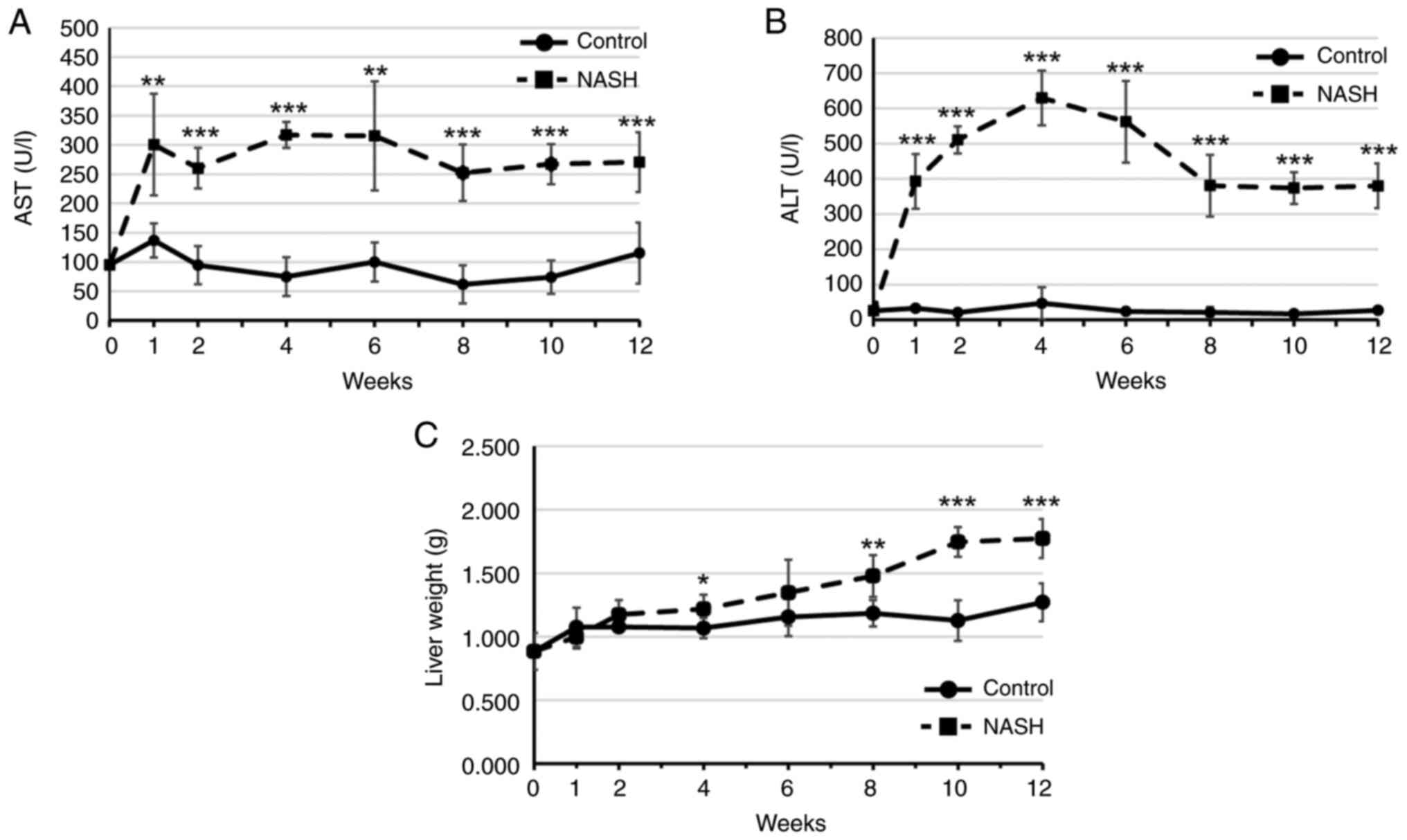
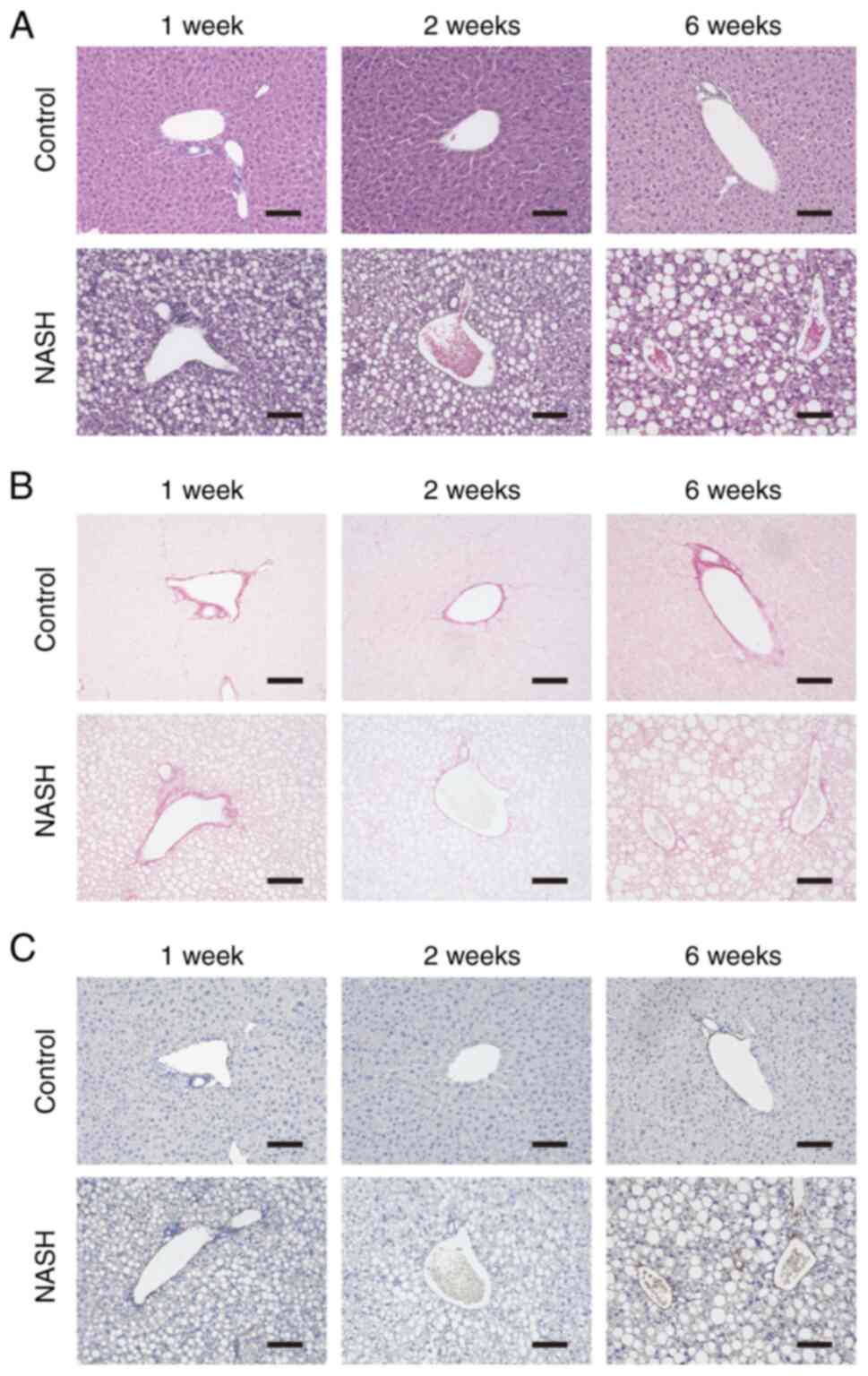
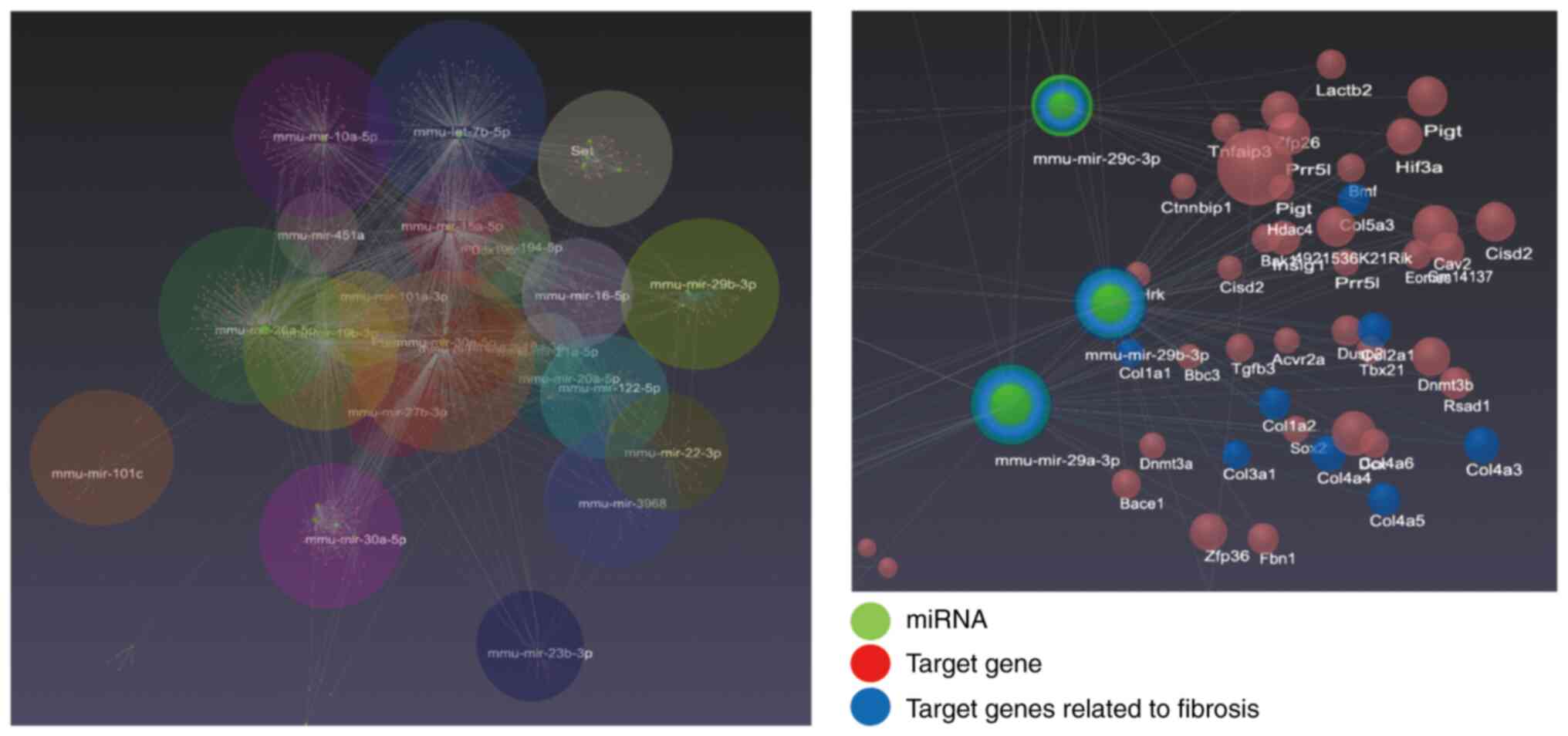
|
1
|
Hashimoto E, Taniai M and Tokushige K:
Characteristics and diagnosis of NAFLD/NASH. J Gastroenterol
Hepatol. 28:64–70. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Younossi ZM, Golabi P, Paik JM, Henry A,
Van Dongen C and Henry L: The global epidemiology of nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
(NASH): A systematic review. Hepatology. 77:1335–1347.
