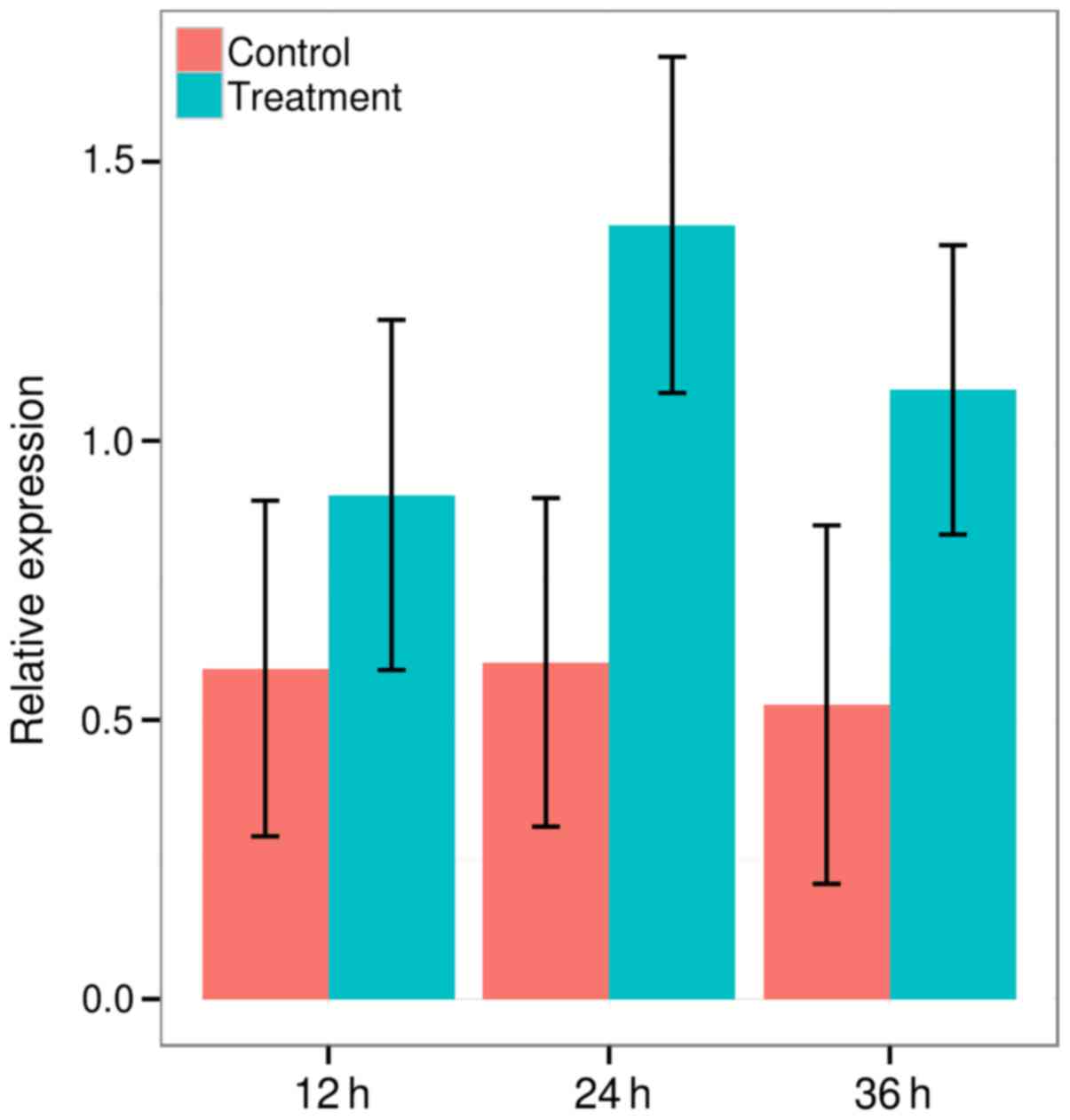
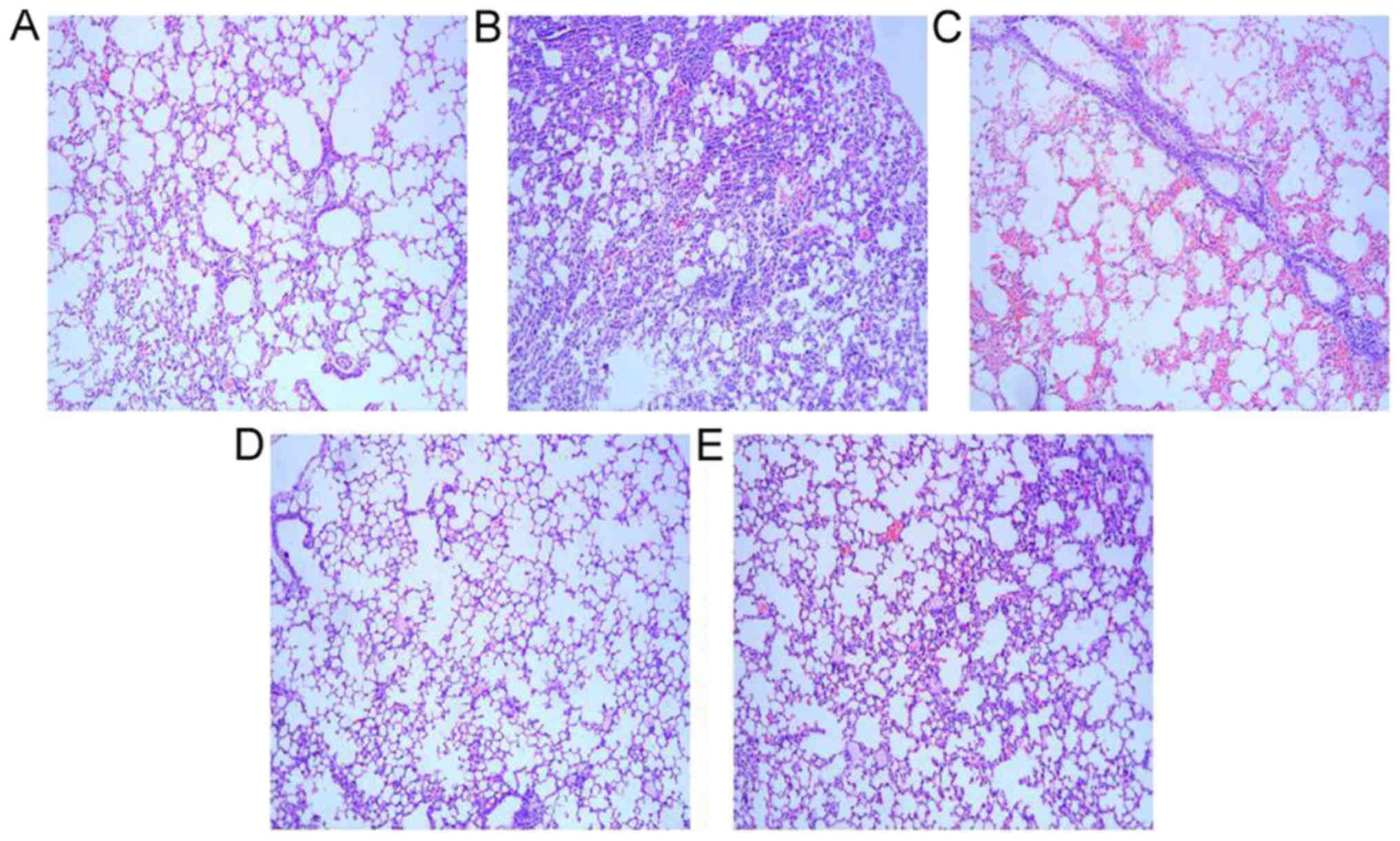
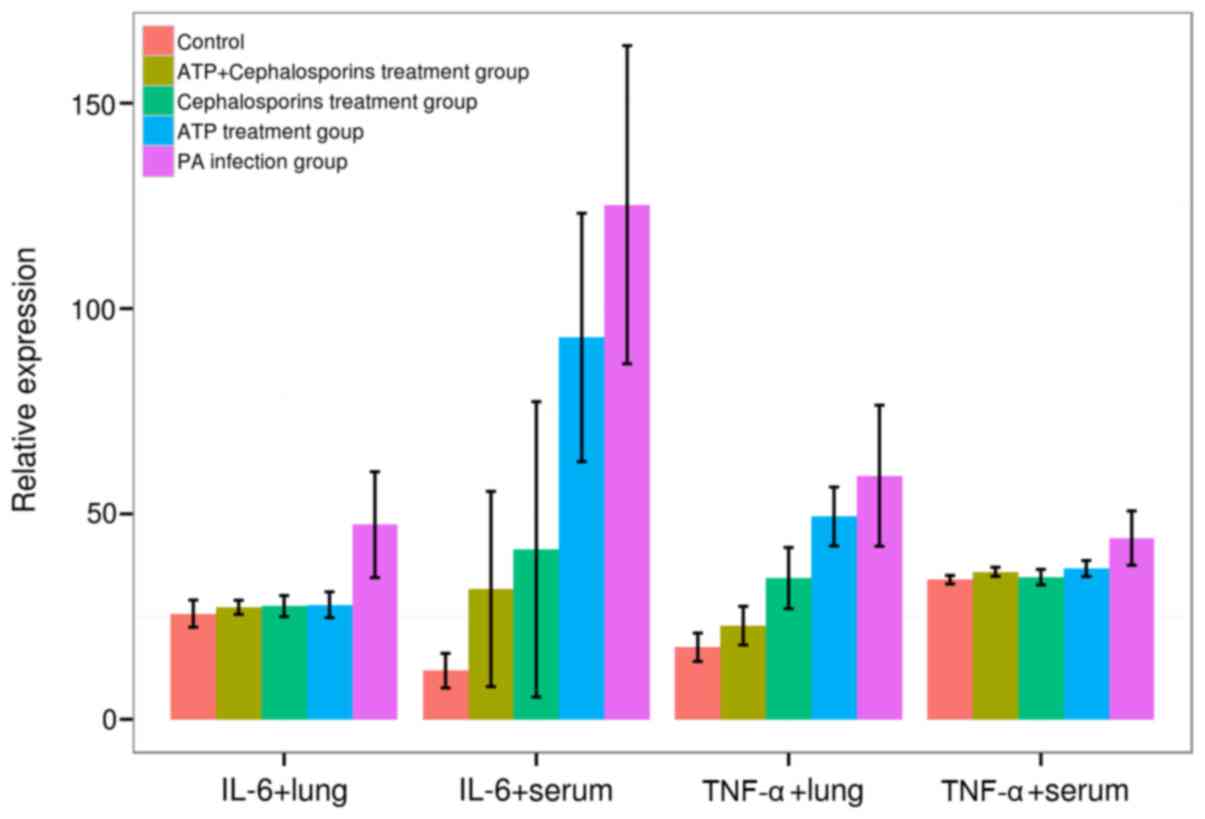
|
1
|
Schutte BC and McCray PB Jr:
[beta]-defensins in lung host defense. Annu Rev Physiol.
64:709–748. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Bensch KW, Raida M, Mägert HJ,
Schulz-Knappe P and Forssmann WG: hBD-1: A novel β-defensin from
human plasma. FEBS Lett. 368:331–335. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Harder J, Bartels J, Christophers E and
Schröder JM: A peptide antibiotic from human skin. Nature.
387:8611997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Harder J, Bartels J, Christophers E and
Schröder JM: Isolation and characterization of human β-defensin-3,
a novel human inducible peptide antibiotic. J Biol Chem.
