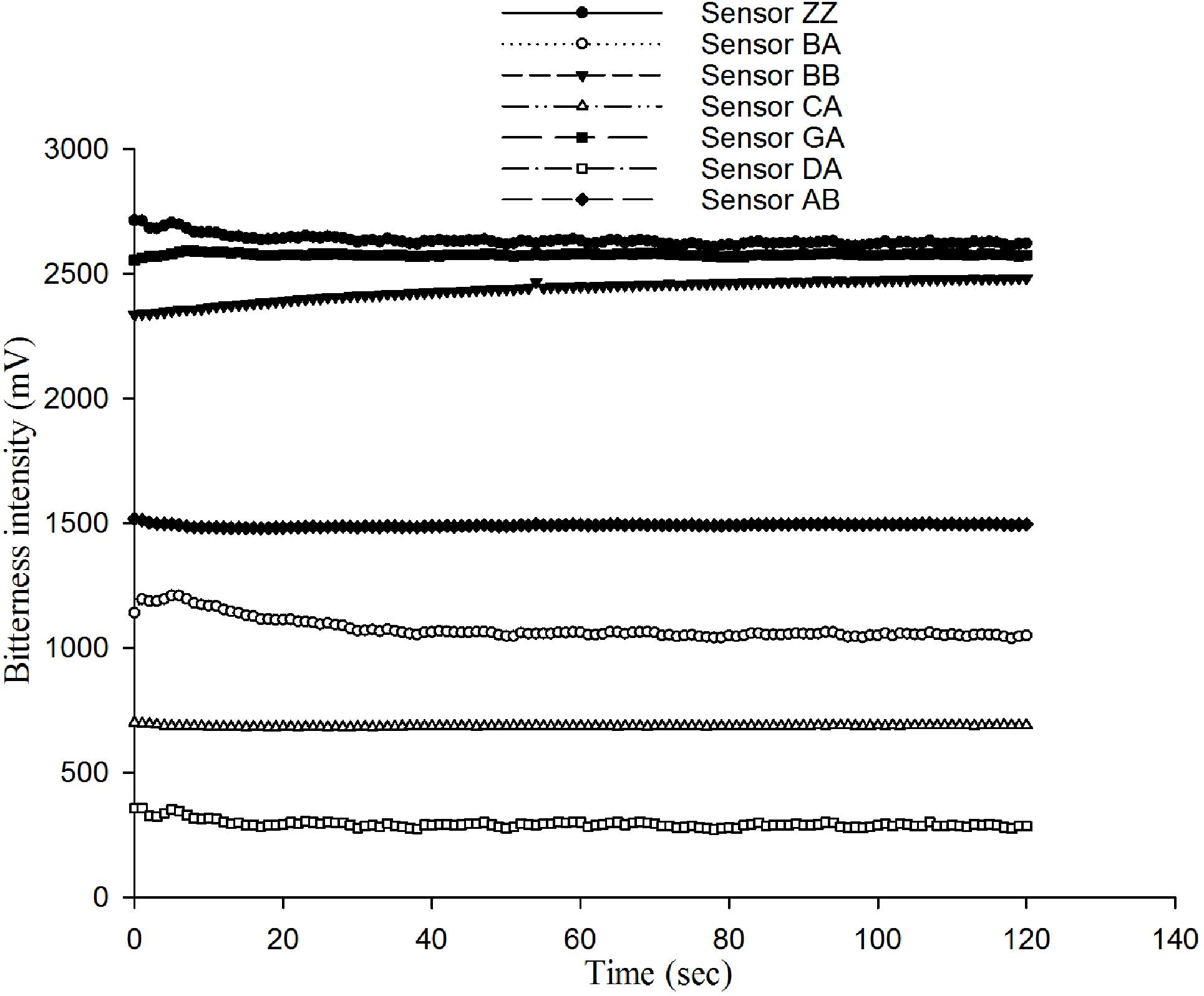
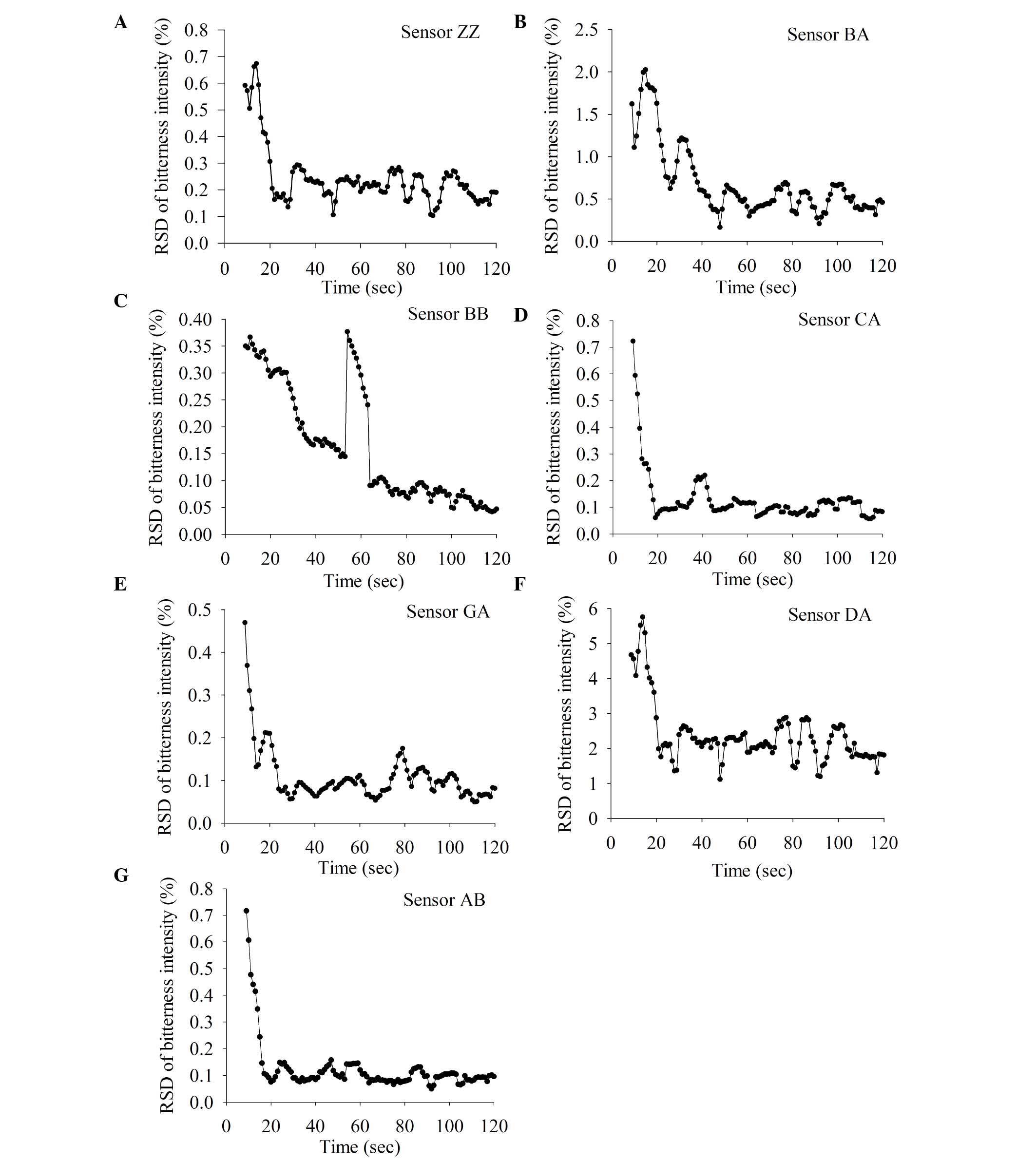
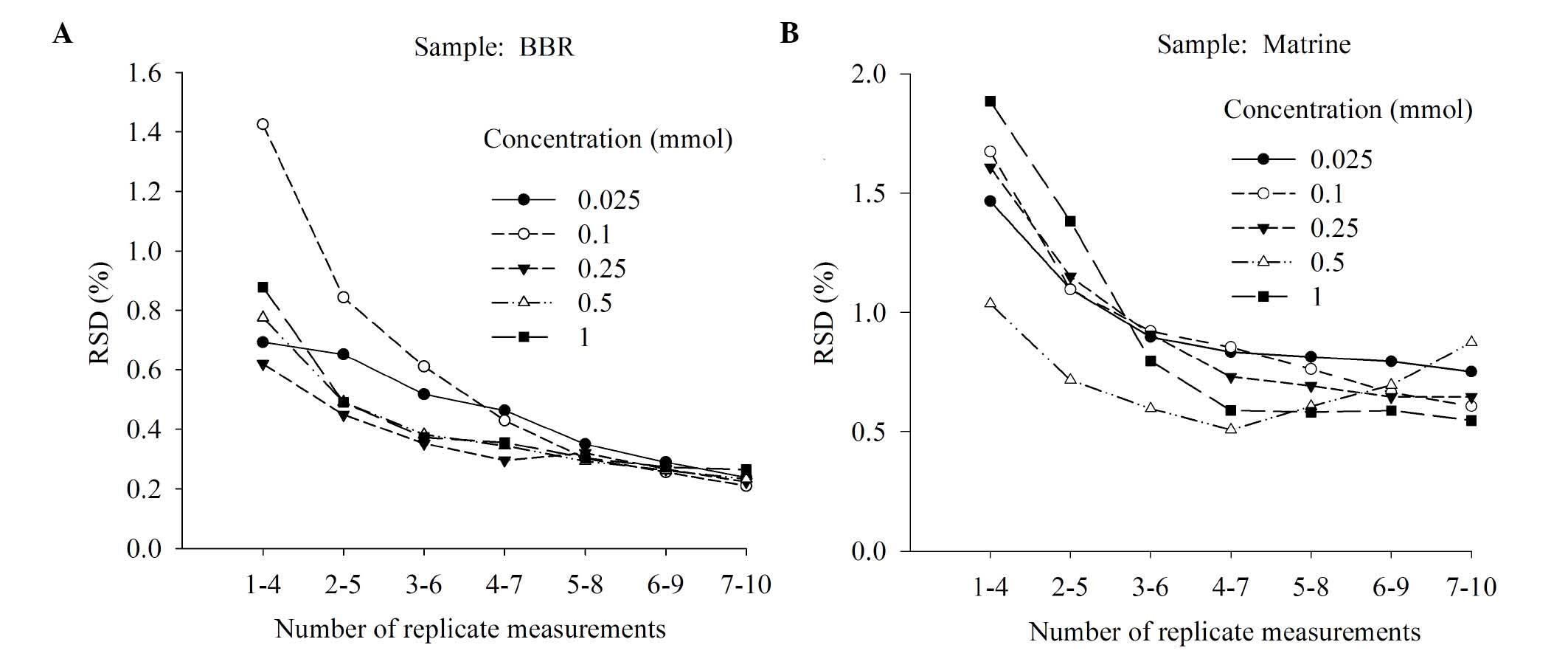
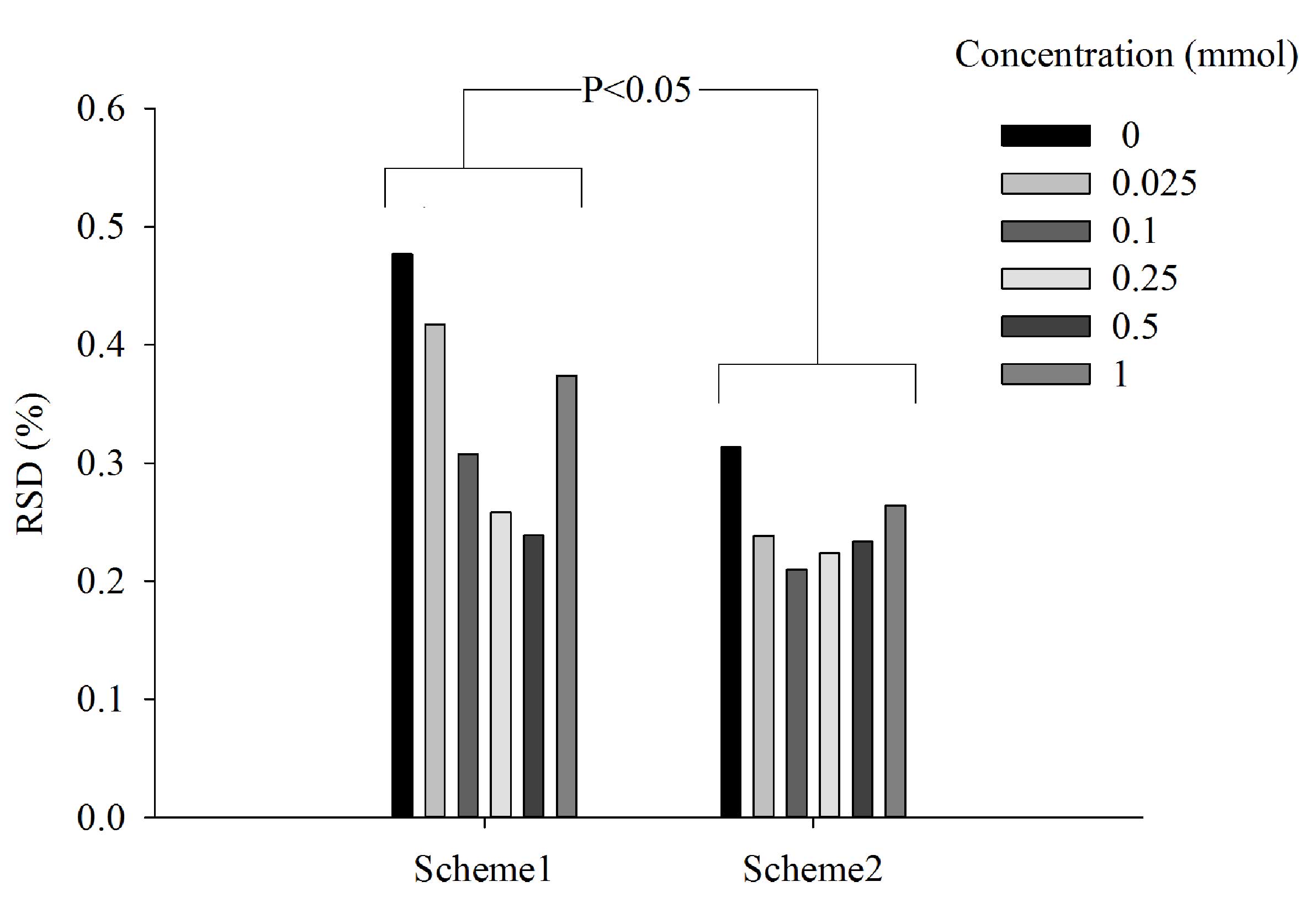
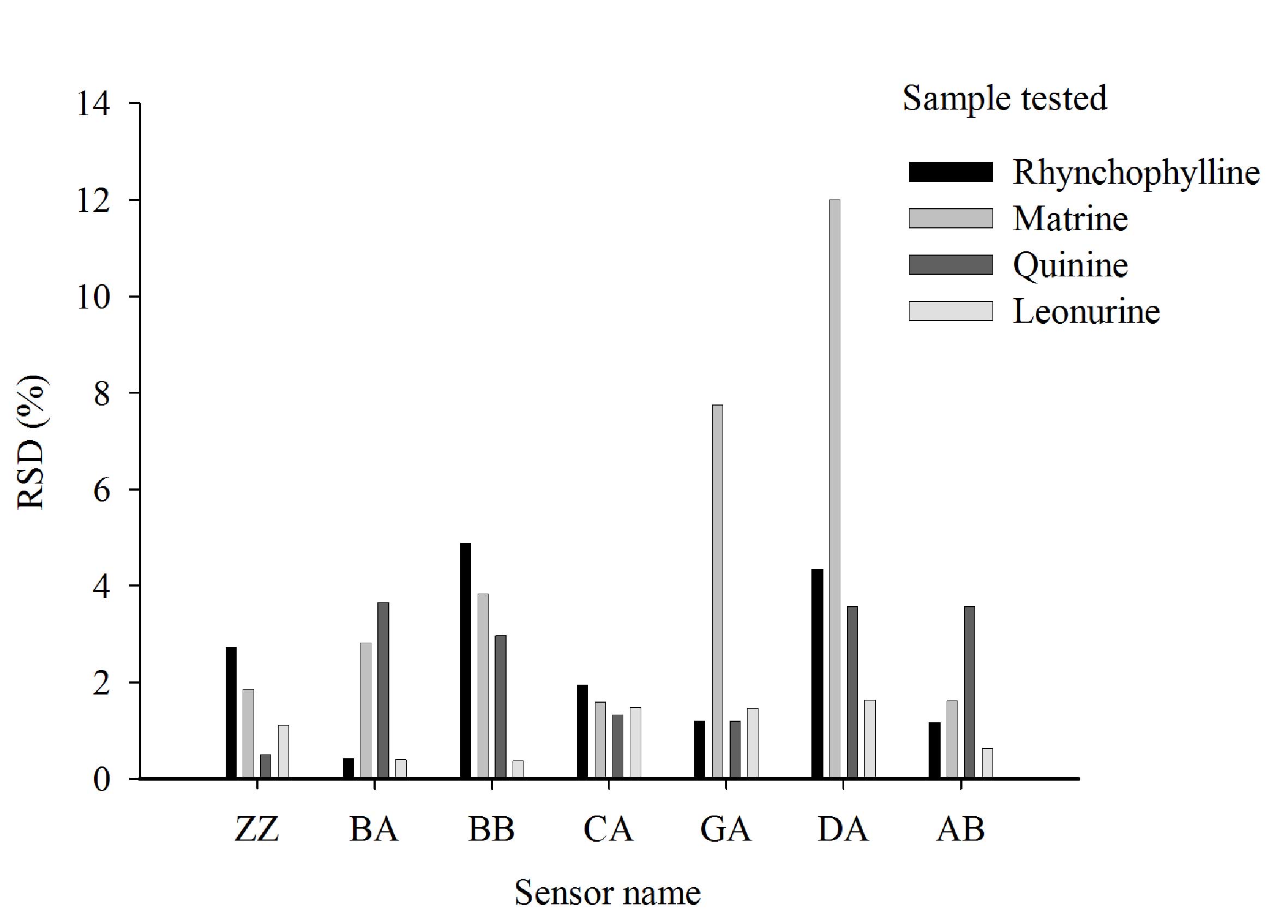
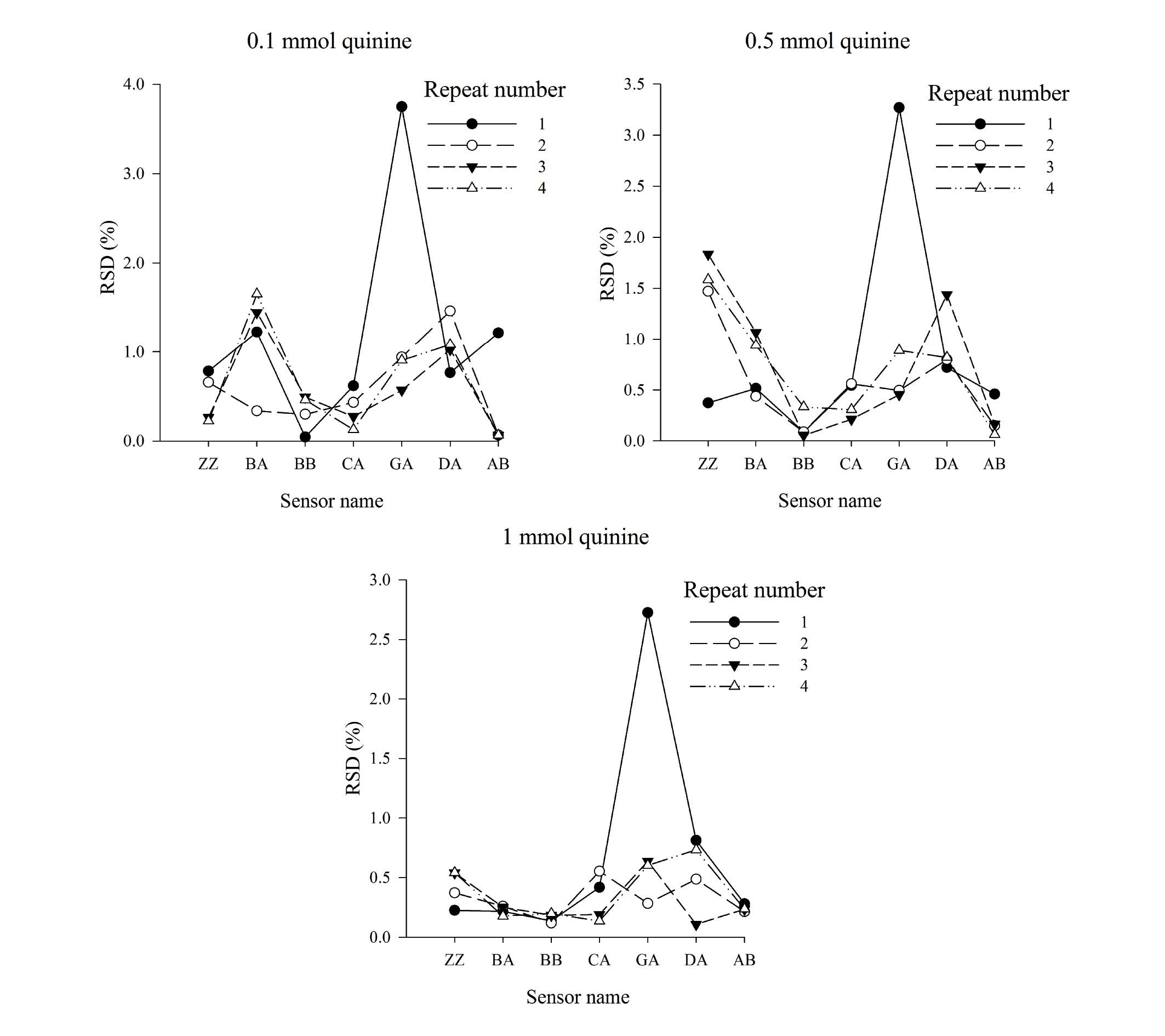
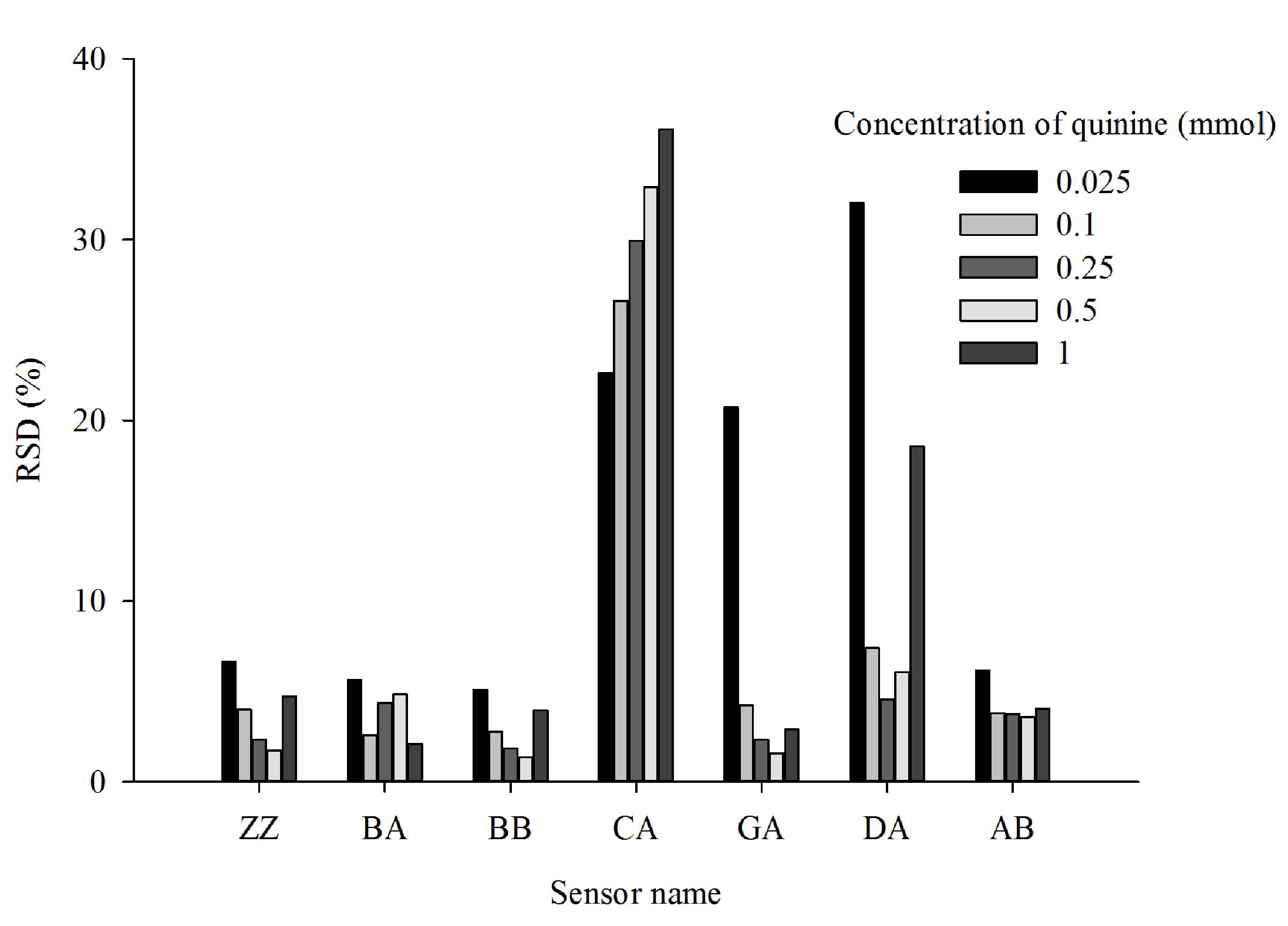
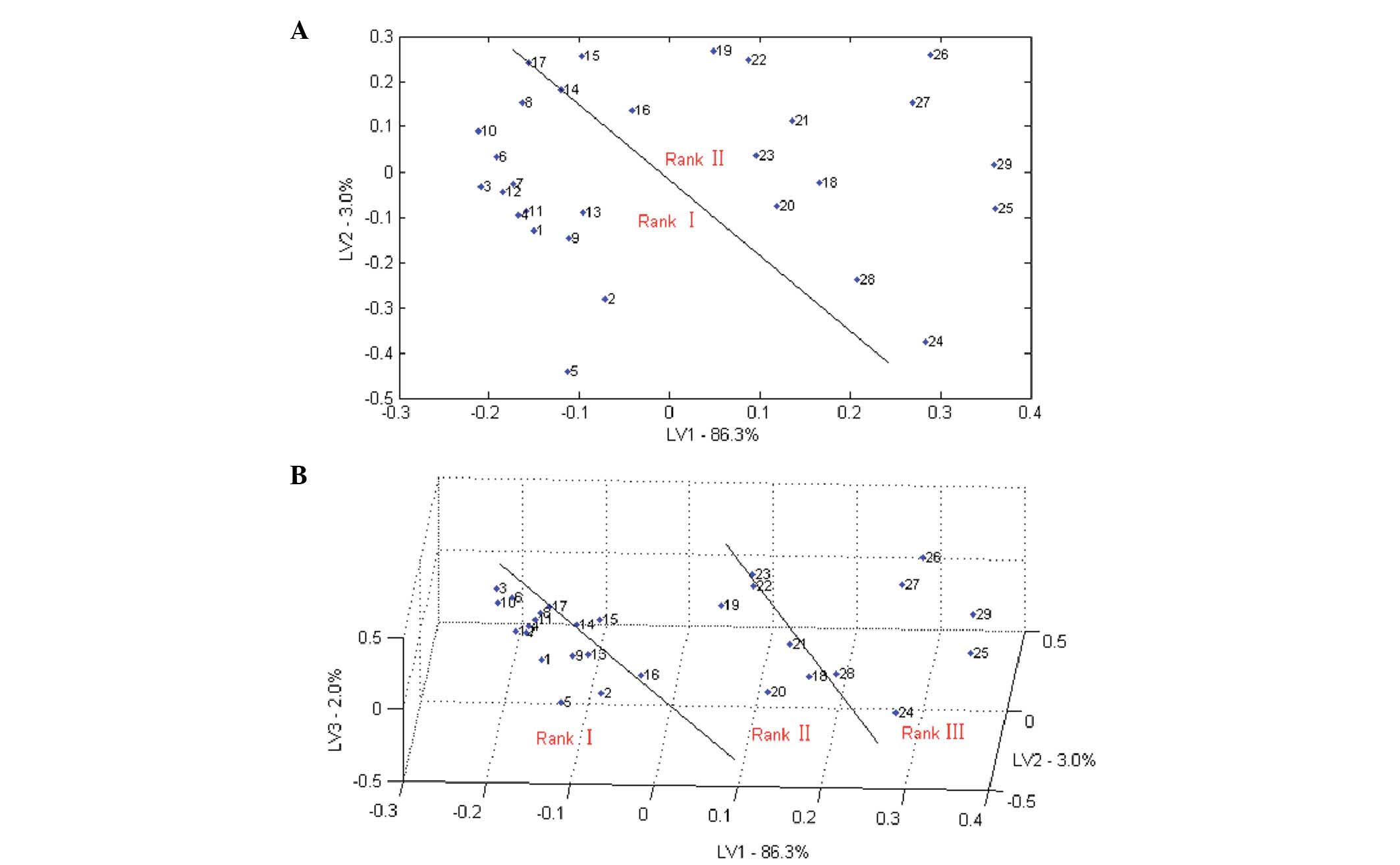
|
1
|
Gupta H, Sharma A, Kumar S and Roy SK:
E-tongue: A tool for taste evaluation. Recent Pat Drug Deliv
Formul. 4:82–89. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ayenew Z, Puri V, Kumar L and Bansal AK:
