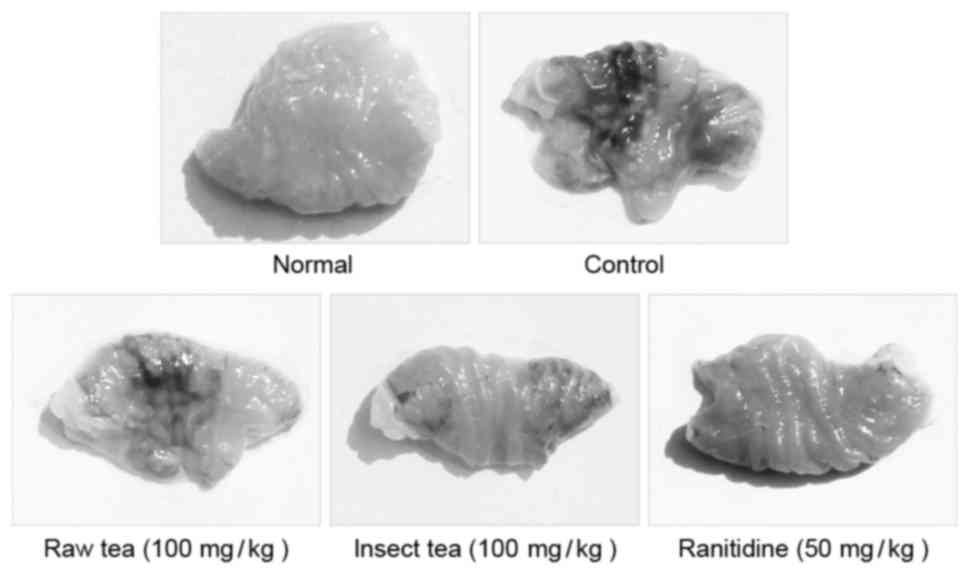
|
1
|
Malfertheiner P, Chan FK and McColl KE:
Peptic ulcer disease. Lancet. 374:1449–1461. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hsu CC, Hsu YC, Chang KH, Lee CY, Chong
LW, Lin CL, Shang CS, Sung FC and Kao CH: Depression and the risk
of peptic ulcer disease: A nationwide population-based study.
Medicine (Baltimore). 94:e23332015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gyires K: Neuropeptides and gastric
mucosal homeostasis. Curr Top Med Chem. 4:63–74. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen CY and Tsai CY: Ghrelin and motilin
in the gastrointestinal system. Curr Pharm Des. 18:4755–4765. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Long DM, Leonard AS, Story J and French
LA: Hypothalamus and gastric ulceration: II. production of
gastrointestinal ulceration by chronic hypothalamic Stimulation.
Arch Neurol. 7:167–183. 1962. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Mejia A and Kraft WK: Acid peptic
diseases: Pharmacological approach to treatment. Expert Rev Clin
Pharmacol. 2:295–314. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Thomson AB, Sauve MD, Kassam N and
Kamitakahara H: Safety of the long-term use of proton pump
inhibitors. World J Gastroenterol. 16:2323–2330. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhao X, Wang R, Qian Y, Li G, Zhou Y and
Sun P: In vivo preventive effects of insect tea on buccal mucosa
cancer in ICR mice. J Cancer Res Ther. 10:651–657. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Xu L, Pan H, Lei Q, Xiao W, Peng Y and
Xiao P: Insect tea, a wonderful work in the Chinese tea culture.
Food Res Int. 53:629–635. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Qian Y, Li GJ, Wang R, Zhou YL, Sun P and
Zhao X: In vitro anticancer effects of insect tea in TCA8113 cells.
J Cancer Res Ther. 10:1045–1051. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ao C: Scavenging effects of sandy-tea
ethanol extract on super oxide anion and hydroxyl radical. Meat
Res. 4:60–64. 2010.
|
|
12
|
Zhao X, Wang Q, Qian Y and Song JL: Ilex
kudingcha C.J. Tseng (Kudingcha) prevents HCl/ethanol-induced
gastric injury in Sprague-Dawley rats. Mol Med Rep. 7:1613–1616.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wen L, Guo H, Li J, Yin R and Duan Z:
Analyse of thebiological safety and major chemical components of
Sanye insect tea. J Hunan Agric Univ. 22:574–579. 1996.
|
|
14
|
Guo S, Xu W, Wen L, Huang Y and Wang F:
The nutrient analysis and evaluation of Sanye insect-fermented tea.
Chin Bull Entomol. 45:128–132. 2008.
|
|
15
|
Beauchamp RD, Townsend CM, Singh P, Glass
EJ and Thompson JC: Proglumide, a gastrin receptor antagonist,
inhibits growth of colon cancer and enhances survival in mice. Ann
Surg. 202:303–309. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Brzozowski T, Konturek SJ, Sliwowski Z,
Drozdowicz D, Zaczek M and Kedra D: Role of arginine, a substrate
for nitric oxide-synthase, in gastroprotection and ulcer healing. J
Gastroenterol. 32:442–452. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yatabe J, Saito F, Ishida I, Sato A, Hoshi
M, Suzuki K, Kameda T, Ueno S, Yatabe MS, Watanabe T and Sanada H:
Lower plasma arginine in enteral tube-fed patients with pressure
ulcer and improved pressure ulcer healing after arginine
supplementation by arginaid water. J Nutr Health Aging. 15:282–286.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Desneves KJ, Todorovic BE, Cassar A and
Crowe TC: Treatment with supplementary arginine, vitamin C and zinc
in patients with pressure ulcers: A randomized controlled trial.