2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Parthasarathy G, Revelo X and Malhi H:
Pathogenesis of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: An overview. Hepatol
Commun. 4:478–492. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Fraile JM, Palliyil S, Barelle C, Porter
AJ and Kovaleva M: Non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH)-A review of
a crowded clinical landscape, driven by a complex disease. Drug Des
Dev Ther. 15:3997–4009. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Sanyal AJ, Van Natta ML, Clark J,
Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Diehl A, Dasarathy S, Loomba R, Chalasani N,
Kowdley K, Hameed B, et al: Prospective study of outcomes in adults
with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. N Engl J Med. 385:1559–1569.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Schuppan D, Surabattula R and Wang XY:
Determinants of fibrosis progression and regression in NASH. J
Hepatol. 68:238–250. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
European Association for the Study of the
Liver. Electronic address: simpleeasloffice@easloffice.eu;
Clinical Practice Guideline Panel, Chair:; EASL Governing Board
representative:; and Panel members. EASL clinical practice
guidelines on non-invasive tests for evaluation of liver disease
severity and prognosis-2021 update. J Hepatol. 75:659–689.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Ratziu V, Charlotte F, Heurtier A, Gombert
S, Giral P, Bruckert E, Grimaldi A, Capron F and Poynard T: LIDO
study group. Sampling variability of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology. 128:1898–1906.
2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Merriman RB, Ferrell LD, Patti MG, Weston
SR, Pabst MS, Aouizerat BE and Bass NM: Correlation of paired liver
biopsies in morbidly obese patients with suspected nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 44:874–880. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Ajmera V and Loomba R: Imaging biomarkers
of NAFLD, NASH, and fibrosis. Mol Metab. 50(101167)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Seko Y, Sumida Y, Tanaka S, Mori K,
Taketani H, Ishiba H, Hara T, Okajima A, Yamaguchi K, Moriguchi M,
et al: Serum alanine aminotransferase predicts the histological
course of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in Japanese patients.
Hepatol Res. 45:E53–E61. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
McGill MR: The past and present of serum
aminotransferases and the future of liver injury biomarkers. Excli
J. 15:817–828. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kruger FC, Daniels CR, Kidd M, Swart G,
Brundyn K, van Rensburg C and Kotze M: APRI: A simple bedside
marker for advanced fibrosis that can avoid liver biopsy in
patients with NAFLD/NASH. S Afr Med J. 101:477–480. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shah AG, Lydecker A, Murray K, Tetri BN,
Contos MJ and Sanyal AJ: Nash Clinical Research Network. Comparison
of noninvasive markers of fibrosis in patients with nonalcoholic
fatty liver disease. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:1104–1112.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Angulo P, Hui JM, Marchesini G, Bugianesi
E, George J, Farrell GC, Enders F, Saksena S, Burt AD, Bida JP, et
al: The NAFLD fibrosis score: A noninvasive system that identifies
liver fibrosis in patients with NAFLD. Hepatology. 45:846–854.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wieckowska A, Zein NN, Yerian LM, Lopez
AR, McCullough AJ and Feldstein AE: In vivo assessment of liver
cell apoptosis as a novel biomarker of disease severity in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology. 44:27–33.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Pimentel CF, Jiang ZG, Otsubo T,
Feldbrügge L, Challies TL, Nasser I, Robson S, Afdhal N and Lai M:
Poor inter-test reliability between CK18 kits as a biomarker of
NASH. Dig Dis Sci. 61:905–912. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Cusi K, Chang Z, Harrison S, Lomonaco R,
Bril F, Orsak B, Ortiz-Lopez C, Hecht J, Feldstein AE, Webb A, et
al: Limited value of plasma cytokeratin-18 as a biomarker for NASH
and fibrosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J
Hepatol. 60:167–174. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Felekkis K, Touvana E, Stefanou Ch and
Deltas C: MicroRNAs: A newly described class of encoded molecules
that play a role in health and disease. Hippokratia. 14:236–240.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Saliminejad K, Khorshid HR, Fard SS and
Ghaffari SH: An overview of microRNAs: Biology, functions,
therapeutics, and analysis methods. J Cell Physiol. 234:5451–5465.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yu X, Odenthal M and Fries JW: Exosomes as
miRNA carriers: Formation-function-future. Int J Mol Sci.
17(2028)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Kleiner DE, Brunt EM, Van Natta M, Behling
C, Contos MJ, Cummings OW, Ferrell LD, Liu YC, Torbenson MS,
Unalp-Arida A, et al: Design and validation of a histological
scoring system for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology.
