|
1
|
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Barton A, Burmester
GR, Emery P, Firestein GS, Kavanaugh A, McInnes IB, Solomon DH,
Strand V and Yamamoto K: Rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Dis Primers.
4(18001)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Rosa-Gonçalves D, Bernardes M and Costa L:
Quality of life and functional capacity in patients with rheumatoid
arthritis-cross-sectional study. Reumatol Clin (Engl Ed).
14:360–366. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Giannini D, Antonucci M, Petrelli F, Bilia
S, Alunno A and Puxeddu I: One year in review 2020: Pathogenesis of
rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 38:387–397.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Jahid M, Rehan-Ul-Haq Jha PK, Chawla D,
Avasthi RS and Ahmed RS: Tumor necrosis factor-α-308 polymorphism
in North Indian rheumatoid arthritis patients and association with
mRNA and serum TNF-α. Clin Rheumatol. 36:2209–2216. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Boechat AL, Boechat Nde O, Ogusku MM,
Alencar MR, Abensur Tda C, Cardoso Neto J, Amorim Lde S, de
Oliveira LM, Sadahiro A and Dos-Santos MC: The influence of a TNF
gene polymorphism on the severity of rheumatoid arthritis in the
Brazilian Amazon. Cytokine. 61:406–412. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Sun R, Huang Y, Zhang H and Liu R: MMP-2,
TNF-α and NLRP1 polymorphisms in Chinese patients with ankylosing
spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Mol Biol Rep. 40:6303–6308.
2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Cadena-Sandoval D, Alemán-Ávila I,
Barbosa-Cobos RE, Becerril-Mendoza LT, Fragoso JM and Ramírez-Bello
J: Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and TNFR1 polymorphisms are not risk
factors for rheumatoid arthritis in a Mexican population. Mol Biol
Rep. 45:227–232. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Zheng G, Zhang W, Xu J, Yuan A, Li Q and
