inflammatory
bowel disease. Autoimmun Rev. 13:3–10. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Oppmann B, Lesley R, Blom B, et al: Novel
p19 protein engages IL-12p40 to form a cytokine, IL-23, with
biological activities similar as well as distinct from IL-12.
Immunity. 13:715–725. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cua DJ, Sherlock J, Chen Y, et al:
Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine
for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature. 421:744–748.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Vignali DA and Kuchroo VK: IL-12 family
cytokines: immunological playmakers. Nat Immunol. 13:722–728. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Duvallet E, Semerano L, Assier E,
Falgarone G and Boissier MC: Interleukin-23: a key cytokine in
inflammatory diseases. Ann Med. 43:503–511. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Duerr RH, Taylor KD, Brant SR, et al: A
genome-wide association study identifies IL23R as an inflammatory
bowel disease gene. Science. 314:1461–1463. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
McGeachy MJ, Chen Y, Tato CM, et al: The
interleukin 23 receptor is essential for the terminal
differentiation of interleukin 17-producing effector T helper cells
in vivo. Nat Immunol. 10:314–324. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Rovedatti L, Kudo T, Biancheri P, et al:
Differential regulation of interleukin 17 and interferon gamma
production in inflammatory bowel disease. Gut. 58:1629–1636. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sarra M, Pallone F, Macdonald TT and
Monteleone G: IL-23/IL-17 axis in IBD. Inflamm Bowel Dis.
16:1808–1813. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Siakavellas SI and Bamias G: Role of the
IL-23/IL-17 axis in Crohn’s disease. Discov Med. 14:253–262.
2012.
|
|
11
|
Toussirot E: The IL23/Th17 pathway as a
therapeutic target in chronic inflammatory diseases. Inflamm
Allergy Drug Targets. 1:159–168. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Imaeda H, Takahashi K, Fujimoto T, et al:
Clinical utility of newly developed immunoassays for serum
concentrations of adalimumab and anti-adalimumab antibodies in
patients with Crohn’s disease. J Gastroenterol. 49:100–109.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Peyrin-Biroulet L and Danese S: Stopping
infliximab in Crohn’s disease: still an ongoing STORI. Inflamm
Bowel Dis. 18:2201–2202. 2012.
|
|
14
|
Kilkenny C, Browne WJ, Cuthill IC, Emerson
M and Altman DG: Improving bioscience research reporting: the
ARRIVE guidelines for reporting animal research. PLoS Biol.
8:e10004122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Morris GP, Beck PL, Herridge MS, et al:
Hapten-induced model of chronic inflammation and ulceration in the
rat colon. Gastroenterology. 96:795–803. 1989.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Murthy SN, Cooper HS, Shim H, Shah RS,
Ibrahim SA and Sedergran DJ: Treatment of dextran sulfate
sodium-induced murine colitis by intracolonic cyclosporin. Dig Dis
Sci. 38:1722–1734. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Murano M, Maemura K, Hirata I, et al:
Therapeutic effect of intracolonically administered nuclear factor
kappa B (p65) antisense oligonucleotide on mouse dextran sulphate
sodium (DSS)-induced colitis. Clin Exp Immunol. 120:51–58. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wallace JL and Keenan CM: An orally active
inhibitor of leukotriene synthesis accelerates healing in a rat
model of colitis. Am J Physiol. 258:G527–G534. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo L, Ye C, Hao X, et al:
Carboxyamidotriazole ameliorates experimental colitis by inhibition
of cytokine production, nuclear factor-κB activation, and colonic
fibrosis. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 342:356–365. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zingarelli B, Hake PW, Burroughs TJ,
Piraino G, O’Connor M and Denenberg A: Activator protein-1
signalling pathway and apoptosis are modulated by poly(ADP-ribose)
polymerase-1 in experimental colitis. Immunology. 113:509–517.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Neurath MF, Fuss I, Kelsall BL, Stüber E
and Strober W: Antibodies to interleukin 12 abrogate established
experimental colitis in mice. J Exp Med. 182:1281–1290. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Strober W, Lúdvíksson BR and Fuss IJ: The
pathogenesis of mucosal inflammation in murine models of
inflammatory bowel disease and Crohn disease. Ann Intern Med.
128:848–856. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Torres MI, Garcia-Martin M, Fernandez MI,
Nieto N, Gil A and Rios A: Experimental colitis induced by
trinitrobenzenesulfonic acid: an ultrastructural and histochemical
study. Dig Dis Sci. 44:2523–2529. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Lakatos PL and Lakatos L: Ulcerative
proctitis: a review of pharmacotherapy and management. Expert Opin
Pharmacother. 9:741–749. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Burger D and Travis S: Conventional
medical management of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology.
140:1827–1837. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Magro F and Portela F: Management of
inflammatory bowel disease with infliximab and other anti-tumor
necrosis factor alpha therapies. BioDrugs. 24:3–14. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Mariette X, Matucci-Cerinic M, Pavelka K,
et al: Malignancies associated with tumour necrosis factor
inhibitors in registries and prospective observational studies: a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis. 70:1895–1904.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Deepak P, Sifuentes H, Sherid M, Stobaugh
D, Sadozai Y and Ehrenpreis ED: T-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas
reported to the FDA AERS with tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)
inhibitors: results of the REFURBISH study. Am J Gastroenterol.
108:99–105. 2013.
|
|
29
|
Huang R, Valerian BT and Lee EC:
Laparoscopic approach in patients with recurrent Crohn’s disease.
Am Surg. 78:595–599. 2012.
|
|
30
|
Ivanov II, McKenzie BS, Zhou L, et al: The
orphan nuclear receptor RORgammat directs the differentiation
program of proinflammatory IL-17+ T helper cells. Cell.
126:1121–1133. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ono Y, Kanai T, Sujino T, et al: T-helper
17 and interleukin-17-producing lymphoid tissue inducer-like cells
make different contributions to colitis in mice. Gastroenterology.
143:1288–1297. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Guan Q, Ma Y, Hillman CL, et al: Targeting
IL-12/IL-23 by employing a p40 peptide-based vaccine ameliorates
TNBS-induced acute and chronic murine colitis. Mol Med. 17:646–656.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
De Nitto D, Sarra M, Cupi ML, Pallone F
and Monteleone G: Targeting IL-23 and Th17-cytokines in
inflammatory bowel diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 16:3656–3660.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Monteleone I, Pallone F and Monteleone G:
Interleukin-23 and Th17 cells in the control of gut inflammation.
Mediators Inflamm. 2009:2976452009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Cho JH and Brant SR: Recent insights into
the genetics of inflammatory bowel disease. Gastroenterology.
140:1704–1712. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Kurzeja M, Rudnicka L and Olszewska M: New
interleukin-23 pathway inhibitors in dermatology: ustekinumab,
briakinumab and secukinumab. Am J Clin Dermatol. 12:113–125. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Tzellos T, Kyrgidis A, Trigoni A and
Zouboulis CC: Association of ustekinumab and briakinumab with major
adverse cardiovascular events: An appraisal of meta-analyses and
industry sponsored pooled analyses to date. Dermatoendocrinol.
4:320–323. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|