Trends in pharmaceutical taste masking technologies: A patent
review. Recent Pat Drug Deliv Formul. 3:26–39. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ito M, Ikehama K, Yoshida K, Haraguchi T,
Yoshida M, Wada K and Uchida T: Bitterness prediction of
H1-antihistamines and prediction of masking effects of artificial
sweeteners using an electronic tongue. Int J Pharm. 441:121–127.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Anand V, Kataria M, Kukkar V, Saharan V
and Choudhury PK: The latest trends in the taste assessment of
pharmaceuticals. Drug Discov Today. 12:257–265. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dickinson TA, Michael KL, Kauer JS and
Walt DR: Convergent, self-encoded bead sensor arrays in the design
of an artificial nose. Anal Chem. 71:2192–2198. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Goodey A, Lavigne JJ, Savoy SM, Rodriguez
MD, Curey T, Tsao A, Simmons G, Wright J, Yoo SJ, Sohn Y, et al:
Development of multianalyte sensor arrays composed of chemically
derivatized polymeric microspheres localized in micromachined
cavities. J Am Chem Soc. 123:2559–2570. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jokerst JV, Jacobson JW, Bhagwandin BD,
Floriano PN, Christodoulides N and McDevitt JT: Programmable
nano-bio-chip sensors: Analytical meets clinical. Anal Chem.
82:1571–1579. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Riul A Jr, Dantas CA, Miyazaki CM and
Oliveira ON Jr: Recent advances in electronic tongues. Analyst.
135:2481–2495. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Baldwin EA, Bai J, Plotto A and Dea S:
