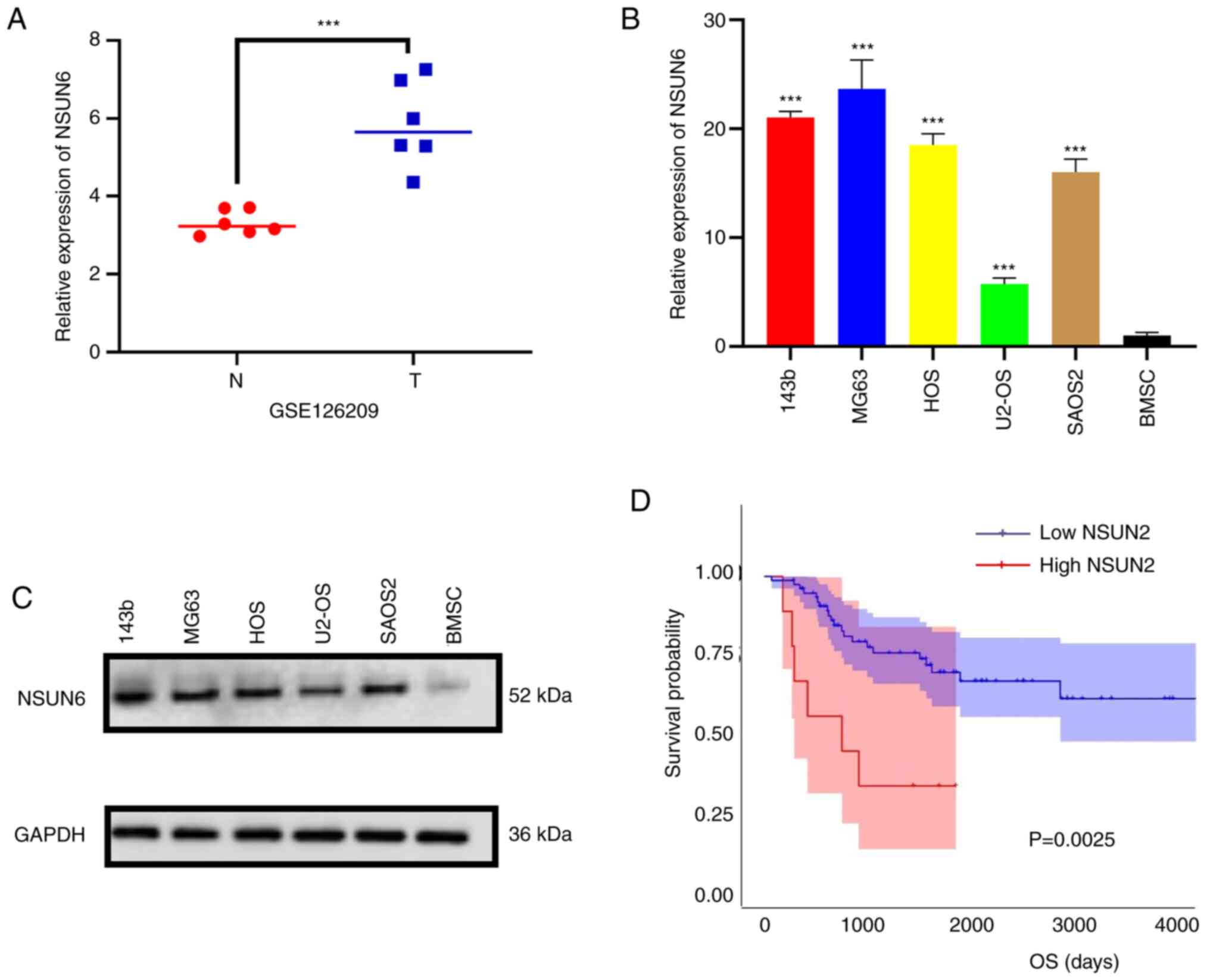
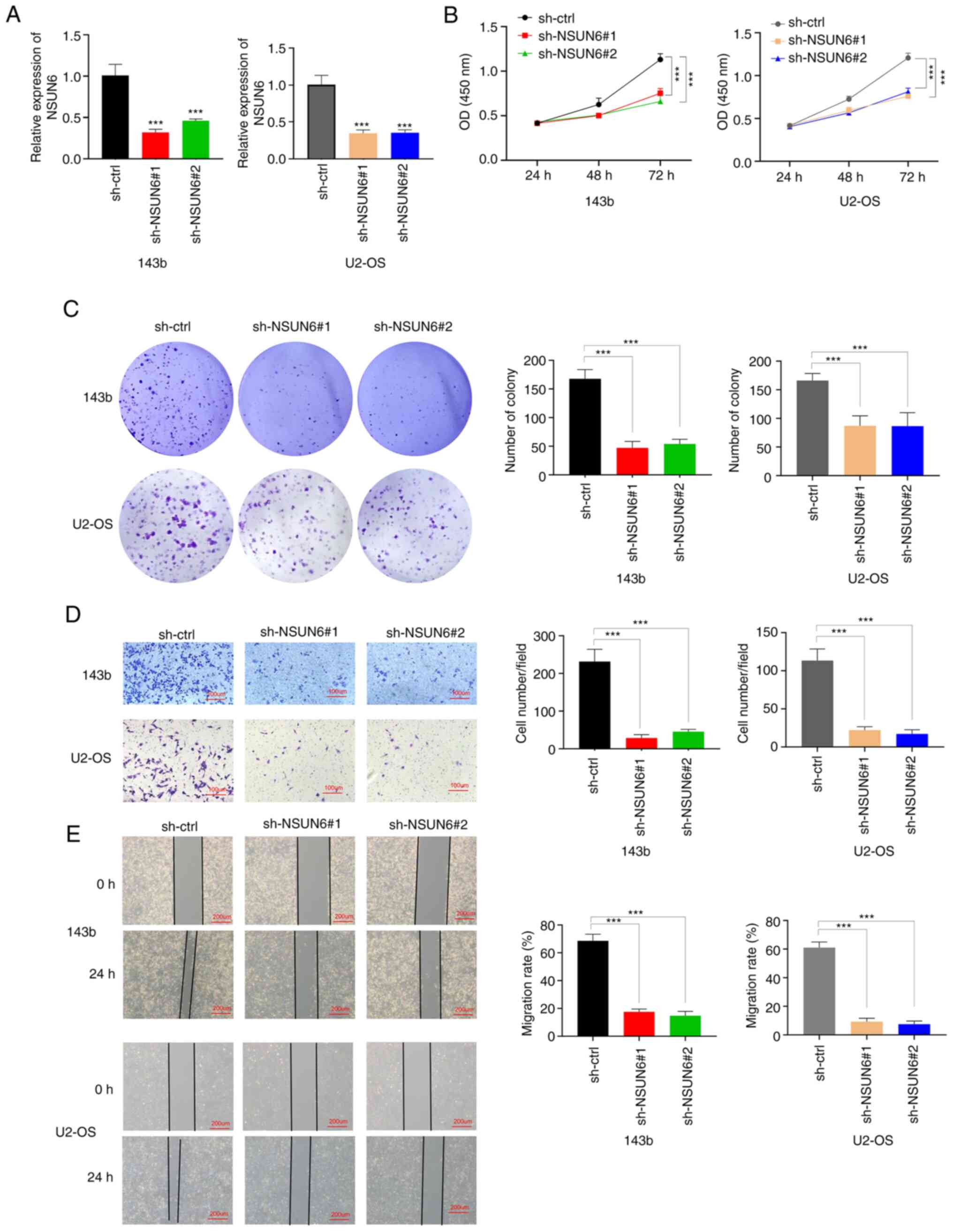
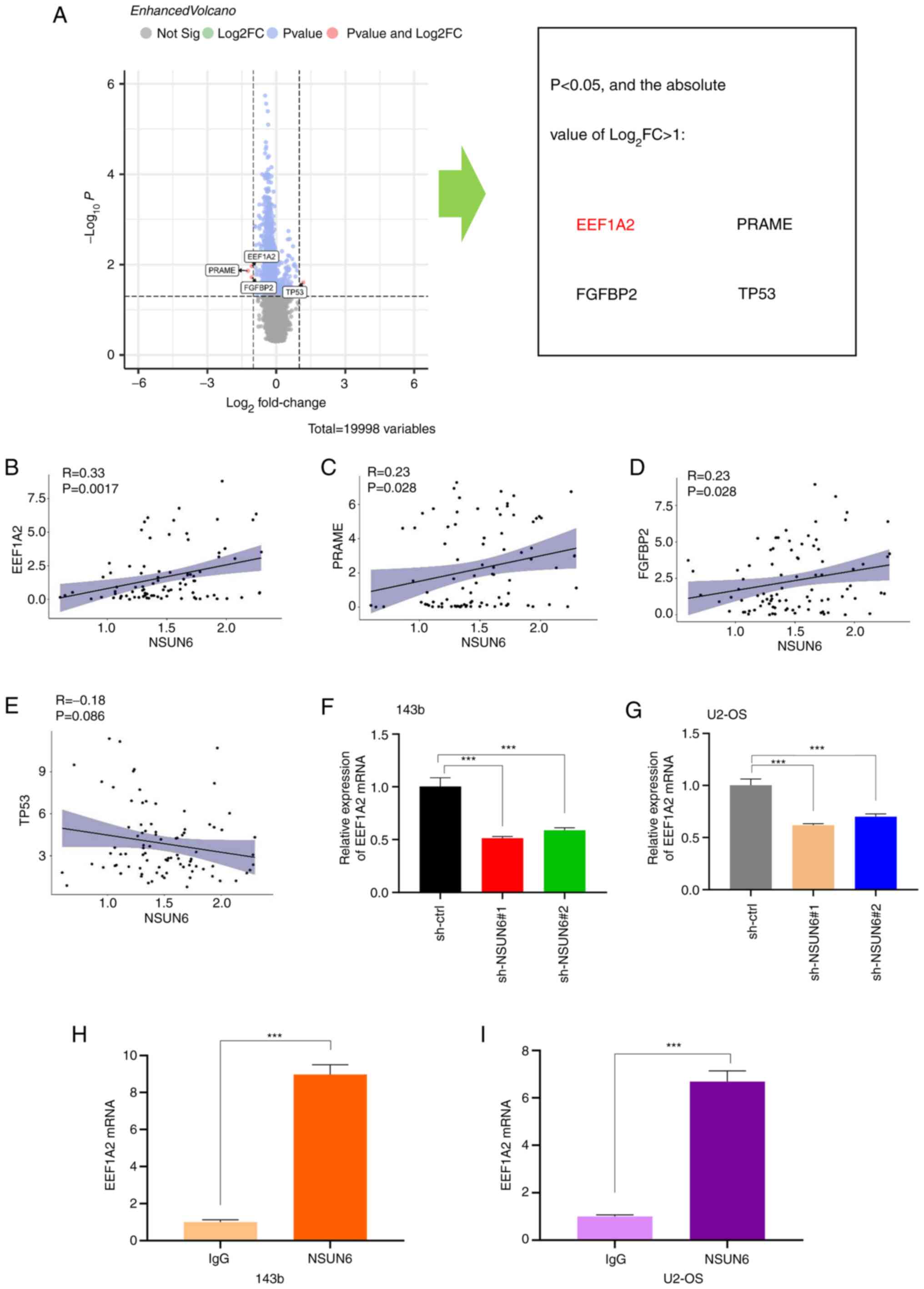
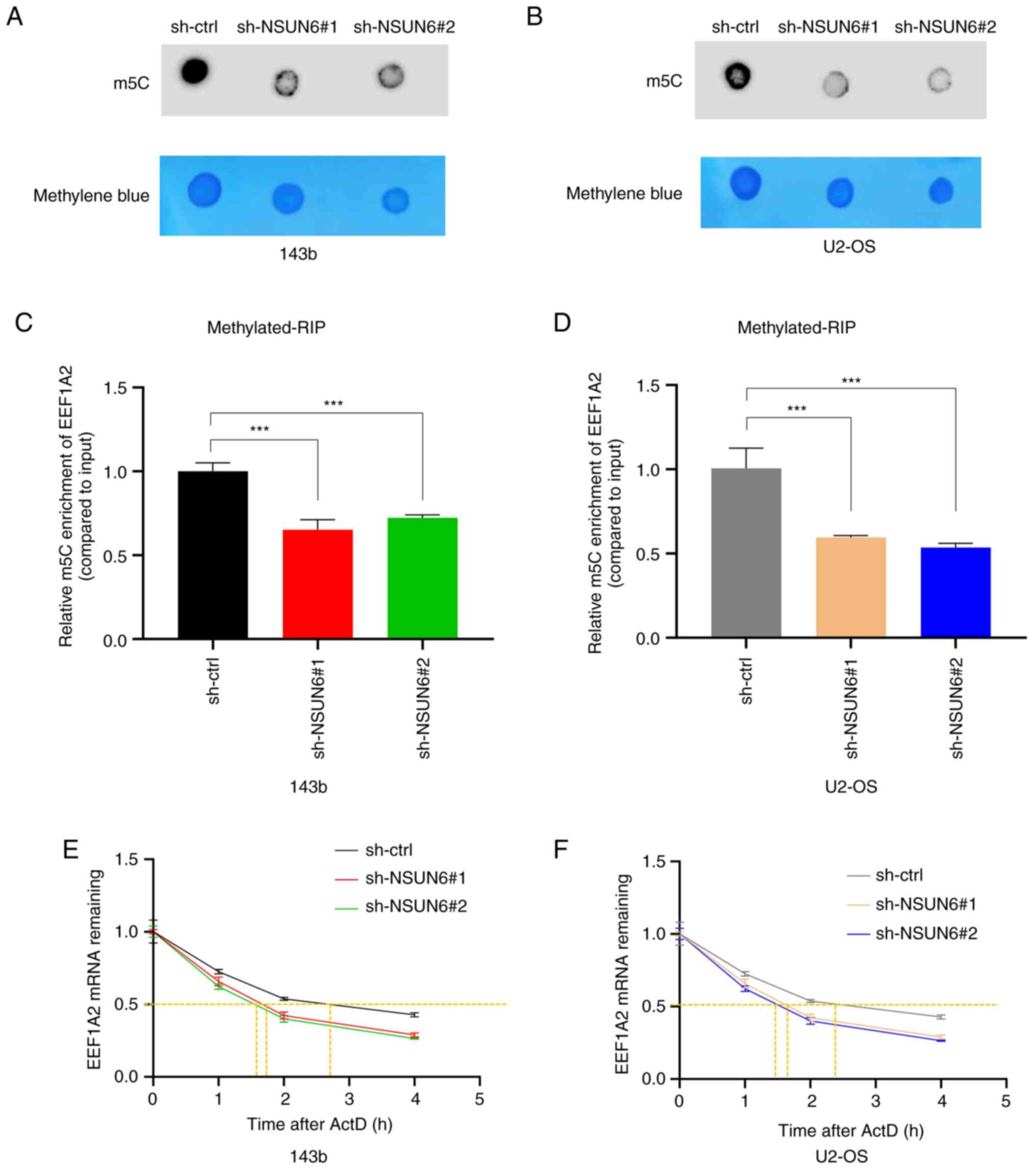
|
1
|
Durfee RA, Mohammed M and Luu HH: Review
of osteosarcoma and current management. Rheumatol Ther. 3:221–243.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Li S, Zhang H, Liu J and Shang G: Targeted
therapy for osteosarcoma: A review. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol: Feb
18, 2023 (Epub ahead of print).
|
|
3
|
Chen S, Li Y, Zhi S, Ding Z, Wang W, Peng
Y, Huang Y, Zheng R, Yu H, Wang J, et al: WTAP promotes
osteosarcoma tumorigenesis by repressing HMBOX1 expression in an
m6A-dependent manner. Cell Death Dis.