276:5707–5713. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jia HP, Schutte BC, Schudy A, Linzmeier R,
Guthmiller JM, Johnson GK, Tack BF, Mitros JP, Rosenthal A, Ganz T,
et al: Discovery of new human beta-defensins using a genomics-based
approach. Gene. 263:211–218. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yanagi S, Ashitani J, Ishimoto H, Date Y,
Mukae H, Chino N and Nakazato M: Isolation of human beta-defensin-4
in lung tissue and its increase in lower respiratory tract
infection. Respir Res. 6:1302005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yamaguchi Y, Nagase T, Makita R, Fukuhara
S, Tomita T, Tominaga T, Kurihara H and Ouchi Y: Identification of
multiple novel epididymis-specific beta-defensin isoforms in humans
and mice. J Immunol. 169:2516–2523. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lehrer RI, Lichtenstein AK and Ganz T:
Defensins: Antimicrobial and cytotoxic peptides of mammalian cells.
Annu Rev Immunol. 11:105–128. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ganz T: Defensins: Antimicrobial peptides
of innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol. 3:710–720. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Méndez-Samperio P, Miranda E and Trejo A:
Regulation of human β-defensin-2 by Mycobacterium bovis bacillus
Calmette-Guérin (BCG): Involvement of PKC, JNK, and PI3K in human
lung epithelial cell line (A549). Peptides. 29:1657–1663. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tsutsumi-Ishii Y and Nagaoka I: NF-kappa
B-mediated transcriptional regulation of human beta-defensin-2 gene
following lipopolysaccharide stimulation. J Leukoc Biol.
