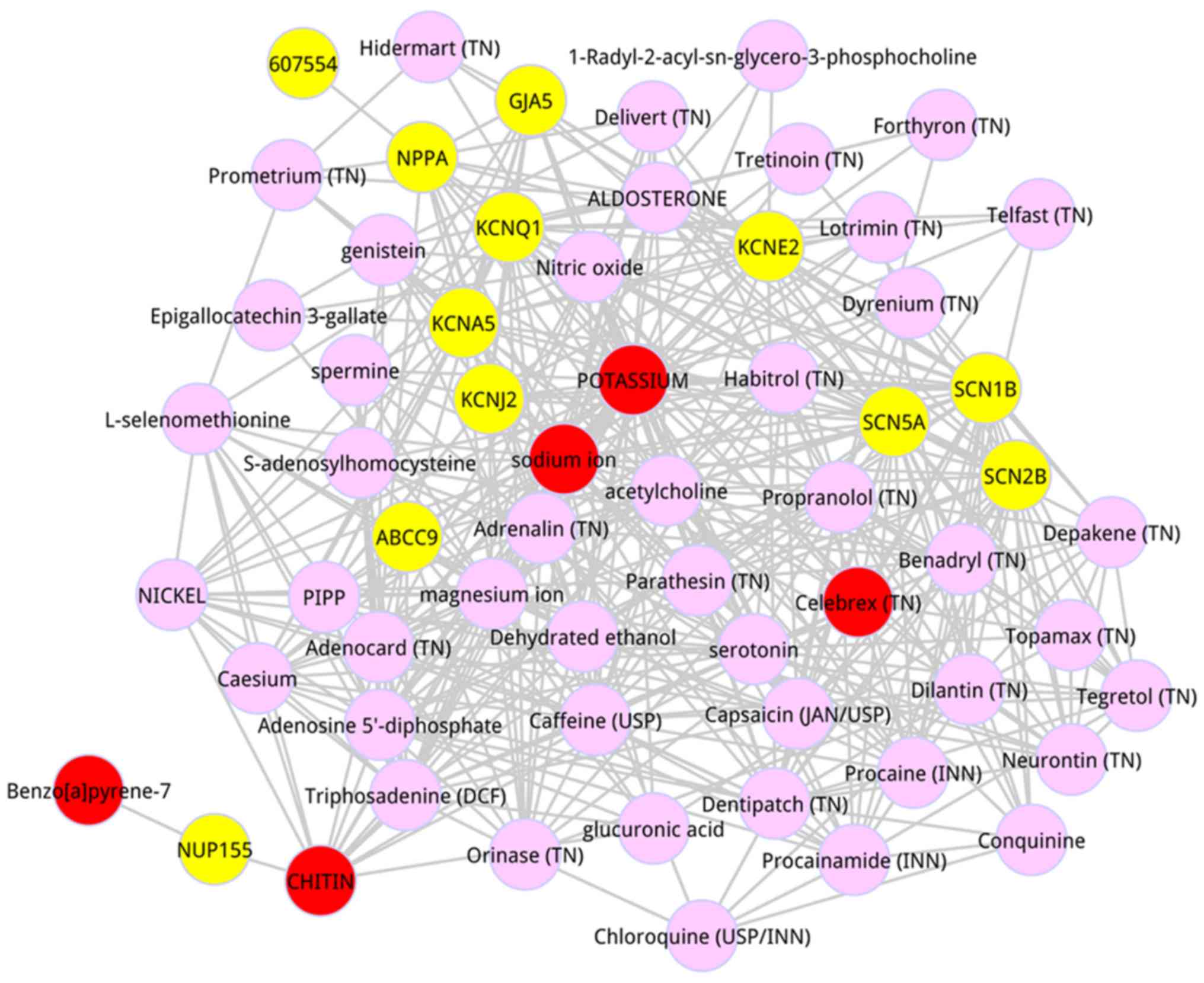
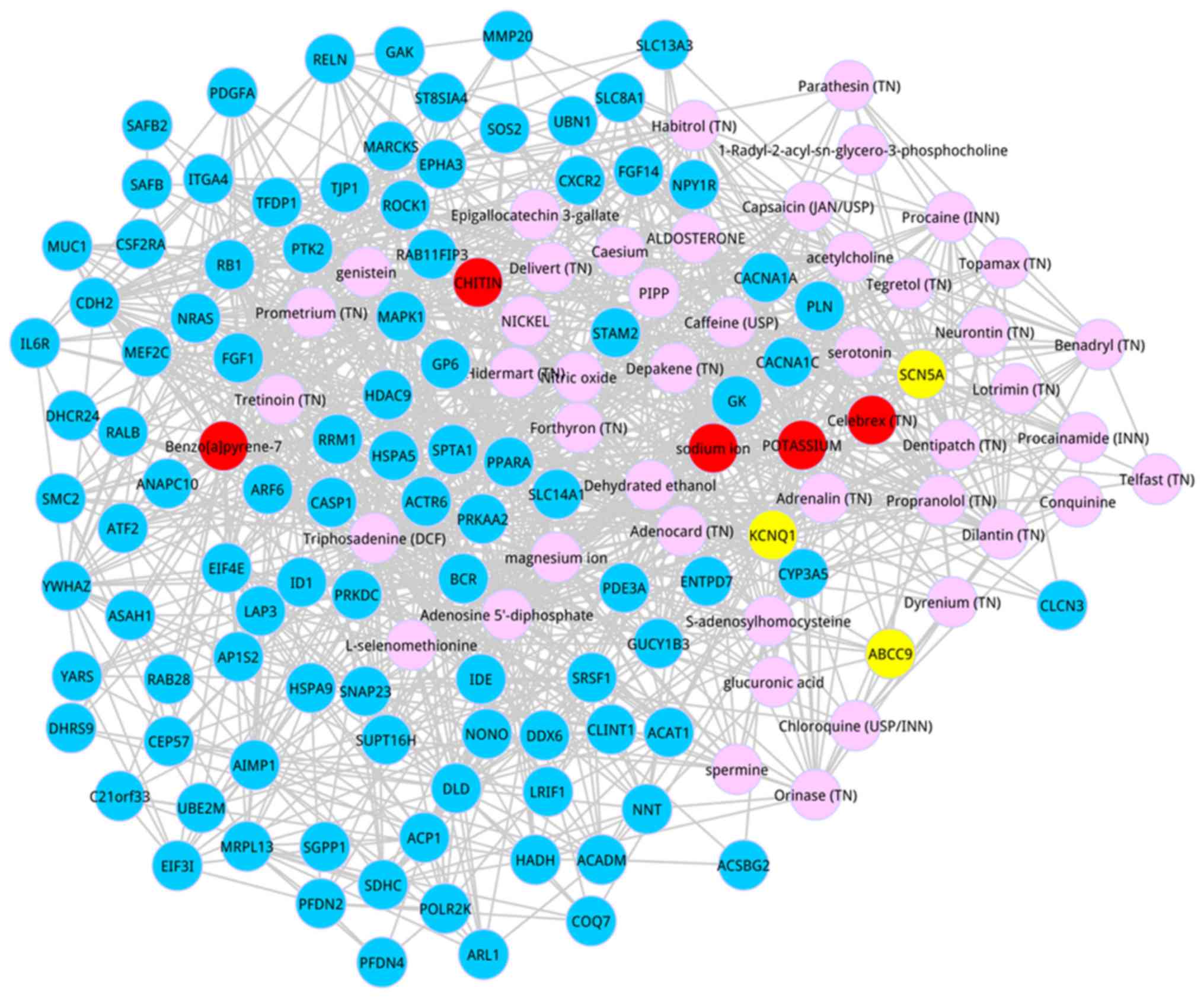
|
1
|
Mahida S: Transcription factors and atrial
fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 101:194–202. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Santulli G and Totary-Jain H: Tailoring
mTOR-based therapy: Molecular evidence and clinical challenges.
Pharmacogenomics. 14:1517–1526. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Thomas IC and Sorrentino MJ: Bleeding risk
prediction models in atrial fibrillation. Curr Cardiol Rep.
16:4322014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Garg A and Akoum N: Atrial fibrillation
and heart failure: Beyond the heart rate. Curr Opin Cardiol.
28:332–336. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Santulli G, Iaccarino G, De Luca N,
Trimarco B and Condorelli G: Atrial fibrillation and microRNAs.
Front Physiol. 5:152014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fiehn O: Metabolomics - the link between
genotypes and phenotypes. Plant Mol Biol. 48:155–171. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nicholson JK and Wilson ID: Opinion:
Understanding ‘global’ systems biology: Metabonomics and the
continuum of metabolism. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2:668–676. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Holmes E, Wilson ID and Nicholson JK:
Metabolic phenotyping in health and disease. Cell. 134:714–717.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ritchie MD, Holzinger ER, Li R,
Pendergrass SA and Kim D: Methods of integrating data to uncover
genotype-phenotype interactions. Nat Rev Genet. 16:85–97. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Blekherman G, Laubenbacher R, Cortes DF,
Mendes P, Torti FM, Akman S, Torti SV and Shulaev V: Bioinformatics
tools for cancer metabolomics. Metabolomics. 7:329–343. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tsai FC, Lin YC, Chang SH, Chang GJ, Hsu
YJ, Lin YM, Lee YS, Wang CL and Yeh YH: Differential left-to-right
atria gene expression ratio in human sinus rhythm and atrial
fibrillation: Implications for arrhythmogenesis and thrombogenesis.
