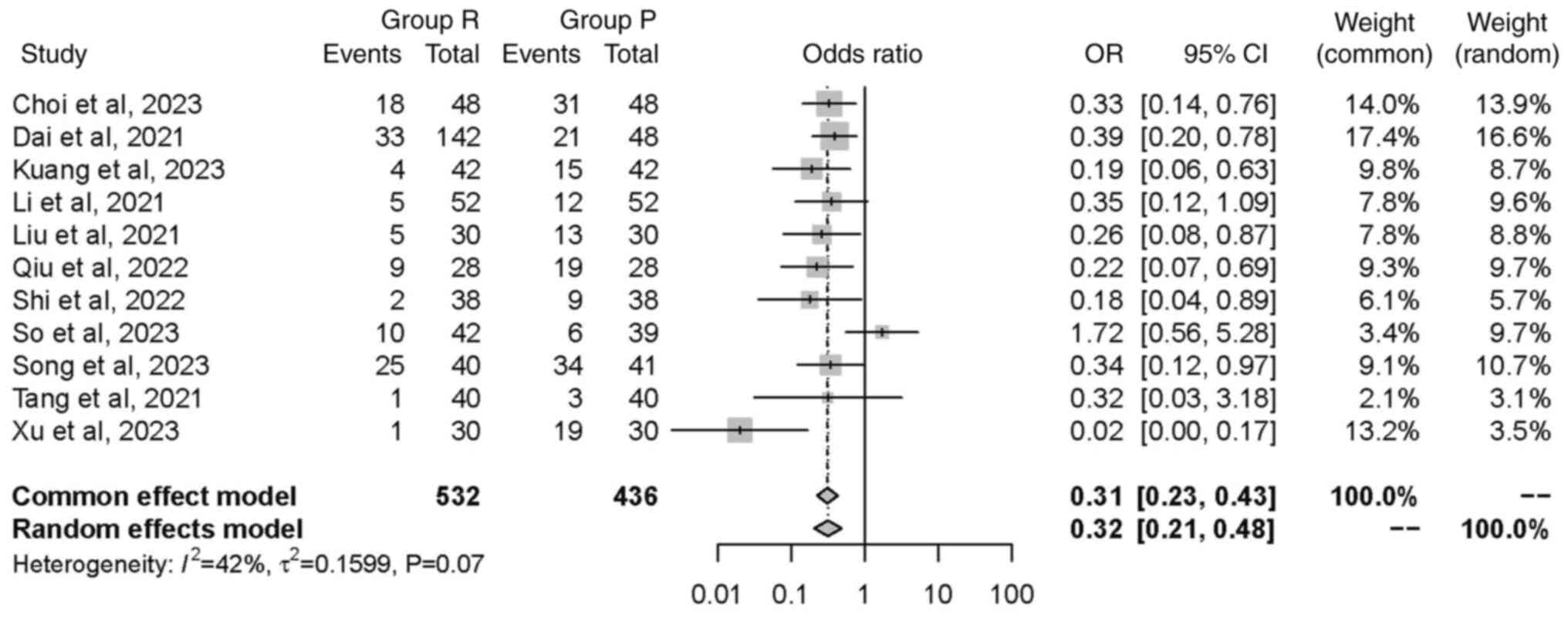
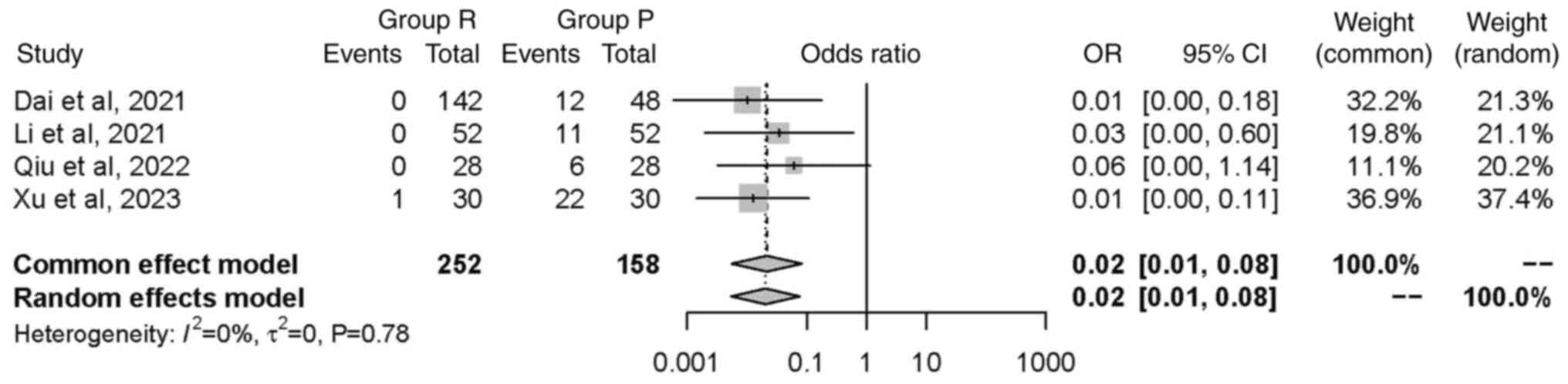
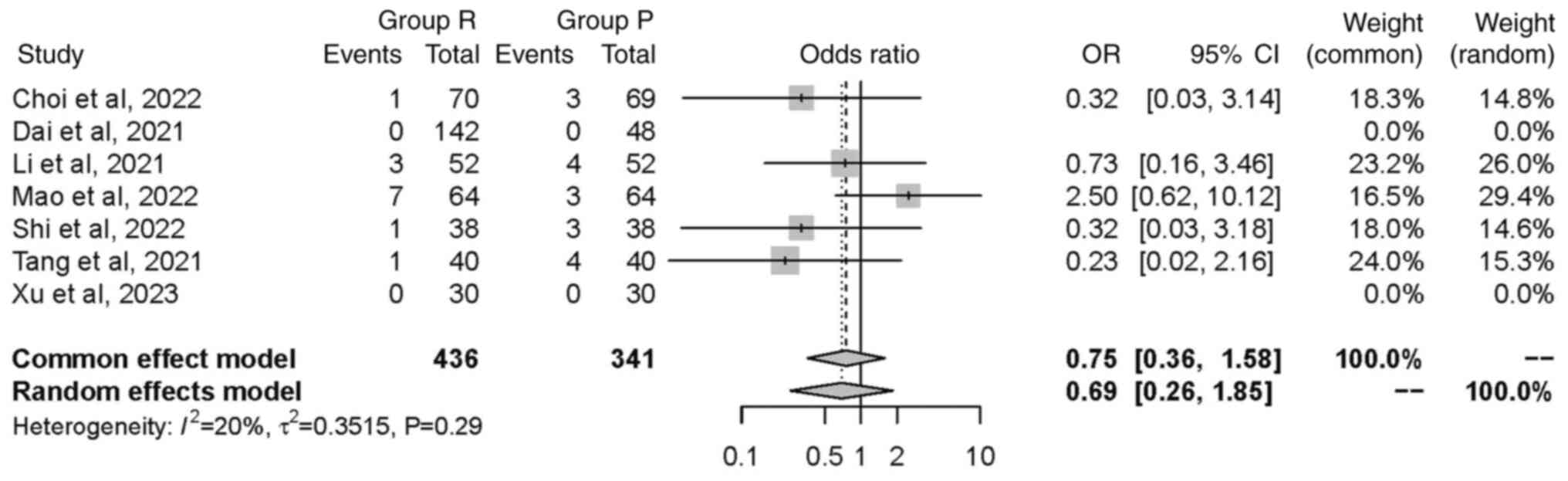
