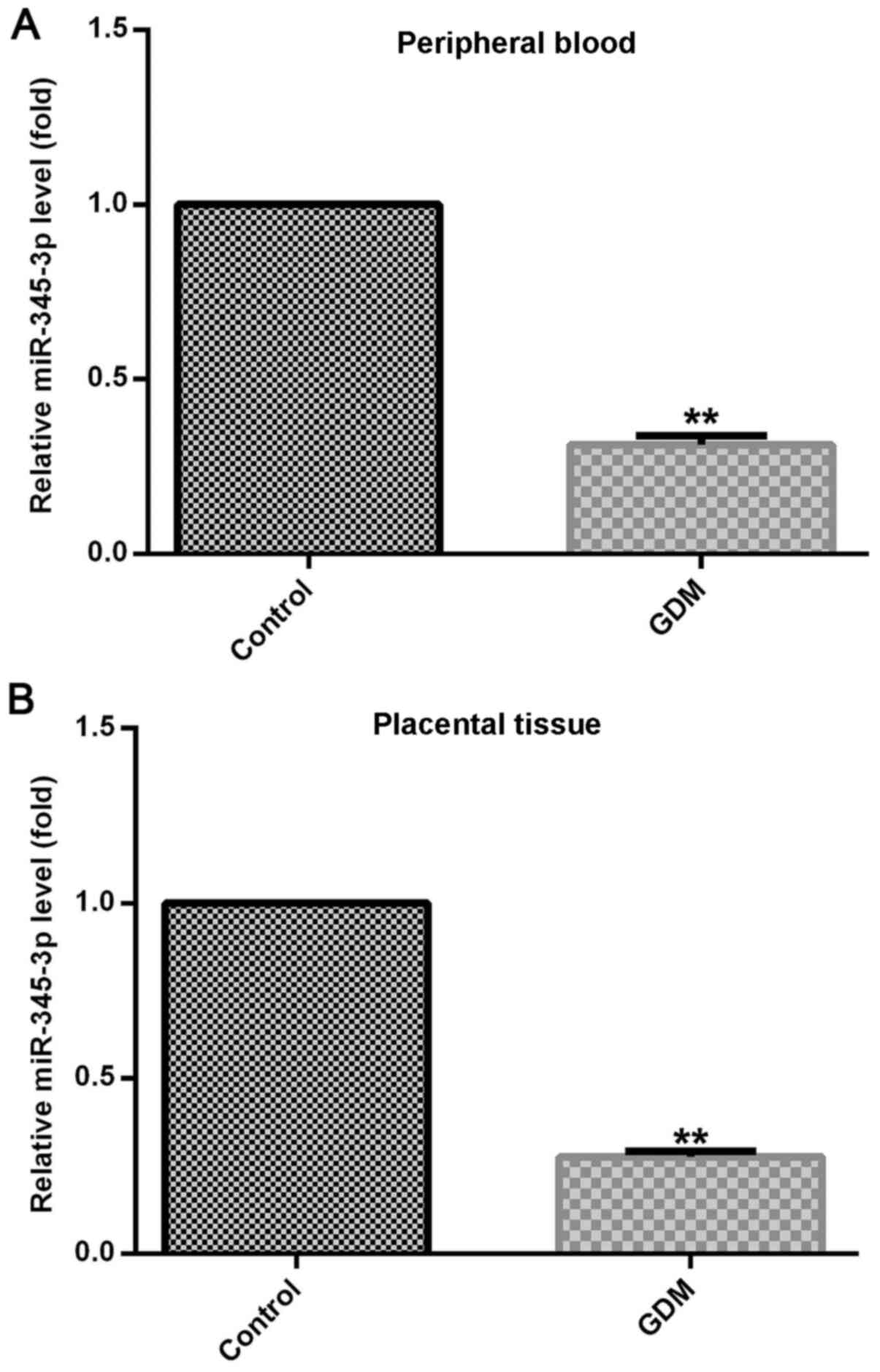
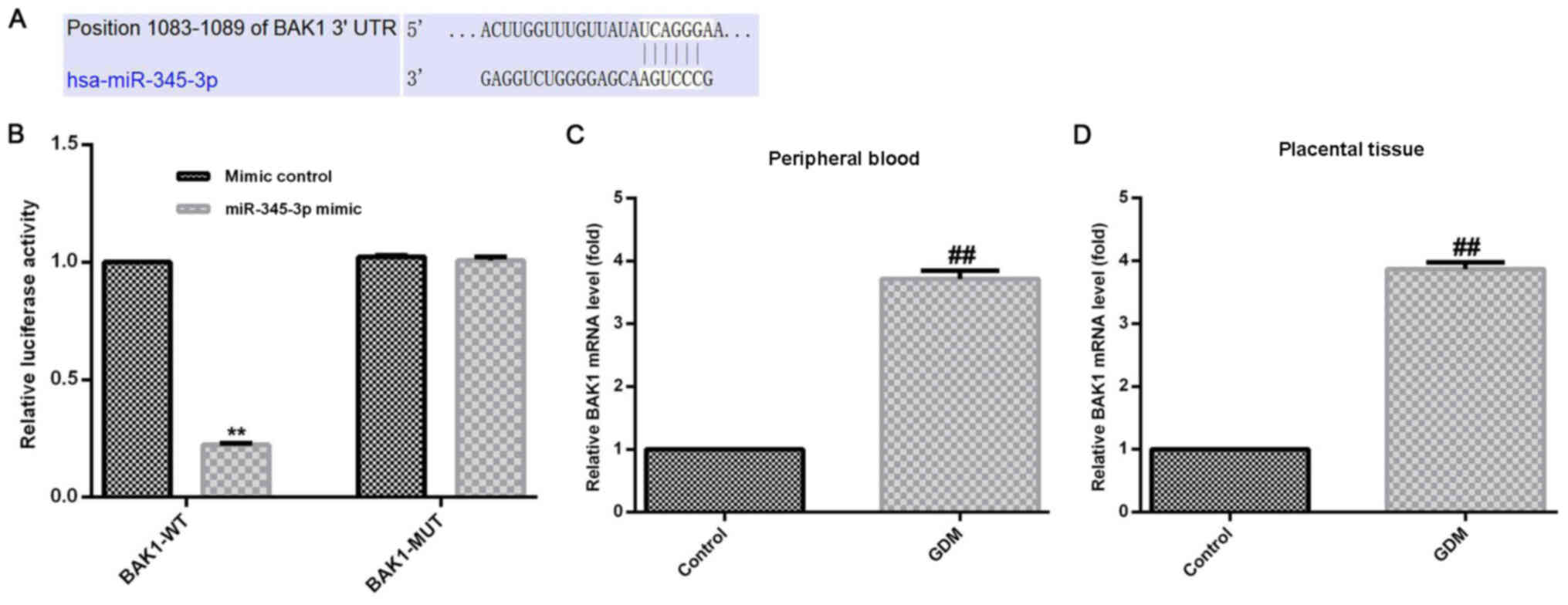
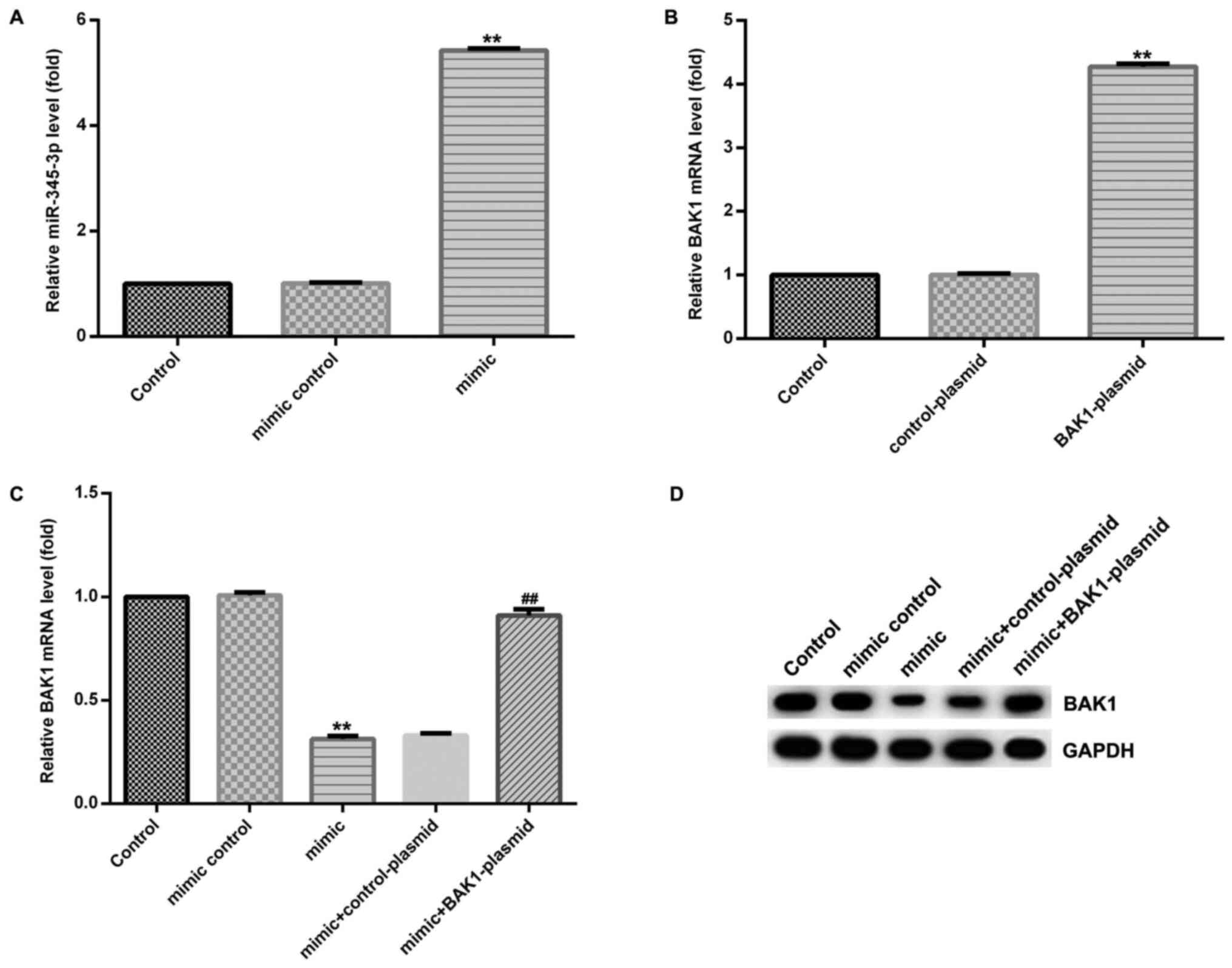
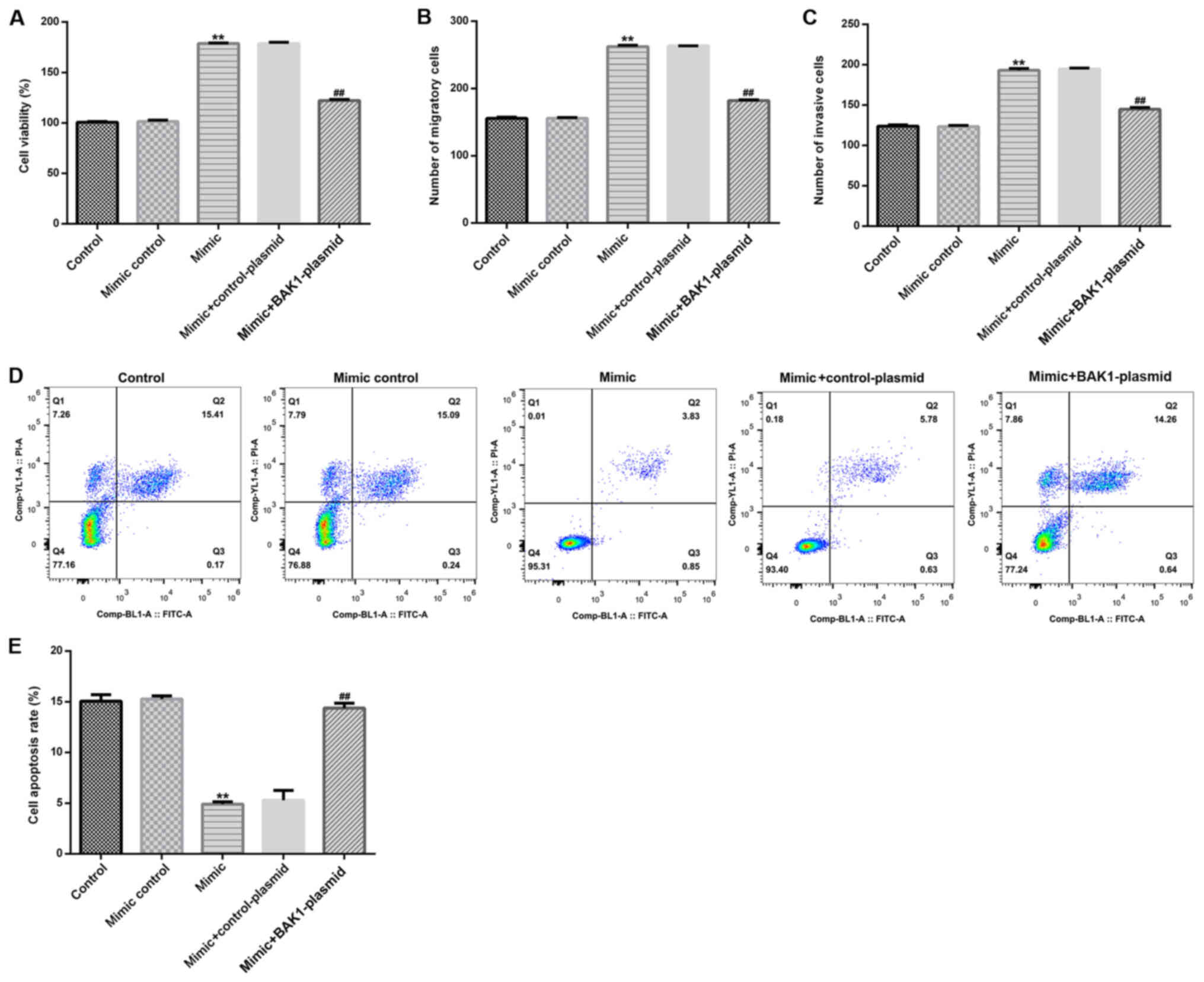
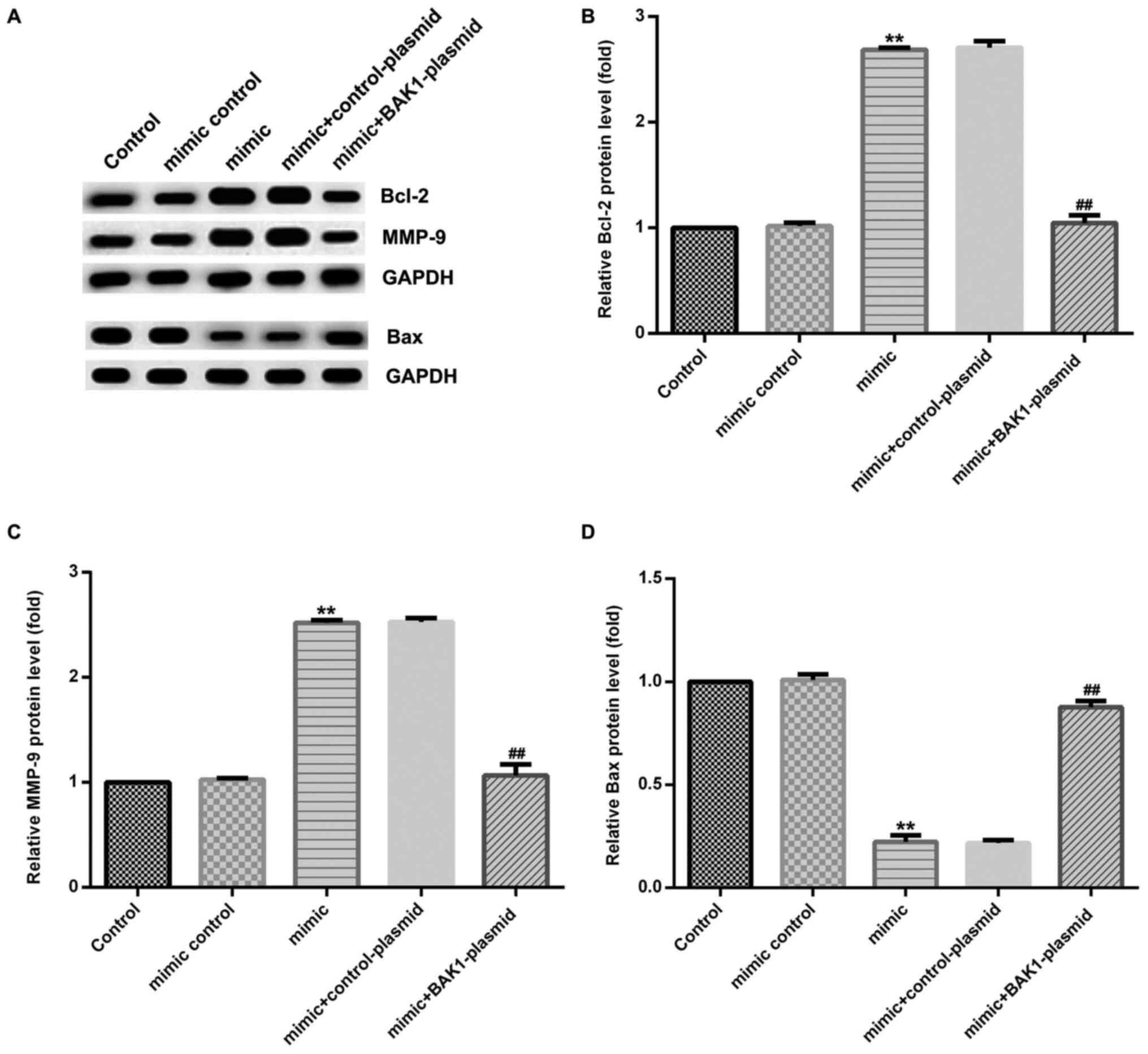
|
1
|
Metzger BE and Coustan DR: Summary and
recommendations of the Fourth International Workshop-Conference on
Gestational Diabetes Mellitus. The Organizing Committee. Diabetes
Care. 21 (Suppl 2):B161–B167. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Chiefari E, Arcidiacono B, Foti D and
Brunetti A: Gestational diabetes mellitus: An updated overview. J
Endocrinol Invest. 40:899–909. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhu Y and Zhang C: Prevalence of
gestational diabetes and risk of progression to type 2 diabetes: A
global perspective. Curr Diab Rep. 16(7)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yuen L and Wong VW: Gestational diabetes
mellitus: Challenges for different ethnic groups. World J Diabetes.
6:1024–1032. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Egan AM, Bogdanet D, Griffin TP,
Kgosidialwa O, Cervar-Zivkovic M, Dempsey E, Allotey J, Alvarado F,
Clarson C, Cooray SD, et al: A core outcome set for studies of
gestational diabetes mellitus prevention and treatment.