41:1313–1321. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Matsumoto M, Hada N, Sakamaki Y, Uno A,
Shiga T, Tanaka C, Ito T, Katsume A and Sudoh M: An improved mouse
model that rapidly develops fibrosis in non-alcoholic
steatohepatitis. Int J Exp Pathol. 94:93–103. 2013.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Wang M, Huo Z, He X, Liu F, Liang J, Wu L
and Yang D: The role of MiR-29 in the mechanism of fibrosis. Mini
Rev Med Chem. 23:1846–1858. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ebada MA, Mostafa A, Gadallah AHA, Alkanj
S, Alghamdi BS, Ashraf GM, Abuzenadah AM, Alserihi RF, Wadaa-Allah
A and Salama M: Potential regulation of miRNA-29 and miRNA-9 by
estrogens in neurodegenerative disorders: An insightful
perspective. Brain Sci. 13(243)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Amirian M, Jafari-Nozad AM, Darroudi M,
Farkhondeh T and Samarghandian S: Overview of the miR-29 family
members' function in breast cancer. Int J Biol Macromol.
230(123280)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang T, Li Y, Chen J, Xie L and Xiao T:
TGF-β1/Smad3 signaling promotes collagen synthesis in pulmonary
artery smooth muscle by down-regulating miR-29b. Int J Clin Exp
Pathol. 11:5592–5601. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ezhilarasan D: MicroRNA interplay between
hepatic stellate cell quiescence and activation. Eur J Pharmacol.
885(173507)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Matsumoto Y, Itami S, Kuroda M, Yoshizato
K, Kawada N and Murakami Y: MiR-29a assists in preventing the
activation of human stellate cells and promotes recovery from liver
fibrosis in mice. Mol Ther. 24:1848–1859. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Lin HY, Wang FS, Yang YL and Huang YH:
MicroRNA-29a suppresses CD36 to ameliorate high fat diet-induced
steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis in mice. Cells.
8(1298)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
López-Riera M, Conde I, Quintas G, Pedrola
L, Zaragoza Á, Perez-Rojas J, Salcedo M, Benlloch S, Castell JV and
Jover R: Non-invasive prediction of NAFLD severity: A
comprehensive, independent validation of previously postulated
serum microRNA biomarkers. Sci Rep. 8(10606)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Kim TH, Lee Y, Lee YS, Gim JA, Ko E, Yim
SY, Jung YK, Kang S, Kim MY, Kim H, et al: Circulating miRNA is a
useful diagnostic biomarker for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in
nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci Rep. 11(14639)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Liu J, Xiao Y, Wu X, Jiang L, Yang S, Ding
Z, Fang Z, Hua H, Kirby MS and Shou J: A circulating microRNA
signature as noninvasive diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers for
nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. BMC Genomics. 19(188)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Khalifa O, Errafii K, Al-Akl NS and
Arredouani A: Noncoding RNAs in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:
Potential diagnosis and prognosis biomarkers. Dis Markers.
2020(8822859)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Jampoka K, Muangpaisarn P, Khongnomnan K,
Treeprasertsuk S, Tangkijvanich P and Payungporn S: Serum miR-29a
and miR-122 as potential biomarkers for non-alcoholic fatty liver
disease (NAFLD). Microrna. 7:215–222. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Zhou Z, Zhang R, Li X, Zhang W, Zhan Y,
Lang Z, Tao Q, Yu J, Yu S, Yu Z and Zheng J: Circular RNA cVIM
promotes hepatic stellate cell activation in liver fibrosis via
miR-122-5p/miR-9-5p-mediated TGF-β signaling cascade. Commun Biol.
7(113)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sun Y, Wang H, Li Y, Liu S, Chen J and
Ying H: MiR-24 and miR-122 negatively regulate the transforming
growth factor-β/Smad signaling pathway in skeletal muscle fibrosis.
Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 11:528–537. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Xu R, Zhang Z and Wang FS: Liver fibrosis:
Mechanisms of immune-mediated liver injury. Cell Mol Immunol.
9:296–301. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Dietrich P and Hellerbrand C:
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, obesity and the metabolic
syndrome. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 28:637–653.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Younossi ZM, Koenig AB, Abdelatif D, Fazel
Y, Henry L and Wymer M: Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty
liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence,
and outcomes. Hepatology. 64:73–84. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|