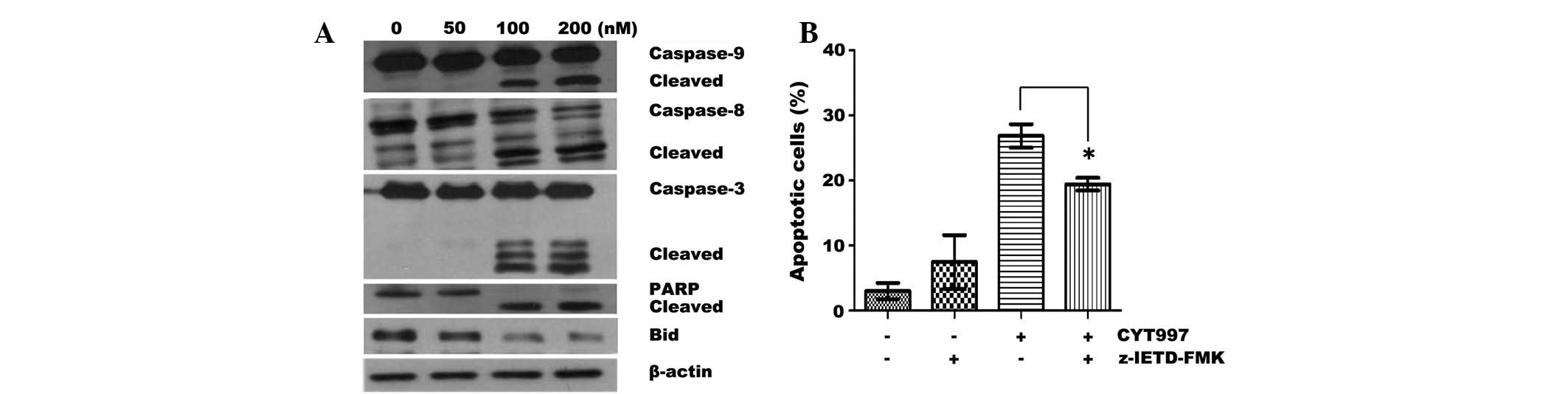
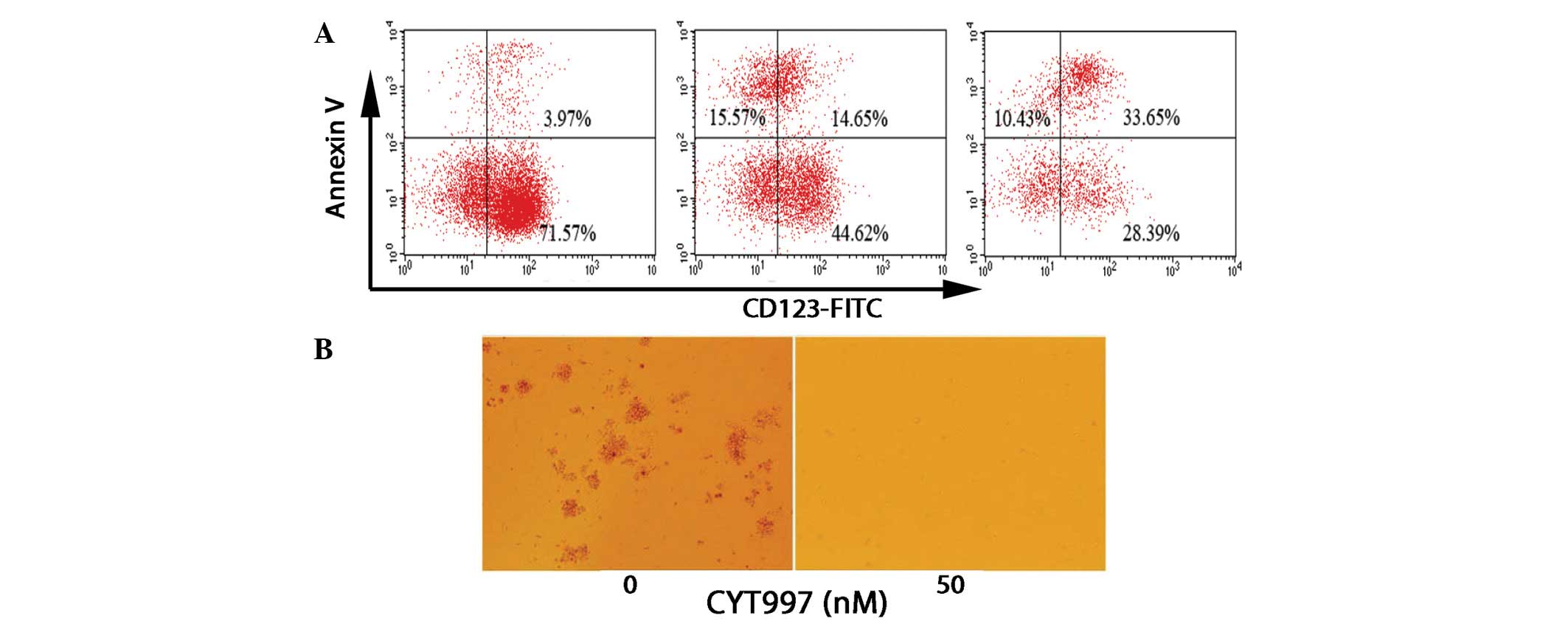
