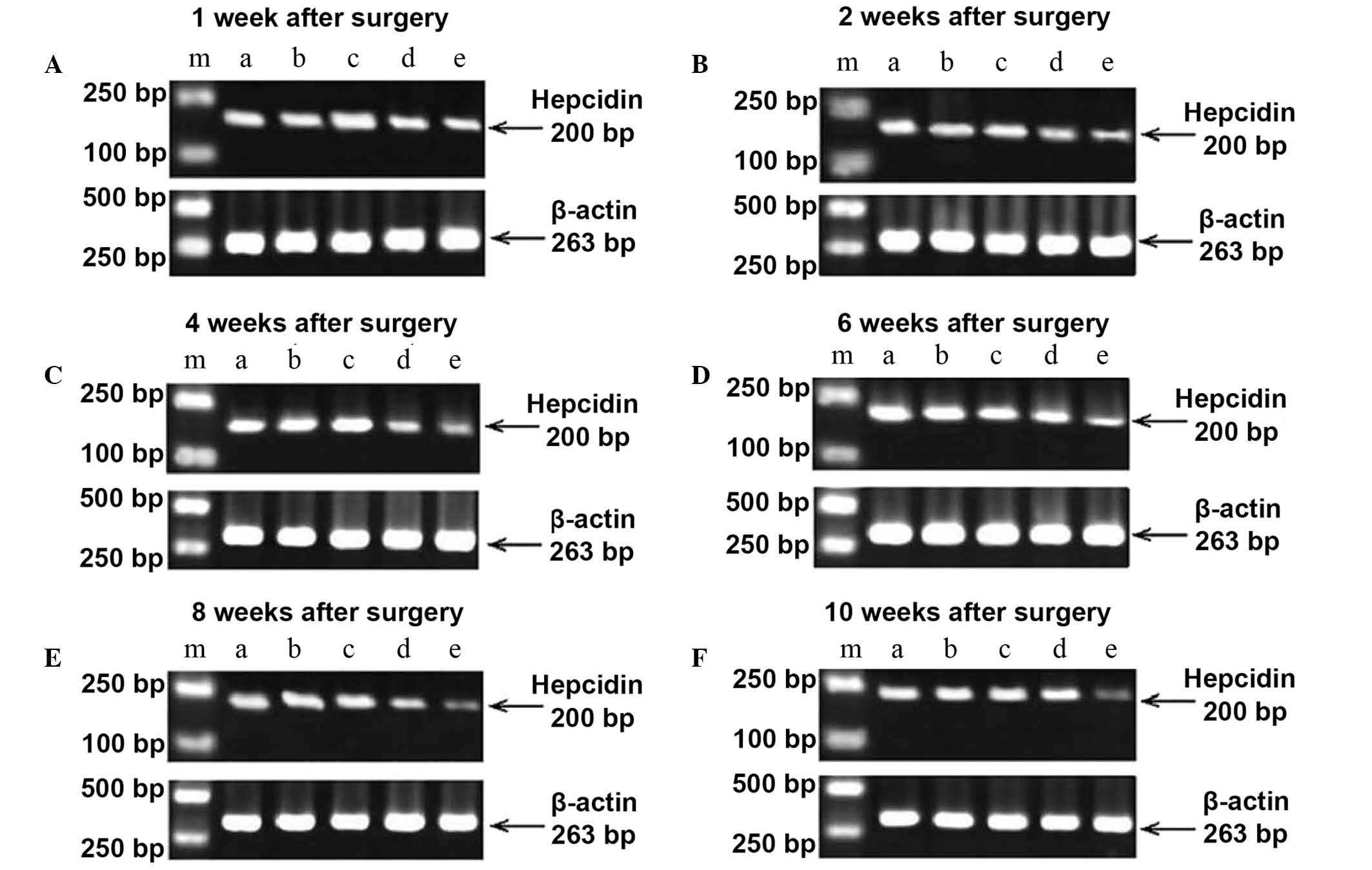
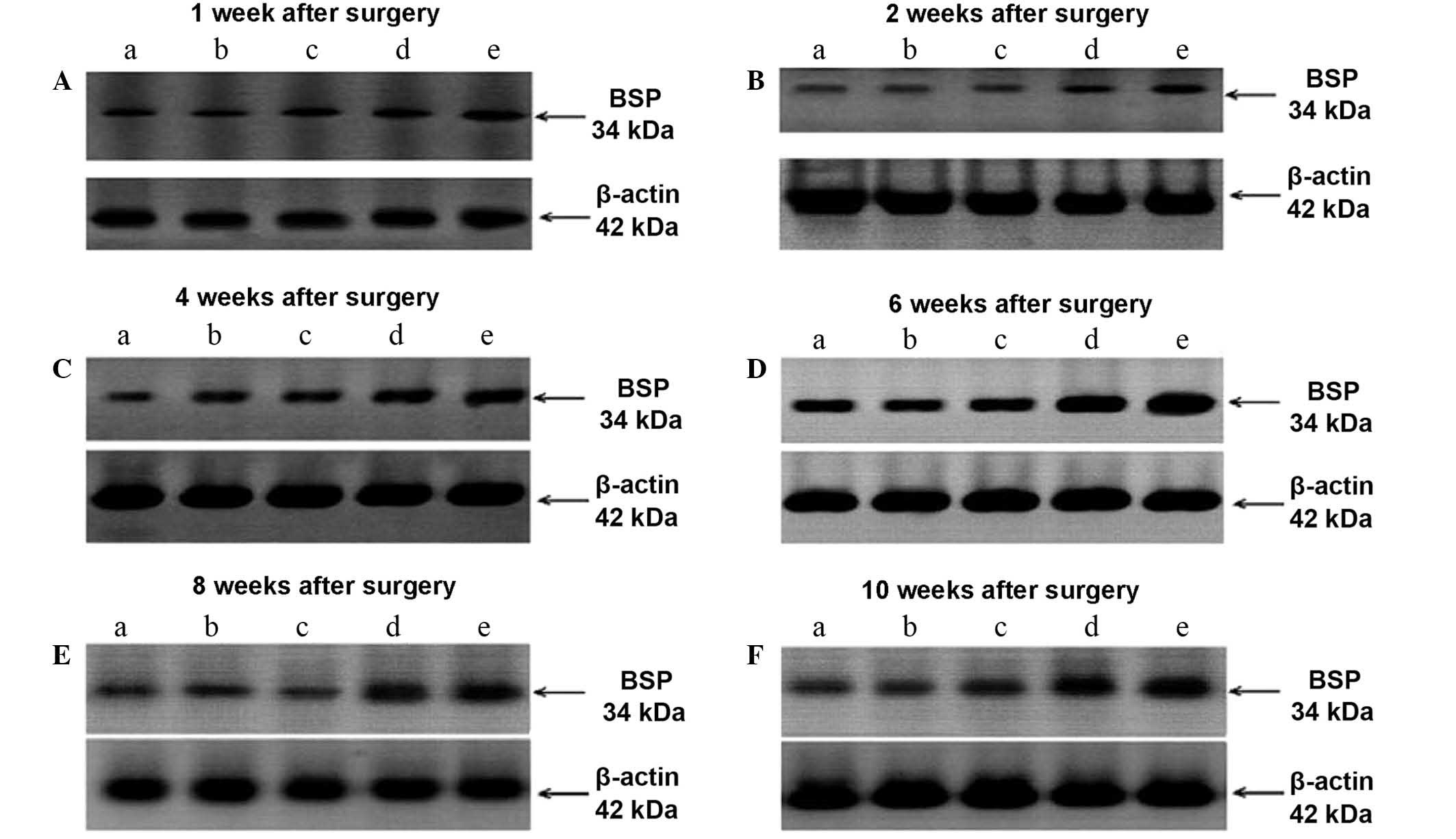
|
1.
|
Nielson JL, Guandique CF, Liu AW, Burke
DA, Lash AT, Moseanko R, Hawbecker S, Strand SC, Zdunowski S,
Irvine A, et al: Development of a database for translational spinal
cord injury research. J Neurotrauma. 31:1789–1799. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2.
|
Hamid S and Hayek R: Role of electrical
stimulation for rehabilitation and regeneration after spinal cord
injury: An overview. Eur Spine J. 17:1256–1269. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3.
|
Troy KL and Morse LR: Measurement of bone:
Diagnosis of SCI-induced osteoporosis and fracture risk prediction.
Top Spinal Cord Inj Rehabil. 21:267–274. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Li J, Meng Q, Shan Q, Mao Z, Wang B, Zhang
F, Zhao T and Yu P: Extract of Cornus officinalis SIEB
ameliorates osteoporosis in spinal cord injured rats. Zhong Guo Gu
Zhi Shu Song Za Zhi She. 60:627–633. 2015.(In Chinese).
|
|
5.
|
Niu Y and Zheng HX: Effect of herbs with
function of reinforcing kidney and replenish marrow on mRNA and
protein expression of calcium binding protein - D9K in kidney
tissue of rats with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Ji Lin
Zhong Yi Yao. 32:68–69. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
6.
|
Wang J, Zheng HX, Liu Y, Zhang JP and Liu
RH: Effect of reinforcing kidney to replenish marrow herbs compound
on mRNA and protein expression of osterix in kidney tissues of rats
with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Guang Ming Zhong Yi Za
Zhi. 27:673–677. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
7.
|
Wang J, Zheng HX, Zong ZH, Yang F, Zhu H
and Zhang ZG: Effect of herbs with function of reinforcing kidney
and replenish marrow on mRNA and protein expression of Runx2 in
bone tissue of rats with glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis. Zhong
Guo Gu Zhi Shu Song Za Zhi. 17:120–125. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
8.
|
Zhou DA, Deng YN and Liu L: Effect of
kidney-reinforcing and marrow-beneficial traditional Chinese
medicine-intervened serum on the proliferation and osteogenic
differentiation of bone marrow stromal cells. Exp Ther Med.
