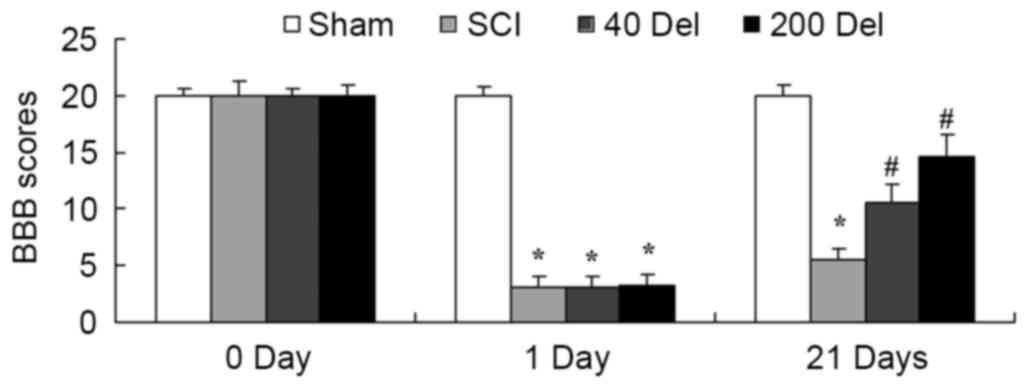
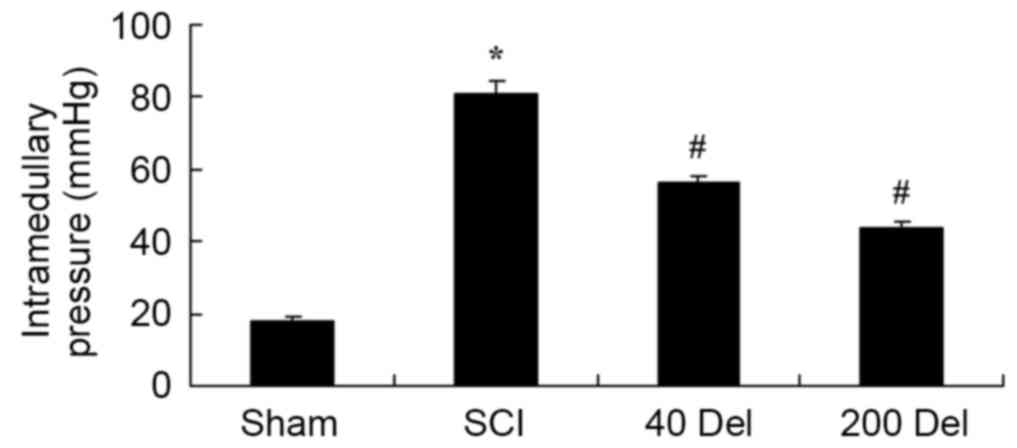
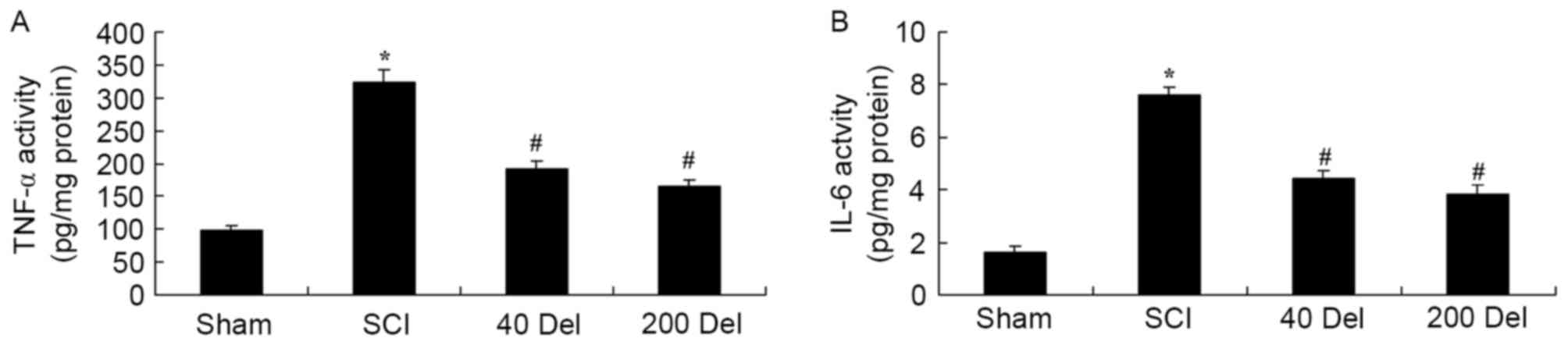
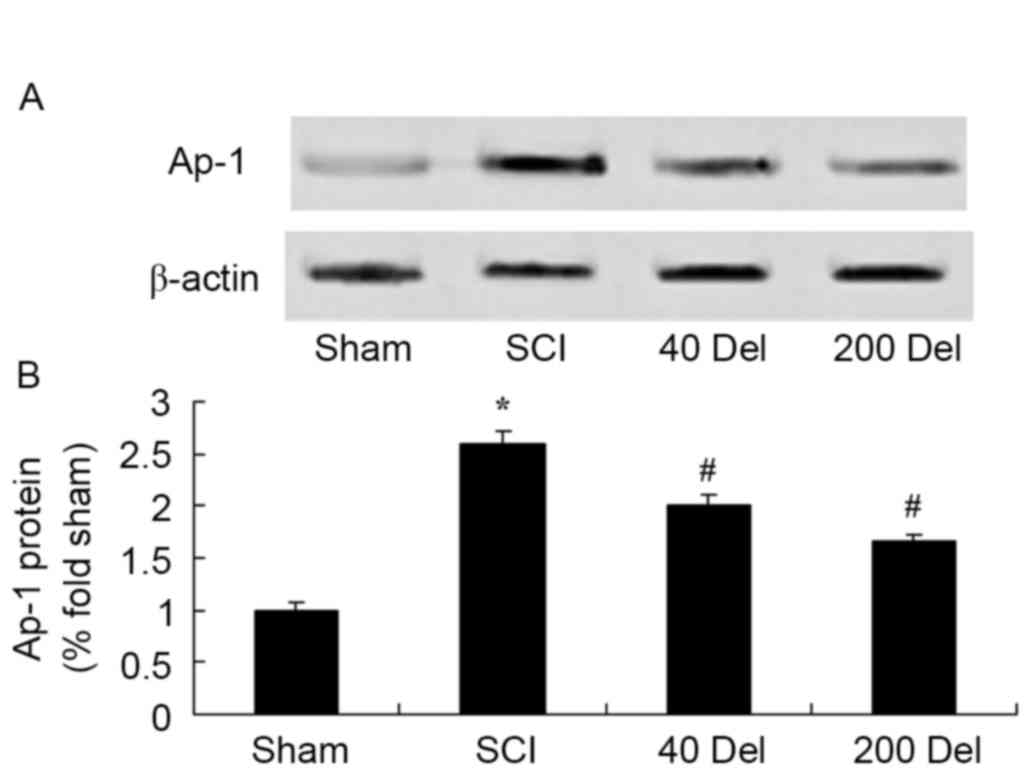
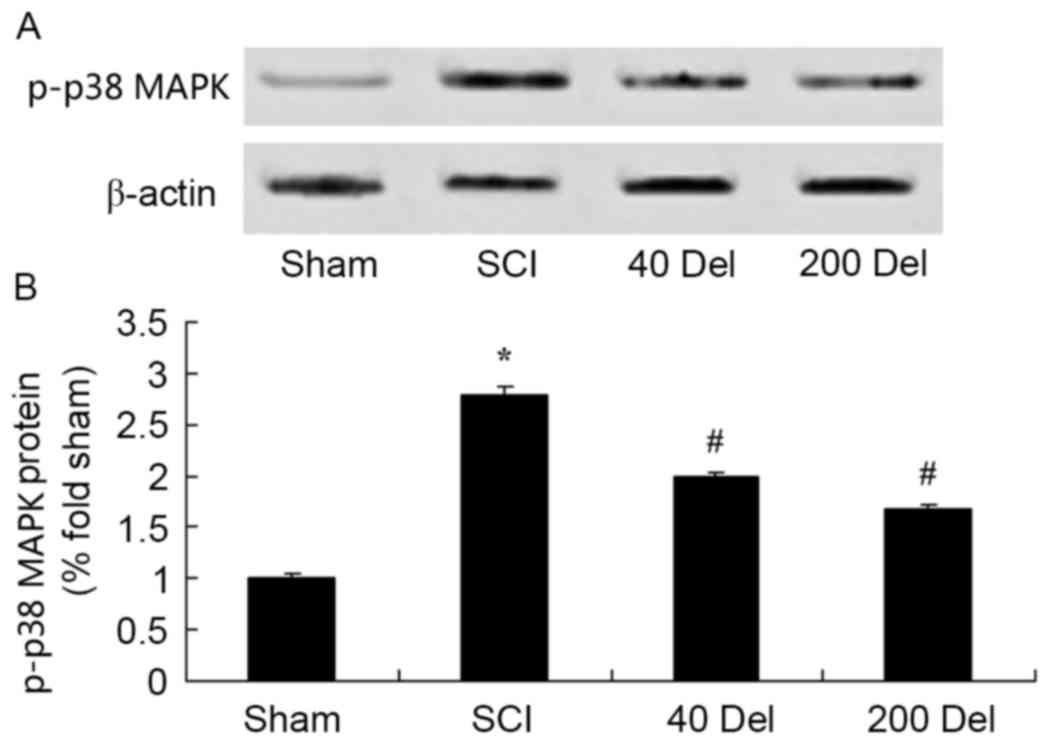
|
1
|
de Rivero Vaccari JP, Marcillo A, Nonner
D, Dietrich WD and Keane RW: Neuroprotective effects of bone
morphogenetic protein 7 (BMP7) treatment after spinal cord injury.
Neurosci Lett. 465:226–229. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
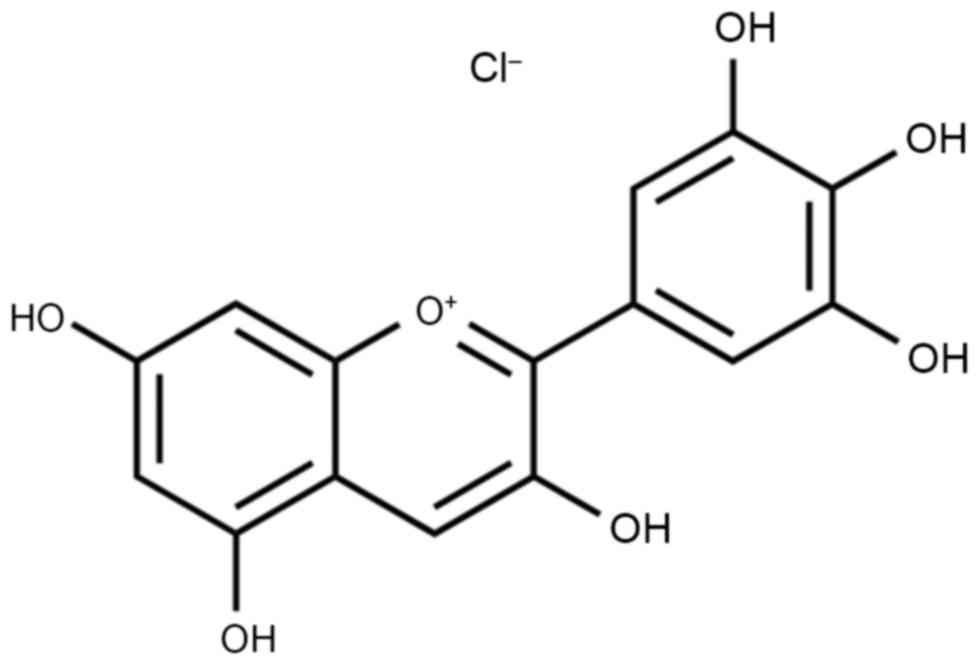
2
|
Lim JH, Muguet-Chanoit AC, Smith DT, Laber
E and Olby NJ: Potassium channel antagonists 4-aminopyridine and
the T-butyl carbamate derivative of 4-aminopyridine improve hind
limb function in chronically non-ambulatory dogs; a blinded,
placebo-controlled trial. PLoS One. 9:e1161392014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
DePaul MA, Palmer M, Lang BT, Cutrone R,
Tran AP, Madalena KM, Bogaerts A, Hamilton JA, Deans RJ, Mays RW,
et al: Intravenous multipotent adult progenitor cell treatment
decreases inflammation leading to functional recovery following