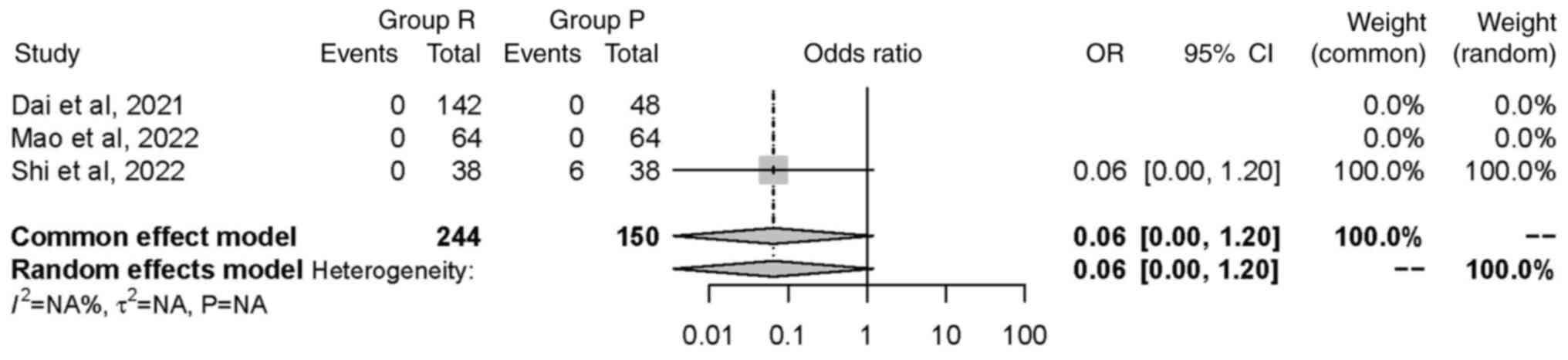
|
1
|
Wojciechowski PJ: 17-General Anesthesia.