Clin Nutr. 24:979–987. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhenyukh O, Civantos E, Ruiz-Ortega M,
Sánchez MS, Vázquez C, Peiró C, Egido J and Mas S: High
concentration of branched-chain amino acids promotes oxidative
stress, inflammation and migration of human peripheral blood
mononuclear cells via mTORC1 activation. Free Radic Biol Med.
104:165–177. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang XJ, Chinkes DL and Wolfe RR: Leucine
supplementation has an anabolic effect on proteins in rabbit skin
wound and muscle. J Nutr. 134:3313–3318. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Alphin RS, Vokac VA, Gregory RL, Bolton PM
and Tawes JW III: Role of intragastric pressure, pH and pepsin in
gastric ulceration in the rat. Gastroenterology. 73:495–500.
1977.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Venables CW: Mucus, pepsin, and peptic
ulcer. Gut. 27:233–238. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yamamoto O, Okada Y and Okabe S: Effects
of a proton pump inhibitor, omeprazole, on gastric secretion and
gastric and duodenal ulcers or erosions in rats. Dig Dis Sci.
29:394–401. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Delaney JP, Cheng JW, Butler BA and
Ritchie WP Jr: Gastric ulcer and regurgitation gastritis. Gut.
11:715–719. 1970. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Guth PH: Pathogenesis of gastric mucosal
injury. Annu Rev Med. 33:183–196. 1982. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sandor A, Kidd M, Lawton GP, Miu K, Tang
LH and Modlin IM: Neurohormonal modulation of rat
enterochromaffin-like cell histamine secretion. Gastroenterology.
110:1084–1092. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Xie XZ, Zhao ZG, Qi DS and Wang ZM: Assay
of gastrin and somatostatin in gastric antrum tissues of children
with chronic gastritis and duodenal ulcer. World J Gastroenterol.
12:2288–2290. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Geoghegan JG and Pappas TN: Central
peptidergic control of gastric acid secretion. Gut. 40:164–166.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Taché Y, Garrick T and Raybould H: Central
nervous system action of peptides to influence gastrointestinal
motor function. Gastroenterology. 98:517–528. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Holzer P: Neural emergency system in the
stomach. Gastroenterology. 114:823–839. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Erin N, Türker S, Elpek Ö and Yıldırım B:
Differential changes in Substance P, VIP as well as neprilysin
levels in patients with gastritis or ulcer. Peptides. 35:218–224.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Brown JC and Parkes CO: Effect on fundic
pouch motor activity of stimulatory and inhibitory fractions
separated from pancreozymin. Gastroenterology. 53:731–736.
1967.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ruppin H, Domschke S, Domschke W, Wünsch
E, Jaeger E and Demling L: Effects of 13-nle-motilin in
man-inhibition of gastric evacuation and stimulation of pepsin
secretion. Scand J Gastroenterol. 10:199–202. 1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Itoh Z, Honda R, Hiwatashi K, Takeuchi S,
Aizawa I, Takayanagi R and Couch EF: Motilin-induced mechanical
activity in the canine alimentary tract. Scand J Gastroenterol
Suppl. 39:93–110. 1976.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yanagisawa M, Kurihara H, Kimura S, Tomobe
Y, Kobayashi M, Mitsui Y, Yazaki Y, Goto K and Masaki T: A novel
potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial
cells. Nature. 332:411–415. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Lazaratos S, Kashimura H, Nakahara A,
Fukutomi H, Osuga T, Urushidani T, Miyauchi T and Goto K: Gastric
ulcer induced by submucosal injection of ET-1: Role of potent
vasoconstriction and intraluminal acid. Am J Physiol.
265:G491–G498. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Michida T, Kawano S, Masuda E, Kobayashi
I, Nishimura Y, Tsujii M, Takei Y, Tsuji S, Nagano K, Fusamoto H,
et al: Endothelin-1 in the gastric mucosa in stress ulcers of
critically ill patients. Am J Gastroenterol. 92:1177–1181.
1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Masuda E, Kawano S, Nagano K, Tsuji S,
Takei Y, Hayashi N, Tsujii M, Oshita M, Michida T, Kobayashi I, et
al: Role of endogenous endothelin in pathogenesis of
ethanol-induced gastric mucosal injury in rats. Am J Physiol.
265:G474–G481. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Lloyd KC, Wang J, Aurang K, Grönhed P, Coy
DH and Walsh JH: Activation of somatostatin receptor subtype 2
inhibits acid secretion in rats. Am J Physiol. 268:G102–G106.
