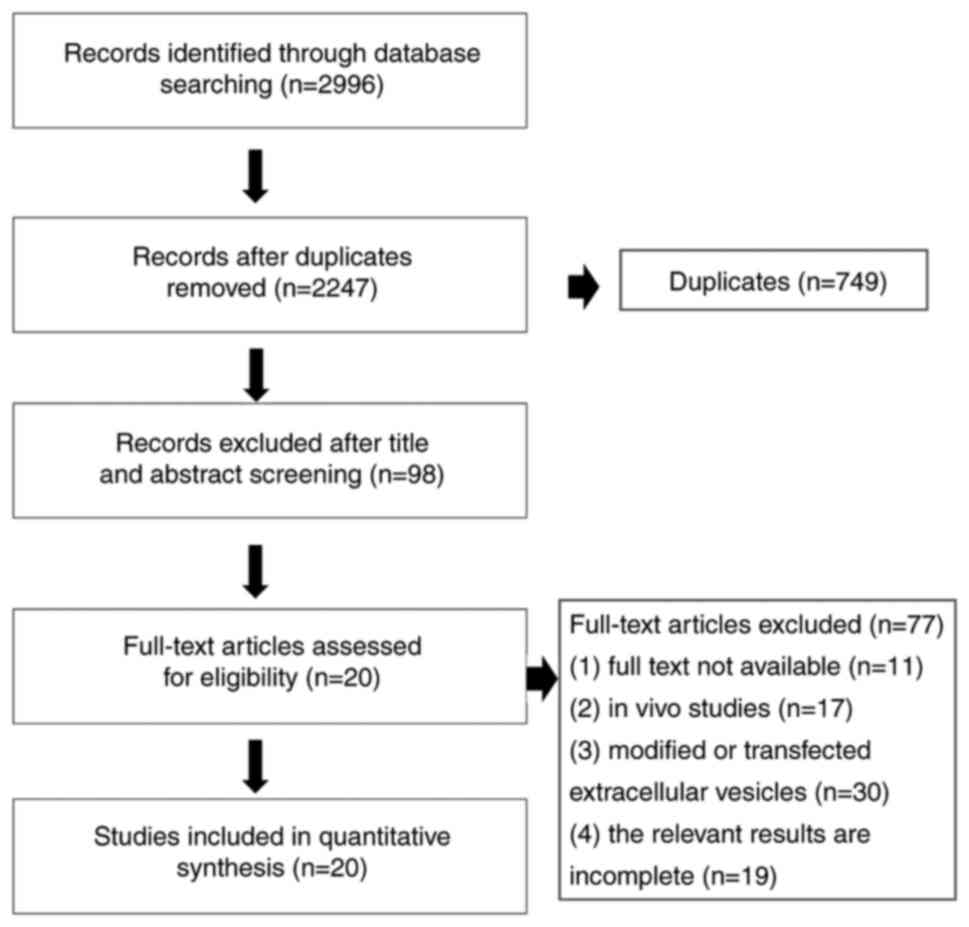
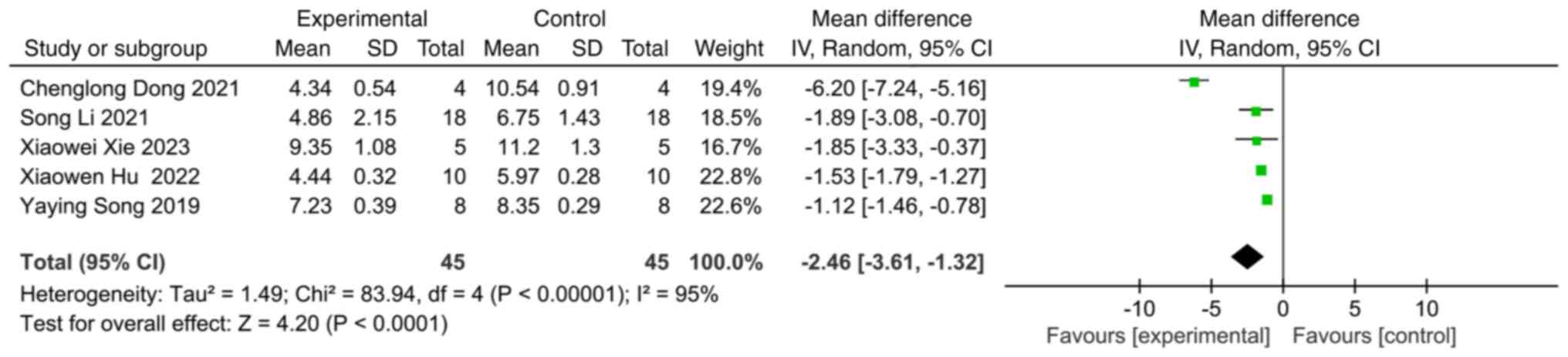
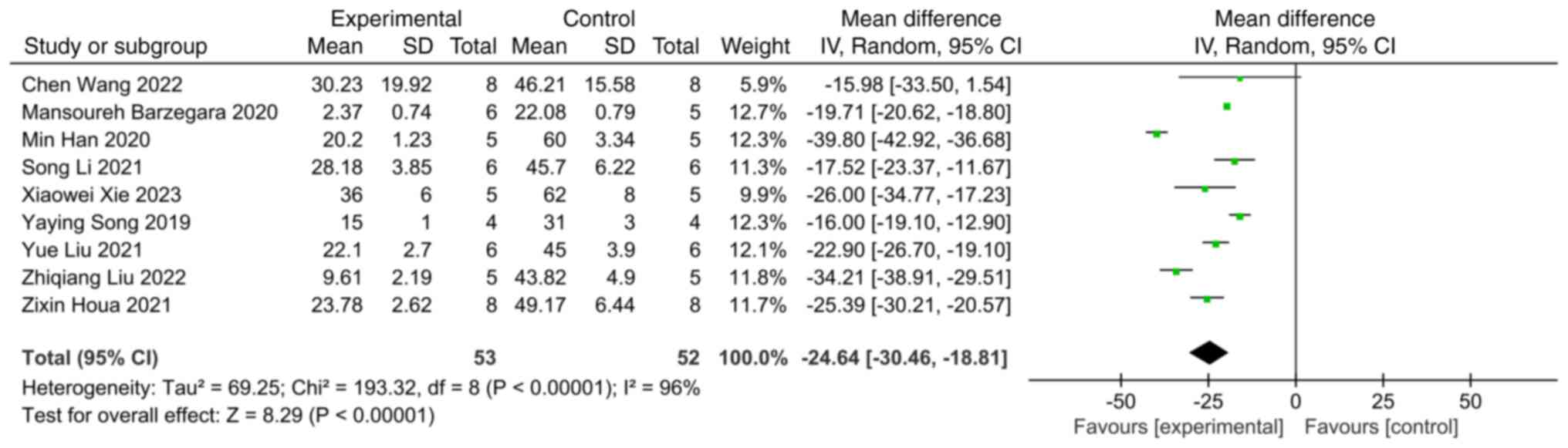
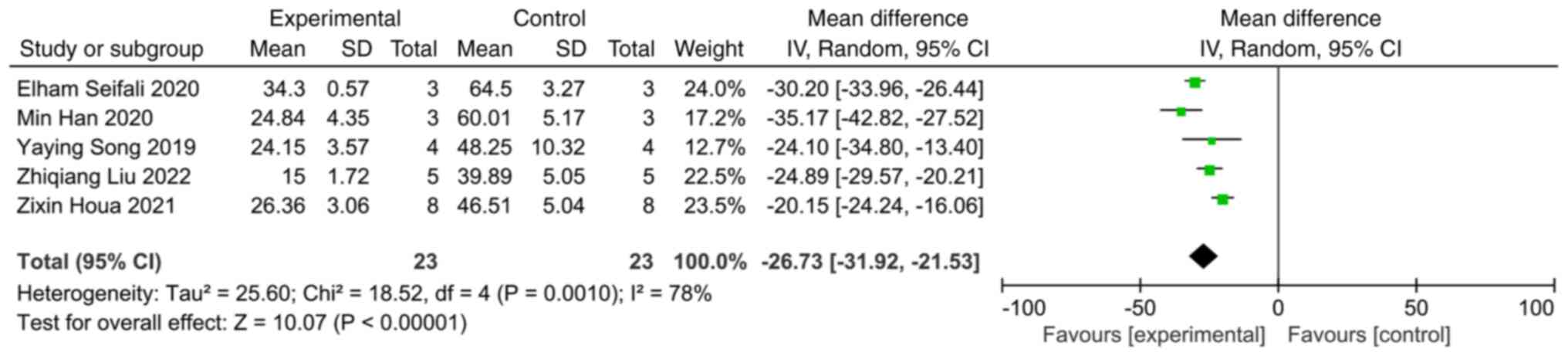
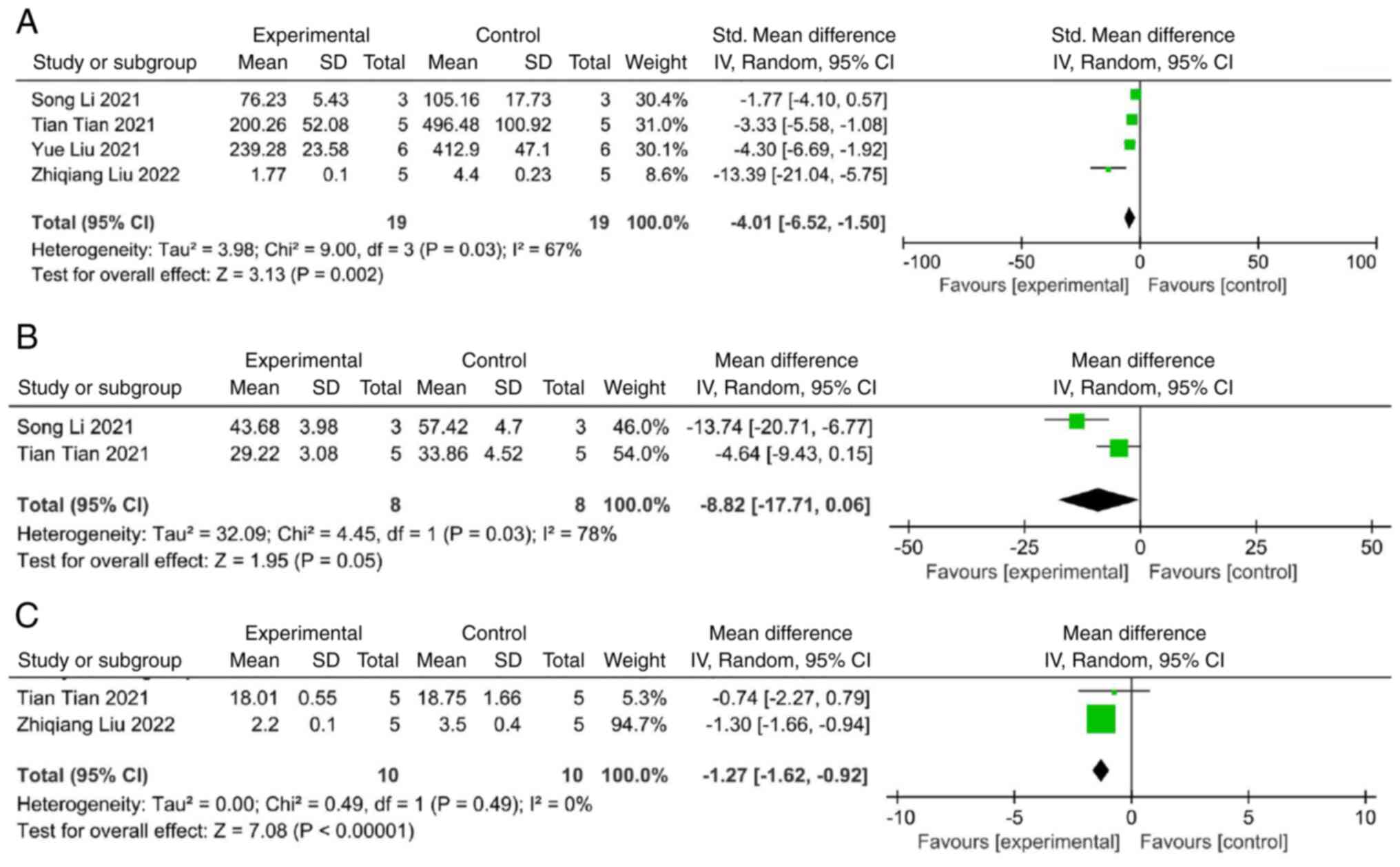
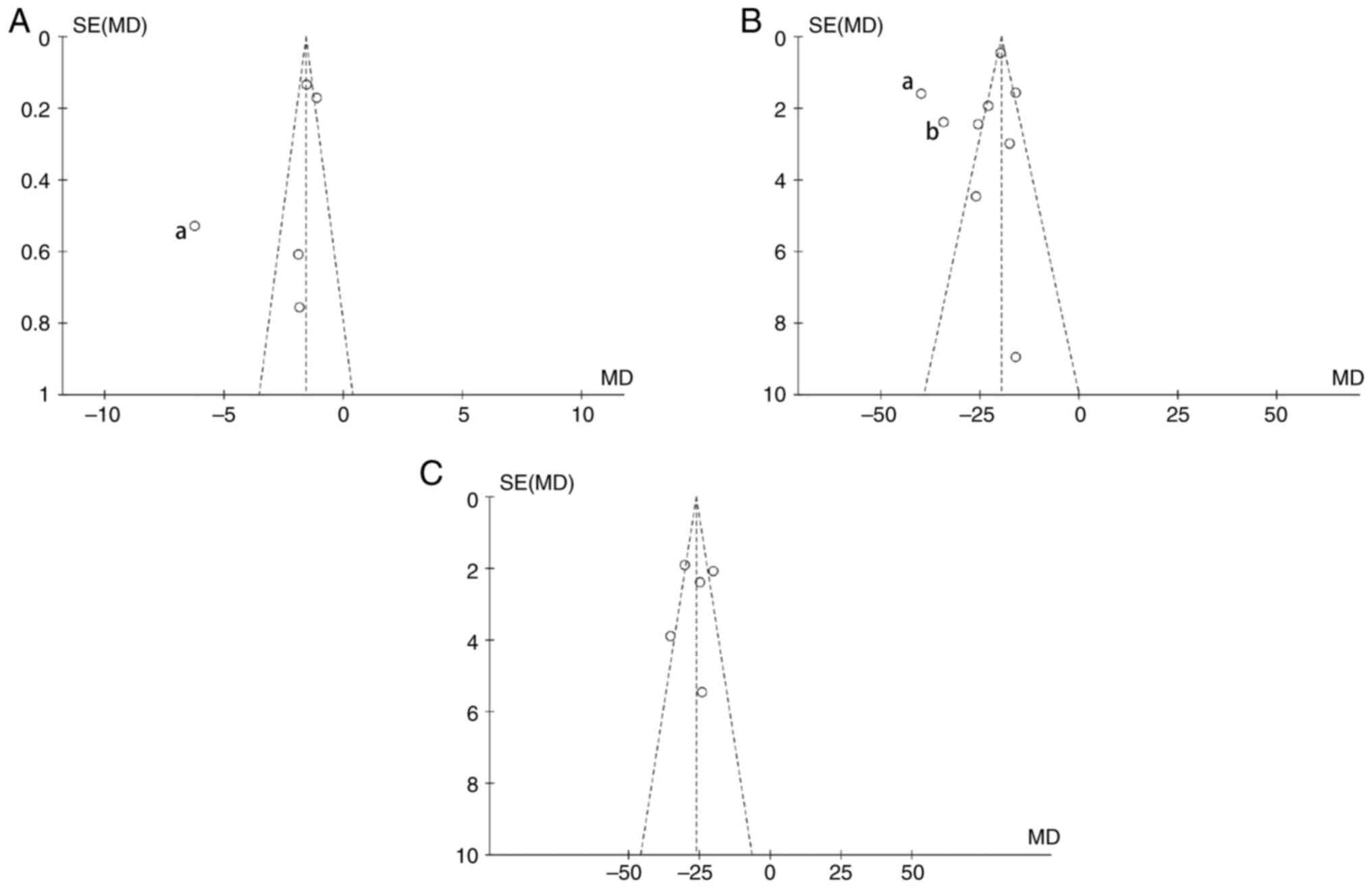
|
1
|
Huang M, Hong Z, Xiao C, Li L, Chen L,
Cheng S, Lei T and Zheng H: Effects of exosomes on neurological
function recovery for ischemic stroke in pre-clinical studies: A
meta-analysis. Front Cell Neurosci. 14(593130)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Zhao J, Deng H, Xun C, Chen C, Hu Z, Ge L
and Jiang Z: Therapeutic potential of stem cell extracellular
vesicles for ischemic stroke in preclinical rodent models: A
meta-analysis. Stem Cell Res Ther. 14(62)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Campbell BCV, De Silva DA, Macleod MR,
Coutts SB, Schwamm LH, Davis SM and Donnan GA: Ischaemic stroke.
Nat Rev Dis Primers. 5(70)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Zhang ZG and Chopp M: Exosomes in stroke
pathogenesis and therapy. J Clin Invest. 126:1190–1197.
