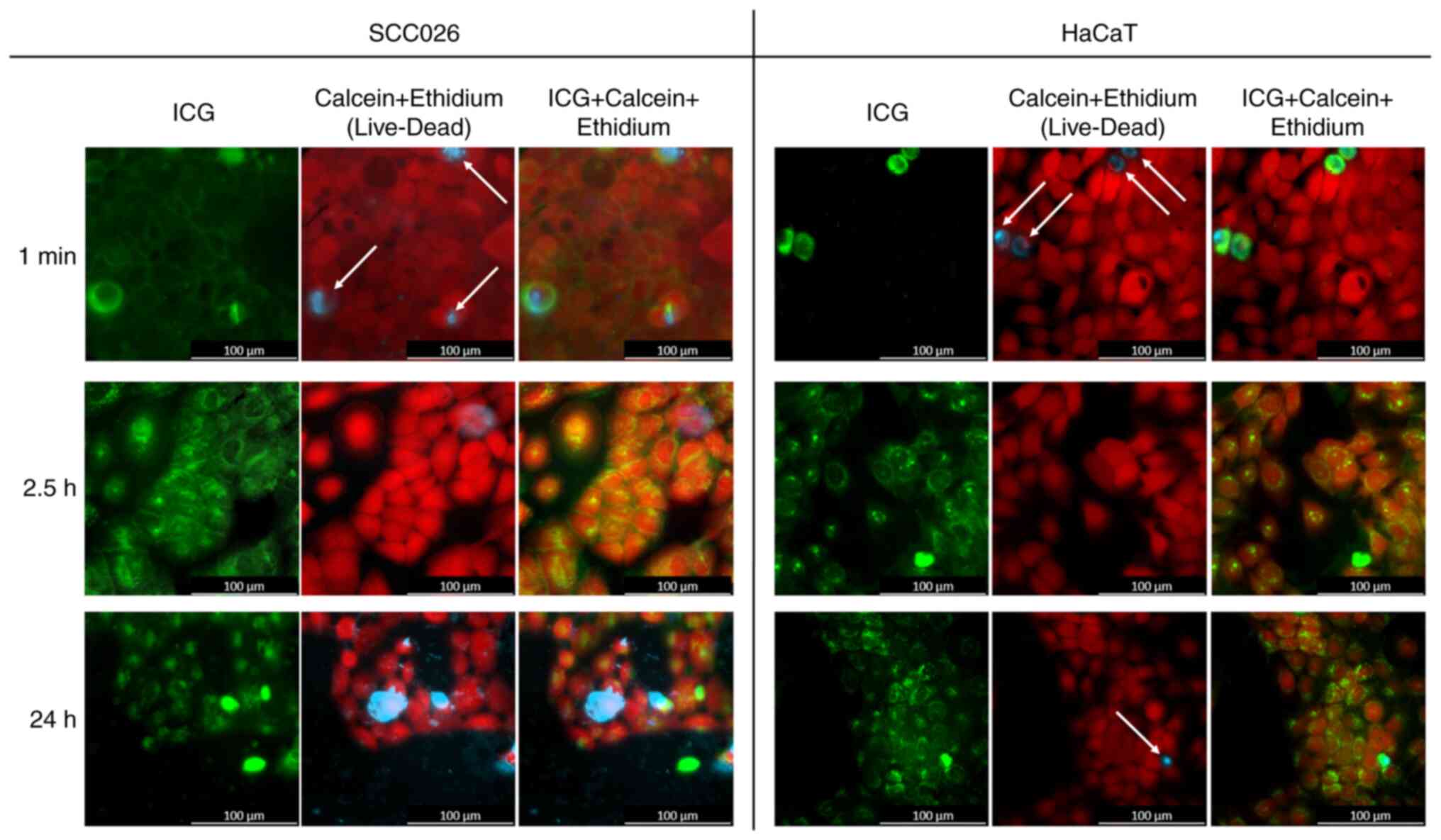
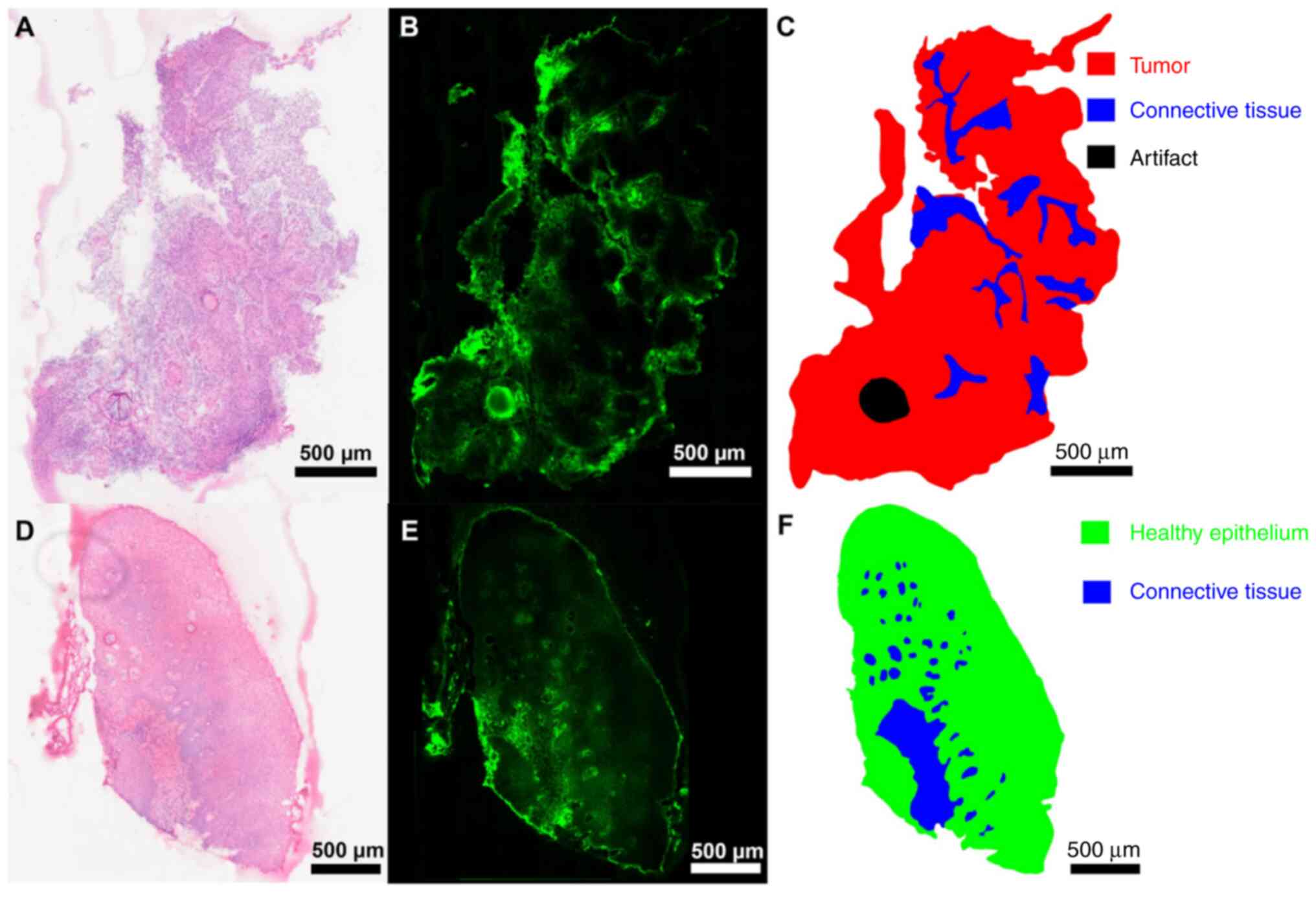
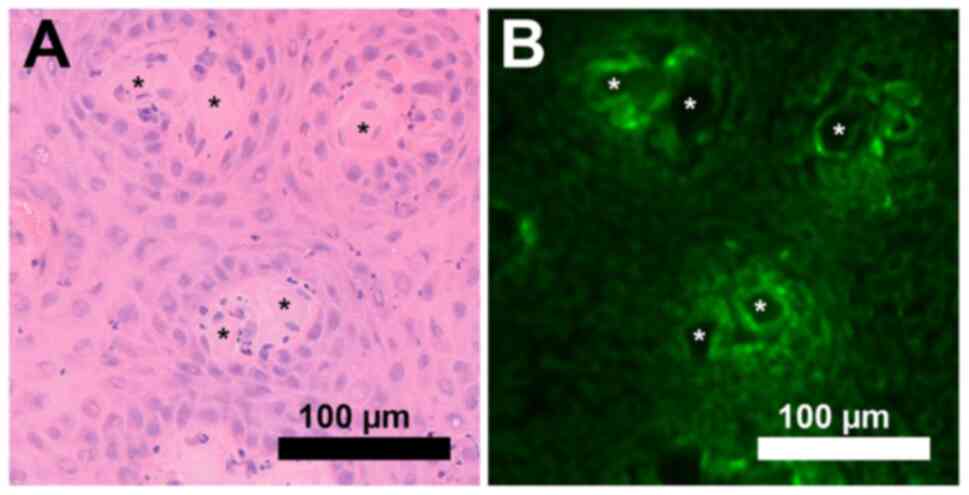
|
1
|
Iseli TA, Lin MJ, Tsui A, Guiney A,
Wiesenfeld D and Iseli CE: Are wider surgical margins needed for
early oral tongue cancer? J Laryngol Otol. 126:289–294.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Dittberner A, Ziadat R, Hoffmann F,
Pertzborn D, Gassler N and Guntinas-Lichius O: Fluorescein-Guided
panendoscopy for head and neck cancer using handheld probe-based
confocal laser endomicroscopy: A pilot study. Front Oncol.
11(671880)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Schmidt F, Dittberner A, Koscielny S,
Petersen I and Guntinas-Lichius O: Feasibility of real-time
near-infrared indocyanine green fluorescence endoscopy for the
evaluation of mucosal head and neck lesions. Head Neck. 39:234–240.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Schaafsma BE, Mieog JS, Hutteman M, van
der Vorst JR, Kuppen PJ, Löwik CW, Frangioni JV, van de Velde CJ