Gastwirth JL: Genetic risks and genetic model specification. J
Theor Biol. 403:68–74. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Stang A: Critical evaluation of the
Newcastle-Ottawa scale for the assessment of the quality of
nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Eur J Epidemiol.
25:603–605. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
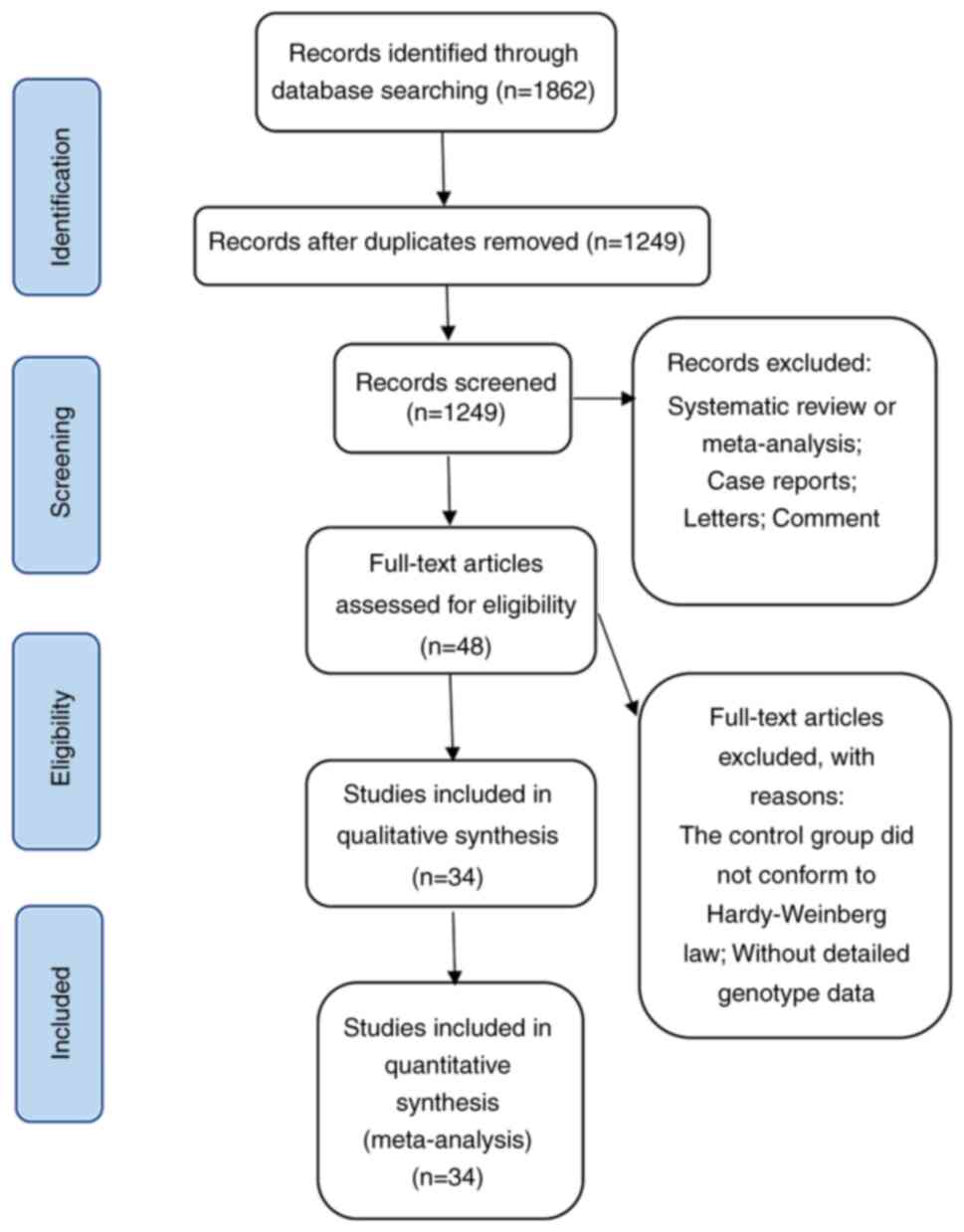
Page MJ, McKenzie JE, Bossuyt PM, Boutron
I, Hoffmann TC, Mulrow CD, Shamseer L, Tetzlaff JM, Akl EA, Brennan
SE, et al: The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for
reporting systematic reviews. J Clin Epidemiol. 134:178–189.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
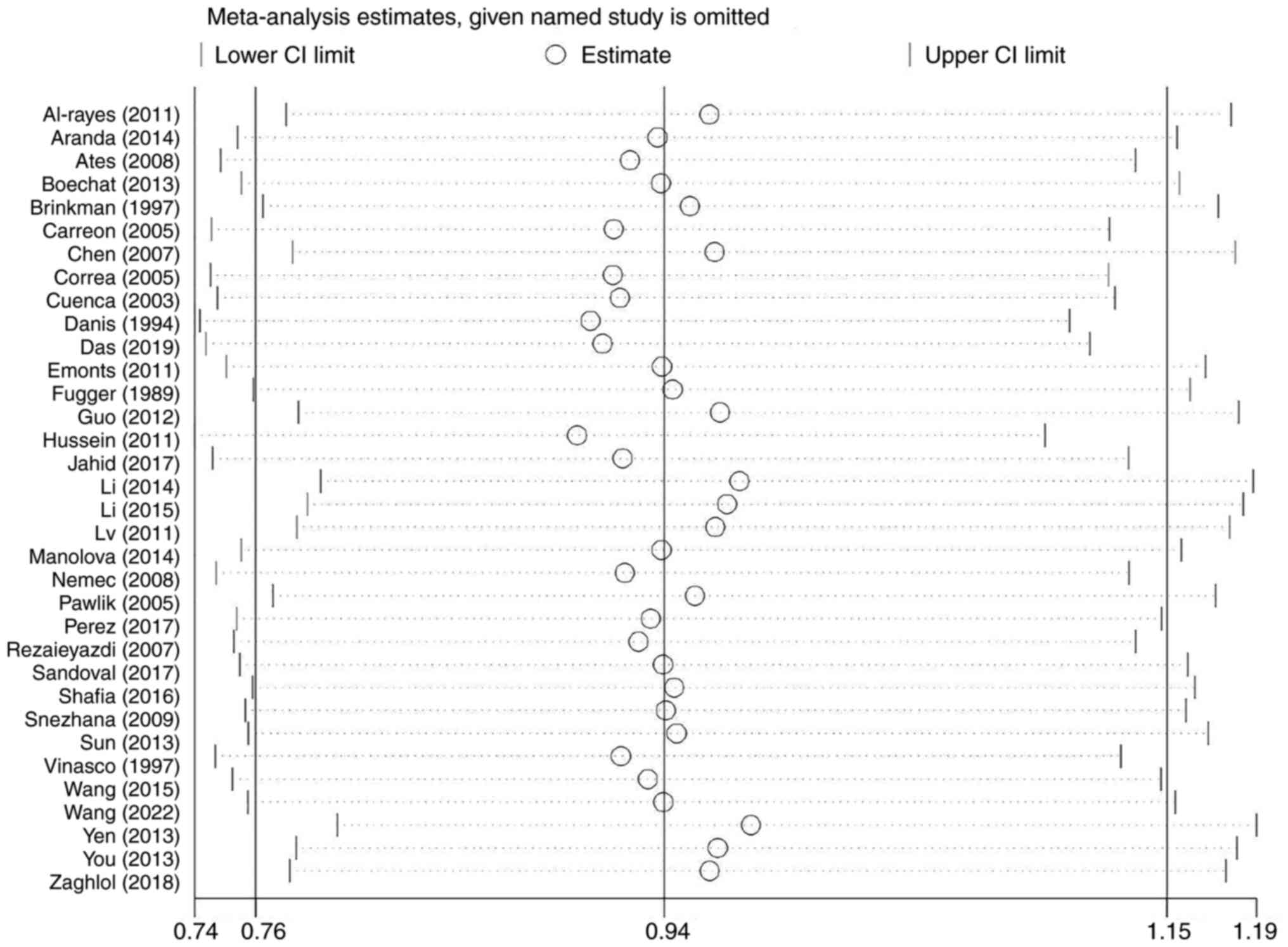
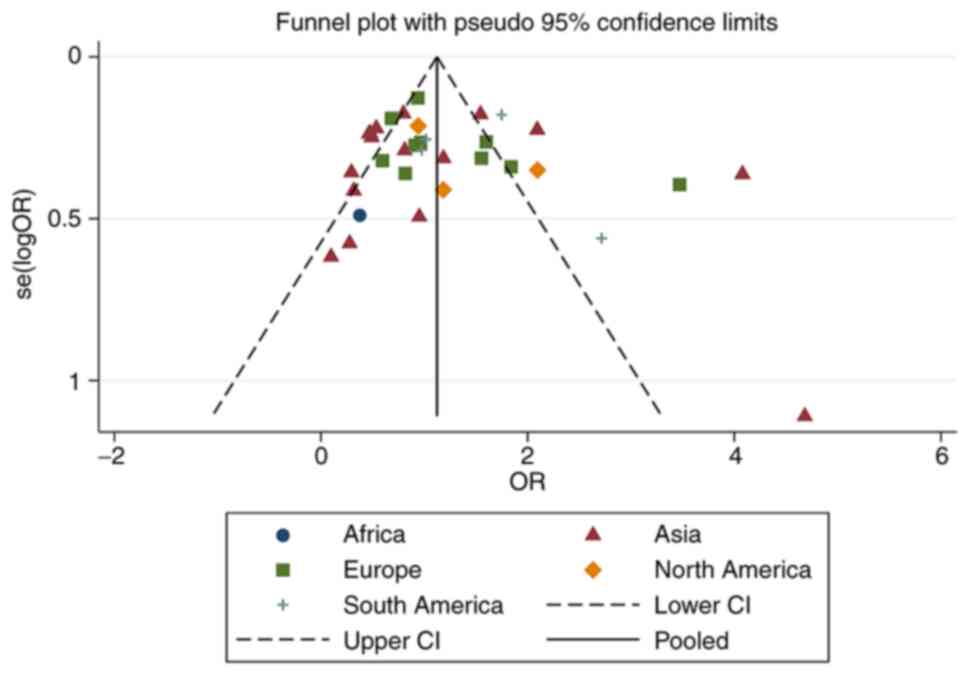
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M and
Minder C: Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical
test. BMJ. 315:629–634. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Al-Rayes H, Al-Swailem R, Albelawi M,
Arfin M, Al-Asmari A and Tariq M: TNF-α and TNF-β gene polymorphism
in Saudi rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Med Insights Arthritis
Musculoskelet Disord. 4:55–63. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Aranda F, Perés Wingeyer SD, Schneeberger
E, Valerio M, Saint Martin E, Dal Pra F, Correa Mde L, Citera G,
Martínez L, Mannucci P, et al: The-308 G/A polymorphism in the
tumor necrosis factor-α gene is not associated with development and
progression of rheumatoid arthritis in Argentinean patients. Int J
Rheum Dis. 19:476–481. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ates O, Hatemi G, Hamuryudan V and
Topal-Sarikaya A: Tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-10
gene promoter polymorphisms in Turkish rheumatoid arthritis
patients. Clin Rheumatol. 27:1243–1248. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Brinkman BM, Huizinga TW, Kurban SS, van
der Velde EA, Schreuder GM, Hazes JM, Breedveld FC and Verweij CL:
Tumour necrosis factor alpha gene polymorphisms in rheumatoid
arthritis: Association with susceptibility to, or severity of,
disease? Br J Rheumatol. 36:516–521. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
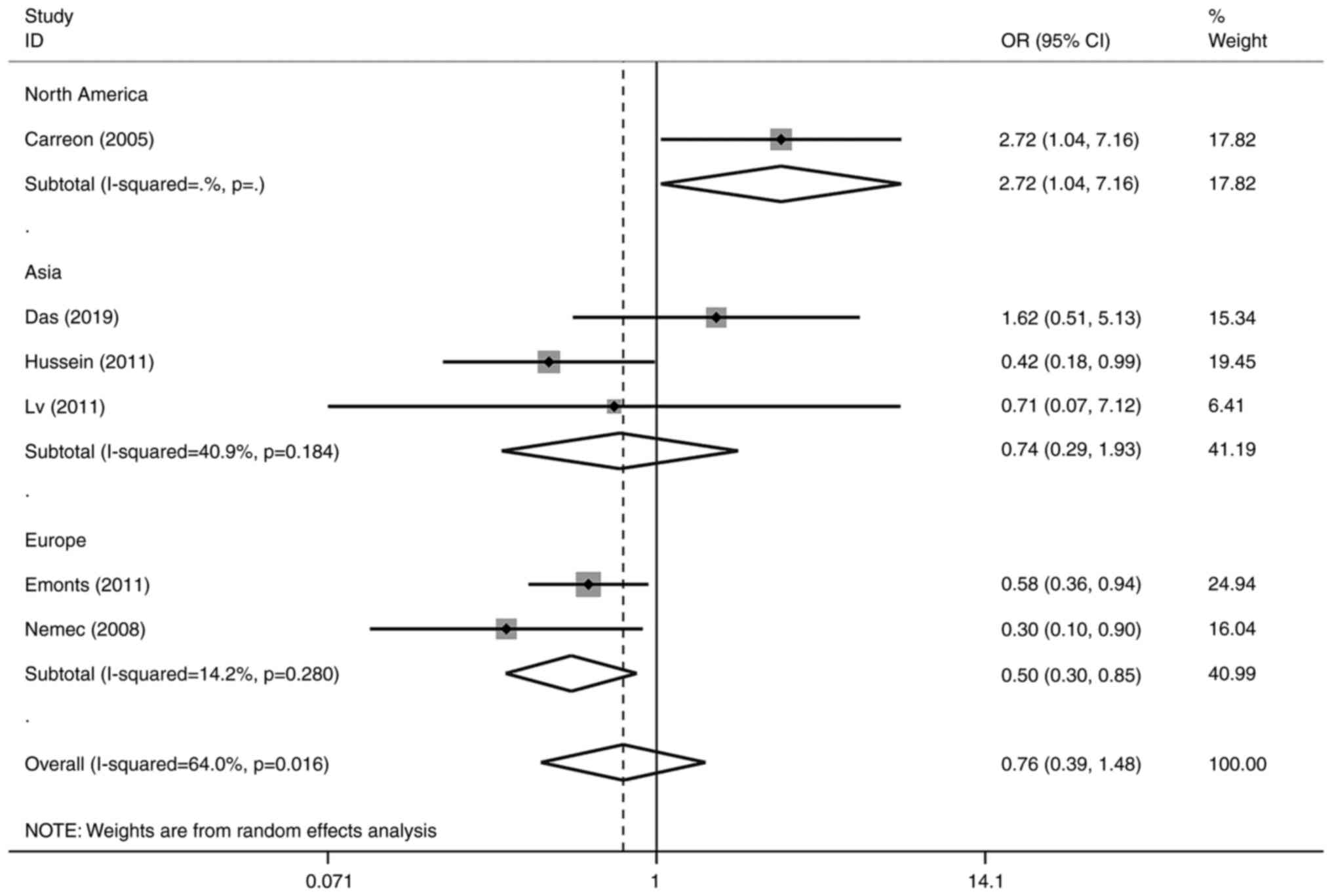
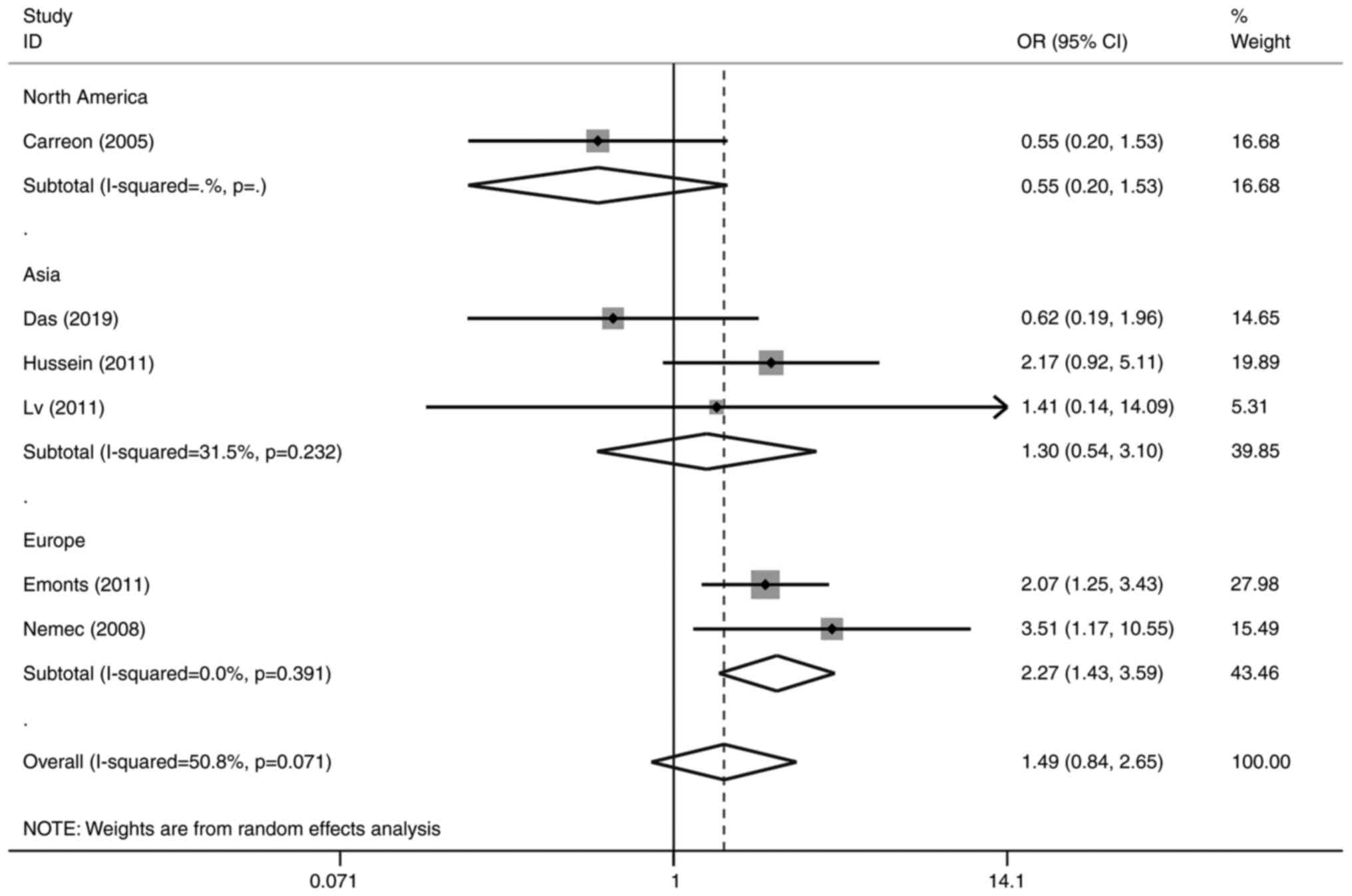
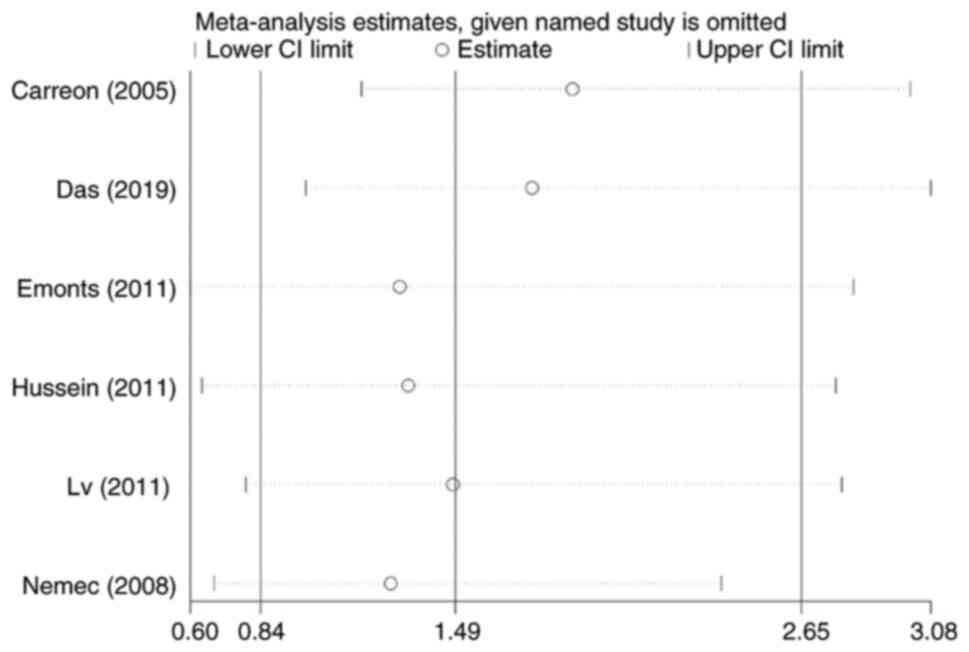
Rodríguez-Carreón AA, Zúñiga J,
Hernández-Pacheco G, Rodríguez-Pérez JM, Pérez-Hernández N, Montes
de Oca JV, Cardiel MH, Granados J and Vargas-Alarcón G: Tumor
necrosis factor-alpha-308 promoter polymorphism contributes
independently to HLA alleles in the severity of rheumatoid
arthritis in Mexicans. J Autoimmun. 24:63–68. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chen R, Fang M, Cai Q, Duan S, Lv K, Cheng
N, Ren D, Shen J, He D, He L and Sun S: Tumor necrosis factor
alpha-308 polymorphism is associated with rheumatoid arthritis in
Han population of Eastern China. Rheumatol Int. 28:121–126.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Correa PA, Gomez LM, Cadena J and Anaya
JM: Autoimmunity and tuberculosis. Opposite association with TNF
polymorphism. J Rheumatol. 32:219–224. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cuenca J, Cuchacovich M, Pérez C, Ferreira
L, Aguirre A, Schiattino I, Soto L, Cruzat A, Salazar-Onfray F and
Aguillón JC: The-308 polymorphism in the tumour necrosis factor
(TNF) gene promoter region and ex vivo lipopolysaccharide-induced
TNF expression and cytotoxic activity in Chilean patients with
rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 42:308–313.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Danis VA, Millington M, Hyland V, Lawford
R, Huang Q and Grennan D: Increased frequency of the uncommon
allele of a tumour necrosis factor alpha gene polymorphism in
rheumatoid arthritis and systemic lupus erythematosus. Dis Markers.