2016.PubMed/NCBI View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zakrzewski W, Dobrzyński M, Szymonowicz M
and Rybak Z: Stem cells: Past, present, and future. Stem Cell Res
Ther. 10(68)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Nistor-Cseppentö DC, Jurcău MC, Jurcău A,
Andronie-Cioară FL and Marcu F: Stem cell- and cell-based therapies
for ischemic stroke. Bioengineering (Basel). 9(717)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Li Y, Hu G and Cheng Q: Implantation of
human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells for ischemic stroke:
Perspectives and challenges. Front Med. 9:20–29. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Chopp M and Zhang ZG: Emerging potential
of exosomes and noncoding microRNAs for the treatment of
neurological injury/diseases. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 20:523–526.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Doeppner TR, Bähr M, Hermann DM and Giebel
B: Concise review: Extracellular vesicles overcoming limitations of
cell therapies in ischemic stroke. Stem Cells Transl Med.
6:2044–2052. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Rao D, Sang C, Lai Z, Zhong J and Tang Z:
Roles of extracellular vesicles in cerebral protection of ischemic
stroke. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 42:160–170. 2021.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Burda BU, O'Connor EA, Webber EM, Redmond
N and Perdue LA: Estimating data from figures with a web-based
program: Considerations for a systematic review. Res Synth Methods.
8:258–262. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Bahr-Hosseini M, Bikson M, Iacoboni M,
Liebeskind DS, Hinman JD, Carmichael ST and Saver JL: PRIMED2
Preclinical evidence scoring tool to assess readiness for
translation of neuroprotection therapies. Transl Stroke Res.
13:222–227. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Seifali E, Hassanzadeh G, Mahdavipour M,
Mortezaee K, Moini A, Satarian L, Shekari F, Nazari A, Movassaghi S
and Akbari M: Extracellular vesicles derived from human umbilical
cord perivascular cells improve functional recovery in brain
ischemic rat via the inhibition of apoptosis. Iran Biomed J.
24:347–360. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Wang C, Börger V, Mohamud Yusuf A, Tertel
T, Stambouli O, Murke F, Freund N, Kleinschnitz C, Herz J, Gunzer
M, et al: Postischemic neuroprotection associated with
anti-inflammatory effects by mesenchymal stromal cell-derived small
extracellular vesicles in aged mice. Stroke. 53:e14–e18.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hu X, Pan J, Li Y, Jiang Y, Zheng H, Shi
R, Zhang Q, Liu C, Tian H, Zhang Z, et al: Extracellular vesicles
from adipose-derived stem cells promote microglia M2 polarization
and neurological recovery in a mouse model of transient middle
cerebral artery occlusion. Stem Cell Res Ther.
13(21)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gregorius J, Wang C, Stambouli O, Hussner
T, Qi Y, Tertel T, Börger V, Mohamud Yusuf A, Hagemann N, Yin D, et
al: Small extracellular vesicles obtained from hypoxic mesenchymal
stromal cells have unique characteristics that promote cerebral
angiogenesis, brain remodeling and neurological recovery after
focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Basic Res Cardiol.
116(40)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Dumbrava DA, Surugiu R, Börger V, Ruscu M,
Tertel T, Giebel B, Hermann DM and Popa-Wagner A: Mesenchymal
stromal cell-derived small extracellular vesicles promote
neurological recovery and brain remodeling after distal middle
cerebral artery occlusion in aged rats. GeroScience. 44:293–310.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Hu B, Chen S, Zou M, He Z, Shao S and Liu
B: Effect of extracellular vesicles on neural functional recovery
and immunologic suppression after rat cerebral apoplexy. Cell
Physiol Biochem. 40:155–162. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Li S, Luo L, He Y, Li R, Xiang Y, Xing Z,
Li Y, Albashari AA, Liao X, Zhang K, et al: Dental pulp stem
cell-derived exosomes alleviate cerebral ischaemia-reperfusion
injury through suppressing inflammatory response. Cell Prolif.
54(e13093)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tian T, Cao L, He C, Ye Q, Liang R, You W,
Zhang H, Wu J, Ye J, Tannous BA and Gao J: Targeted delivery of
neural progenitor cell-derived extracellular vesicles for
anti-inflammation after cerebral ischemia. Theranostics.
11:6507–6521. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Han M, Cao Y, Xue H, Chu X, Li T, Xin D,
Yuan L, Ke H, Li G and Wang Z: Neuroprotective effect of
mesenchymal stromal cell-derived extracellular vesicles against
cerebral ischemia-reperfusion-induced neural functional injury: A
pivotal role for AMPK and JAK2/STAT3/NF-κB signaling pathway
modulation. Drug Des Devel Ther. 14:2865–2876. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Hou Z, Chen J, Yang H, Hu X and Yang F:
microRNA-26a shuttled by extracellular vesicles secreted from
adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells reduce neuronal damage
through KLF9-mediated regulation of TRAF2/KLF2 axis. Adipocyte.