and Vahrmeijer AL: The clinical use of indocyanine green as a
near-infrared fluorescent contrast agent for image-guided oncologic
surgery. J Surg Oncol. 104:323–332. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Atallah I, Milet C, Quatre R, Henry M,
Reyt E, Coll JL, Hurbin A and Righini CA: Role of near-infrared
fluorescence imaging in the resection of metastatic lymph nodes in
an optimized orthotopic animal model of HNSCC. Eur Ann
Otorhinolaryngol Head Neck Dis. 132:337–342. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Lu CH and Hsiao JK: Indocyanine green: An
old drug with novel applications. Tzu Chi Med J. 33:317–322.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kitai T, Inomoto T, Miwa M and Shikayama
T: Fluorescence navigation with indocyanine green for detecting
sentinel lymph nodes in breast cancer. Breast Cancer. 12:211–215.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yokoyama J, Fujimaki M, Ohba S, Anzai T,
Yoshii R, Ito S, Kojima M and Ikeda K: A feasibility study of NIR
fluorescent image-guided surgery in head and neck cancer based on
the assessment of optimum surgical time as revealed through dynamic
imaging. Onco Targets Ther. 6:325–330. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kedrzycki MS, Leiloglou M, Chalau V,
Chiarini N, Thiruchelvam PTR, Hadjiminas DJ, Hogben KR, Rashid F,
Ramakrishnan R, Darzi AW, et al: The impact of temporal variation
in indocyanine green administration on tumor identification during
fluorescence guided breast surgery. Ann Surg Oncol. 28:5617–5625.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vahrmeijer AL, Hutteman M, van der Vorst
JR, van de Velde CJ and Frangioni JV: Image-guided cancer surgery
using near-infrared fluorescence. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 10:507–518.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Akrida I, Michalopoulos NV, Lagadinou M,
Papadoliopoulou M, Maroulis I and Mulita F: An updated review on
the emerging role of indocyanine green (ICG) as a sentinel lymph
node tracer in breast cancer. Cancers (Basel).
