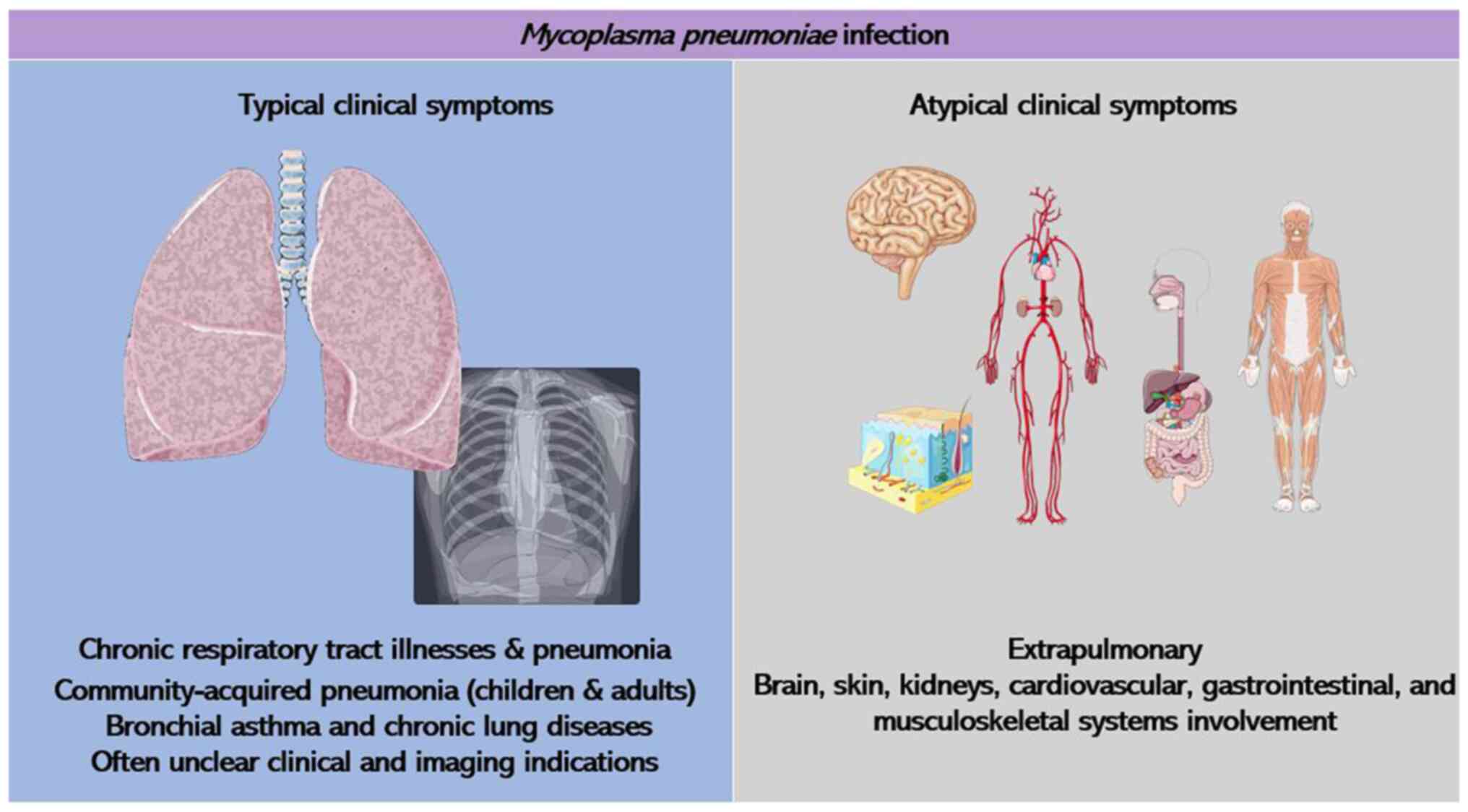
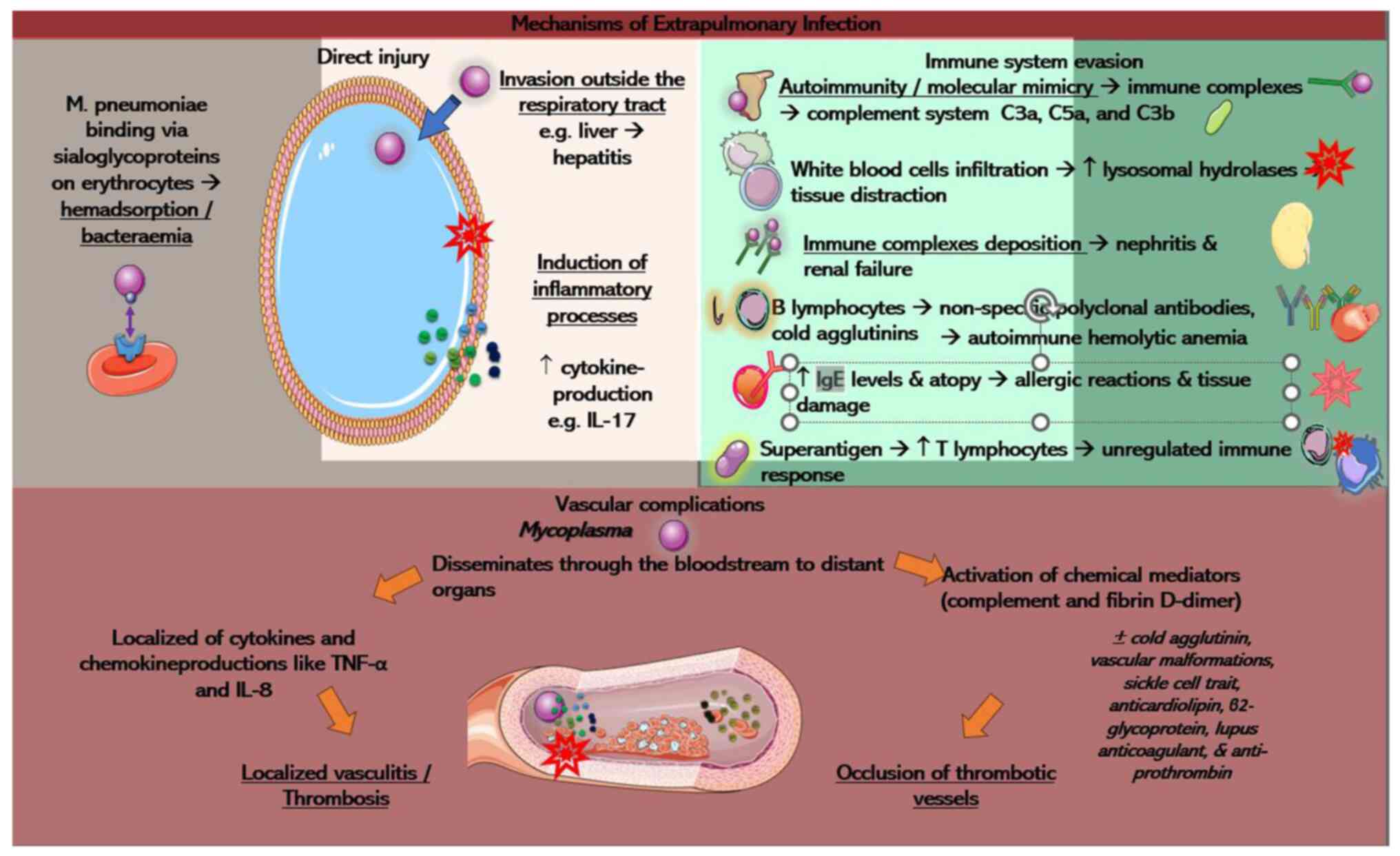
|
1
|
Zhang L, Lai M, Ai T, Liao H, Huang Y,
Zhang Y, Liu Y, Wang L and Hu J: Analysis of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae infection among children with respiratory tract
infections in hospital in Chengdu from 2014 to 2020. Transl
Pediatr. 10:990–997. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bajantri B, Venkatram S and Diaz-Fuentes
G: Mycoplasma pneumoniae: A potentially severe infection. J
Clin Med Res. 10:535–544. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lanao AE, Chakraborty RK and
Pearson-Shaver AL: Mycoplasma. Infections. In: StatPearls.
StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island, FL, 2023. Available from:
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK536927/.
|
|
4
|
Kutty PK, Jain S, Taylor TH, Bramley AM,
Diaz MH, Ampofo K, Arnold SR, Williams DJ, Edwards KM, McCullers
JA, et al: Mycoplasma pneumoniae among children hospitalized
with community-acquired pneumonia. Clin Infect Dis. 68:5–12.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Waites KB, Xiao L, Liu Y, Balish MF and
Atkinson TP: Mycoplasma pneumoniae from the respiratory
tract and beyond. Clin Microbiol Rev. 30:747–809. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Jiang Z, Li S, Zhu C, Zhou R and Leung
PHM: Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections: Pathogenesis and
vaccine development. Pathogens. 10(119)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Waites KB, Xiao L, Paralanov V, Viscardi
RM and Glass JI: Molecular methods for the detection of
Mycoplasma and ureaplasma infections in humans: A paper from
the 2011 William beaumont hospital symposium on molecular
pathology. J Mol Diagn. 14:437–450. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Poddighe D: Extra-pulmonary diseases
related to Mycoplasma pneumoniae in children: Recent
insights into the pathogenesis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 30:380–387.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
He J, Liu M, Ye Z, Tan T, Liu X, You X,
Zeng Y and Wu Y: Insights into the pathogenesis of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae (review). Mol Med Rep. 14:4030–4036. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Yamamoto T, Kida Y and Kuwano K:
Mycoplasma pneumoniae protects infected epithelial cells
from hydrogen peroxide-induced cell detachment. Cell Microbiol.
21(e13015)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Nakane D, Murata K, Kenri T, Shibayama K
and Nishizaka T: Molecular ruler of the attachment organelle in
Mycoplasma pneumoniae. PLoS Pathog.
17(e1009621)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Williams CR, Chen L, Sheppard ES, Chopra
P, Locklin J, Boons GJ and Krause DC: Distinct Mycoplasma
pneumoniae interactions with sulfated and sialylated receptors.
Infect Immun. 88:e00392–20. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Williams CR, Chen L, Driver AD, Arnold EA,
Sheppard ES, Locklin J and Krause DC: Sialylated receptor setting
influences Mycoplasma pneumoniae attachment and gliding
motility. Mol Microbiol. 109:735–744. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Chaudhry R, Ghosh A and Chandolia A:
Pathogenesis of Mycoplasma pneumoniae: An update. Indian J
Med Microbiol. 34:7–16. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Miyata M and Hamaguchi T: Integrated
information and prospects for gliding mechanism of the pathogenic
bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Front Microbiol.
7(960)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Widjaja M, Berry IJ, Jarocki VM, Padula
MP, Dumke R and Djordjevic SP: Cell surface processing of the P1
adhesin of Mycoplasma pneumoniae identifies novel domains
that bind host molecules. Sci Rep. 10(6384)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Romero-Arroyo CE, Jordan J, Peacock SJ,
Willby MJ, Farmer MA and Krause DC: Mycoplasma pneumoniae
protein P30 is required for cytadherence and associated with proper
cell development. J Bacteriol. 181:1079–1087. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Tabassum I, Chaudhry R, Chourasia BK and
Malhotra P: Identification of an N-terminal 27 kDa fragment of
Mycoplasma pneumoniae P116 protein as specific immunogen in
M. pneumoniae infections. BMC Infect Dis. 10(350)2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Fan L, Li D, Zhang L, Hao C, Sun H, Shao
X, Xu J and Chen Z: Pediatric clinical features of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae infection are associated with bacterial P1 genotype.
Exp Ther Med. 14:1892–1898. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sun H, Xue G, Yan C, Li S, Zhao H, Feng Y
and Wang L: Changes in molecular characteristics of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae in clinical specimens from children in Beijing
between 2003 and 2015. PLoS One. 12(e0170253)2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Xue G, Cao L, Wang L, Zhao H, Feng Y, Ma L
and Sun H: Evaluation of P1 adhesin epitopes for the serodiagnosis
of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infections. FEMS Microbiol Lett.
