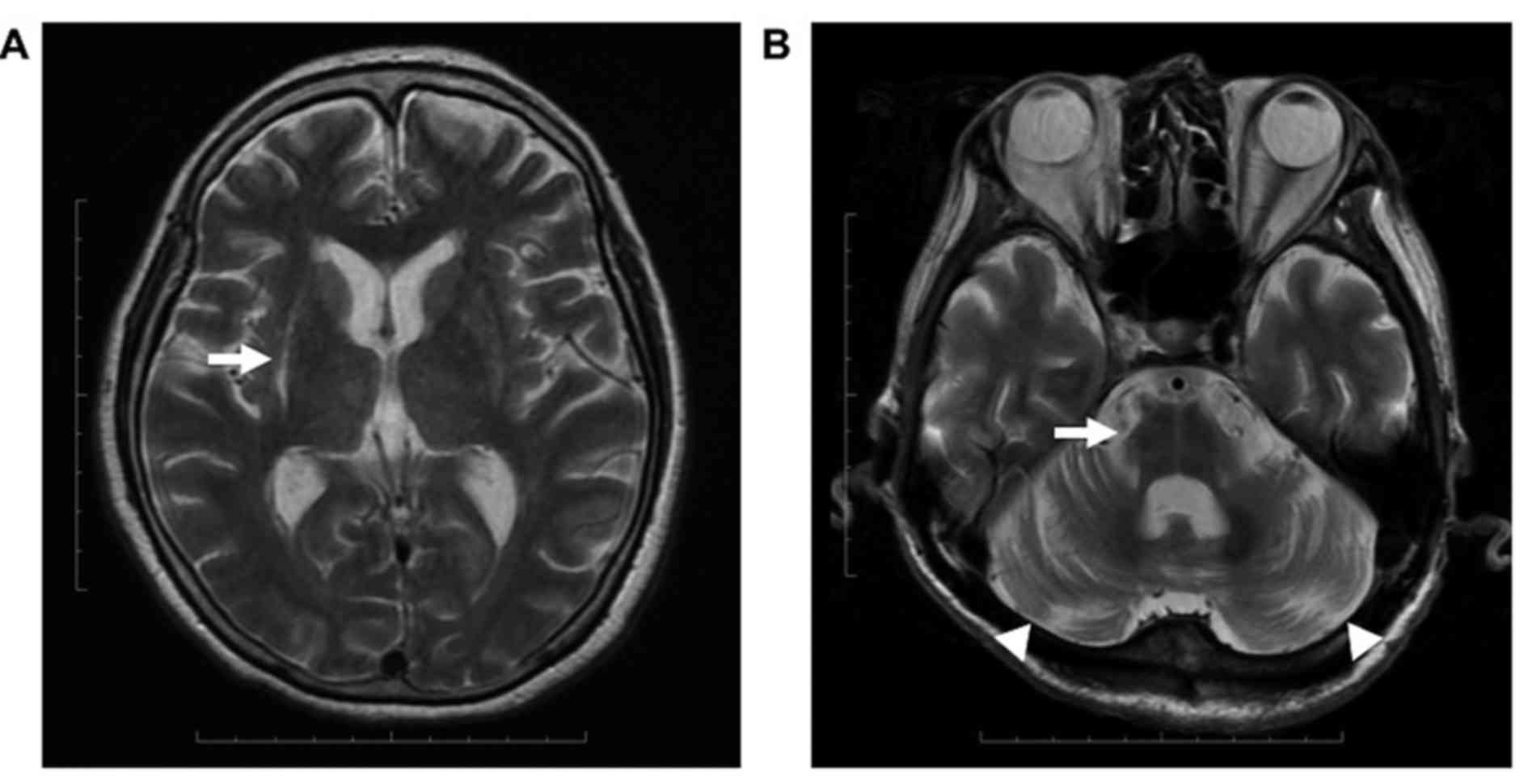
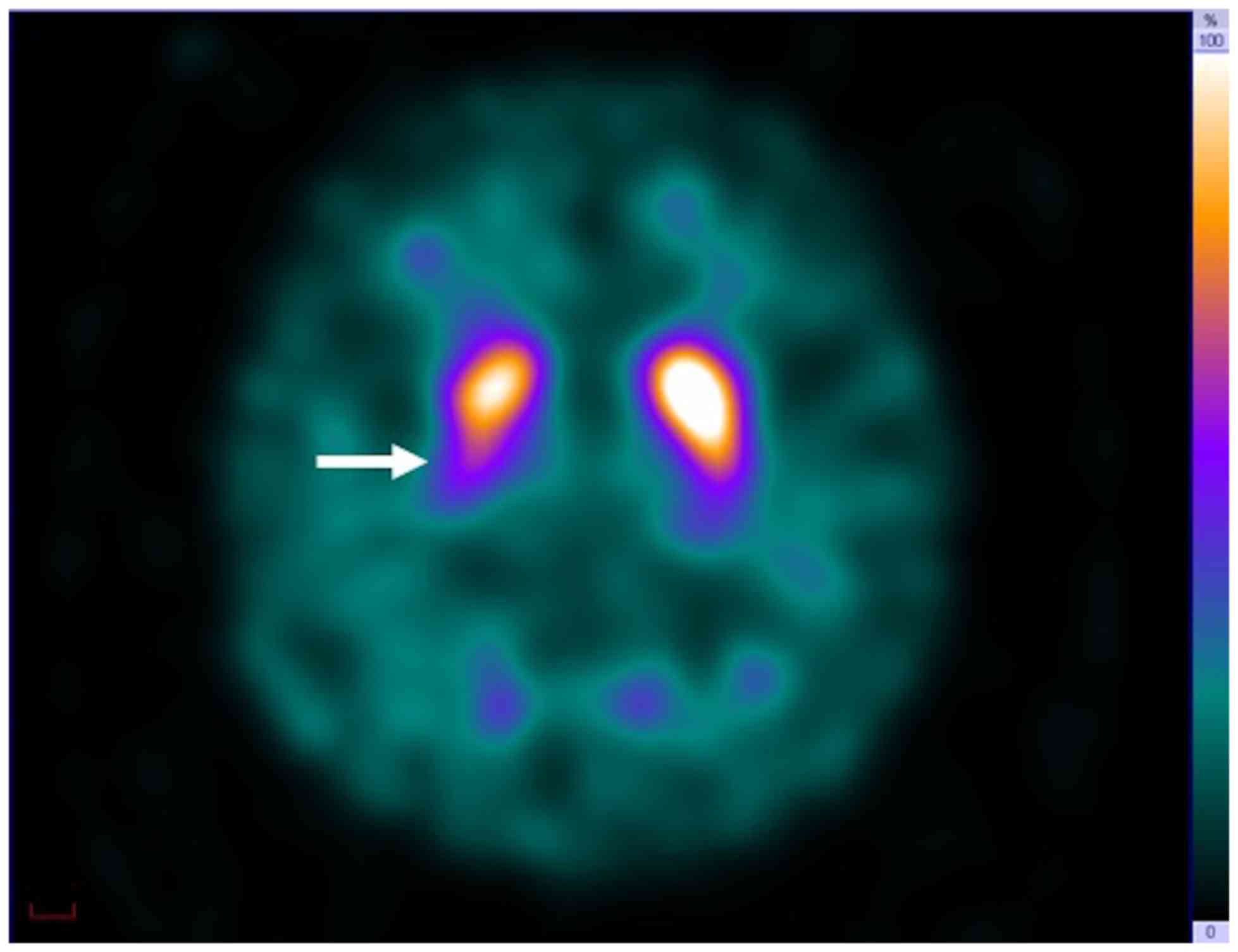
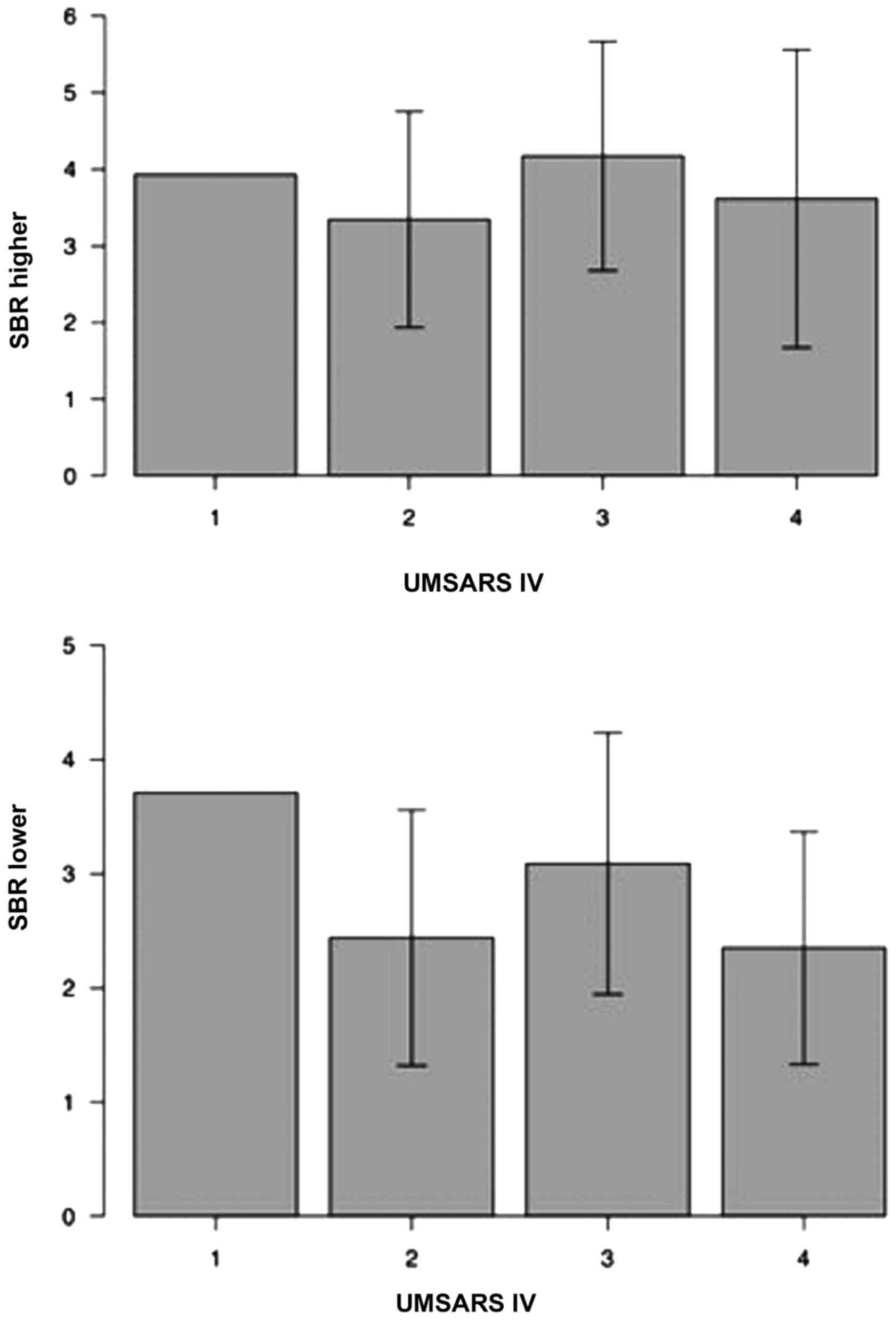
|
1
|
Bhattacharya K, Saadia D, Eisenkraft B,
Yahr M, Olanow W, Drayer B and Kaufmann H: Brain magnetic resonance
imaging in multiple-system atrophy and Parkinson disease: A
diagnostic algorithm. Arch Neurol. 59:835–842. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Naka H, Ohshita T, Murata Y, Imon Y,
Mimori Y and Nakamura S: Characteristic MRI findings in multiple
system atrophy: Comparison of the three subtypes. Neuroradiology.
44:204–209. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Qiao PF, Shi F, Jiang MF, Gao Y and Niu
GM: Application of high-field magnetic resonance imaging in
Parkinson's disease. Exp Ther Med. 13:1665–1670. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gilman S, Wenning GK, Low PA, Brooks DJ,
Mathias CJ, Trojanowski JQ, Wood NW, Colosimo C, Dürr A, Fowler CJ,