15(5755)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Cortese S, Kerrien E, Yakavets I,
Meilender R, Mastronicola R, Renard S, Leroux A, Bezdetnaya L and
Dolivet G: ICG-induced NIR fluorescence mapping in patients with
head & neck tumors after the previous radiotherapy.
Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 31(101838)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hinni ML, Ferlito A, Brandwein-Gensler MS,
Takes RP, Silver CE, Westra WH, Seethala RR, Rodrigo JP, Corry J,
Bradford CR, et al: Surgical margins in head and neck cancer: A
contemporary review. Head Neck. 35:1362–1370. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Onda N, Kimura M, Yoshida T and Shibutani
M: Preferential tumor cellular uptake and retention of indocyanine
green for in vivo tumor imaging. Int J Cancer. 139:673–682.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Wu J: The enhanced permeability and
retention (EPR) Effect: The significance of the concept and methods
to enhance its application. J Pers Med. 11(771)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lim L, Chao M, Shapiro J, Millar JL, Kipp
D, Rezo A, Fong A, Jones IT, McLaughlin S and Gibbs P: Long-term
outcomes of patients with localized rectal cancer treated with
chemoradiation or radiotherapy alone because of medical
inoperability or patient refusal. Dis Colon Rectum. 50:2032–2039.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Dittberner A, Friedl B, Wittig A, Buentzel
J, Kaftan H, Boeger D, Mueller AH, Schultze-Mosgau S, Schlattmann
P, Ernst T and Guntinas-Lichius O: Gender disparities in
epidemiology, treatment, and outcome for head and neck cancer in
germany: A population-based long-term analysis from 1996 to 2016 of
the thuringian cancer registry. Cancers (Basel).
12(3418)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Huang SH and O'Sullivan B: Overview of the
8th edition TNM classification for head and neck cancer. Curr Treat
Options Oncol. 18(40)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hoffmann F: S3_dataset_high resolution
microscopy images.zip., 2023. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.22331380.v1.
|
|
20
|
Stanga PE, Lim JI and Hamilton P:
Indocyanine green angiography in chorioretinal diseases:
Indications and interpretation: An evidence-based update.
Ophthalmology. 110:15–21; quiz 22-3. 2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Sethi HK, Sina EM, Mady LJ and Fundakowski
CE: Sentinel lymph node biopsy for head and neck malignancies
utilizing simultaneous radioisotope gamma probe and indocyanine
green fluorescence navigation. Head Neck. 46:212–217.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
De Ravin E, Venkatesh S, Harmsen S,
Delikatny EJ, Husson MA, Lee JYK, Newman JG and Rajasekaran K:
Indocyanine green fluorescence-guided surgery in head and neck
cancer: A systematic review. Am J Otolaryngol.
43(103570)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Belia F, Biondi A, Agnes A, Santocchi P,
Laurino A, Lorenzon L, Pezzuto R, Tirelli F, Ferri L, D'Ugo D and
Persiani R: The use of indocyanine green (ICG) and near-infrared
(NIR) fluorescence-guided imaging in gastric cancer surgery: A
narrative review. Front Surg. 9(880773)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhang Y, Chen X, Gueydan C and Han J:
Plasma membrane changes during programmed cell deaths. Cell Res.
