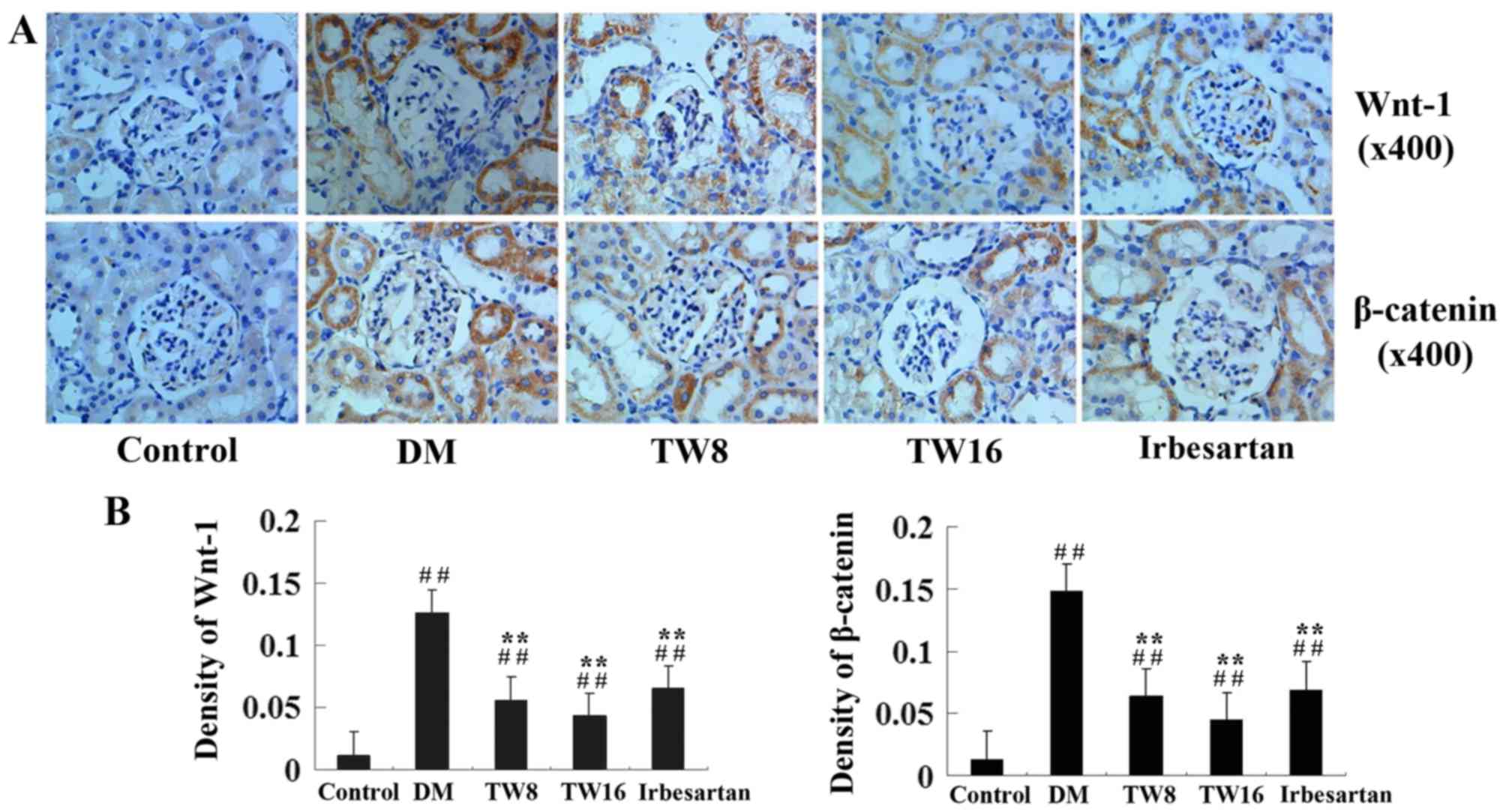
|
1
|
Doi T, Mima A, Matsubara T, Tominaga T,
Arai H and Abe H: The current clinical problems for early phase of
diabetic nephropathy and approach for pathogenesis of diabetic
nephropathy. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 82 Suppl 1:S21–S24. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu B, Wang Y, Jardine M, Jun M, Lv JC,
Cass A, Liyanage T, Chen HY, Wang YJ and Perkovic V:
Tripterygium preparations for the treatment of CKD: A
systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Kidney Dis. 62:515–530.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang D, Dai C, Li Y and Liu Y: Canonical
Wnt/β-catenin signaling mediates transforming growth
factor-β1-driven podocyte injury and proteinuria. Kidney Int.