Electronic noses and tongues: Applications for the food and
pharmaceutical industries. Sensors (Basel). 11:4744–4766. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Toko K, Hara D, Tahara Y, Yasuura M and
Ikezaki H: Relationship between the amount of bitter substances
adsorbed onto lipid/polymer membrane and the electric response of
taste sensors. Sensors (Basel). 14:16274–16286. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Polshin E, Rudnitskaya A, Kirsanov D,
Legin A, Saison D, Delvaux F, Delvaux FR, Nicolaï BM and Lammertyn
J: Talanta. 81:88–94. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Peris M and Escuder-Gilabert L: On-line
monitoring of food fermentation processes using electronic noses
and electronic tongues: A review. Anal Chim Acta. 804:29–36. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gutiérrez-Capitán M, Santiago JL,
Vila-Planas J, Llobera A, Boso S, Gago P, Martínez MC and
Jiménez-Jorquera C: Classification and characterization of
different white grape juices by using a hybrid electronic tongue. J
Agric Food Chem. 61:9325–9332. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Escuder-Gilabert L and Peris M: Review:
Highlights in recent applications of electronic tongues in food
analysis. Anal Chim Acta. 665:15–25. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Apetrei C, Apetrei IM, Villanueva S, de
Saja JA, Gutierrez-Rosales F and Rodriguez-Mendez ML: Combination
of an e-nose, an e-tongue and an e-eye for the characterisation of
olive oils with different degree of bitterness. Anal Chim Acta.