71:154–162. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wu M, McClellan SA, Barrett RP and Hazlett
LD: Beta-defensin-2 promotes resistance against infection with P.
aeruginosa. J Immunol. 182:1609–1616. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dalcin D and Ulanova M: The Role of Human
Beta-Defensin-2 in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pulmonary Infection in
Cystic Fibrosis Patients. Infect Dis Ther. 2:159–166. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Guaní-Guerra E, Negrete-García MC,
Montes-Vizuet R, Asbun-Bojalil J and Terán LM: Human β-defensin-2
induction in nasal mucosa after administration of bacterial
lysates. Arch Med Res. 42:189–194. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Krisanaprakornkit S, Kimball JR, Weinberg
A, Darveau RP, Bainbridge BW and Dale BA: Inducible expression of
human beta-defensin 2 by Fusobacterium nucleatum in oral epithelial
cells: Multiple signaling pathways and role of commensal bacteria
in innate immunity and the epithelial barrier. Infect Immun.
68:2907–2915. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yang D, Chertov O, Bykovskaia SN, Chen Q,
Buffo MJ, Shogan J, Anderson M, Schröder JM, Wang JM, Howard OM, et
al: Beta-defensins: Linking innate and adaptive immunity through
dendritic and T cell CCR6. Science. 286:525–528. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Boniotto M, Jordan WJ, Eskdale J, Tossi A,
Antcheva N, Crovella S, Connell ND and Gallagher G: Human
beta-defensin 2 induces a vigorous cytokine response in peripheral
blood mononuclear cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 50:1433–1441.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Khakh BS and Burnstock G: The double life
of ATP. Sci Am. 301:84–92. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Stoffels M, Zaal R, Kok N, van der Meer
JW, Dinarello CA and Simon A: ATP-Induced IL-1β Specific Secretion:
True Under Stringent Conditions. Front Immunol. 6:542015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ferrari D, Chiozzi P, Falzoni S, Dal
Susino M, Melchiorri L, Baricordi OR and Di Virgilio F:
Extracellular ATP triggers IL-1 beta release by activating the
purinergic P2Z receptor of human macrophages. J Immunol.
159:1451–1458. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Baron L, Gombault A, Fanny M, Villeret B,
Savigny F, Guillou N, Panek C, Le Bert M, Lagente V, Rassendren F,
et al: The NLRP3 inflammasome is activated by nanoparticles through
ATP, ADP and adenosine. Cell Death Dis. 6:e16292015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jia HP, Mills JN, Barahmand-Pour F,
Nishimura D, Mallampali RK, Wang G, Wiles K, Tack BF, Bevins CL and
McCray PB Jr: Molecular cloning and characterization of rat genes
encoding homologues of human beta-defensins. Infect Immun.
67:4827–4833. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Boots AW, Hristova M, Kasahara DI, Haenen
GR, Bast A and van der Vliet A: ATP-mediated activation of the
NADPH oxidase DUOX1 mediates airway epithelial responses to
bacterial stimuli. J Biol Chem. 284:17858–17867. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
de Oliveira S, López-Muñoz A, Candel S,
Pelegrín P, Calado  and Mulero V: ATP modulates acute inflammation
in vivo through dual oxidase 1-derived H2O2 production and NF-κB
activation. J Immunol. 192:5710–5719. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Xiang Y, Wang X, Yan C, Gao Q, Li SA, Liu
J, Zhou K, Guo X, Lee W and Zhang Y: Adenosine-5′-triphosphate
(ATP) protects mice against bacterial infection by activation of
the NLRP3 inflammasome. PLoS One. 8:e637592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Di Virgilio F: Liaisons dangereuses:
P2X(7) and the inflammasome. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 28:465–472.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wada A, Ogushi K, Kimura T, Hojo H, Mori
N, Suzuki S, Kumatori A, Se M, Nakahara Y, Nakamura M, et al:
Helicobacter pylori-mediated transcriptional regulation of the
human beta-defensin 2 gene requires NF-kappaB. Cell Microbiol.
3:115–123. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu Q, Zuo P, Shao B, Yang S, Xu G, Lan F,
Lu X, Xiong W, Xu Y and Xiong S: Administration of nonviral gene
vector encoding rat beta-defensin-2 ameliorates chronic Pseudomonas
aeruginosa lung infection in rats. J Gene Med. 12:276–286.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|