340:86–92. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Meng YL, Wang WM, Lv DD, An QX, Lu WH,
Wang X and Tang G: The effect of Platycodin D on the expression of
cytoadherence proteins P1 and P30 in Mycoplasma pneumoniae
models. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol. 49:188–193. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Rodman Berlot J, Krivec U, Praprotnik M,
Mrvič T, Kogoj R and Keše D: Clinical characteristics of infections
caused by Mycoplasma pneumoniae P1 genotypes in children.
Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 37:1265–1272. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Zhu C, Wu Y, Chen S, Yu M, Zeng Y, You X,
Xiao J and Wang S: Protective immune responses in mice induced by
intramuscular and intranasal immunization with a Mycoplasma
pneumoniae P1C DNA vaccine. Can J Microbiol. 58:644–652.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Varshney AK, Chaudhry R, Kabra SK and
Malhotra P: Cloning, expression, and immunological characterization
of the P30 protein of Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Clin Vaccine
Immunol. 15:215–120. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Blötz C, Singh N, Dumke R and Stülke J:
Characterization of an immunoglobulin binding protein (IbpM) from
Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Front Microbiol.
11(685)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Szczepanek SM, Majumder S, Sheppard ES,
Liao X, Rood D, Tulman ER, Wyand S, Krause DC, Silbart LK and Geary
SJ: Vaccination of BALB/c mice with an avirulent Mycoplasma
pneumoniae P30 mutant results in disease exacerbation upon
challenge with a virulent strain. Infect Immun. 80:1007–1014.
2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Rathore JS and Wang Y: Protective role of
Th17 cells in pulmonary infection. Vaccine. 34:1504–1514.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Yang J, Sundrud MS, Skepner J and Yamagata
T: Targeting Th17 cells in autoimmune diseases. Trends Pharmacol
Sci. 35:493–500. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Hausner M, Schamberger A, Naumann W,
Jacobs E and Dumke R: Development of protective anti-Mycoplasma
pneumoniae antibodies after immunization of guinea pigs with
the combination of a P1-P30 chimeric recombinant protein and
chitosan. Microb Pathog. 64:23–32. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Svenstrup HF, Nielsen PK, Drasbek M,
Birkelund S and Christiansen G: Adhesion and inhibition assay of
Mycoplasma genitalium and M. pneumoniae by
immunofluorescence microscopy. J Med Microbiol. 51:361–373.
2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Duffy MF, Walker ID and Browning GF: The
immunoreactive 116 kDa surface protein of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae is encoded in an operon. Microbiology (Reading).
143:3391–3402. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Vizarraga D, Kawamoto A, Matsumoto U,
Illanes R, Pérez-Luque R, Martín J, Mazzolini R, Bierge P, Pich OQ,
Espasa M, et al: Immunodominant proteins P1 and P40/P90 from human
pathogen Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Nat Commun.
11(5188)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Feng M, Schaff AC, Cuadra Aruguete SA,
Riggs HE, Distelhorst SL and Balish MF: Development of
Mycoplasma pneumoniae biofilms in vitro and the limited role
of motility. Int J Med Microbiol. 324:324–334. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Hu J, Ye Y, Chen X, Xiong L, Xie W and Liu
P: Insight into the pathogenic mechanism of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae. Curr Microbiol. 80(14)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Yang J, Hooper WC, Phillips DJ and
Talkington DF: Cytokines in Mycoplasma pneumoniae
infections. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 15:157–168. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Balasubramanian S, Pandranki L, Maupin S,
Ramasamy K, Taylor AB, Hart PJ, Baseman JB and Kannan TR: Disulfide
bond of Mycoplasma pneumoniae community-acquired respiratory
distress syndrome toxin is essential to maintain the
ADP-ribosylating and vacuolating activities. Cell Microbiol.