80:1159–1169. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dai C, Stolz DB, Kiss LP, Monga SP,
Holzman LB and Liu Y: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes podocyte
dysfunction and albuminuria. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:1997–2008. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ho C, Lee PH, Hsu YC, Wang FS, Huang YT
and Lin CL: Sustained Wnt/β-catenin signaling rescues high glucose
induction of transforming growth factor-β1-mediated renal fibrosis.
Am J Med Sci. 344:374–382. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zain M and Awan FR: Renin angiotensin
aldosterone system (RAAS): Its biology and drug targets for
treating diabetic nephropathy. Pak J Pharm Sci. 27:1379–1391.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ren F, Tang L, Cai Y, Yuan X, Huang W, Luo
L, Zhou J and Zheng Y: Meta-analysis: The efficacy and safety of
combined treatment with ARB and ACEI on diabetic nephropathy. Ren
Fail. 37:548–561. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Wu Y, Ren K, Liang C, Yuan L, Qi X, Dong
J, Shen J and Lin S: Renoprotective effect of total glucosides of
paeony (TGP) and its mechanism in experimental diabetes. J
Pharmacol Sci. 109:78–87. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
He Y, Shi S, Zhang R, Shen W, Tu J, Ding Z
and Fan Y: In vitro immunosuppressive and cytotoxic activities of
Tripterygium wilfordii extract. Drug Chem Toxicol.
38:145–151. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hao L, Pan MS, Zheng Y and Wang RF: Effect
of Cordyceps sinensis Tripterygium wilfordii polyglycosidium
on podocytes in rats with diabetic nephropathy. Exp Ther Med.
7:1465–1470. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu S, Li X, Li H, Liang Q and Chen J and
Chen J: Comparison of Tripterygium wilfordii multiglycosides
and tacrolimus in the treatment of idiopathic membranous
nephropathy: A prospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 16:2002015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ge Y, Xie H, Li S, Jin B, Hou J, Zhang H,
Shi M and Liu Z: Treatment of diabetic nephropathy with
Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F extract: A prospective,
randomized, controlled clinical trial. J Transl Med. 11:1342013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ota T, Takamura T, Ando H, Nohara E,
Yamashita H and Kobayashi K: Preventive effect of cerivastatin on
diabetic nephropathy through suppression of glomerular macrophage
recruitment in a rat model. Diabetologia. 46:843–851. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
He W, Kang YS, Dai C and Liu Y: Blockade
of Wnt/β-catenin signaling by paricalcitol ameliorates proteinuria
and kidney injury. J Am Soc Nephrol. 22:90–103. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fernández Fernández B, Elewa U,
Sánchez-Niño MD, Rojas-Rivera JE, Martin-Cleary C, Eqido J and
Ortiz A: 2012 update on diabetic kidney disease: The expanding
spectrum, novel pathogenic insights and recent clinical trials.
Minerva Med. 103:219–234. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang W, Zhao L, Su SQ, Xu XX and Wu YG:
Total glucosides of paeony attenuate renal tubulointerstitial
injury in STZ-induced diabetic rats: Role of Toll-like receptor 2.
J Pharmacol Sci. 125:59–67. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Li Z, Xu J, Xu P, Liu S and Yang Z:
Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway mediates high glucose induced cell
injury through activation of TRPC6 in podocytes. Cell Prolif.
46:76–85. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
He W, Dai C, Li Y, Zeng G, Monga SP and
Liu Y: Wnt/beta-catenin signaling promotes renal interstitial
fibrosis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 20:765–776. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ma R, Liu L, Liu X, Wang Y, Jiang W and Xu
L: Triptolide markedly attenuates albuminuria and podocyte injury
in an animal model of diabetic nephropathy. Exp Ther Med.
6:649–656. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ma ZJ, Zhang XN, Li L, Yang W, Wang SS,
Guo X, Sun P and Chen LM: Tripterygium glycosides tablet
ameliorates renal tubulointerstitial fibrosis via the toll-like
receptor 4/nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in high-fat
diet fed and streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. J Diabetes Res.
2015:3904282015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Gao Q, Shen W, Qin W, Zheng C, Zhang M,
Zeng C, Wang S, Wang J, Zhu X and Liu Z: Treatment of db/db
diabetic mice with triptolide: a novel therapy for diabetic
nephropathy. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 25:3539–3547. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ma RX, Zhao N and Zhang W: The effects and
mechanism of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F combination with
irbesartan on urinary podocyte excretion in diabetic nephropathy
patients. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2:469–473. 2013.(In Chinese).
|