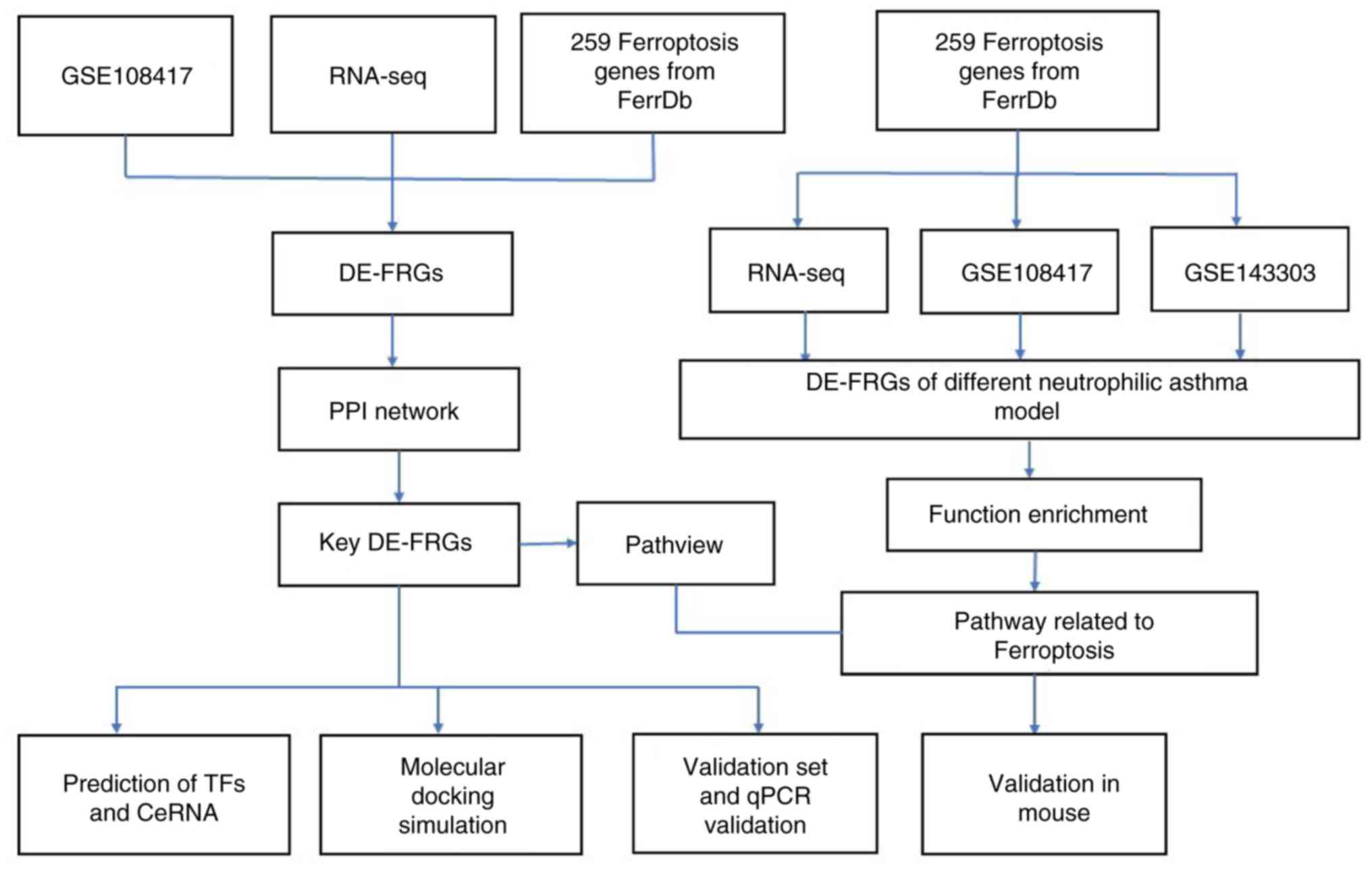
