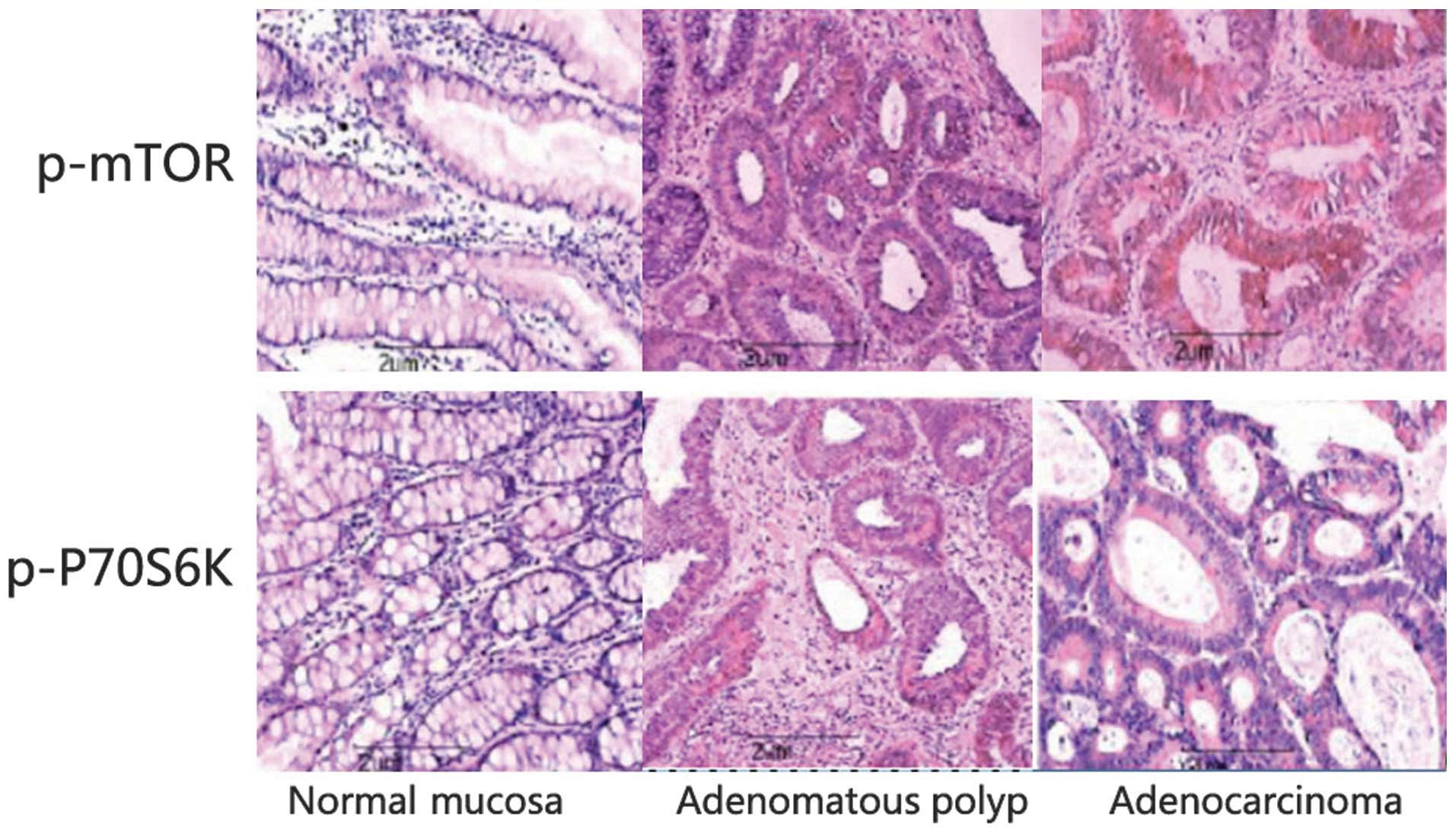
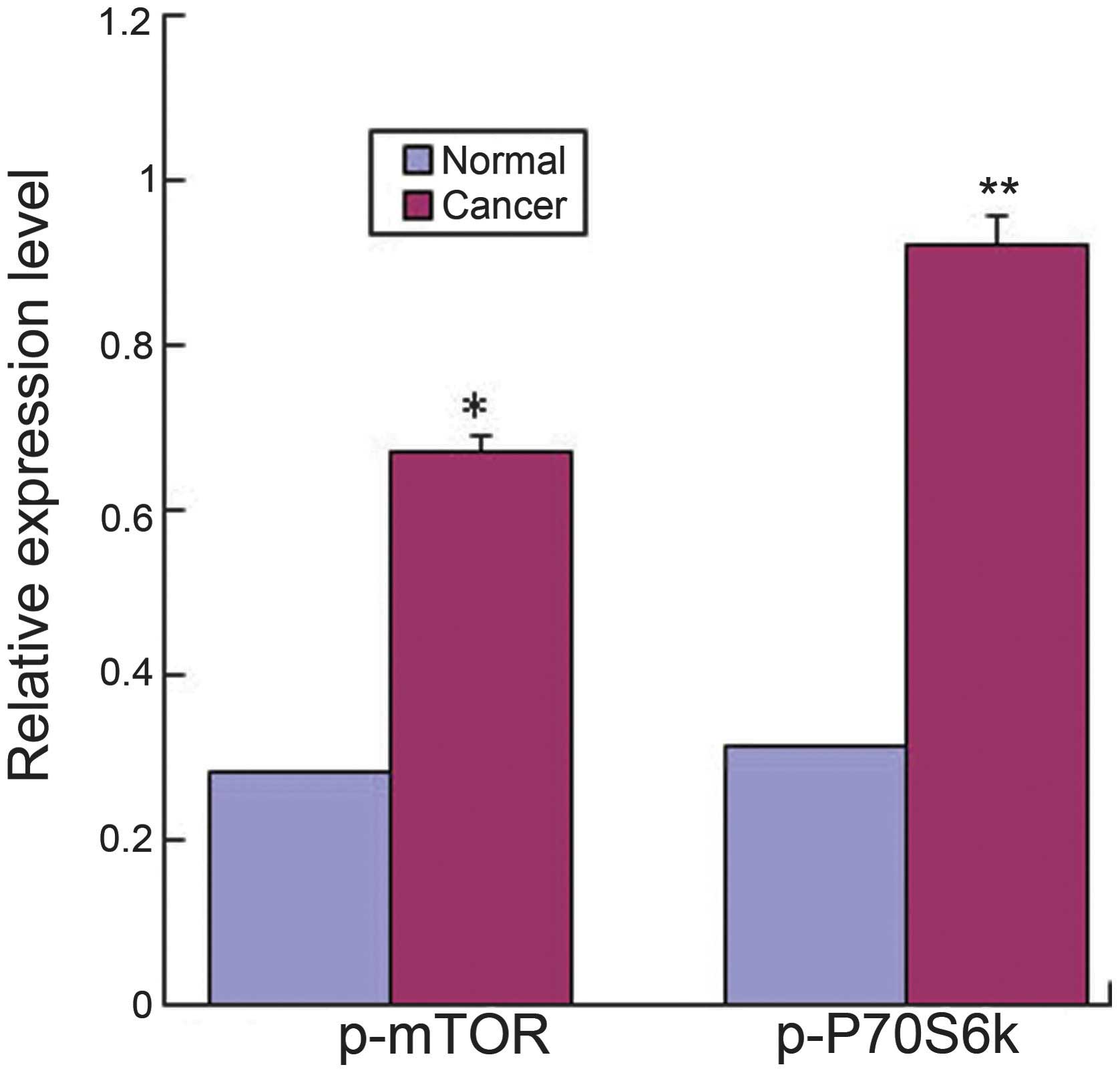
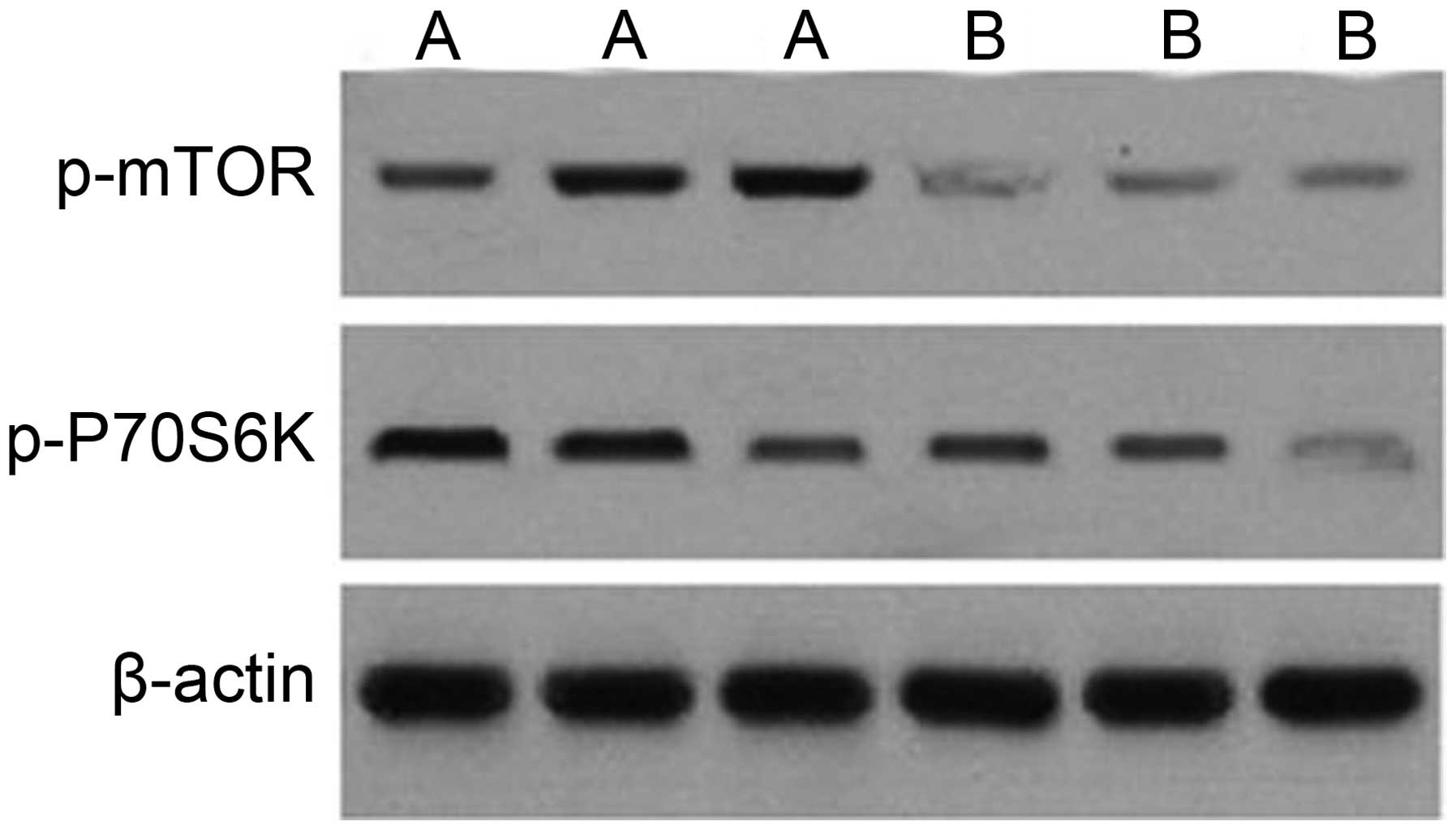
|
1
|
World Health Organization, . The Global
Burden of Disease: 2004 Update. World Health Organization; Geneva:
2008
|
|
2
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, et al:
Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in 2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int
J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Otake S, Takeda H, Fujishima S, et al:
Decreased levels of plasma adiponectin associated with increased
risk of colorectal cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 16:1252–1257.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Buck E, Eyzaguirre A, Brown E, et al:
Rapamycin synergizes with the epidermal growth factor receptor
inhibitor erlotinib in non-small-cell lung, pancreatic, colon, and
breast tumors. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:2676–2684. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Pene F, Claessens YE, Muller O, et al:
Role of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt and mTOR/P70S6-kinase
pathways in the proliferation and apoptosis in multiple myeloma.
Oncogene. 21:6587–6597. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shaw RJ and Cantley LC: Ras, PI(3)K and
mTOR signalling controls tumour cell growth. Nature. 441:424–430.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Foster DA: Phosphatidic acid signaling to
mTOR: Signals for the survival of human cancer cells. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1791:949–955. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Jiang BH and Liu LZ: Role of mTOR in
anticancer drug resistance: Perspectives for improved drug
treatment. Drug Resist Updat. 11:63–76. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang X and Proud CG: The mTOR pathway in
the control of protein synthesis. Physiology (Bethesda).
21:362–369. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kim EK, Kim HA, Koh JS, et al:
Phosphorylated S6K1 is a possible marker for endocrine therapy
resistance in hormone receptor-positive breast cancer. Breast
Cancer Res Treat. 126:93–99. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Han D, Li SJ, Zhu YT, et al:
LKB1/AMPK/mTOR signaling pathway in non-small-cell lung cancer.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:4033–4039. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Raymond E, Alexandre J, Faivre S, et al:
Safety and pharmacokinetics of escalated doses of weekly
intravenous infusion of CCI-779, a novel mTOR inhibitor, in
patients with cancer. J Clin Oncol. 22:2336–2347. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
O’Donnell A, Faivre S, Burris HA III, et
al: Phase I pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic study of the oral
mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitor everolimus in patients with
advanced solid tumors. J Clin Oncol. 26:1588–1595. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rizell M, Andersson M, Cahlin C, et al:
Effects of the mTOR inhibitor sirolimus in patients with
hepatocellular and cholangiocellular cancer. Int J Clin Oncol.