Diabetologia: Mar 20, 2020 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
6
|
Tryggestad JB, Vishwanath A, Jiang S,
Mallappa A, Teague AM, Takahashi Y, Thompson DM and Chernausek SD:
Influence of gestational diabetes mellitus on human umbilical vein
endothelial cell miRNA. Clin Sci (Lond). 21:1955–1967.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gabbay-Benziv R and Baschat AA:
Gestational diabetes as one of the ‘great obstetrical
syndromes’-The maternal, placental, and fetal dialog. Best Pract
Res Clin Obstet Gynaecol. 29:150–155. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Winship A, Sorby K, Correia J, Rainczuk A,
Yap J and Dimitriadis E: Interleukin-11 up-regulates endoplasmic
reticulum stress induced target, PDIA4 in human first trimester
placenta and in vivo in mice. Placenta. 53:92–100. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Antoniotti GS, Coughlan M, Salamonsen LA
and Evans J: Obesity associated advanced glycation end products
within the human uterine cavity adversely impact endometrial
function and embryo implantation competence. Hum Reprod.
33:654–665. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Graham CH, Hawley TS, Hawley RG,
MacDougall JR, Kerbel RS, Khoo N and Lala PK: Establishment and
characterization of first trimester human trophoblast cells with
extended lifespan. Exp Cell Res. 206:204–211. 1993.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Monfared YK, Ghadimi F, Foroughi F,
Honardoost M, Hashemipour S, Sefidi F and Sarookhani MR:
Determination and comparison miR135a in the serum between women
with GDM, non-pregnant type 2 diabetes, healthy pregnant and
control group. Middle East J Fam Med. 2:193–197. 2018.
|
|
12
|
Eminaga O, Fries J, Woetzel F, Alakus H,
Warnecke-Eberz U and Heidenreich A: MP66-12 the expression profiles
of miR-210, miR-375, miR-378, miR-345, miR-143 miR-183 and miR-98
in the progression of prostate cancer from high-grade prostatic
intraepithelial neoplasia to metastatic diseases. J Urology.
4(e877)2016.
|
|
13
|
Mou T, Xie F, Zhong P, Hua H, Lai L, Yang
Q and Wang J: MiR-345-5p functions as a tumor suppressor in
pancreatic cancer by directly targeting CCL8. Biomed Pharmacother.
111:891–900. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Danese E, Minicozzi AM, Benati M, Paviati
E, Lima-Oliveira G, Gusella M, Pasini F, Salvagno GL, Montagnana M
and Lippi G: Reference miRNAs for colorectal cancer: Analysis and
verification of current data. Sci Rep. 7(8413)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Ying X, Zhang W, Fang M, Zhang W, Wang C
and Han L: miR-345-5p regulates proliferation, cell cycle, and
apoptosis of acute myeloid leukemia cells by targeting AKT2. J Cell
Biochem. 2:1620–1629. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wang SY, Shiboski S, Belair CD, Cooperberg
MR, Simko JP, Stoppler H, Cowan J, Carroll PR and Blelloch R:
MiR-19, miR-345, miR-519c-5p serum levels predict adverse pathology
in prostate cancer patients eligible for active surveillance. PLoS
One. 6(e98597)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Tinay I, Tan M, Gui B, Werner L, Kibel AS
and Jia L: Functional roles and potential clinical application of
miRNA-345-5p in prostate cancer. Prostate. 78:927–937.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Srivastava SK, Bhardwaj A, Arora S, Tyagi
N, Singh S, Andrews J, McClellan S, Wang B and Singh AP:
MicroRNA-345 induces apoptosis in pancreatic cancer cells through
potentiation of caspase-dependent and -independent pathways. Brit J
Cancer. 113:660–668. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Tinay I, Gui B, Werner L, Rafiei S,
Gelpi-Hammerschmidt F, Kibel A and Jia L: 24-Upregulation of
microRNAs miR-9, miR-330-3p and miR-345 in prostate cancer. Eur
Urol Suppl. 15:e1286–e1287. 2016.
|
|
20
|
Siengdee P, Trakooljul N, Murani E,
Schwerin M, Wimmers K and Ponsuksili S: MicroRNAs regulate cellular
ATP levels by targeting mitochondrial energy metabolism genes
during C2C12 myoblast differentiation. PLoS One.