et al: Second consensus statement on the diagnosis of multiple
system atrophy. Neurology. 71:670–676. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Watanabe H, Saito Y, Terao S, Ando T,
Kachi T, Mukai E, Aiba I, Abe Y, Tamakoshi A, Doyu M, et al:
Progression and prognosis in multiple system atrophy: An analysis
of 230 Japanese patients. Brain. 125:1070–1083. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kraemmer J, Kovacs GG, Perju-Dumbrava L,
Pirker S, Traub-Weidinger T and Pirker W: Correlation of striatal
dopamine transporter imaging with post mortem substantia nigra cell
counts. Mov Disord. 29:1767–1773. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Piggott MA, Perry EK, Marshall EF, McKeith
IG, Johnson M, Melrose HL, Court JA, Lloyd S, Fairbairn A, Brown A,
et al: Nigrostriatal dopaminergic activities in dementia with Lewy
bodies in relation to neuroleptic sensitivity: Comparisons with
Parkinson's disease. Biol Psychiatry. 44:765–774. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kägi G, Bhatia KP and Tolosa E: The role
of DAT-SPECT in movement disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry.
81:5–12. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Booth TCNM, Nathan M, Waldman AD, Quigley
AM, Schapira AH and Buscombe J: The role of functional
dopamine-transporter SPECT imaging in parkinsonian syndromes, part
2. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 36:236–244. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Tossici-Bolt L, Hoffmann SM, Kemp PM,
Mehta RL and Fleming JS: Quantification of [123I]FP-CIT SPECT brain
images: An accurate technique for measurement of the specific
binding ratio. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 33:1491–1499. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wenning GK, Ben Shlomo Y, Magalhães M,
Daniel SE and Quinn NP: Clinical features and natural history of
multiple system atrophy. An analysis of 100 cases. Brain.