13:66–70. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Benson AB III, Bekaii-Saab T, Chan E, et
al: National Comprehensive Cancer Network: Localized colon cancer,
version 3.2013: featured updates to the NCCN Guidelines. J Natl
Compr Canc Netw. 11:519–528. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Murayama T, Inokuchi M, Takagi Y, Yamada
H, Kojima K, Kumagai J, Kawano T and Sugihara K: Relation between
outcomes and localisation of p-mTOR expression in gastric cancer.
Br J Cancer. 100:782–788. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Herberger B, Puhalla H, Lehnert M, Wrba F,
Novak S, Brandstetter A, Gruenberger B, Gruenberger T, Pirker R and
Filipits M: Activated mammalian target of rapamycin is an adverse
prognostic factor in patients with biliary tract adenocarcinoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 13:4795–4799. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Pham NA, Schwock J, Iakovlev V, Pond G,
Hedley DW and Tsao MS: Immunohistochemical analysis of changes in
signaling pathway activation downstream of growth factor receptors
in pancreatic duct cell carcinogenesis. BMC Cancer. 8:432008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Dobashi Y, Suzuki S, Matsubara H, Kimura
M, Endo S and Ooi A: Critical and diverse involvement of
Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin signaling in human lung
carcinomas. Cancer. 115:107–118. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Sun CH, Chang YH and Pan CC: Activation of
the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway correlates with tumour progression and
reduced survival in patients with urothelial carcinoma of the
urinary bladder. Histopathology. 58:1054–1063. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kremer CL, Klein RR, Mendelson J, Browne
W, Samadzedeh LK, Vanpatten K, Highstrom L, Pestano GA and Nagle
RB: Expression of mTOR signaling pathway markers in prostate cancer
progression. Prostate. 66:1203–1212. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Feng W, Duan X, Liu J, Xiao J and Brown
RE: Morphoproteomic evidence of constitutively activated and
overexpressed mTOR pathway in cervical squamous carcinoma and high
grade squamous intraepithelial lesions. Int J Clin Exp Pathol.
2:249–260. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Walsh S, Flanagan L, Quinn C, Evoy D,
McDermott EW, Pierce A and Duffy MJ: mTOR in breast cancer:
Differential expression in triple-negative and non-triple-negative
tumors. Breast. 21:178–182. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pantuck AJ, Seligson DB, Klatte T, Yu H,
Leppert JT, Moore L, O’Toole T, Gibbons J, Belldegrun AS and Figlin
RA: Prognostic relevance of the mTOR pathway in renal cell
carcinoma: Implications for molecular patient selection for
targeted therapy. Cancer. 109:2257–2267. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chung JY, Hong SM, Choi BY, Cho H, Yu E
and Hewitt SM: The expression of phospho-AKT, phospho-mTOR, and
PTEN in extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Clin Cancer Res.
15:660–667. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yu G, Wang J, Chen Y, Wang X, Pan J, Li G,
Jia Z, Li Q, Yao JC and Xie K: Overexpression of phosphorylated
mammalian target of rapamycin predicts lymph node metastasis and
prognosis of chinese patients with gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res.
15:1821–1829. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Wang D, Chen J, Guo F, Chen H, Duan Z, Wei
MY, Xu QM, Wang LH and Zhong MZ: Clinical significance of mTOR and
p-mTOR protein expression in human colorectal carcinomas. Asian Pac
J Cancer Prev. 12:2581–2584. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
No JH, Jeon YT, Park IA, Kang D, Kim JW,
Park NH, Kang SB and Song YS: Expression of mTOR protein and its
clinical significance in endometrial cancer. Med Sci Monit.
15:BR301–BR305. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Berven LA, Willard FS and Crouch MF: Role
of the p70(S6K) pathway in regulating the actin cytoskeleton and
cell migration. Exp Cell Res. 296:183–195. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Contessa JN, Hampton J, Lammering G, et
al: Ionizing radiation activates Erb-B receptor dependent Akt and
p70 S6 kinase signaling in carcinoma cells. Oncogene. 21:4032–4041.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Xiao L, Wang YC, Li WS and Du Y: The role
of mTOR and phospho-p70S6K in pathogenesis and progression of
gastric carcinomas: An immunohistochemical study on tissue
microarray. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 28:1522009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zhang Y, Ni HJ and Cheng DY: Prognostic
value of phosphorylated mTOR/RPS6KB1 in non- small cell lung
cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:3725–3728. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ji J and Zheng PS: Activation of mTOR
signaling pathway contributes to survival of cervical cancer cells.
Gynecol Oncol. 117:103–108. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Roulin D, Cerantola Y, Dormond-Meuwly A,
Demartines N and Dormond O: Targeting mTORC2 inhibits colon cancer
cell proliferation in vitro and tumor formation in vivo. Mol
Cancer. 9:572010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|