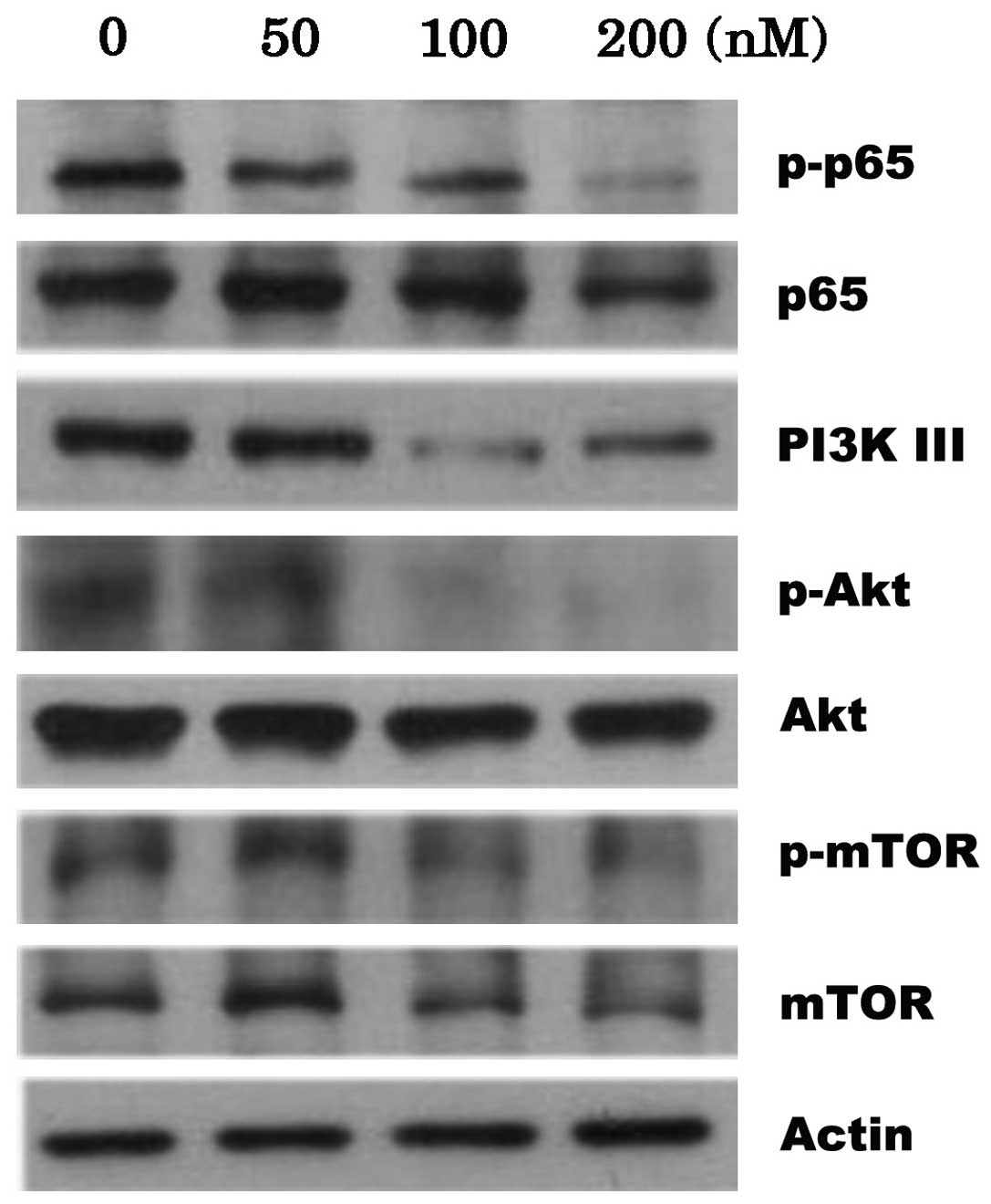
|
1.