11(659)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Xie L, Yao Z, Zhang Y, Li D, Hu F, Liao Y,
Zhou L, Zhou Y, Huang Z, He Z, et al: Deep RNA sequencing reveals
the dynamic regulation of miRNA, lncRNAs, and mRNAs in osteosarcoma
tumorigenesis and pulmonary metastasis. Cell Death Dis.
9(772)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jafari F, Javdansirat S, Sanaie S, Naseri
A, Shamekh A, Rostamzadeh D and Dolati S: Osteosarcoma: A
comprehensive review of management and treatment strategies. Ann
Diagn Pathol. 49(151654)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Wang B, Yao L, Dong Y, Liu J and Wu J:
LncRNA PCED1B-AS1 knockdown inhibits osteosarcoma via
methylation-mediated miR-10a downregulation. J Orthop Surg Res.
17(464)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Tsukamoto S, Righi A, Kido A, Honoki K,
Tanaka Y, Fujii H, Mavrogenis AF, Tanaka Y and Errani C: Effect of
adjuvant chemotherapy on periosteal osteosarcoma: A systematic
review. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 52:896–904. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Liu W, Zhao Y, Wang G, Feng S, Ge X, Ye W,
Wang Z, Zhu Y, Cai W, Bai J and Zhou X: TRIM22 inhibits
osteosarcoma progression through destabilizing NRF2 and thus
activation of ROS/AMPK/mTOR/autophagy signaling. Redox Biol.
53(102344)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Lin H, Chen X, Zhang C, Yang T, Deng Z,
Song Y, Huang L, Li F, Li Q, Lin S and Jin D: EF24 induces
ferroptosis in osteosarcoma cells through HMOX1. Biomed
Pharmacother. 136(111202)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Xiao X, Wang W, Li Y, Yang D, Li X, Shen
C, Liu Y, Ke X, Guo S and Guo Z: HSP90AA1-mediated autophagy
promotes drug resistance in osteosarcoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res.
37(201)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Liu Q and Wang K: The induction of
ferroptosis by impairing STAT3/Nrf2/GPx4 signaling enhances the
sensitivity of osteosarcoma cells to cisplatin. Cell Biol Int.
43:1245–1256. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Dong S, Wu Y, Liu Y, Weng H and Huang H:
N6 -methyladenosine steers RNA metabolism and regulation
in cancer. Cancer Commun (Lond). 41:538–559. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kumar VE, Nambiar R, De Souza C, Nguyen A,
Chien J and Lam KS: Targeting epigenetic modifiers of tumor
plasticity and cancer stem cell behavior. Cells.
11(1403)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Nacev BA, Jones KB, Intlekofer AM, Yu JSE,
Allis CD, Tap WD, Ladanyi M and Nielsen TO: The epigenomics of
sarcoma. Nat Rev Cancer. 20:608–623. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Yang B, Wang JQ, Tan Y, Yuan R, Chen ZS
and Zou C: RNA methylation and cancer treatment. Pharmacol Res.
174(105937)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Han X, Wang M, Zhao YL, Yang Y and Yang
YG: RNA methylations in human cancers. Semin Cancer Biol.
75:97–115. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Dominissini D and Rechavi G:
5-methylcytosine mediates nuclear export of mRNA. Cell Res.
27:717–719. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Garcia-Vilchez R, Sevilla A and Blanco S:
Post-transcriptional regulation by cytosine-5 methylation of RNA.
Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech. 1862:240–252. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Xue C, Zhao Y and Li L: Advances in RNA
cytosine-5 methylation: Detection, regulatory mechanisms,
biological functions and links to cancer. Biomark Res.
