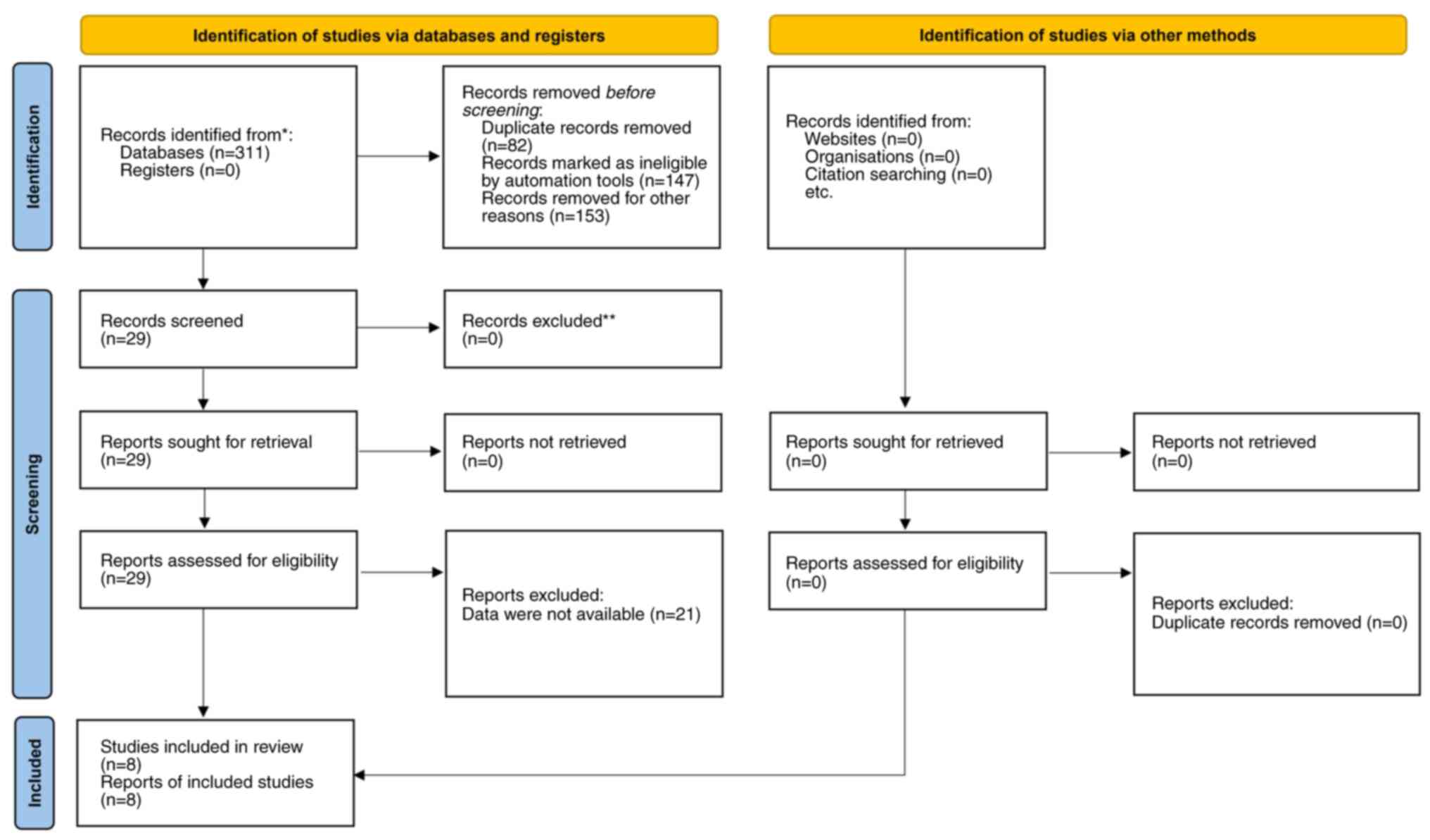
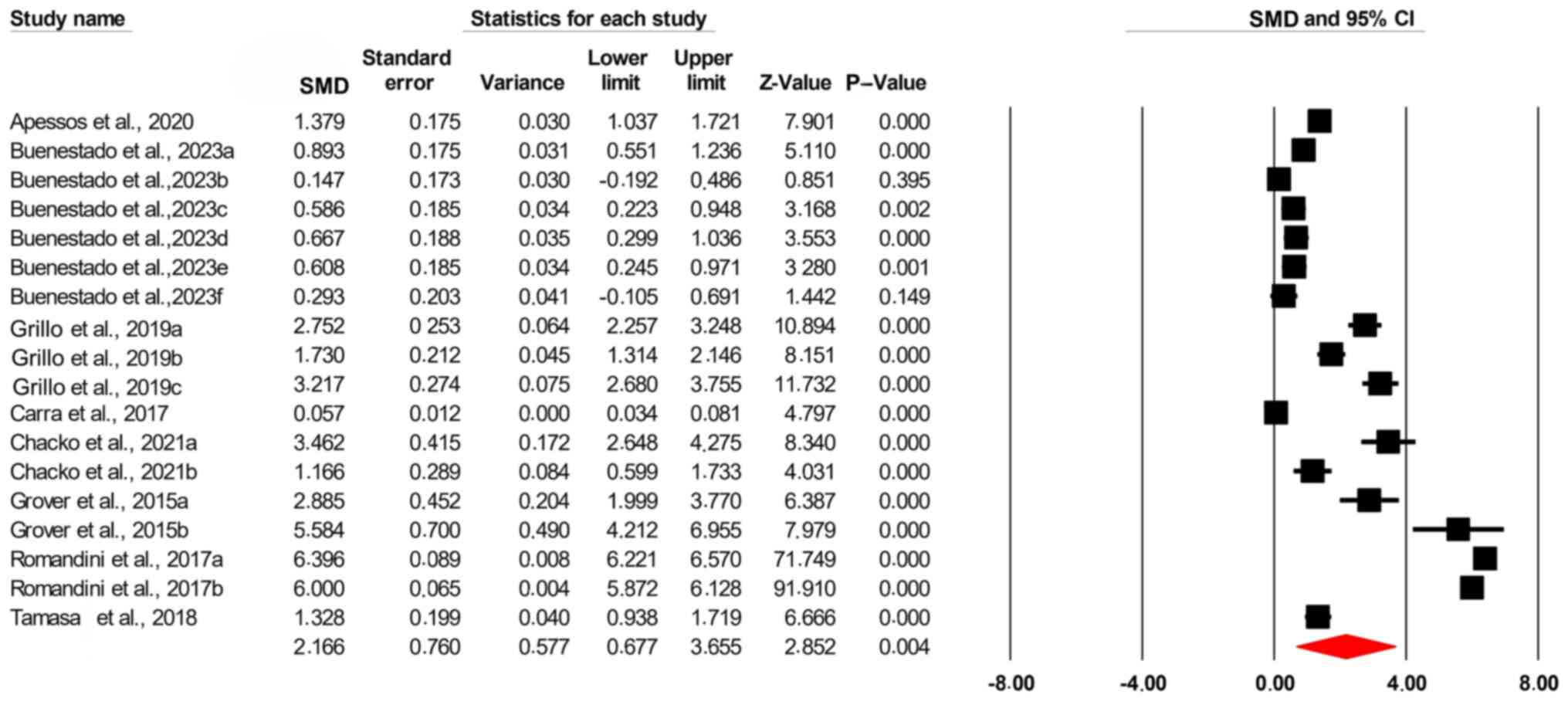
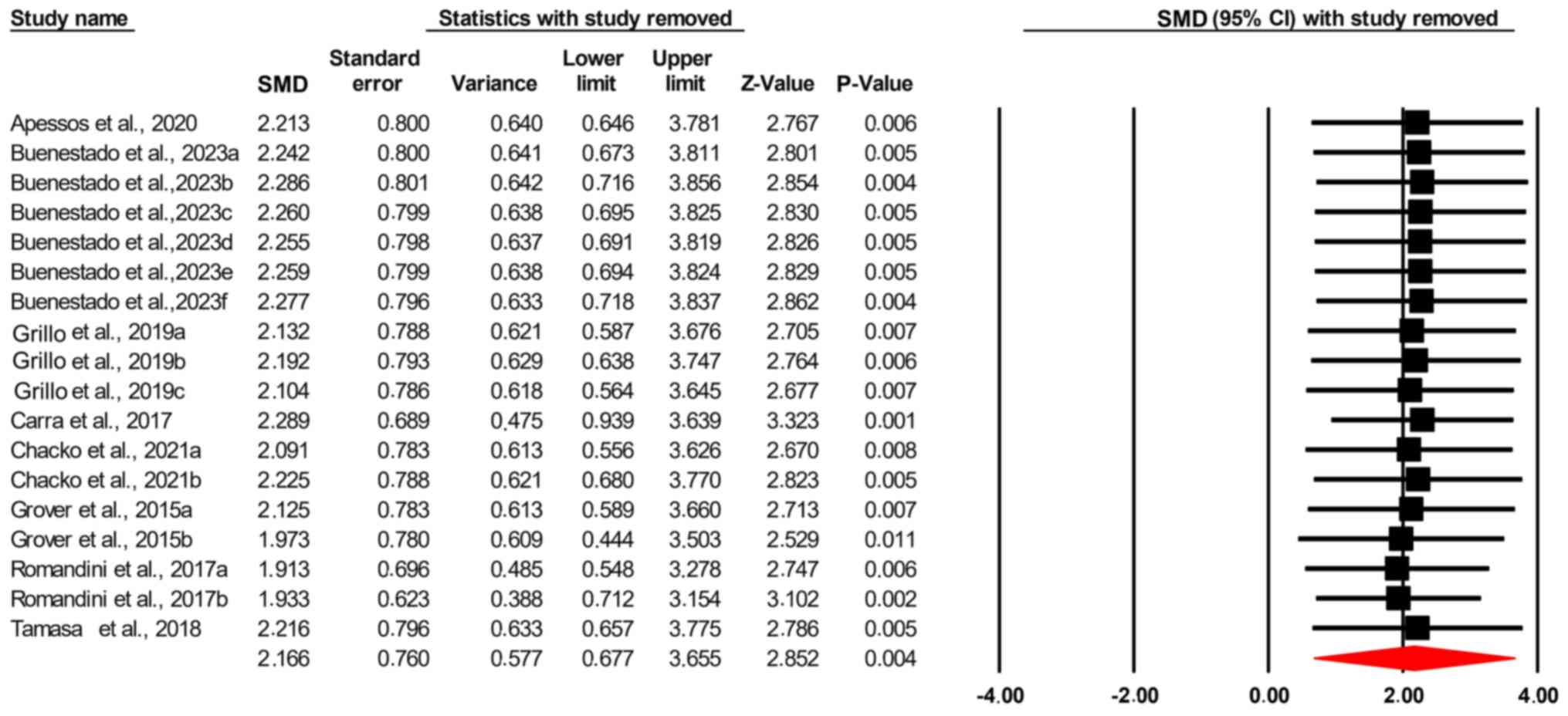
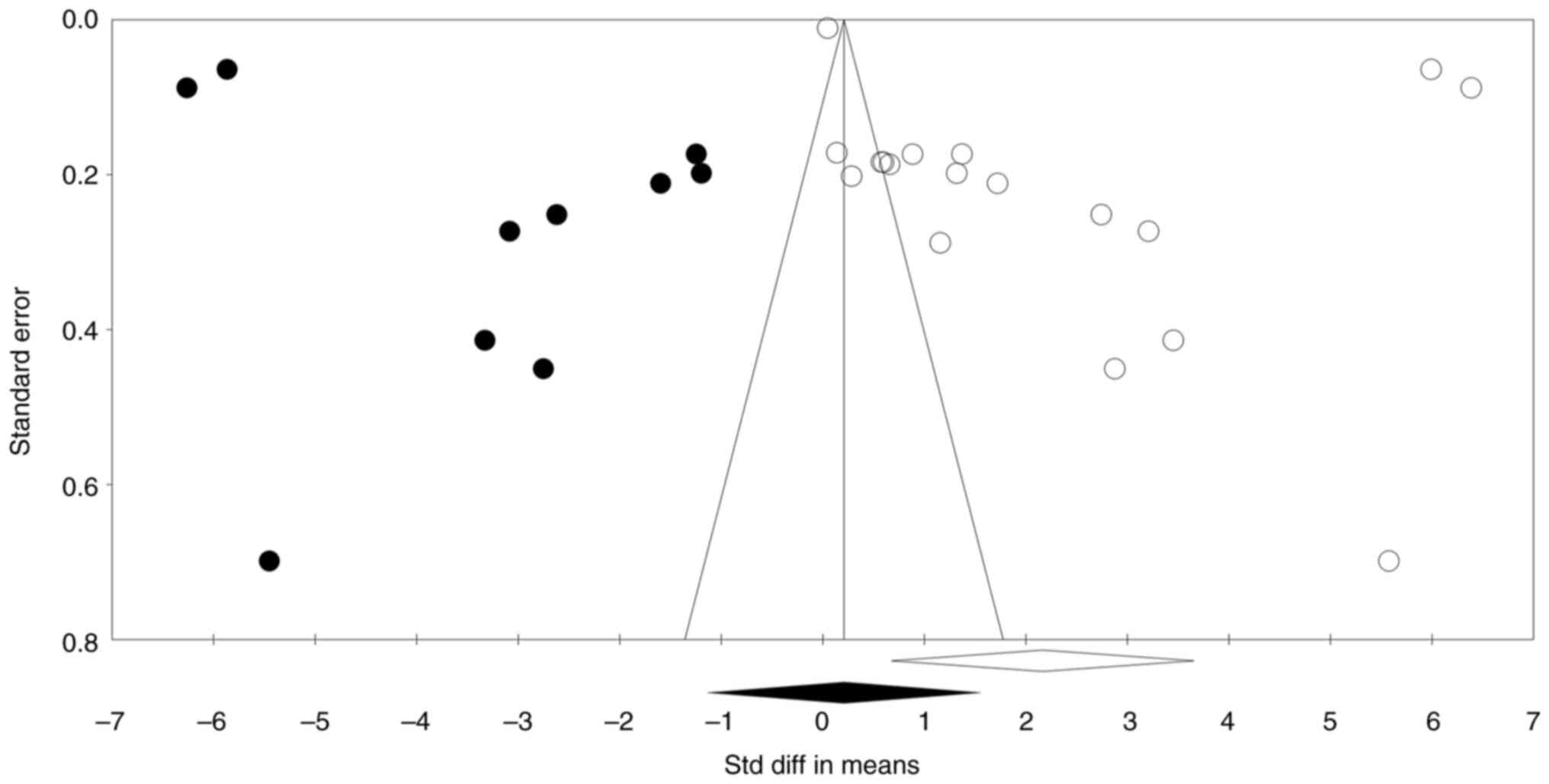
|
1
|
Asawa K, Sen N, Bhat N, Tak M, Sultane P
and Mandal A: Influence of sleep disturbance, fatigue, vitality on
oral health and academic performance in Indian dental students.
Clujul Med. 90:333–343. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Schroeder K and Gurenlian JR: Recognizing
poor sleep quality factors during oral health evaluations. Clin Med
Res. 17:20–28. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Alqaderi H, Tavares M, Hartman M and
Goodson JM: Effect of sleep and salivary glucose on gingivitis in
children. J Dent Res. 95:1387–1393. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Movahed E, Moradi S, Mortezagholi B,
Shafiee A, Moltazemi H, Hajishah H, Siahvoshi S, Monfared AB, Amini
MJ, Safari F and Bakhtiyari M: Investigating oral health among US
adults with sleep disorder: A cross-sectional study. BMC Oral
Health. 23(996)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Grillo C, La Mantia I, Zappala G, Cocuzza
S, Ciprandi G and Andaloro C: Oral health in children with
sleep-disordered breathing: A cross-sectional study. Acta Biomed.