12:127–133. 1995.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Das S, Baruah C, Saikia AK, Tiwari D and
Bose S: Genetic and expression changes in TNF-α as a risk factor
for rheumatoid arthritis pathogenesis in northeast India. J Genet.
98(3)2019.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Emonts M, Hazes MJMW, Houwing-Duistermaat
JJ, van der Gaast-de Jongh CE, de Vogel L, Han HKH, Wouters JMGW,
Laman JD and Dolhain RJEM: Polymorphisms in genes controlling
inflammation and tissue repair in rheumatoid arthritis: A case
control study. BMC Med Genet. 12(36)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Fugger L, Morling N, Ryder LP, Georgsen J,
Jakobsen BK, Svejgaard A, Andersen V, Oxholm P, Karup Pedersen F,
Friis J, et al: NcoI restriction fragment length polymorphism
(RFLP) of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF alpha) region in four
autoimmune diseases. Tissue Antigens. 34:17–22. 1989.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Guo X, You C, Wang L, Ma K, Zhou Y, Shi X,
Li F and Gao L: Correlation analysis of gene polymorphisms of TNF-α
and its receptors with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility and
related serological markers. Acad J Second Mil Med Univ.
32:155–159. 2012.
|
|
25
|
Hussein YM, Mohamed RH, Pasha HF,
El-Shahawy EE and Alzahrani SS: Association of tumor necrosis
factor alpha and its receptor polymorphisms with rheumatoid
arthritis in female patients. Cell Immunol. 271:192–196.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li F, Gao J, Sokolove J, Xu J, Zheng J,
Zhu K and Pan Z: Polymorphisms in the TNF-α, TNFR1 gene and risk of
rheumatoid arthritis in Chinese Han population. Int J Immunogenet.
41:499–502. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Li F, Xie X, Chen J, Gao J and Lu F:
Association of TNF-α gene polymorphisms with the risk of rheumatoid
arthritis in Han Chinese population from Hunan. Zhong Nan Da Xue
Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 40:945–954. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Lv HZ, Lin T, Zhu XY, Zhang JT and Lu J:
Association of TNF-α single nucleotide polymorphisms in human
rheumatoid arthritis of Han nationality in northern China. Cell Mol
Immunol. 27:906–908. 2011.
|
|
29
|
Manolova I, Ivanova M, Stoilov R, Rashkov
R and Stanilova S: Association of single nucleotide polymorphism at
position-308 of the tumor necrosis factor-alpha gene with
ankylosing spondylitis and rheumatoid arthritis. Biotechnol
Biotechnol Equip. 28:1108–1114. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Nemec P, Pavkova-Goldbergova M, Stouracova
M, Vasku A, Soucek M and Gatterova J: Polymorphism in the tumor
necrosis factor-alpha gene promoter is associated with severity of
rheumatoid arthritis in the Czech population. Clin Rheumatol.