117:835–845. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
O'Sullivan SS, Massey LA, Williams DR,
Silveira-Moriyama L, Kempster PA, Holton JL, Revesz T and Lees AJ:
Clinical outcomes of progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple
system atrophy. Brain. 131:1362–1372. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Trouillas P, Takayanagi T, Hallett M,
Currier RD, Subramony SH, Wessel K, Bryer A, Diener HC, Massaquoi
S, Gomez CM, et al: The Ataxia Neuropharmacology Committee of the
World Federation of Neurology: International Cooperative Ataxia
Rating Scale for pharmacological assessment of the cerebellar
syndrome. J Neurol Sci. 145:205–211. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Fahn S and Elton R: Members of the UPDRS
Development Committee (1987) The Unified Parkinson's Disease Rating
ScaleFahn S, Marsden CD, Calne DB and Goldstein M: Recent
Developments in Parkinson's Disease. 2. McMellam Health Care
Information; Florham Park: pp. 153–163. 1987
|
|
15
|
Wenning GK, Tison F, Seppi K, Sampaio C,
Diem A, Yekhlef F, Ghorayeb I, Ory F, Galitzky M, Scaravilli T, et
al: Multiple System Atrophy Study Group: Development and validation
of the Unified Multiple System Atrophy Rating Scale (UMSARS). Mov
Disord. 19:1391–1402. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wakai M, Kume A, Takahashi A, Ando T and
Hashizume Y: A study of parkinsonism in multiple system atrophy:
Clinical and MRI correlation. Acta Neurol Scand. 90:225–231. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shimosegawa E, Fujino K, Kato H and
Hatazawa J: Quantitative CBF measurement using an integrated
SPECT/CT system: Validation of three-dimensional ordered-subset
expectation maximization and CT-based attenuation correction by
comparing with O-15 water PET. Ann Nucl Med. 27:822–833. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ichihara T, Ogawa K, Motomura N, Kubo A
and Hashimoto S: Compton scatter compensation using the
triple-energy window method for single- and dual-isotope SPECT. J
Nucl Med. 34:2216–2221. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ito S, Shirai W and Hattori T: Evaluating
posterolateral linearization of the putaminal margin with magnetic
resonance imaging to diagnose the Parkinson variant of multiple
system atrophy. Mov Disord. 22:578–581. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kanda Y: Investigation of the freely
available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone
Marrow Transplant. 48:452–458. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ozawa T, Paviour D, Quinn NP, Josephs KA,
Sangha H, Kilford L, Healy DG, Wood NW, Lees AJ, Holton JL, et al:
The spectrum of pathological involvement of the striatonigral and
olivopontocerebellar systems in multiple system atrophy:
Clinicopathological correlations. Brain. 127:2657–2671. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Papp MI, Kahn JE and Lantos PL: Glial
cytoplasmic inclusions in the CNS of patients with multiple system
atrophy (striatonigral degeneration, olivopontocerebellar atrophy
and Shy-Drager syndrome). J Neurol Sci. 94:79–100. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Seppi K, Schocke MF, Mair KJ, Esterhammer
R, Scherfler C, Geser F, Kremser C, Boesch S, Jaschke W, Poewe W,
et al: Progression of putaminal degeneration in multiple system
atrophy: A serial diffusion MR study. Neuroimage. 31:240–245. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Hashimoto M, Kawasaki K, Suzuki M, Mitani
K, Murayama S, Mishina M, Oda K, Kimura Y, Ishiwata K, Ishii K, et
al: Presynaptic and postsynaptic nigrostriatal dopaminergic
functions in multiple system atrophy. Neuroreport. 19:145–150.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Antonini A, Leenders KL, Vontobel P,
Maguire RP, Missimer J, Psylla M and Günther I: Complementary PET
studies of striatal neuronal function in the differential diagnosis
between multiple system atrophy and Parkinson's disease. Brain.
120:2187–2195. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Schrag A, Ben-Shlomo Y and Quinn NP:
Prevalence of progressive supranuclear palsy and multiple system
atrophy: A cross-sectional study. Lancet. 354:1771–1775. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Baronica KB, Ivkić G, Ozretić D and
Milicević G: Differential diagnostic relevance of high resolution
magnetic resonance in patients with possible multiple system
atrophy (MSA) - A case report. Coll Antropol. 35 Suppl 1:287–292.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kasahara S, Miki Y, Kanagaki M, Kondo T,
Yamamoto A, Morimoto E, Okada T, Ito H, Takahashi R and Togashi K:
“Hot cross bun” sign in multiple system atrophy with predominant
cerebellar ataxia: A comparison between proton density-weighted
imaging and T2-weighted imaging. Eur J Radiol. 81:2848–2852. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|