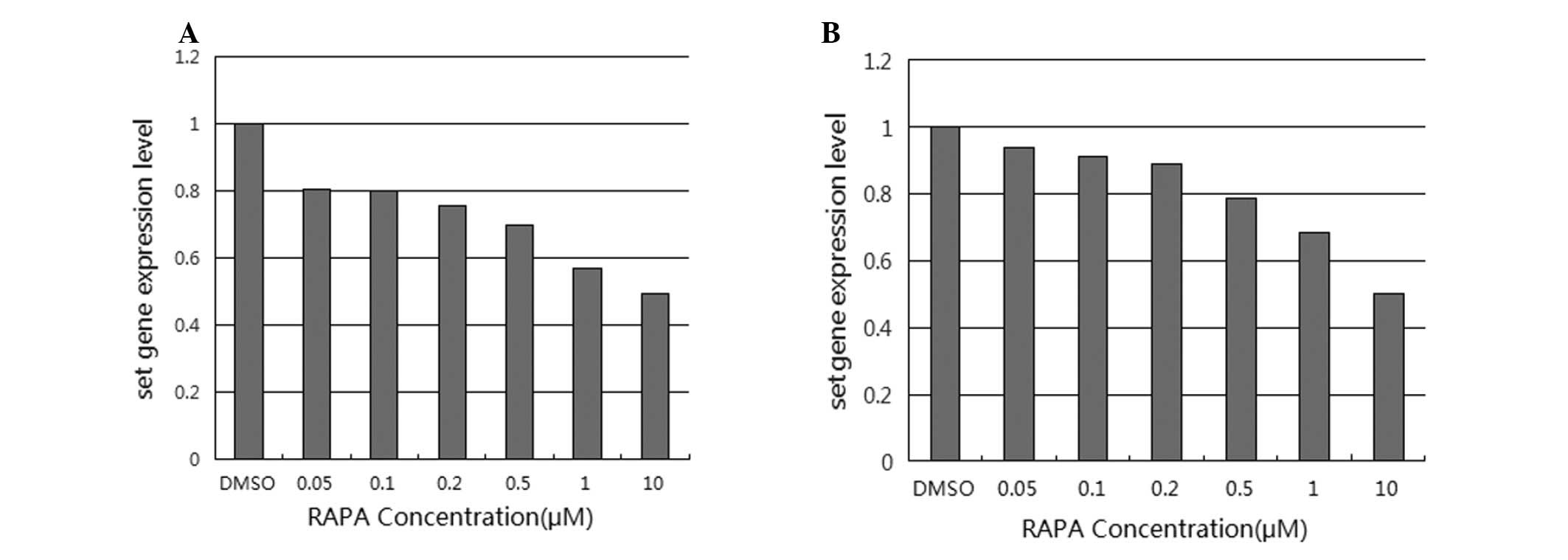
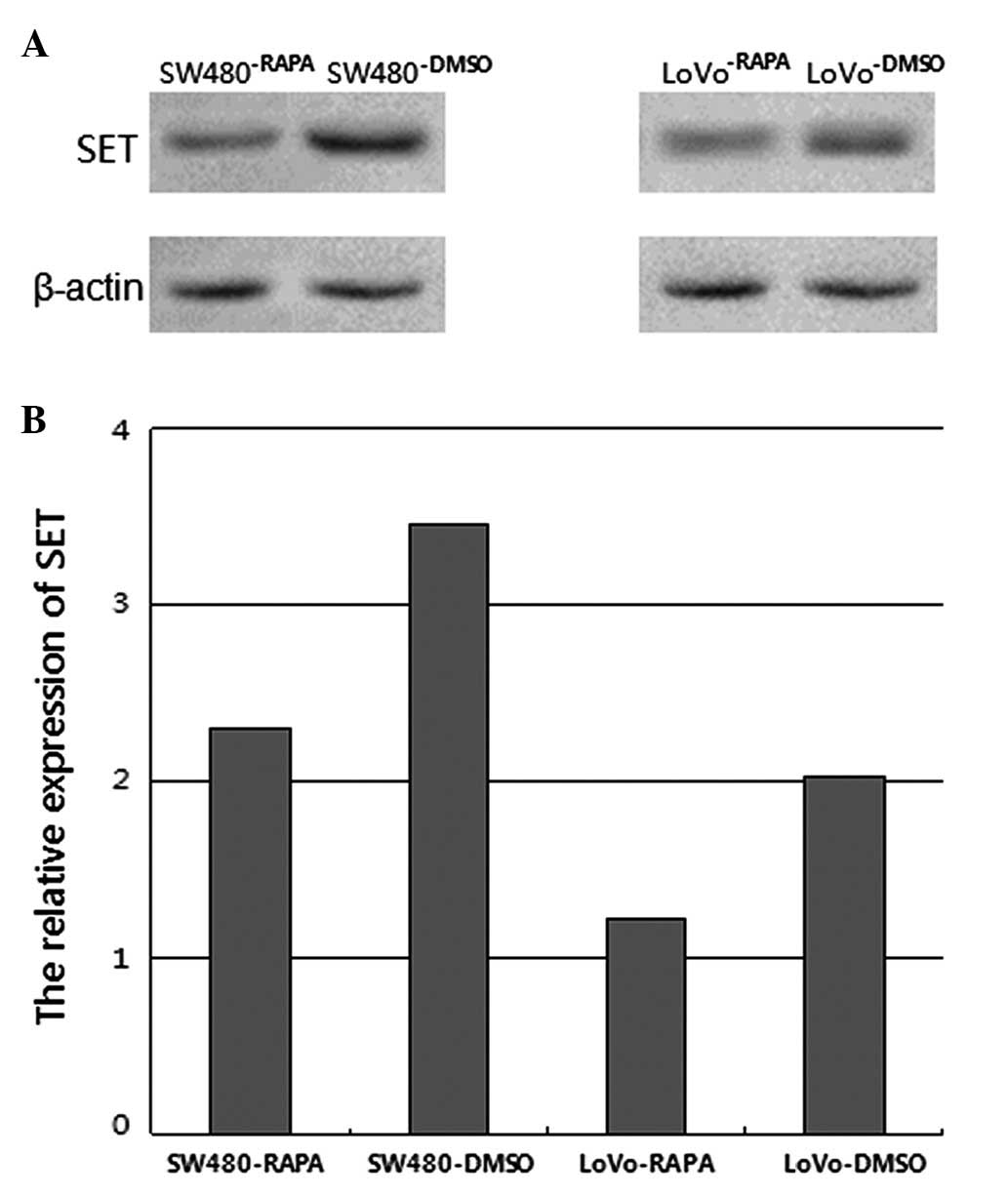
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Herrinton LJ, Liu L, Levin TR, Allison JE,
Lewis JD and Velayos F: Incidence and mortality of colorectal
adenocarcinoma in persons with inflammatory bowel disease from 1998
to 2010. Gastroenterology. 143:382–389. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Chen Y, Zhang Y, Zhou Z, Wang G and Yi Z:
Identification of differentially expressed genes in human
colorectal adenocarcinoma. World J Gastroenterol. 12:1025–1032.