|
Steffen B, Müller-Tidow C, Schwäble J,
Berdel WE and Serve H: The molecular pathogenesis of acute myeloid
leukemia. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 56:195–221. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Kuppens IE: Current state of the art of
new tubulin inhibitors in the clinic. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 1:57–70.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Rovini A, Savry A, Braguer D and Carré M:
Microtubule-targeted agents: when mitochondria become essential to
chemotherapy. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1807:679–688. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Lysaght J, Verma NK, Maginn EN, et al: The
microtubule targeting agent PBOX-15 inhibits integrin-mediated cell
adhesion and induces apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic leukaemia
cells. Int J Oncol. 42:239–246. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Petit I, Karajannis MA, Vincent L, et al:
The microtubule-targeting agent CA4P regresses leukemic xenografts
by disrupting interaction with vascular cells and
mitochondrial-dependent cell death. Blood. 111:1951–1961. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Greene LM, Kelly L, Onnis V, et al:
STI-571 (imatinib mesylate) enhances the apoptotic efficacy of
pyrrolo-1,5-benzoxazepine-6, a novel microtubule-targeting agent,
in both STI-571-sensitive and -resistant Bcr-Abl-positive human
chronic myeloid leukemia cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 321:288–297.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7.
|
Burns CJ, Harte MF, Bu X, et al: Discovery
of CYT997: a structurally novel orally active microtubule targeting
agent. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 19:4639–4642. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Burns CJ, Fantino E, Phillips ID, et al:
CYT997: a novel orally active tubulin polymerization inhibitor with
potent cytotoxic and vascular disrupting activity in vitro and in
vivo. Mol Cancer Ther. 8:3036–3045. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Monaghan K, Khong T, Smith G and Spencer
A: CYT997 causes apoptosis in human multiple myeloma. Invest New
Drugs. 29:232–238. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Burns CJ, Fantino E, Powell AK, et al: The
microtubule depolymerizing agent CYT997 causes extensive ablation
of tumor vasculature in vivo. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 339:799–806.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Lickliter JD, Francesconi AB, Smith G, et
al: Phase I trial of CYT997, a novel cytotoxic and
vascular-disrupting agent. Br J Cancer. 103:597–606. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Burge M, Francesconi AB, Kotasek D, et al:
Phase I, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of CYT997,
an orally-bioavailable cytotoxic and vascular-disrupting agent.
Invest New Drugs. 31:126–135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Jordan CT, Upchurch D, Szilvassy SJ, et
al: The interleukin-3 receptor alpha chain is a unique marker for
human acute myelogenous leukemia stem cells. Leukemia.
14:1777–1784. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Xu Q, Simpson SE, Scialla TJ, Bagg A and
Carroll M: Survival of acute myeloid leukemia cells requires PI3
kinase activation. Blood. 102:972–980. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Nathwani SM, Butler S, Fayne D, et al:
Novel microtubule-targeting agents, pyrrolo-1, 5-benzoxazepines,
induce apoptosis in multi-drug-resistant cancer cells. Cancer
Chemother Pharmacol. 66:585–596. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Fojo AT, Ueda K, Slamon DJ, Poplack DG,
Gottesman MM and Pastan I: Expression of a multidrug-resistance
gene in human tumors and tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
84:265–269. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Calligaris D, Verdier-Pinard P, Devred F,
Villard C, Braguer D and Lafitte D: Microtubule targeting agents:
from biophysics to proteomics. Cell Mol Life Sci. 67:1089–1104.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Martelli AM, Evangelisti C, Chiarini F and
McCubrey JA: The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt/mTOR signaling
network as a therapeutic target in acute myelogenous leukemia
patients. Oncotarget. 1:89–103. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Meng H, Jin Y, Liu H, et al: SNS-032
inhibits mTORC1/mTORC2 activity in acute myeloid leukemia cells and
has synergistic activity with perifosine against Akt. J Hematol
Oncol. 6:182013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20.
|
Min YH, Eom JI, Cheong JW, et al:
Constitutive phosphorylation of Akt/PKB protein in acute myeloid
leukemia: its significance as a prognostic variable. Leukemia.
17:995–997. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Récher C, Beyne-Rauzy O, Demur C, et al:
Antileukemic activity of rapamycin in acute myeloid leukemia.
Blood. 105:2527–2534. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Chapuis N, Tamburini J, Green AS, et al:
Dual inhibition of PI3K and mTORC1/2 signaling by NVP-BEZ235 as a
new therapeutic strategy for acute myeloid leukemia. Clin Cancer
Res. 16:5424–5435. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Gavet O and Pines J: Progressive
activation of CyclinB1-Cdk1 coordinates entry to mitosis. Dev Cell.
18:533–543. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Lu LX, Domingo-Sananes MR, Huzarska M,
Novak B and Gould KL: Multisite phosphoregulation of Cdc25 activity
refines the mitotic entrance and exit switches. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 109:9899–8904. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|