90:52–59. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Carra MC, Schmitt A, Thomas F, Danchin N,
Pannier B and Bouchard P: Sleep disorders and oral health: A
cross-sectional study. Clin Oral Investig. 21:975–983.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Safak ED, Celik F, Mazicioglu MM, Akin S,
Manav TY, Kesim S and Ozturk A: The relationship between oral
health and sleep quality in community-dwelling older adults. Niger
J Clin Pract. 26:1449–1455. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Taştan Eroğlu Z, Özkan Şen D, Uçan Yarkac
F and Altiparmak F: The association between sleep quality, fatigue
and periodontal status: A pilot study. Odovtos Int J Dent Sci.
25:99–117. 2023.
|
|
9
|
Hirotsu C, Tufik S and Andersen ML:
Interactions between sleep, stress, and metabolism: From
physiological to pathological conditions. Sleep Sci. 8:143–152.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Wiener RC: Relationship of routine
inadequate sleep duration and periodontitis in a nationally
representative sample. Sleep Disord. 2016(9158195)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Beydoun HA, Hossain S, Beydoun MA, Weiss
J, Zonderman AB and Eid SM: Periodontal disease, sleep duration,
and white blood cell markers in the 2009 to 2014 National Health
and Nutrition Examination Surveys. J Periodontol. 91:582–595.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Corker KS: Strengths and weaknesses of
meta-analyses. In: Research Integrity: Best Practices for the
Social and Behavioral Sciences. Jussim L, Krosnick JA and Stevens
ST (eds). Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp150-174, 2022.
|
|
13
|
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. BMJ. 372(n71)2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Peterson J, Welch V, Losos M and Tugwell
P: The Newcastle-Ottawa scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of
nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. Ottawa: Ottawa Hospital
Research Institute. 2:1–12. 2011.
|
|
15
|
IntHout J, Ioannidis JP, Rovers MM and
Goeman JJ: Plea for routinely presenting prediction intervals in
meta-analysis. BMJ Open. 6(e010247)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Apessos I, Andreadis D, Steiropoulos P,
Tortopidis D and Angelis L: Investigation of the relationship
between sleep disorders and xerostomia. Clin Oral Investig.
24:1709–1716. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Arroyo Buenestado A and Ribas-Pérez D:
Early childhood caries and sleep disorders. J Clin Med.
12(1378)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chacko NL, Raje M, Rakhewar P and Bhamare
R: The association between sleep deprivation and periodontitis: A
cross sectional study. IOSR J Dent Med Sci (IOSR-JDMS). 20:1–8.
2021.
|
|
19
|
Grover V, Malhotra R and Kaur H: Exploring
association between sleep deprivation and chronic periodontitis: A
pilot study. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 19:304–307. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Romandini M, Gioco G, Perfetti G, Deli G,
Staderini E and Laforì A: The association between periodontitis and
sleep duration. J Clin Periodontol. 44:490–501. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Tamasa B, Godfrey G, Nelson T and Chen M:
Oral health status of children with high risk of sleep-disordered
breathing. J Dent Sleep Med. 5:31–38. 2018.
|
|
22
|
Pereira D, Progiante P, Pattussi M, Grossi
P and Grossi M: Study on the association between sleep disorders
versus oral health related variables. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir
Bucal. 26:e164–e71. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Han S, Jee D, Kang YJ, Park YJ and Cho JH:
Possible association between oral health and sleep duration: A
cross-sectional study based on the Korean National Health and
Nutrition Examination Surveys from 2010 to 2015. Medicine
(Baltimore). 100(e28035)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Alawady A, Alharbi A, Alharbi H, Almesbah
S, Alshammari N, Alkandari A, Alhazmi H and Alqaderi H: Association
between sleep duration and dental caries in a nationally
representative U.S. population. BMC Oral Health.
23(497)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ju X, Hedges J, Sethi S and Jamieson LM:
Poor self-rated sleep quality and quantity associated with poor
oral health-related quality of life among indigenous Australian
adults. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 21(453)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|