21(e13032)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Ramasamy K, Balasubramanian S, Kirkpatrick
A, Szabo D, Pandranki L, Baseman JB and Kannan TR: Mycoplasma
pneumoniae CARDS toxin exploits host cell endosomal acidic pH
and vacuolar ATPase proton pump to execute its biological
activities. Sci Rep. 11(11571)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Blötz C and Stülke J: Glycerol metabolism
and its implication in virulence in Mycoplasma. FEMS
Microbiol Rev. 41:640–652. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Schumacher M, Nicholson P, Stoffel MH,
Chandran S, D'Mello A, Ma L, Vashee S, Jores J and Labroussaa F:
Evidence for the cytoplasmic localization of the
L-α-glycerophosphate oxidase in members of the ‘Mycoplasma
mycoides cluster’. Front Microbiol. 10(1344)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Waites KB, Balish MF and Atkinson TP: New
insights into the pathogenesis and detection of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae infections. Future Microbiol. 3:635–648.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Segovia JA, Chang TH, Winter VT, Coalson
JJ, Cagle MP, Pandranki L, Bose S, Baseman JB and Kannan TR: NLRP3
is a critical regulator of inflammation and innate immune cell
response during Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Infect
Immun. 86:e00548–17. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Shimizu T, Kimura Y, Kida Y, Kuwano K,
Tachibana M, Hashino M and Watarai M: Cytadherence of Mycoplasma
pneumoniae induces inflammatory responses through autophagy and
toll-like receptor 4. Infect Immun. 82:3076–3086. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Li S, Xue G, Zhao H, Feng Y, Yan C, Cui J
and Sun H: The Mycoplasma pneumoniae HapE alters the
cytokine profile and growth of human bronchial epithelial cells.
Biosci Rep. 39(BSR20182201)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Luo H, He J, Qin L, Chen Y, Chen L, Li R,
Zeng Y, Zhu C, You X and Wu Y: Mycoplasma pneumoniae lipids
license TLR-4 for activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and autophagy to
evoke a proinflammatory response. Clin Exp Immunol. 203:66–79.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Mara AB, Gavitt TD, Tulman ER, Geary SJ
and Szczepanek SM: Lipid moieties of Mycoplasma pneumoniae
lipoproteins are the causative factor of vaccine-enhanced disease.
NPJ Vaccines. 5(31)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Narita M: Classification of extrapulmonary
manifestations due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae Infection on the
basis of possible pathogenesis. Front Microbiol.
7(23)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Li G, Fan L, Wang Y, Huang L, Wang M, Zhu
C, Hao C, Ji W, Liang H, Yan Y and Chen Z: High co-expression of
TNF-α and CARDS toxin is a good predictor for refractory
Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. Mol Med.
25(38)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Zhao Y, Ma G and Yang X: HDAC5 promotes
Mycoplasma pneumoniae-induced inflammation in macrophages
through NF-κB activation. Life Sci. 221:13–19. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Hakim MS, Annisa L, Jariah ROA and Vink C:
The mechanisms underlying antigenic variation and maintenance of
genomic integrity in Mycoplasma pneumoniae and Mycoplasma
genitalium. Arch Microbiol. 203:413–429. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Kenri T, Kawakita Y, Kudo H, Matsumoto U,
Mori S, Furukawa Y, Tahara YO, Shibayama K, Hayashi Y, Arai M and
Miyata M: Production and characterization of recombinant P1 adhesin
essential for adhesion, gliding, and antigenic variation in the
human pathogenic bacterium Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 508:1050–1055. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Lee D, Lal NK, Lin ZD, Ma S, Liu J, Castro
B, Toruño T, Dinesh-Kumar SP and Coaker G: Regulation of reactive
oxygen species during plant immunity through phosphorylation and
ubiquitination of RBOHD. Nat Commun. 11(1838)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Chen LS, Li C, You XX, Lin YW and Wu YM:
The mpn668 gene of Mycoplasma pneumoniae encodes a novel
organic hydroperoxide resistance protein. Int J Med Microbiol.
308:776–783. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Yu Y, Wang J, Han R, Wang L, Zhang L,
Zhang AY, Xin J, Li S, Zeng Y, Shao G, et al: Mycoplasma
hyopneumoniae evades complement activation by binding to factor H
via elongation factor thermo unstable (EF-Tu). Virulence.
11:1059–1074. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Waites KB and Talkington DF: Mycoplasma
pneumoniae and its role as a human pathogen. Clin Microbiol
Rev. 17:697–728, table of contents. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Mirijello A, La Marca A, D'Errico MM,
Curci S, Vendemiale G, Grandone E and De Cosmo S: Venous
thromboembolism during Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection: Case
report and review of the literature. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci.
