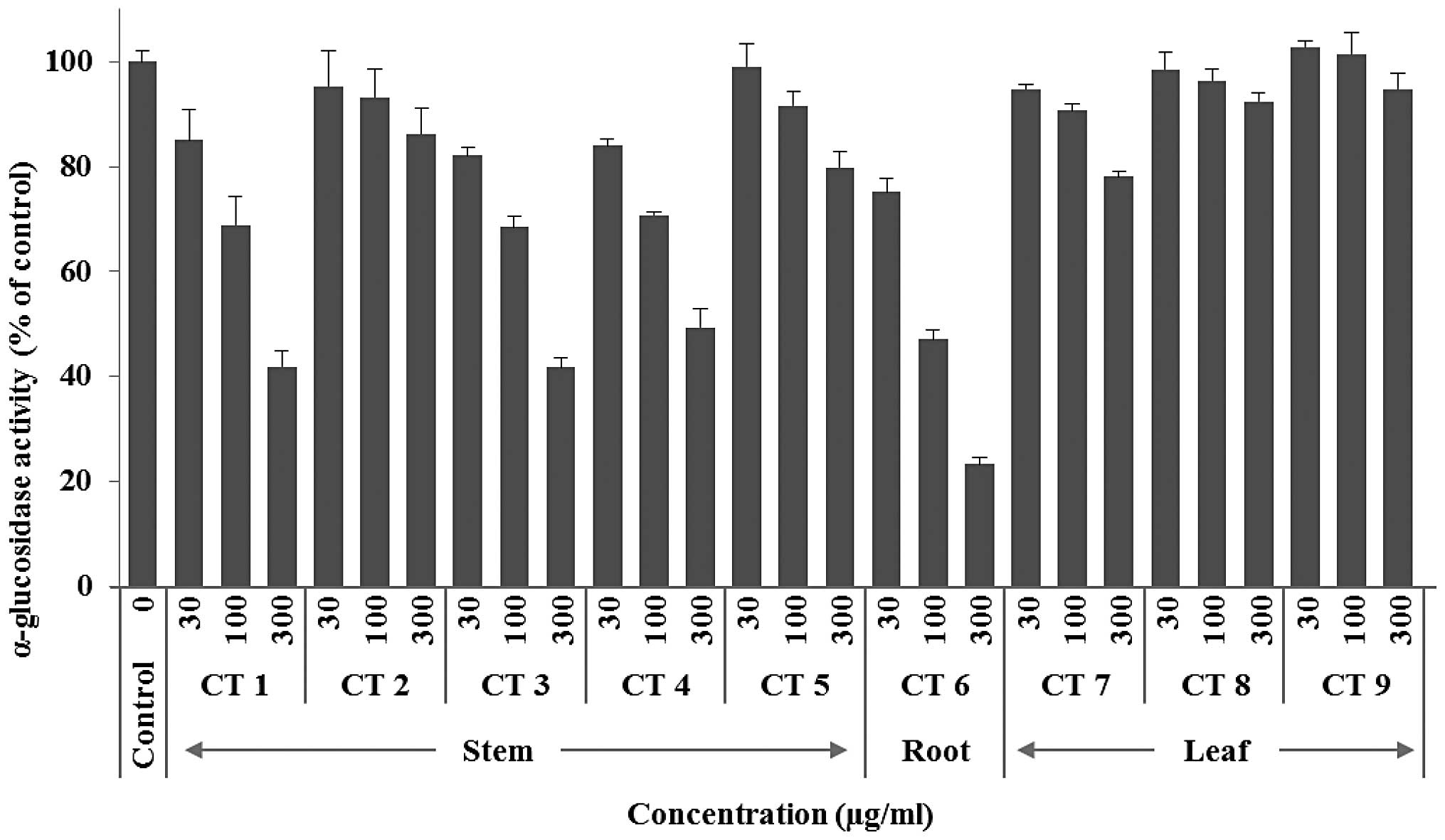
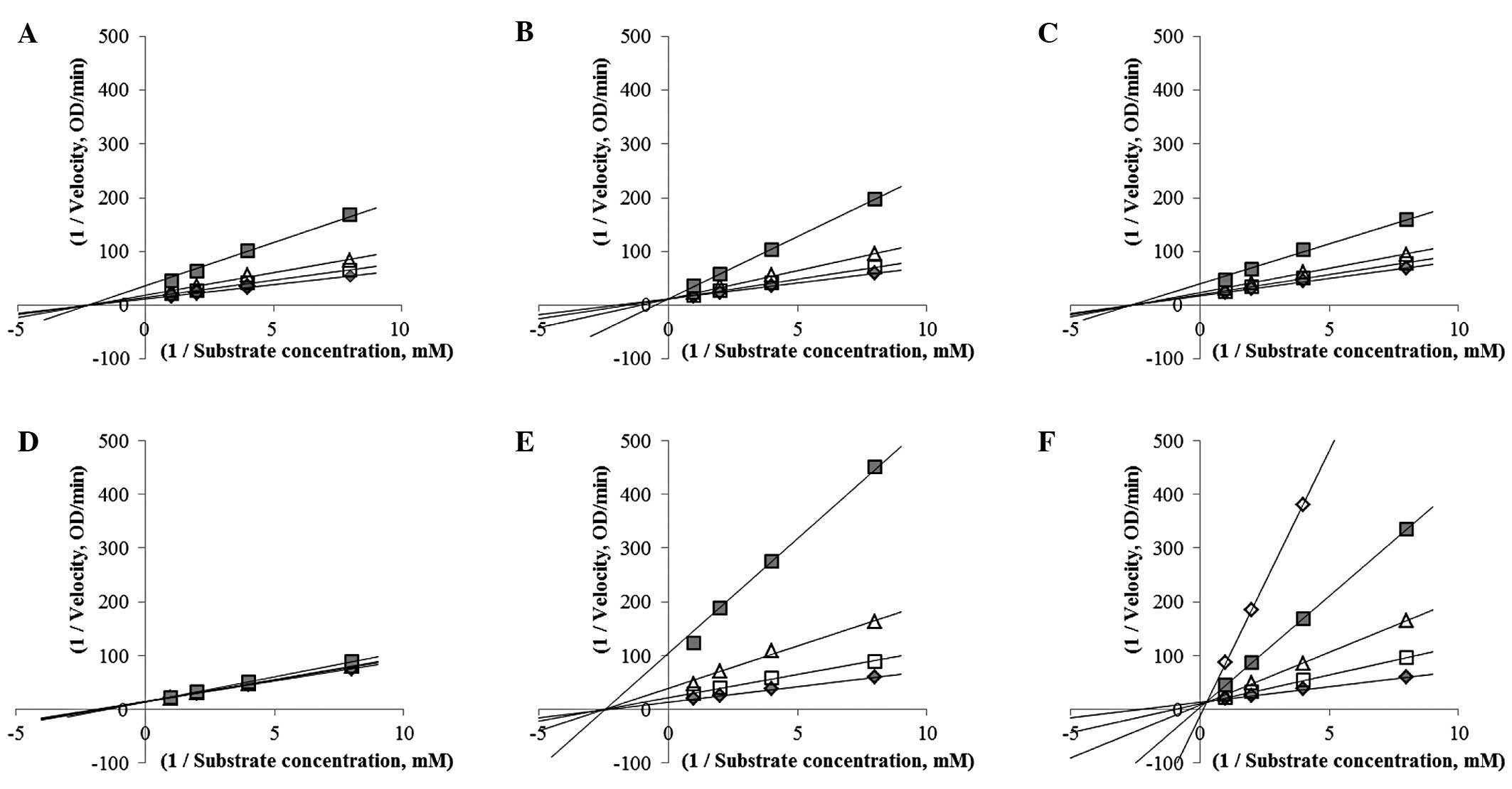
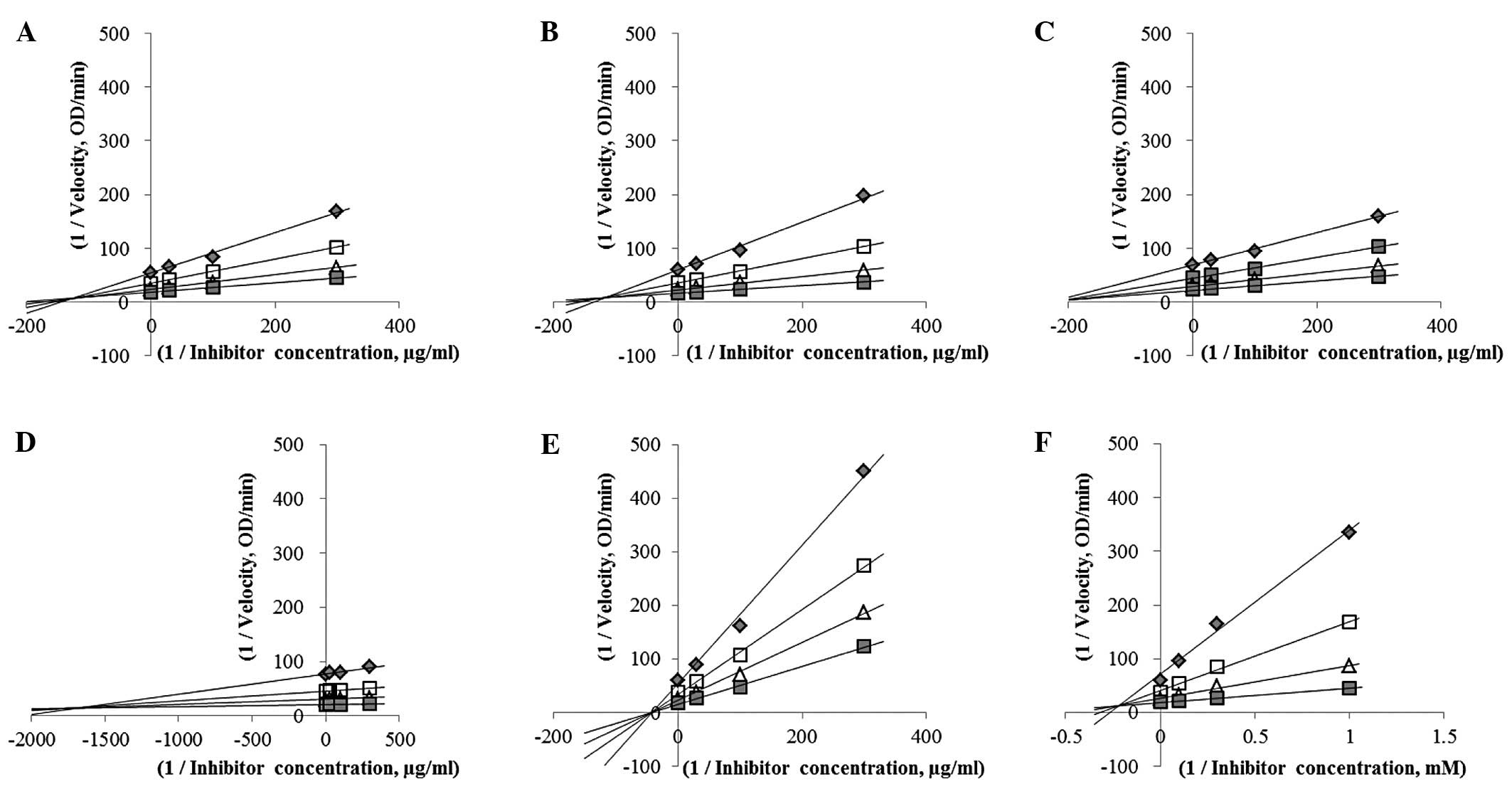
|
1
|
Li YQ, Zhou FC, Gao F, Bian JS and Shan F:
Comparative evaluation of quercetin, isoquercetin and rutin as
inhibitors of alpha-glucosidase. J Agric Food Chem. 57:11463–11468.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Seo EJ, Curtis-Long MJ, Lee BW, Kim HY,
Ryu YB, Jeong TS, Lee WS and Park KH: Xanthones from Cudrania
tricuspidata displaying potent alpha-glucosidase inhibition.
Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 17:6421–6424. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Osonoi T, Saito M, Mochizuki K, Fukaya N,
Muramatsu T, Inoue S, Fuchigami M and Goda T: The α-glucosidase
inhibitor miglitol decreases glucose fluctuations and inflammatory
cytokine gene expression in peripheral leukocytes of Japanese
patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism. 59:1816–1822.
2010.
|
|
4
|
Lee BW, Lee JH, Gal SW, Moon YH and Park
KH: Selective ABTS radical-scavenging activity of prenylated
flavonoids form Cudrania tricuspidata. Biosci Biotechnol
Biochem. 70:427–432. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Guan Y, Yin Z, Guo L, Huang X, Ye W and
Shen W: Studies on chemical constituents from stems of Cudrania
tricuspidata. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 34:1108–1110. 2009.(In
Chinese).
|
|
6
|
Lee HJ, Do JR, Kwon JH and Kim HK:
Physiological activities of extracts from different parts of
Cudrania tricuspidata. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr.
40:942–948. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cha JY and Cho YS: Antioxidative activity
of extracts from fruit of Cudrania tricuspidata. J Korean
Soc Food Sci Nutr. 30:547–551. 2001.
|
|
8
|
Chang SH, Jung EJ, Lim DG, Oyungerel B,
Lim KI, Her E, Choi WS, Jun MH, Choi KD, Han DJ and Kim SC:
Anti-inflammatory action of Cudrania tricuspidata on spleen
cell and T lymphocyte proliferation. J Pharm Pharmacol.
60:1221–1226. 2008.
|
|
9
|
Hwang JH, Hong SS, Han XH, Hwang JS, Lee
D, Lee H, Yun YP, Kim Y, Ro JS and Hwang BY: Prenylated xanthones
from the root bark of Cudrania tricuspidata. J Nat Prod.
70:1207–1209. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Choi CW, Choi YH, Cha MR, Yoo DS, Kim YS,
Yon GH, Hong KS, Kim YH and Ryu SY: Yeast α-glucosidase inhibition
by isoflavones from plants of Leguminosae as an in vitro
alternative to acarbose. J Agric Food Chem. 58:9988–9993. 2010.
|
|
11
|
Nishio T, Hakamata W, Kimura A, Chiba S,
Takatsuki A, Kawachi R and Oku T: Glycon specificity profiling of
alpha-glucosidases using monodeoxy and mono-O-methyl derivatives of
p-nitrophenyl alpha-D-glucopyranoside. Carbohydr Res. 124:629–634.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li GL, He JY, Zhang A, Wan Y, Wang B and
Chen WH: Toward potent α-glucosidase inhibitors based on xanthones:
a closer look into the structure-activity correlations. Eur J Med
Chem. 46:4050–4055. 2011.
|
|
13
|
Dixon M: The determination of enzyme
inhibitor constants. Biochem J. 55:170–171. 1953.
|
|
14
|
Kim MJ, Lee SB, Lee HS, Lee SY, Baek JS,
Kim D, Moon TW, Robyt JF and Park KH: Comparative study of the
inhibition of alpha-glucosidase, alpha-amylase, and
cyclomaltodextrin glucanosyltransferase by acarbose, isoacarbose,
and acarviosine-glucose. Arch Biochem Biophys. 371:277–283. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Sen S and Mukherji S: Season-controlled
changes in biochemical constituents and oxidase enzyme activities
in tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.). J Environ Biol.
30:479–483. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|