8(43)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yang X, Yang Y, Sun BF, Chen YS, Xu JW,
Lai WY, Li A, Wang X, Bhattarai DP, Xiao W, et al: 5-methylcytosine
promotes mRNA export-NSUN2 as the methyltransferase and ALYREF as
an m5C reader. Cell Res. 27:606–625. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Chellamuthu A and Gray SG: The RNA
methyltransferase NSUN2 and its potential roles in cancer. Cells.
9(1758)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Zhang Q, Liu F, Chen W, Miao H, Liang H,
Liao Z, Zhang Z and Zhang B: The role of RNA m5C
modification in cancer metastasis. Int J Biol Sci. 17:3369–3380.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Sun Z, Xue S, Zhang M, Xu H, Hu X, Chen S,
Liu Y, Guo M and Cui H: Aberrant NSUN2-mediated m5C
modification of H19 lncRNA is associated with poor differentiation
of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncogene. 39:6906–6919.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen X, Li A, Sun BF, Yang Y, Han YN, Yuan
X, Chen RX, Wei WS, Liu Y, Gao CC, et al: 5-methylcytosine promotes
pathogenesis of bladder cancer through stabilizing mRNAs. Nat Cell
Biol. 21:978–990. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Gao Y, Wang Z, Zhu Y, Zhu Q, Yang Y, Jin
Y, Zhang F, Jiang L, Ye Y, Li H, et al: NOP2/Sun RNA
methyltransferase 2 promotes tumor progression via its interacting
partner RPL6 in gallbladder carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 110:3510–3519.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Hu Y, Chen C, Tong X, Chen S, Hu X, Pan B,
Sun X, Chen Z, Shi X, Hu Y, et al: NSUN2 modified by SUMO-2/3
promotes gastric cancer progression and regulates mRNA m5C
methylation. Cell Death Dis. 12(842)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Mei L, Shen C, Miao R, Wang JZ, Cao MD,
Zhang YS, Shi LH, Zhao GH, Wang MH, Wu LS and Wei JF: RNA
methyltransferase NSUN2 promotes gastric cancer cell proliferation
by repressing p57Kip2 by an m5C-dependent
manner. Cell Death Dis. 11(270)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yang R, Liang X, Wang H, Guo M, Shen H,
Shi Y, Liu Q, Sun Y, Yang L and Zhan M: The RNA methyltransferase
NSUN6 suppresses pancreatic cancer development by regulating cell
proliferation. Ebiomedicine. 63(103195)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Awah CU, Winter J, Mazdoom CM and Ogunwobi
OO: NSUN6, an RNA methyltransferase of 5-mC controls glioblastoma
response to temozolomide (TMZ) via NELFB and RPS6KB2 interaction.
Cancer Biol Ther. 22:587–597. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Blaze J, Navickas A, Phillips HL, Heissel
S, Plaza-Jennings A, Miglani S, Asgharian H, Foo M, Katanski CD,
Watkins CP, et al: Neuronal Nsun2 deficiency produces tRNA
epitranscriptomic alterations and proteomic shifts impacting
synaptic signaling and behavior. Nat Commun.
12(4913)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Lu L, Zhu G, Zeng H, Xu Q and Holzmann K:
High tRNA Transferase NSUN2 Gene expression is associated with poor
prognosis in head and neck squamous carcinoma. Cancer Invest.
36:246–253. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Haag S, Warda AS, Kretschmer J, Gunnigmann
MA, Hobartner C and Bohnsack MT: NSUN6 is a human RNA
methyltransferase that catalyzes formation of m5C72 in specific
tRNAs. RNA. 21:1532–1543. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zhou L, Yang C, Zhang N, Zhang X, Zhao T
and Yu J: Silencing METTL3 inhibits the proliferation and invasion
of osteosarcoma by regulating ATAD2. Biomed Pharmacother.
125(109964)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Zhou X, Yang Y, Li Y, Liang G, Kang D,
Zhou B and Li Q: METTL3 contributes to osteosarcoma progression by
increasing DANCR mRNA stability via m6A modification. Front Cell
Dev Biol. 9(784719)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jiang R, Dai Z, Wu J, Ji S, Sun Y and Yang
W: METTL3 stabilizes HDAC5 mRNA in an m6A-dependent
manner to facilitate malignant proliferation of osteosarcoma cells.