10:378–393. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Doeppner TR, Herz J, Görgens A, Schlechter
J, Ludwig AK, Radtke S, de Miroschedji K, Horn PA, Giebel B and
Hermann DM: Extracellular vesicles improve post-stroke
neuroregeneration and prevent postischemic immunosuppression. Stem
Cells Transl Med. 4:1131–1143. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Heras-Romero Y, Morales-Guadarrama A,
Santana-Martínez R, Ponce I, Rincón-Heredia R, Poot-Hernández AC,
Martínez-Moreno A, Urrieta E, Bernal-Vicente BN, Campero-Romero AN,
et al: Improved post-stroke spontaneous recovery by astrocytic
extracellular vesicles. Mol Ther. 30:798–815. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Li Z, Song Y, He T, Wen R, Li Y, Chen T,
Huang S, Wang Y, Tang Y, Shen F, et al: M2 microglial small
extracellular vesicles reduce glial scar formation via the
miR-124/STAT3 pathway after ischemic stroke in mice. Theranostics.
11:1232–1248. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Barzegar M, Wang Y, Eshaq RS, Yun JW,
Boyer CJ, Cananzi SG, White LA, Chernyshev O, Kelley RE, Minagar A,
et al: Human placental mesenchymal stem cells improve stroke
outcomes via extracellular vesicles-mediated preservation of
cerebral blood flow. EBioMedicine. 63(103161)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Feng B, Meng L, Luan L, Fang Z, Zhao P and
Zhao G: Upregulation of extracellular vesicles-encapsulated mir-132
released from mesenchymal stem cells attenuates ischemic neuronal
injury by inhibiting Smad2/c-jun pathway via Acvr2b
suppression. Front Cell Dev Biol. 8(568304)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Song Y, Li Z, He T, Qu M, Jiang L, Li W,
Shi X, Pan J, Zhang L, Wang Y, et al: M2 microglia-derived exosomes
protect the mouse brain from ischemia-reperfusion injury via
exosomal miR-124. Theranostics. 9:2910–2923. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Liu Y, Li YP, Xiao LM, Chen LK, Zheng SY,
Zeng EM and Xu CH: Extracellular vesicles derived from M2 microglia
reduce ischemic brain injury through microRNA-135a-5p/TXNIP/NLRP3
axis. Lab Invest. 101:837–850. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Dong C, Chen M, Cai B, Zhang C, Xiao G and
Luo W: Mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes improved cerebral
infarction via transferring miR-23a-3p to activate microglia.
Neuromolecular Med. 24:290–298. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Liu Z, Li X, Ye Z and Lin H:
Neuroprotective effect of exosomes derived from bone marrow
mesenchymal stem cells via activating TGR5 and suppressing
apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 593:13–19. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xie X, Cao Y, Dai L and Zhou D: Bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomal lncRNA KLF3-AS1
stabilizes Sirt1 protein to improve cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
injury via miR-206/USP22 axis. Mol Med. 29(3)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Thomas JM, Cunningham CJ, Lawrence CB,
Pinteaux E and Allan SM: Therapeutic potential of extracellular
vesicles in preclinical stroke models: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. BMJ Open Sci. 44(e100047)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Gupta D, Zickler AM and El Andaloussi S:
Dosing extracellular vesicles. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.
178(113961)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Haupt M, Gerner ST, Bähr M and Doeppner
TR: Neuroprotective strategies for ischemic stroke-future
perspectives. Int J Mol Sci. 24(4334)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
DeLong JH, Ohashi SN, O'Connor KC and
Sansing LH: Inflammatory responses after ischemic stroke. Semin
Immunopathol. 44:625–648. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Jiang L, Chen W, Ye J and Wang Y:
Potential role of exosomes in ischemic stroke treatment.
Biomolecules. 12(115)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Liu T, Zhang Q, Zhang J, Li C, Miao YR,
Lei Q, Li Q and Guo AY: EVmiRNA: A database of miRNA profiling in
extracellular vesicles. Nucleic Acids Res. 47:D89–D93.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Li F, Kang X, Xin W and Li X: The emerging
role of extracellular vesicle derived from neurons/neurogliocytes
in central nervous system diseases: Novel insights into ischemic
stroke. Front Pharmacol. 13(890698)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|