663:91–97. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Major N, Marković K, Krpan M, Sarić G,
Hruškar M and Vahčić N: Rapid honey characterization and botanical
classification by an electronic tongue. Talanta. 85:569–574. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Cetó X, Gutiérrez-Capitán M, Calvo D and
del Valle M: Beer classification by means of a potentiometric
electronic tongue. Food Chem. 141:2533–2540. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Söderström C, Borén H, Winquist F and
Krantz-Rülcker C: Use of an electronic tongue to analyze mold
growth in liquid media. Int J Food Microbiol. 83:253–261. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhao G, Lin X, Dou W, Tian S, Deng S and
Shi J: Use of the smart tongue to monitor mold growth and
discriminate between four mold species grown in liquid media. Anal
Chim Acta. 690:240–247. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Woertz K, Tissen C, Kleinebudde P and
Breitkreutz J: A comparative study on two electronic tongues for
pharmaceutical formulation development. J Pharm Biomed Anal.
55:272–281. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Harada T, Uchida T, Yoshida M, Kobayashi
Y, Narazaki R and Ohwaki T: A new method for evaluating the
bitterness of medicines in development using a taste sensor and a
disintegration testing apparatus. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo).
58:1009–1014. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lorenz JK, Reo JP, Hendl O, Worthington JH
and Petrossian VD: Evaluation of a taste sensor instrument
(electronic tongue) for use in formulation development. Int J
Pharm. 367:65–72. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zheng JY and Keeney MP: Taste masking
analysis in pharmaceutical formulation development using an
electronic tongue. Int J Pharm. 310:118–124. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Rachid O, Simons FE, Rawas-Qalaji M and
Simons KJ: An electronic tongue: Evaluation of the masking efficacy
of sweetening and/or flavoring agents on the bitter taste of
epinephrine. AAPS PharmSciTech. 11:550–557. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tanigake A, Miyanaga Y, Nakamura T, Tsuji
E, Matsuyama K, Kunitomo M and Uchida T: The bitterness intensity
of clarithromycin evaluated by a taste sensor. Chem Pharm Bull
(Tokyo). 51:1241–1245. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li L, Naini V and Ahmed SU: Utilization of
a modified special-cubic design and an electronic tongue for
bitterness masking formulation optimization. J Pharm Sci.
96:2723–2734. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Haraguchi T, Uchida T, Hazekawa M, Yoshida
M, Nakashima M, Sanda H, Hase T and Tomoda Y: Ability of food/drink
to reduce the bitterness intensity of topiramate as determined by
taste sensor analysis. Chem Pharm Bull (Tokyo). 64:14–20. 2016.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yaroshenko I, Kirsanov D, Kartsova L,
Sidorova A, Sun Q, Wan H, He Y, Wang P and Legin A: Exploring
bitterness of traditional Chinese medicine samples by
potentiometric electronic tongue and by capillary electrophoresis
and liquid chromatography coupled to UV detection. Talanta.
152:105–111. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Pharmacopoeia of the People's Republic of
China 2010. 8th. I. China Medical Science and Technology Press;
Beijing: 2010
|
|
30
|
Liu R, Zhang X, Zhang L, Gao X, Li H, Shi
J and Li X: Bitterness intensity prediction of berberine
hydrochloride using an electronic tongue and a GA-BP neural
network. Exp Ther Med. 7:1696–1702. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shi J, Zhang X, Qiu J, Li X and Liu R:
Investigation of bitter masking mechanism of β-cyclodextrin to
several traditional Chinese medicines. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji
Xue Za Zhi. 19:1–4. 2013.(In Chinese).
|
|
32
|
Li X, Wu Z, Liu R, Xu Z, Shi J and Li H:
Study on bitterness evaluation of Chinese herbal decoction by
THTPM. Zhong Guo Shi Yan Fang Ji Xue Za Zhi. 17:11–13. 2011.(In
Chinese).
|
|
33
|
Verboven S and Hubert M: Matlab library
LIBRA. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Computational Statistics.
2:509–515. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Verboven S and Hubert M: LIBRA: A MATLAB
library for robust analysis. Chemometr Intell Lab Syst. 75:127–136.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Lin Z, Zhang Q, Liu R, Gao X, Zhang L,
Kang B, Shi J, Wu Z, Gui X and Li X: Evaluation of the bitterness
of traditional Chinese medicines using an E-tongue coupled with a
robust partial least squares regression method. Sensors (Basel).
16:1512016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Newman J, Egan T, Harbourne N, O'Riordan
D, Jacquier JC and O'Sullivan M: Correlation of sensory bitterness
in dairy protein hydrolysates: Comparison of prediction models
built using sensory, chromatographic and electronic tongue data.
Talanta. 126:46–53. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kuligowski J, Pérez-Guaita D and Quintás
G: Application of discriminant analysis and cross-validation on
proteomics data. Methods Mol Biol. 1362:175–184. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|