Int J Cardiol. 222:104–112. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Benjamini Y, Drai D, Elmer G, Kafkafi N
and Golani I: Controlling the false discovery rate in behavior
genetics research. Behav Brain Res. 125:279–284. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Xia J and Wishart DS: MSEA: A web-based
tool to identify biologically meaningful patterns in quantitative
metabolomic data. Nucleic Acids Res 38 (Web Server). W71–7. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Jewison T, Su Y, Disfany FM, Liang Y, Knox
C, Maciejewski A, Poelzer J, Huynh J, Zhou Y, Arndt D, et al: SMPDB
2.0: Big improvements to the Small Molecule Pathway Database.
Nucleic Acids Res. 42:478–484. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Kuhn M, Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A,
Campillos M, von Mering C, Jensen LJ, Beyer A and Bork P: STITCH 2:
An interaction network database for small molecules and proteins.
Nucleic Acids Res. 38:552–556. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
van Driel MA, Bruggeman J, Vriend G,
Brunner HG and Leunissen JA: A text-mining analysis of the human
phenome. Eur J Hum Genet. 14:535–542. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yao Q, Xu Y, Yang H, Shang D, Zhang C,
Zhang Y, Sun Z, Shi X, Feng L, Han J, et al: Global prioritization
of disease candidate metabolites based on a multi-omics composite
network. Sci Rep. 5:172012015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wu X, Jiang R, Zhang MQ and Li S:
Network-based global inference of human disease genes. Mol Syst
Biol. 4:1892008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Macdonald JE and Struthers AD: What is the
optimal serum potassium level in cardiovascular patients? J Am Coll
Cardiol. 43:155–161. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Atienza F, Almendral J, Moreno J,
Vaidyanathan R, Talkachou A, Kalifa J, Arenal A, Villacastín JP,
Torrecilla EG, Sánchez A, et al: Activation of inward rectifier
potassium channels accelerates atrial fibrillation in humans:
Evidence for a reentrant mechanism. Circulation. 114:2434–2442.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gaborit N, Steenman M, Lamirault G, Le
Meur N, Le Bouter S, Lande G, Léger J, Charpentier F, Christ T,
Dobrev D, et al: Human atrial ion channel and transporter subunit
gene-expression remodeling associated with valvular heart disease
and atrial fibrillation. Circulation. 112:471–481. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nattel S, Maguy A, Le Bouter S and Yeh YH:
Arrhythmogenic ion-channel remodeling in the heart: Heart failure,
myocardial infarction, and atrial fibrillation. Physiol Rev.
87:425–456. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wakili R, Voigt N, Kääb S, Dobrev D and
Nattel S: Recent advances in the molecular pathophysiology of
atrial fibrillation. J Clin Invest. 121:2955–2968. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Olesen MS, Bentzen BH, Nielsen JB,
Steffensen AB, David JP, Jabbari J, Jensen HK, Haunsø S, Svendsen
JH and Schmitt N: Mutations in the potassium channel subunit KCNE1
are associated with early-onset familial atrial fibrillation. BMC
Med Genet. 13:242012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Linz D, Schotten U, Neuberger H, Böhm M
and Wirth K: Combined blockade of early and late activated atrial
potassium currents suppresses atrial fibrillation in a pig model of
obstructive apnea. Heart rhythm. 8:1933–1999. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Darbar D, Kannankeril PJ, Donahue BS,
Kucera G, Stubblefield T, Haines JL, George AL Jr and Roden DM:
Cardiac sodium channel (SCN5A) variants associated with atrial
fibrillation. Circulation. 117:1927–1935. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Nattel S: New ideas about atrial
fibrillation 50 years on. Nature. 415:219–226. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Terrenoire C, Simhaee D and Kass RS: Role
of sodium channels in propagation in heart muscle: How subtle
genetic alterations result in major arrhythmic disorders. J
Cardiovasc Electrophysiol. 18:900–905. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Opacic D, van Bragt KA, Nasrallah HM,
Schotten U and Verheule S: Atrial metabolism and tissue perfusion
as determinants of electrical and structural remodelling in atrial
fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res. 109:527–541. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Watanabe H, Darbar D, Kaiser DW,
Jiramongkolchai K, Chopra S, Donahue BS, Kannankeril PJ and Roden
DM: Mutations in sodium channel β1- and β2-subunits associated with
atrial fibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2:268–275. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|