Cell Death Discov. 8(179)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yang M, Wei R, Zhang S, Hu S, Liang X,
Yang Z, Zhang C, Zhang Y, Cai L and Xie Y: NSUN2 promotes
osteosarcoma progression by enhancing the stability of FABP5 mRNA
via m5C methylation. Cell Death Dis.
14(125)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Yang J, Tang J, Li J, Cen Y, Chen J and
Dai G: Effect of activation of the Akt/mTOR signaling pathway by
EEF1A2 on the biological behavior of osteosarcoma. Ann Transl Med.
9(158)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Selmi T, Hussain S, Dietmann S, Heiβ M,
Borland K, Flad S, Carter JM, Dennison R, Huang YL, Kellner S, et
al: Sequence- and structure-specific cytosine-5 mRNA methylation by
NSUN6. Nucleic Acids Res. 49:1006–1022. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wu S, Zhang S, Wu X and Zhou X:
m6A RNA methylation in cardiovascular diseases. Mol
Ther. 28:2111–2119. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Shen H, Lan Y, Zhao Y, Shi Y, Jin J and
Xie W: The emerging roles of N6-methyladenosine RNA methylation in
human cancers. Biomark Res. 8(24)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wang S, Sun C, Li J, Zhang E, Ma Z, Xu W,
Li H, Qiu M, Xu Y, Xia W, et al: Roles of RNA methylation by means
of N6-methyladenosine (m6A) in human cancers.
Cancer Lett. 408:112–120. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Shinoda S, Kitagawa S, Nakagawa S, Wei FY,
Tomizawa K, Araki K, Araki M and Suzuki T and Suzuki T: Mammalian
NSUN2 introduces 5-methylcytidines into mitochondrial tRNAs.
Nucleic Acids Res. 47:8734–8745. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Auxilien S, Guerineau V,
Szweykowska-Kulinska Z and Golinelli-Pimpaneau B: The human tRNA m
(5) C methyltransferase Misu is multisite-specific. RNA Biol.
9:1331–1338. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Hussain S: The emerging roles of
cytosine-5 methylation in mRNAs. Trends Genet. 37:498–500.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Xu X, Zhang Y, Zhang J and Zhang X: NSUN2
promotes cell migration through methylating autotaxin mRNA. J Biol
Chem. 295:18134–18147. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Su J, Wu G, Ye Y, Zhang J, Zeng L, Huang
X, Zheng Y, Bai R, Zhuang L, Li M, et al: NSUN2-mediated RNA
5-methylcytosine promotes esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
progression via LIN28B-dependent GRB2 mRNA stabilization. Oncogene.
40:5814–5828. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Jia L, Ge X, Du C, Chen L, Zhou Y, Xiong
W, Xiang J, Li G, Xiao G, Fang L and Li Z: EEF1A2 interacts with
HSP90AB1 to promote lung adenocarcinoma metastasis via enhancing
TGF-β/SMAD signalling. Br J Cancer. 124:1301–1311. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Losada A, Munoz-Alonso MJ, Martinez-Diez
M, Gago F, Dominguez JM, Martinez-Leal JF and Galmarini CM: Binding
of eEF1A2 to the RNA-dependent protein kinase PKR modulates its
activity and promotes tumour cell survival. Br J Cancer.
119:1410–1420. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Sun Y, Du C, Wang B, Zhang Y, Liu X and
Ren G: Up-regulation of eEF1A2 promotes proliferation and inhibits
apoptosis in prostate cancer. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 450:1–6.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Lee MH, Choi BY, Cho YY, Lee SY, Huang Z,
Kundu JK, Kim MO, Kim DJ, Bode AM, Surh YJ, et al: Tumor suppressor
p16 (INK4a) inhibits cancer cell growth by downregulating eEF1A2
through a direct interaction. J Cell Sci. 126:1744–1752.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|