In: Stehr W, editor. The mont reid surgical handbook (sixth
edition). Philadelphia: W.B. Saunders 181-191, 2008.
|
|
2
|
Chau PL: New insights into the molecular
mechanisms of general anaesthetics. Br J Pharmacol. 161:288–307.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Mahmoud M and Mason KP: Recent advances in
intravenous anesthesia and anesthetics. F1000Res.
7(F1000)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Propofol. In: Aronson JK, editor. Meyler's
side effects of drugs (sixteenth edition). Oxford: Elsevier;
988-1016, 2016.
|
|
5
|
Sahinovic MM, Struys MMRF and Absalom AR:
Clinical pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of propofol. Clin
Pharmacokinet. 57:1539–1558. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Conway A, Chang K, Mafeld S and Sutherland
J: Midazolam for sedation before procedures in adults and children:
A systematic review update. Syst Rev. 10(69)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kotani Y, Piersanti G, Maiucci G, Fresilli
S, Turi S, Montanaro G, Zangrillo A, Lee TC and Landoni G:
Etomidate as an induction agent for endotracheal intubation in
critically ill patients: A meta-analysis of randomized trials. J
Critical Care. 77(154317)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Khare A, Sharma SP, Deganwa ML, Sharma M
and Gill N: Effects of dexmedetomidine on intraoperative
hemodynamics and propofol requirement in patients undergoing
laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Anesth Essays Res. 11:1040–1045.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Rex DK, Bhandari R, Desta T, DeMicco MP,
Schaeffer C, Etzkorn K, Barish CF, Pruitt R, Cash BD, Quirk D, et
al: A phase III study evaluating the efficacy and safety of
remimazolam (CNS 7056) compared with placebo and midazolam in
patients undergoing colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc.
88:427–437.e6. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Pambianco DJ, Borkett KM, Riff DS, Winkle
PJ, Schwartz HI, Melson TI and Wilhelm-Ogunbiyi K: A phase IIb
study comparing the safety and efficacy of remimazolam and
midazolam in patients undergoing colonoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc.
83:984–992. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Borkett KM, Riff DS, Schwartz HI, Winkle
PJ, Pambianco DJ, Lees JP and Wilhelm-Ogunbiyi K: A phase IIa,
randomized, double-blind study of remimazolam (CNS 7056) versus
midazolam for sedation in upper gastrointestinal endoscopy. Anesth
Analg. 120:771–780. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Goudra BG and Singh PM: . Remimazolam: The
future of its sedative potential. Saudi J Anaesth. 8:388–391.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kilpatrick GJ: Remimazolam: Non-clinical
and clinical profile of a new sedative/anesthetic agent. Front
Pharmacol. 12(690875)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Hu Q, Liu X, Wen C, Li D and Lei X:
Remimazolam: An updated review of a new sedative and anaesthetic.
Drug Des Devel Ther. 16:3957–3974. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Doi M, Morita K, Takeda J, Sakamoto A,
Yamakage M and Suzuki T: Efficacy and safety of remimazolam versus
propofol for general anesthesia: A multicenter, single-blind,
randomized, parallel-group, phase IIb/III trial. J Anesth.
34:543–553. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
R Core Team. The R Project for Statistical
Computing [updated 14/06/2024. Available from: https://www.r-project.org/.
|
|
18
|
Lin L and Chu H: Quantifying publication
bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics. 74:785–794. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li J, Zhou D, Jin Y, Zhou HS, Fang CL, Zhu
ZQ and Xiong LL: Difference between remimazolam toluenesulfonic
acid and propofol in waking quality and conscious state after
general anesthesia. Ibrain. 7:171–180. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Xu Q, Wu J, Shan W, Duan G and Lan H:
Effects of remimazolam combined with sufentanil on hemodynamics
during anesthetic induction in elderly patients with mild
hypertension undergoing orthopedic surgery of the lower limbs: A
randomized controlled trial. BMC Anesthesiol.