24:10061–10068. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Choi SY, Choi YJ, Choi JH and Choi KD:
Isolated optic neuritis associated with Mycoplasma
pneumoniae infection: Report of two cases and literature
review. Neurol Sci. 38:1323–1327. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Song WJ, Kang B, Lee HP, Cho J, Lee HJ and
Choe YH: Pediatric Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection
presenting with acute cholestatic hepatitis and other
extrapulmonary manifestations in the absence of pneumonia. Pediatr
Gastroenterol Hepatol Nutr. 20:124–129. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Mitsuo N: Classifcation of extrapulmonary
manifestations due to Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection on the
basis of possible pathogenesis. Fron Microbiol.
7(23)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Wang Z, Sun J, Liu Y and Wang Y: Impact of
atopy on the severity and extrapulmonary manifestations of
childhood Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia. J Clin Lab Anal.
33(e22887)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Naghib M, Hatam-Jahromi M, Niktab M,
Ahmadi R and Kariminik A: Mycoplasma pneumoniae and
toll-like receptors: A mutual avenue. Allergol Immunopathol (Madr).
46:508–513. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Fink CG, Sillis M, Read SJ, Butler L and
Pike M: Neurological disease associated with Mycoplasma
pneumoniae infection. PCR evidence against a direct invasive
mechanism. Clin Mol Pathol. 48:M51–M54. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Shimizu T, Kida Y and Kuwano K: A
dipalmitoylated lipoprotein from Mycoplasma pneumoniae
activates NF-kappa B through TLR1, TLR2, and TLR6. J Immunol.
175:4641–4646. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Meyer Sauteur PM, de Bruijn ACJM, Graça C,
Tio-Gillen AP, Estevão SC, Hoogenboezem T, Hendriks RW, Berger C,
Jacobs BC, van Rossum AMC, et al: Antibodies to protein but not
glycolipid structures are important for host defense against
Mycoplasma pneumoniae. Infect Immun. 87:e00663–18.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Widén J, Jönsson G and Karlsson U:
Mycoplasma pneumonia with severe cold agglutinin hemolysis,
thrombocytosis, leukemoid reaction and acute renal failure.
IDCases. 31(e01689)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Poddighe D, Comi EV, Brambilla I, Licari
A, Bruni P and Marseglia GL: Increased total serum immunoglobulin e
in children developing Mycoplasma pneumoniae-related
extra-pulmonary diseases. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol.
17:490–496. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Poddighe D and Marseglia GL: Is there any
relationship between extra-pulmonary manifestations of
Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection and atopy/respiratory
allergy in children? Pediatr Rep. 8(6395)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Ye Q, Mao JH, Shu Q and Shang SQ:
Mycoplasma pneumoniae induces allergy by producing
P1-specific immunoglobulin E. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol.
121:90–97. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Liu J, He R, Wu R, Wang B, Xu H, Zhang Y,
Li H and Zhao S: Mycoplasma pneumoniae pneumonia associated
thrombosis at Beijing Children's hospital. BMC Infect Dis.
20(51)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Hirshberg SJ, Charles RS and Ettinger JB:
Pediatric priapism associated with Mycoplasma pneumoniae.
Urology. 47:745–746. 1996.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Liu J and Li Y: Thrombosis associated with
Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection (Review). Exp Ther Med.
22(967)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Pachet A, Dumestre-Perard C, Moine M,
Marlu R, Rubio A and Bost-Bru C: Splenic infarction associated with
transient anti-prothrombin antibodies is a rare manifestation of
acute Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Arch Pediatr.
26:483–486. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Dietz SM, van Stijn D, Burgner D, Levin M,
Kuipers IM, Hutten BA and Kuijpers TW: Dissecting Kawasaki disease:
A state-of-the-art review. Eur J Pediatr. 176:995–1009.
2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
74
|
Okoli K, Gupta A, Irani F and Kasmani R:
Immune thrombocytopenia associated with Mycoplasma
pneumoniae infection: A case report and review of literature.
Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 20:595–598. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
75
|
Rastawicki W, Rokosz N and Jagielski M:
Subclass distribution of human IgG antibodies to Mycoplasma
pneumoniae in the course of mycoplasmosis. Med Dosw Mikrobiol.
61:375–379. 2009.PubMed/NCBI(In Polish).
|