28:9–21. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Egloff-Juras C, Yakavets I, Scherrer V,
Francois A, Bezdetnaya L, Lassalle HP and Dolivet G: Validation of
a three-dimensional head and neck spheroid model to evaluate
cameras for NIR fluorescence-guided cancer surgery. International
Journal of Molecular Sciences. 22(1966)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chan CD, Brookes MJ, Tanwani R, Hope C,
Pringle TA, Knight JC and Rankin KS: Investigating the mechanisms
of indocyanine green (ICG) cellular uptake in sarcoma. BioRxiv
2021.2004. 2005.438013, 2021.
|
|
27
|
Jiang JX, Keating JJ, De Jesus EM, Judy
RP, Madajewski B, Venegas O, Okusanya OT and Singhal S:
Optimization of the enhanced permeability and retention effect for
near-infrared imaging of solid tumors with indocyanine green. Am J
Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 5:390–400. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cherrick GR, Stein SW, Leevy CM and
Davidson CS: Indocyanine green: Observations on its physical
properties, plasma decay, and hepatic extraction. J Clin Invest.
39:592–600. 1960.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Digonnet A, Van Kerckhove S, Moreau M,
Willemse E, Quiriny M, Ahmed B, de Saint Aubain N, Andry G and
Bourgeois P: Near infrared fluorescent imaging after intravenous
injection of indocyanine green during neck dissection in patients
with head and neck cancer: A feasibility study. Head Neck 38 Suppl.
1:E1833–E1837. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ahn HM, Son GM, Lee IY, Shin DH, Kim TK,
Park SB and Kim HW: Optimal ICG dosage of preoperative colonoscopic
tattooing for fluorescence-guided laparoscopic colorectal surgery.
Surg Endosc. 36:1152–1163. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Teng CW, Huang V, Arguelles GR, Zhou C,
Cho SS, Harmsen S and Lee JYK: Applications of indocyanine green in
brain tumor surgery: Review of clinical evidence and emerging
technologies. Neurosurg Focus. 50(E4)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Boogerd LSF, Handgraaf HJM, Huurman VAL,
Lam HD, Mieog JSD, van der Made WJ, van de Velde CJH and Vahrmeijer
AL: The best approach for laparoscopic fluorescence
cholangiography: Overview of the literature and optimization of
dose and dosing time. Surg Innov. 24:386–396. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Egloff-Juras C, Bezdetnaya L, Dolivet G
and Lassalle HP: NIR fluorescence-guided tumor surgery: New
strategies for the use of indocyanine green. Int J Nanomedicine.
14:7823–7838. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Borlan R, Focsan M, Maniu D and Astilean
S: Interventional NIR fluorescence imaging of cancer: Review on
next generation of dye-loaded protein-based nanoparticles for
real-time feedback during cancer surgery. Int J Nanomedicine.
16:2147–2171. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Achterberg FB, Sibinga Mulder BG, Meijer
RP, Bonsing BA, Hartgrink HH, Mieog JSD, Zlitni A, Park SM, Farina
Sarasqueta A, Vahrmeijer AL and Swijnenburg RJ: Real-time surgical
margin assessment using ICG-fluorescence during laparoscopic and
robot-assisted resections of colorectal liver metastases. Ann
Transl Med. 8(1448)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Achterberg FB, Bijlstra OD, Slooter MD,
Sibinga Mulder BG, Boonstra MC, Bouwense SA, Bosscha K, Coolsen
MME, Derksen WJM, Gerhards MF, et al: ICG-Fluorescence imaging for
margin assessment during minimally invasive colorectal liver
metastasis resection. JAMA Netw Open. 7(e246548)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Pal R, Lwin TM, Krishnamoorthy M, Collins
HR, Chan CD, Prilutskiy A, Nasrallah MP, Dijkhuis TH, Shukla S,
Kendall AL, et al: Fluorescence lifetime of injected indocyanine
green as a universal marker of solid tumours in patients. Nat
Biomed Eng. 7:1649–1666. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|