2006.
|
|
4
|
Zhang C and Chen Y: Electronic cloning and
validating of the suppression subtractive hybridization EST
ES274070 of human colorectal adenocarcinoma. US Chin J Lymphol
Oncol. 6:83–88. 2007.
|
|
5
|
Jiang Q, Zhang C, Zhu J, Chen Q and Chen
Y: The set gene is a potential oncogene in human colorectal
adenocarcinoma and oral squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep.
4:993–999. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zoncu R, Efeyan A and Sabatini DM: mTOR:
from growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nat
Rev Mol Cell Biol. 12:21–35. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Laplante M and Sabatini DM: mTOR signaling
at a glance. J Cell Sci. 122:3589–3594. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Feng Z, Zhang H, Levine AJ and Jin S: The
coordinate regulation of the p53 and mTOR pathways in cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:8204–8209. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gulhati P, Cai Q, Li J, et al: Targeted
inhibition of mammalian target of rapamycin signaling inhibits
tumorigenesis of colorectal cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 15:7207–7216.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chiang GG and Abraham RT: Targeting the
mTOR signaling network in cancer. Trends Mol Med. 13:433–442. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Miyake N, Chikumi H, Takata M, Nakamoto M,
Igishi T and Shimizu E: Rapamycin induces p53-independent apoptosis
through the mitochondrial pathway in non-small cell lung cancer
cells. Oncol Rep. 28:848–854. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bustin SA, Benes V, Garson JA, Hellemans
J, et al: The MIQE guidelines: minimum information for publication
of quantitative real-time PCR experiments. Clin Chem. 55:611–622.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ouellet V, Le Page C, Guyot MC, Lussier C,
Tonin PN, Provencher DM and Mes-Masson AM: SET complex in serous
epithelial ovarian cancer. Int J Cancer. 119:2119–2126. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
von Lindern M, Van Baal S, Wiegant J, Raap
A, Hagemeijer A and Grosveld G: Can, a putative oncogene associated
with myeloid leukemogenesis, may be activated by fusion of its 3′
half to different genes: characterization of the set gene. Mol Cell
Biol. 12:3346–3355. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cristóbal I, Garcia-Orti L, Cirauqui C,
Cortes-Lavaud X, García-Sánchez MA, Calasanz MJ and Odero MD:
Overexpression of SET is a recurrent event associated with poor
outcome and contributes to protein phosphatase 2A inhibition in
acute myeloid leukemia. Haematologica. 97:543–550. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Almeida LO, Goto RN, Pestana CR, Uyemura
SA, Gutkind S, Curti C and Leopoldino AM: SET overexpression
decreases cell detoxification efficiency: ALDH2 and GSTP1 are
downregulated, DDR is impaired and DNA damage accumulates. FEBS J.
279:4615–4628. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Leopoldino AM, Squarize CH, Garcia CB, et
al: Accumulation of the SET protein in HEK293T cells and mild
oxidative stress: cell survival or death signaling. Mol Cell
Biochem. 363:65–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lei Y, Huang K, Gao C, et al: Proteomics
identification of ITGB3 as a key regulator in reactive oxygen
species-induced migration and invasion of colorectal cancer cells.
Mol Cell Proteomics. 10:M110.0053972011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kim DD and Eng C: The promise of mTOR
inhibitors in the treatment of colorectal cancer. Expert Opin
Investig Drugs. 21:1775–1788. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Thimmaiah KN, Easton J, Huang S, Veverka
KA, Germain GS, Harwood FC and Houghton PJ: Insulin-like growth
factor I-mediated protection from rapamycin-induced apoptosis is
independent of Ras-Erk1-Erk2 and phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase-Akt
signaling pathways. Cancer Res. 63:364–374. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Boffa DJ, Luan F, Thomas D, Yang h, Sharma
VK, Lagman M and Suthanthiran M: Rapamycin inhibits the growth and
metastatic progression of non-small cell lung cancer. Clin Cancer
Res. 10:293–300. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Samkari A, Cooper ZA, Holloway MP, Liu J
and Altura RA: Rapamycin induces the anti-apoptotic protein
survivin in neuroblastoma. Int J Biochem Mol Biol. 3:28–35.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|