1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Aurang K, Wang J and Lloyd K: Somatostatin
inhibition of acid and histamine release by activation of
somatostatin receptor subtype 2 receptors in rats. J Pharmacol Exp
Ther. 281:245–252. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Martinez V, Curi AP, Torkian B, Schaeffer
JM, Wilkinson HA, Walsh JH and Taché Y: High basal gastric acid
secretion in somatostatin receptor subtype 2 knockout mice.
Gastroenterology. 114:1125–1132. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Saadé NE, Abdallah LE, Barada KA, Atweh SF
and Nassar CF: Effects of intracerebral injections of VIP on
jejunal alanine absorption and gastric acid secretion in rats.
Regul Pept. 55:269–276. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Nassar CF, Abdallah LE, Barada KA, Atweh
SF and Saadé NE: Effects of intravenous vasoactive intestinal
peptide injection on jejunal alanine absorption and gastric acid
secretion in rats. Regul Pept. 55:261–267. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yoshikawa T, Ueda S, Naito Y, Takahashi S,
Oyamada H, Morita Y, Yoneta T and Kondo M: Role of oxygen-derived
free radicals in gastric mucosal injury induced by ischemia or
ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Free Radic Res Commun. 7:285–291.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Yoshikawa T, Naito Y, Ueda S, Oyamada H,
Takemura T, Yoshida N, Sugino S and Kondo M: Role of oxygen-derived
free radicals in the pathogenesis of gastric mucosal lesions in
rats. J Clin Gastroenterol. 12 Suppl 1:S65–S71. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Yoshikawa T, Naito Y, Kishi A, Tomii T,
Kaneko T, Iinuma S, Ichikawa H, Yasuda M, Takahashi S and Kondo M:
Role of active oxygen, lipid peroxidation, and antioxidants in the
pathogenesis of gastric mucosal injury induced by indomethacin in
rats. Gut. 34:732–737. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Itoh M and Guth PH: Role of oxygen-derived
free radicals in hemorrhagic shock-induced gastric lesions in the
rat. Gastroenterology. 88:1162–1167. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Jung HK, Lee KE, Chu SH and Yi SY:
Reactive oxygen species activity, mucosal lipoperoxidation and
glutathione in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric mucosa. J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 16:1336–1340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Akiba Y, Nakamura M, Mori M, Suzuki H, Oda
M, Kimura H, Miura S, Tsuchiya M and Ishii H: Inhibition of
inducible nitric oxide synthase delays gastric ulcer healing in the
rat. J Clin Gastroenterol. 27 Suppl 1:S64–S73. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Rajnakova A, Goh PM, Chan ST, Ngoi SS,
Alponat A and Moochhala S: Expression of differential nitric oxide
synthase isoforms in human normal gastric mucosa and gastric cancer
tissue. Carcinogenesis. 18:1841–1845. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Barrachina M, Esplugues J, Martinezcuesta
M, Calatayud S, Bello R and Wittle B: Nitric-oxide donors
preferentially inhibit neuronally stimulated gastric-acid
secretion. Gastroenterology. 47:1994.
|
|
52
|
Takeuchi K, Ohuchi T and Okabe S:
Nitric-oxide mediates inhibition of gastric-acid secretion in the
damaged stomach-interaction with endogenous prostaglandins.
Gastroenterology. 1921994.
|
|
53
|
Ma L and Wallace JL: Endothelial nitric
oxide synthase modulates gastric ulcer healing in rats. Am J
Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 279:G341–G346. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Guo JS, Cho CH, Wang WP, Shen XZ, Cheng CL
and Koo MW: Expression and activities of three inducible enzymes in
the healing of gastric ulcers in rats. World J Gastroenterol.
9:1767–1771. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Gambhir S, Vyas D, Hollis M, Aekka A and
Vyas A: Nuclear factor kappa B role in inflammation-associated
gastrointestinal malignancies. World J Gastroenterol. 21:3174–3183.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Yanai A, Maeda S, Shibata W, Hikiba Y,
Sakamoto K, Nakagawa H, Ohmae T, Hirata Y, Ogura K, Muto S, et al:
Activation of IKappaB kinase and NF-kappaB is essential for
Helicobacter pylori-induced chronic gastritis in Mongolian gerbils.
Infect Immun. 76:781–787. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Brzozowski T, Konturek SJ, Majka J,
Dembinski A and Drozdowicz D: Epidermal growth factor, polyamines,
and prostaglandins in healing of stress-induced gastric lesions in
rats. Dig Dis Sci. 38:276–283. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Konturek JW, Bielanski W, Konturek SJ,
Bogdal J and Oleksy J: Distribution and release of epidermal growth
factor in man. Gut. 30:1194–1200. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Reeves J, Richards R and Cooke T: The
effects of intracolonic EGF on mucosal growth and experimental
carcinogenesis. Br J Cancer. 63:223–226. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Challacombe DN and Wheeler EE: Trophic
action of epidermal growth factor on human duodenal mucosa cultured
in vitro. Gut. 32:991–993. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|