23(311)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Gao J, Yang C, Ji Q and Li J: Effect of
remimazolam versus propofol for the induction of general anesthesia
on cerebral blood flow and oxygen saturation in elderly patients
undergoing carotid endarterectomy. BMC Anesthesiol.
23(153)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Qiu Y, Gu W, Zhao M, Zhang Y and Wu J: The
hemodynamic stability of remimazolam compared with propofol in
patients undergoing endoscopic submucosal dissection: A randomized
trial. Front Med. 9(938940)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Tang F, Yi JM, Gong HY, Lu ZY, Chen J,
Fang B, Chen C and Liu ZY: Remimazolam benzenesulfonate anesthesia
effectiveness in cardiac surgery patients under general anesthesia.
World J Clin Cases. 9:10595–10603. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Song SW, Kim S, Park JH, Cho YH and Jeon
YG: Post-induction hypotension with remimazolam versus propofol in
patients routinely administered angiotensin axis blockades: A
randomized control trial. BMC Anesthesiol. 23(219)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Choi JY, Lee HS, Kim JY, Han DW, Yang JY,
Kim MJ and Song Y: Comparison of remimazolam-based and
propofol-based total intravenous anesthesia on postoperative
quality of recovery: A randomized non-inferiority trial. J Clin
Anesth. 82(110955)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shi F, Chen Y, Li H, Zhang Y and Zhao T:
Efficacy and safety of remimazolam tosilate versus propofol for
general anesthesia in cirrhotic patients undergoing endoscopic
variceal ligation. Int J Gen Med. 15:583–591. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
So KY, Park J and Kim SH: Safety and
efficacy of remimazolam for general anesthesia in elderly patients
undergoing laparoscopic cholecystectomy: A randomized controlled
trial. Front Med (Lausanne). 10(1265860)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Choi EK, Jang Y and Park SJ: Comparison of
remimazolam and propofol induction on hemodynamic response in
hypertensive patients. Medicine (Baltimore).
102(e34358)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Dai G, Pei L, Duan F, Liao M, Zhang Y, Zhu
M, Zhao Z and Zhang X: Safety and efficacy of remimazolam compared
with propofol in induction of general anesthesia. Minerva
Anestesiol. 87:1073–1079. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Kuang Q, Zhong N, Ye C, Zhu X and Wei F:
Propofol versus remimazolam on cognitive function, hemodynamics,
and oxygenation during one-lung ventilation in older patients
undergoing pulmonary lobectomy: A randomized controlled trial. J
Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 37:1996–2005. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu T, Lai T, Chen J, Lu Y, He F, Chen Y
and Xie Y: Effect of remimazolam induction on hemodynamics in
patients undergoing valve replacement surgery: A randomized,
double-blind, controlled trial. Pharmacol Res Perspect.
9(e00851)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Mao Y, Guo J, Yuan J, Zhao E and Yang J:
Quality of recovery after general anesthesia with remimazolam in
patients' undergoing urologic surgery: A randomized controlled
trial comparing remimazolam with propofol. Drug Des Devel Ther.
16:1199–209. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kim KM: Remimazolam: Pharmacological
characteristics and clinical applications in anesthesiology. Anesth
Pain Med. 17:1–11. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Nakayama J, Ogihara T, Yajima R, Innami Y
and Ouchi T: Anesthetic management of super-elderly patients with
remimazolam: A report of two cases. JA Clin Rep.
7(71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Satoh T, Nishihara N, Sawashita Y, Ohno S,
Hirata N and Yamakage M: Remimazolam anesthesia for mitraclip
implantation in a patient with advanced heart failure. Case Rep
Anesthesiol. 2021(5536442)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Hohjoh H, Horikawa I, Nakagawa K,
Segi-Nishida E and Hasegawa H: Induced mRNA expression of matrix
metalloproteinases Mmp-3, Mmp-12, and Mmp-13 in the infarct
cerebral cortex of photothrombosis model mice. Neurosci Lett.
739(135406)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wu Q, Xu F, Wang J and Jiang M: Comparison
of remimazolam-flumazenil versus propofol for recovery from general
anesthesia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Med.
12(7316)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|