9:191–196. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Xie L, Shen YX and Fan ZH: Establishment
of rat models of complete spinal cord transection and several
relative problems. Ji Zhu Wai Ke Za Zhi. 8:377–380. 2010.(In
Chinese).
|
|
10.
|
Meng BL, Ba YC, Song SN, Chen SS and Wang
TH: Establishment of spinal cord transection injury models in rats.
Zhong Guo Zu Zhi Gong Cheng Yan Jiu Yu Lin Chuang Kang Fu.
15:1215–1218. 2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
11.
|
Basso DM, Beattie MS and Bresnahan JC: A
sensitive and reliable locomotor rating scale for open filed
testing in rats. J Neurotrauma. 12:1–21. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Chen M, Kong XY, Ma Q, Zheng X, Zhao S and
Zheng XY: Establishment of completely transected spinal cord model
and influence of minocycline pretreatment on GFAP expression in
rats. Jie Po Xue Za Zhi. 37:352–355. 2014.(In Chinese).
|
|
13.
|
Nakae A, Nakai K, Yano K, Hosokawa K,
Shibata M and Mashimo T: The animal model of spinal cord injury as
an experimental pain model. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011:9390232011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Lim JH, Piedrahita JA, Jackson L,
Ghashghaei T and Olby NJ: Development of a model of sacrocaudal
spinal cord injury in cloned Yucatan minipigs for cellular
transplantation research. Cell Reprogram. 12:689–697. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Yu D, Li M, Ni B, Kong J and Zhang Z:
Induction of neuronal mitophagy in acute spinal cord injury in
rats. Neurotox Res. 24:512–522. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Lukovic D, Moreno Manzano V, Stojkovic M,
Bhattacharya SS and Erceg S: Concise review: Human pluripotent stem
cells in the treatment of spinal cord injury. Stem Cells.
30:1787–1792. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Ward PJ and Hubscher CH: Persistent
polyuria in a rat spinal contusion model. J Neurotrauma.
29:2490–2498. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Rufus P, Mohamed N and Shuid AN:
Beneficial effects of traditional Chinese medicine on the treatment
of osteoporosis on ovariectomised rat models. Curr Drug Targets.
14:1689–1693. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Ye CQ, Ji SR, Zhang QM, Du LJ and Ren XF:
The influence of spinal cord injury on bone metabolism and bone
mass density in rats. Zhong Guo Kang Fu Yi Xue Za Zhi. 20:258–260.
2005.(In Chinese).
|
|
20.
|
Battaglino RA, Lazzari AA, Garshick E and
Morse LR: Spinal cord injury-induced osteoporosis: Pathogenesis and
emerging therapies. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 10:278–285. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Lin SJ, Ho HC, Lee YF, Liu NC, Liu S, Li
G, Shyr CR and Chang C: Reduced osteoblast activity in the mice
lacking TR4 nuclear receptor leads to osteoporosis. Reprod Biol
Endocrinol. 10:432012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Liang HD, Yu F, Tong ZH, Zhang HQ and
Liang W: Cistanches herba aqueous extract affecting serum
BGP and TRAP and bone marrow Smad1 mRNA, Smad5 mRNA, TGF-β1 mRNA
and TIEG1 mRNA expression levels in osteoporosis disease. Mol Biol
Rep. 40:757–763. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Atalay S, Elci A, Kayadibi H, Onder CB and
Aka N: Diagnostic utility of osteocalcin, undercarboxylated
osteocalcin, and alkaline phosphatase for osteoporosis in
premenopausal and postmenopausal women. Ann Lab Med. 32:23–30.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Rossi F, Perrotta S, Bellini G, Luongo L,
Tortora C, Siniscalco D, Francese M, Torella M, Nobili B, Di Marzo
V and Maione S: Iron overload causes osteoporosis in thalassemia
major patients through interaction with transient receptor
potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) channels. Haematologia.
99:1876–1884. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25.
|
Tsay J, Yang Z, Ross FP,
Cunningham-Rundles S, Lin H, Coleman R, Mayer-Kuckuk P, Doty SB,
Grady RW, Giardina PJ, et al: Bone loss caused by iron overload in
a murine model: Importance of oxidative stress. Blood.
116:2582–2589. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Jensen ED, Gopalakrishnan R and Westendorf
JJ: Regulation of gene expression in osteoblasts. Biofactors.
36:25–32. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Marie PJ and Kassem M: Osteoblasts in
osteoporosis: Past, emerging, and future anabolic targets. Eur J
Endocrinol. 165:1–10. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Kruger TE, Miller AH, Godwin AK and Wang
J: Bone sialoprotein and osteopontin in bone metastasis of
osteotropic cancers. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 89:330–341. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29.
|
Yang Y, Mkhonto D, Cui Q and Sahai N:
Theoretical study of bone sialoprotein in bone biomineralization.
Cells Tissues Organs. 194:182–187. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30.
|
Uccello M, Malaguarnera G, Vacante M and
Motta A: Serum bone sialoprotein levels and bone metastases. J
Cancer Res Ther. 7:115–119. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|