spinal cord injury. Sci Rep. 5:167952015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Galluzzi F, De Rensis F, Saleri R and
Spattini G: Effect of urethral infusion of atracurium besylate on
manual bladder expression in dogs and cats with spinal cord
injuries: A randomised trial. Vet Rec. 176:5452015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Wilson JR, Grossman RG, Frankowski RF,
Kiss A, Davis AM, Kulkarni AV, Harrop JS, Aarabi B, Vaccaro A,
Tator CH, et al: A clinical prediction model for long-term
functional outcome after traumatic spinal cord injury based on
acute clinical and imaging factors. J Neurotrauma. 29:2263–2271.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rosety-Rodriguez M, Camacho A, Rosety I,
Fornieles G, Rosety MA, Diaz AJ, Bernardi M, Rosety M and Ordonez
FJ: Low-grade systemic inflammation and leptin levels were improved
by arm cranking exercise in adults with chronic spinal cord injury.
Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 95:297–302. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Oudega M: Inflammatory response after
spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol. 250:151–155. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fan QQ, Li L, Wang WT, Yang X, Suo ZW and
Hu XD: Activation of α2 adrenoceptors inhibited NMDA
receptor-mediated nociceptive transmission in spinal dorsal horn of
mice with inflammatory pain. Neuropharmacology. 77:185–192. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Cho JS, Kang JH, Shin JM, Park IH and Lee
HM: Inhibitory effect of delphinidin on extracellular matrix
production via the MAPK/NF-κB pathway in nasal polyp-derived
fibroblasts. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 7:276–282. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dayoub O, Andriantsitohaina R and Clere N:
Pleiotropic beneficial effects of epigallocatechin gallate,
quercetin and delphinidin on cardiovascular diseases associated
with endothelial dysfunction. Cardiovasc Hematol Agents Med Chem.
11:249–264. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yuan B, Okusumi S, Yoshino Y, Moriyama C,
Tanaka S, Hirano T, Takagi N and Toyoda H: Delphinidin induces
cytotoxicity and potentiates cytocidal effect in combination with
arsenite in an acute promyelocytic leukemia NB4 cell line. Oncol
Rep. 34:431–438. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Pal HC, Chamcheu JC, Adhami VM, Wood GS,
Elmets CA, Mukhtar H and Afaq F: Topical application of delphinidin
reduces psoriasiform lesions in the flaky skin mouse model by
inducing epidermal differentiation and inhibiting inflammation. Br
J Dermatol. 172:354–364. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hafeez BB, Siddiqui IA, Asim M, Malik A,
Afaq F, Adhami VM, Saleem M, Din M and Mukhtar H: A dietary
anthocyanidin delphinidin induces apoptosis of human prostate
cancer PC3 cells in vitro and in vivo: Involvement of nuclear
factor-kappaB signaling. Cancer Res. 68:8564–8572. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sutbeyaz ST, Koseoglu BF and Gokkaya NK:
The combined effects of controlled breathing techniques and
ventilatory and upper extremity muscle exercise on cardiopulmonary
responses in patients with spinal cord injury. Int J Rehabil Res.