10(e0127850)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using realtime quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Uren RT, O'Hely M, Iyer S, Bartolo R, Shi
MX, Brouwer JM, Alsop AE, Dewson G and Kluck RM: Disordered
clusters of Bak dimers rupture mitochondria during apoptosis.
Elife. 6(pii: 19944)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Loegl J, Nussbaumer E, Cvitic S, Huppertz
B, Desoye G and Hiden U: GDM alters paracrine regulation of
feto-placental angiogenesis via the trophoblast. Lab Invest.
97:409–418. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Mohr AM and Mott JL: Overview of microRNA
biology. Semin Liver Dis. 35:3–11. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Lu TX and Rothenberg ME: MicroRNA. J
Allergy Clin Immunol. 141:1202–1207. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li J, Song L, Zhou L, Wu J, Sheng C, Chen
H, Liu Y, Gao S and Huang W: A MicroRNA signature in gestational
diabetes mellitus associated with risk of macrosomia. Cell Physiol
Bioche. 1:243–252. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Erener S, Marwaha A, Tan R,
Panagiotopoulos C and Kieffer TJ: Profiling of circulating
microRNAs in children with recent onset of type 1 diabetes. JCI
Insight. 4(e89656)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Silva VA, Polesskaya A, Sousa TA, Corrêa
VM, André ND, Reis RI, Kettelhut IC, Harel-Bellan A and De Lucca
FL: Expression and cellular localization of microRNA-29b and RAX,
an activator of the RNA-dependent protein kinase (PKR), in the
retina of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Mol Vis.
17:2228–2240. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chen HY, Zhong X, Huang XR, Meng XM, You
Y, Chung AC and Lan HY: MicroRNA-29b inhibits diabetic nephropathy
in db/db mice. Mol Ther. 22:842–853. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Knöfler M, Haider S, Saleh L, Pollheimer
J, Gamage TKJB and James J: Human placenta and trophoblast
development: Key molecular mechanisms and model systems. Cell Mol
Life Sci. 76:3479–3496. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Pollheimer J, Vondra S, Baltayeva J,
Beristain AG and Knöfler M: Regulation of placental extravillous
trophoblasts by the maternal uterine environment. Front Immunol.
9(2597)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Haider S, Meinhardt G, Saleh L, Kunihs V,
Gamperl M, Kaindl U, Ellinger A, Burkard TR, Fiala C, Pollheimer J,
et al: Self-renewing trophoblast organoids recapitulate the
developmental program of the early human placenta. Stem Cell
Reports. 11:537–551. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Wang X, Peng S, Cui K, Hou F, Ding J, Li
A, Wang M and Geng L: MicroRNA-576-5p enhances the invasion ability
of trophoblast cells in preeclampsia by targeting TFAP2A. Mol Genet
Genomic Med. 8(e1025)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Baines KJ and Renaud SJ: Transcription
factors that regulate trophoblast development and function. Prog
Mol Biol Transl Sci. 145:39–88. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Aplin JD: Developmental cell biology of
human villous trophoblast: Current research problems. Int J Dev
Biol. 54:323–329. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Meekins JW, Pijnenborg R, Hanssens M,
McFadyen IR and van Asshe A: A study of placental bed spiral
arteries and trophoblast invasion in normal and severe
pre-eclamptic pregnancies. Brit J Obstet Gynaec. 8:669–674.
1994.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Mayama R, Izawa T, Sakai K, Suciu N and
Iwashita M: Improvement of insulin sensitivity promotes
extravillous trophoblast cell migration stimulated by insulin-like
growth factor-I. Endocr J. 60:359–368. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Aires MB and Anne Carolline Veríssimo dos
Santos: Effects of maternal diabetes on trophoblast cells. World J
Diabetes. 6:338–344. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|