27:59–65. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Pawlik A, Florczak M, Ostanek L, Brzosko
M, Brzosko I and Szklarz BG: TNF-alpha-308 promoter polymorphism in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol. 34:22–26.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Domínguez-Pérez RA, Loyola-Rodriguez JP,
Abud-Mendoza C, Alpuche-Solis AG, Ayala-Herrera JL and
Martínez-Martínez RE: Association of cytokines polymorphisms with
chronic peridontitis and rheumatoid arthritis in a Mexican
population. Acta Odontol Scand. 75:243–248. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Rezaieyazdi Z, Afshari JT, Sandooghi M and
Mohajer F: Tumour necrosis factor a-308 promoter polymorphism in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int. 28:189–191.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Shafia S, Sofi FA, Dilafroze Rasool R,
Rasool R, Javeed S and Shah ZA: The association between TNFα gene
polymorphisms and susceptibility to rheumatoid arthritis in an
ethnic Kashmiri population: Relationship with disease activity and
severity markers. Int J Rheum Dis. 19:362–369. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Trajkov D, Mishevska-Perchinkova S,
Karadzova-Stojanoska A, Petlichkovski A, Strezova A and Spiroski M:
Association of 22 cytokine gene polymorphisms with rheumatoid
arthritis in population of ethnic Macedonians. Clin Rheumatol.
28:1291–1300. 2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Vinasco J, Beraún Y, Nieto A, Fraile A,
Mataran L, Pareja E and Martín J: Polymorphism at the TNF loci in
rheumatoid arthritis. Tissue Antigens. 49:74–78. 1997.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Wang P, He YL, Zeng YQ, Wang LM and Hu LH:
Association between TNF-α gene polymorphisms and rheumatoid
arthritis. J Clin Hematol. 28:97–99. 2015.
|
|
38
|
Wang Z, Kong L, Zhang H, Sun F, Guo Z,
Zhang R and Dou Y: Tumor necrosis factor alpha-308G/A gene
polymorphisms combined with neutrophil-to-lymphocyte and
platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio predicts the efficacy and safety of
Anti-TNF-α therapy in patients with ankylosing spondylitis,
rheumatoid arthritis, and psoriasis arthritis. Front Pharmacol.
12(811719)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Yen JH, Chen CJ, Tsai WC, Lin CH, Ou TT,
Wu CC and Liu HW: Tumor necrosis factor promoter polymorphisms in
patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Taiwan. J Rheumatol.
28:1788–1792. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
You CG, Li XJ, Li YM, Wang LP, Li FF, Guo
XL and Gao LN: Association analysis of single nucleotide
polymorphisms of proinflammatory cytokine and their receptors genes
with rheumatoid arthritis in northwest Chinese Han population.
Cytokine. 61:133–138. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Zaghlol HM, Abdelshafy S, Mohamed RA and
Abdelaleem EA: Tumour necrosis factor gene polymorphisms in
Egyptian patients with rheumatoid arthritis and their relation to
disease activity and severity. Cent Eur J Immunol. 44:277–284.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Wacholder S, Chanock S, Garcia-Closas M,
El Ghormli L and Rothman N: Assessing the probability that a
positive report is false: An approach for molecular epidemiology
studies. J Natl Cancer Inst. 96:434–442. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Buch MH, Eyre S and McGonagle D:
Persistent inflammatory and non-inflammatory mechanisms in
refractory rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 17:17–33.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Klein K and Gay S: Epigenetics in
rheumatoid arthritis. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 27:76–82.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Zelová H and Hošek J: TNF-α signalling and
inflammation: Interactions between old acquaintances. Inflamm Res.
62:641–651. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Idriss HT and Naismith JH: TNF alpha and
the TNF receptor superfamily: Structure-function relationship(s).
Microsc Res Tech. 50:184–195. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Balkwill F: TNF-alpha in promotion and
progression of cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 25:409–416.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Song GG, Bae SC, Kim JH and Lee YH:
Association between TNF-α promoter-308 A/G polymorphism and
rheumatoid arthritis: A meta-analysis. Rheumatol Int. 34:465–471.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|