28:273–276. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schulz R, Czaja SJ, Lustig A, Zdaniuk B,
Martire LM and Perdomo D: Improving the quality of life of
caregivers of persons with spinal cord injury: A randomized
controlled trial. Rehabil Psychol. 54:1–15. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Whiteneck GG, Gassaway J, Dijkers MP,
Lammertse DP, Hammond F, Heinemann AW, Backus D, Charlifue S,
Ballard PH and Zanca JM: Inpatient and postdischarge rehabilitation
services provided in the first year after spinal cord injury:
Findings from the SCIRehab study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil.
92:361–368. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ellenbroek D, Kressler J, Cowan RE, Burns
PA, Mendez AJ and Nash MS: Effects of prandial challenge on
triglyceridemia, glycemia, and pro-inflammatory activity in persons
with chronic paraplegia. J Spinal Cord Med. 38:468–475. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Jorgensen V, Elfving B and Opheim A:
Assessment of unsupported sitting in patients with spinal cord
injury. Spinal Cord. 49:838–843. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Tyagi P, Kadekawa K, Kashyap M, Pore S and
Yoshimura N: Spontaneous recovery of reflex voiding following
spinal cord injury mediated by anti-inflammatory and
neuroprotective factors. Urology. 88:57–65. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ji H, Tang H, Lin H, Mao J, Gao L, Liu J
and Wu T: Rho/Rock cross-talks with transforming growth
factor-β/Smad pathway participates in lung fibroblast-myofibroblast
differentiation. Biomed Rep. 2:787–792. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Rathore KI, Redensek A and David S: Iron
homeostasis in astrocytes and microglia is differentially regulated
by TNF-α and TGF-β1. Glia. 60:738–750. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Banovac K, Williams JM, Patrick LD and
Levi A: Prevention of heterotopic ossification after spinal cord
injury with COX-2 selective inhibitor (rofecoxib). Spinal Cord.
42:707–710. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wang G, Huang C, Wang Y, Guo Q, Jiang H
and Wen J: Changes in expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in the spinal
dorsal horn after intrathecal p38MAPK inhibitor SB203580 on
neuropathic pain in rats. Ann Palliat Med. 2:124–129.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Quan HH, Kang KS, Sohn YK and Li M: Tempol
reduces injury area in rat model of spinal cord contusion injury
through suppression of iNOS and COX-2 expression. Neurol Sci.
34:1621–1628. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Coronel MF, Labombarda F, De Nicola AF and
González SL: Progesterone reduces the expression of spinal
cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase and prevents
allodynia in a rat model of central neuropathic pain. Eur J Pain.
18:348–359. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hwang MK, Kang NJ, Heo YS, Lee KW and Lee
HJ: Fyn kinase is a direct molecular target of delphinidin for the
inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 expression induced by tumor necrosis
factor-alpha. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:1213–1222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
He BR, Xie ST, Wu MM, Hao DJ and Yang H:
Phagocytic removal of neuronal debris by olfactory ensheathing
cells enhances neuronal survival and neurite outgrowth via p38MAPK
activity. Mol Neurobiol. 49:1501–1512. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Taves S, Berta T, Liu DL, Gan S, Chen G,
Kim YH, Van de Ven T, Laufer S and Ji RR: Spinal inhibition of p38
MAP kinase reduces inflammatory and neuropathic pain in male but
not female mice: Sex-dependent microglial signaling in the spinal
cord. Brain Behav Immun. 55:70–81. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gwak YS, Unabia GC and Hulsebosch CE:
Activation of P-38alpha MAPK contributes to neuronal
hyperexcitability in caudal regions remote from spinal cord injury.
Exp Neurol. 220:154–161. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Oak MH, Bedoui JE, Madeira SV, Chalupsky K
and Schini-Kerth VB: Delphinidin and cyanidin inhibit
PDGF(AB)-induced VEGF release in vascular smooth muscle cells by
preventing activation of p38 MAPK and JNK. Br J Pharmacol.
149:283–290. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|