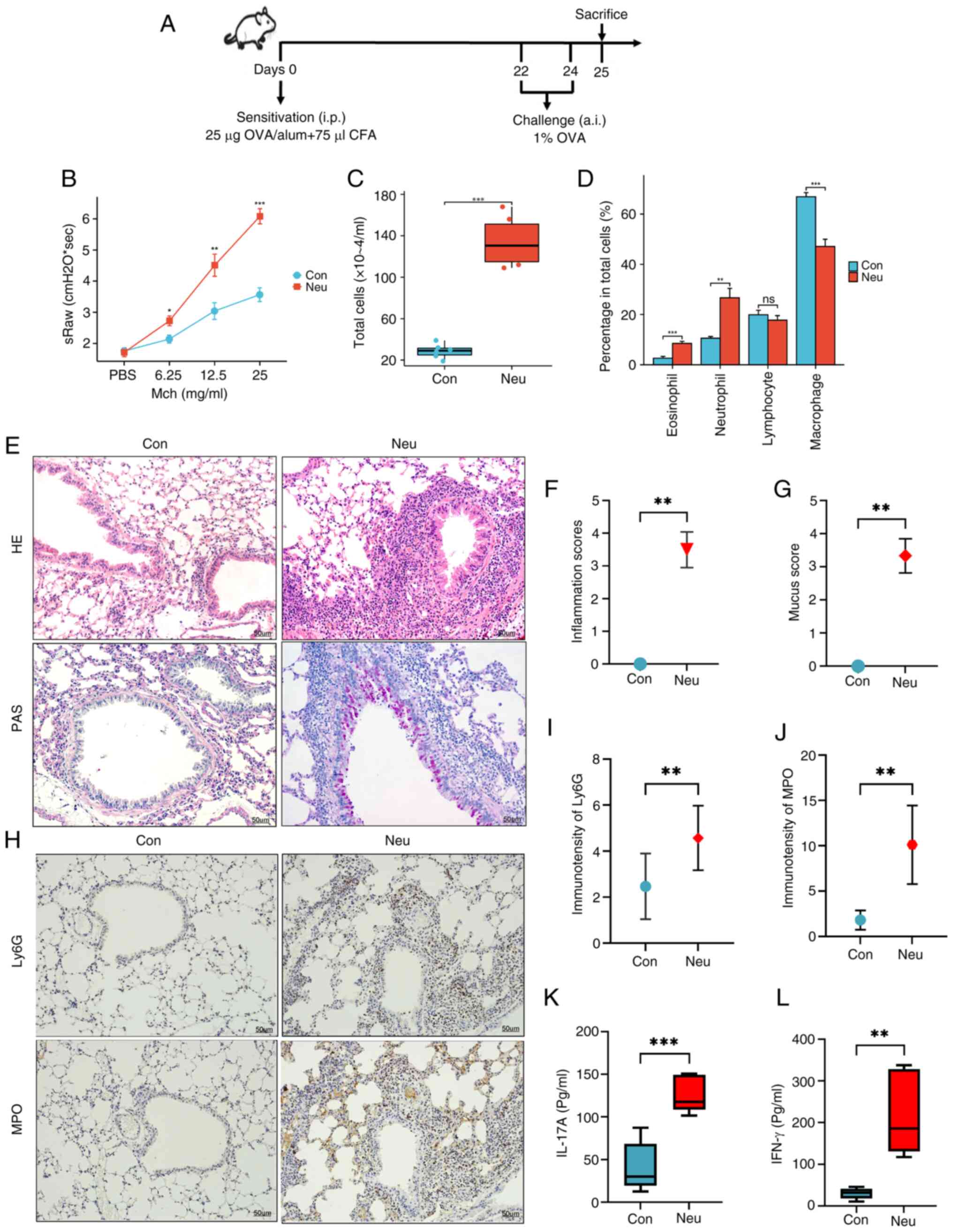
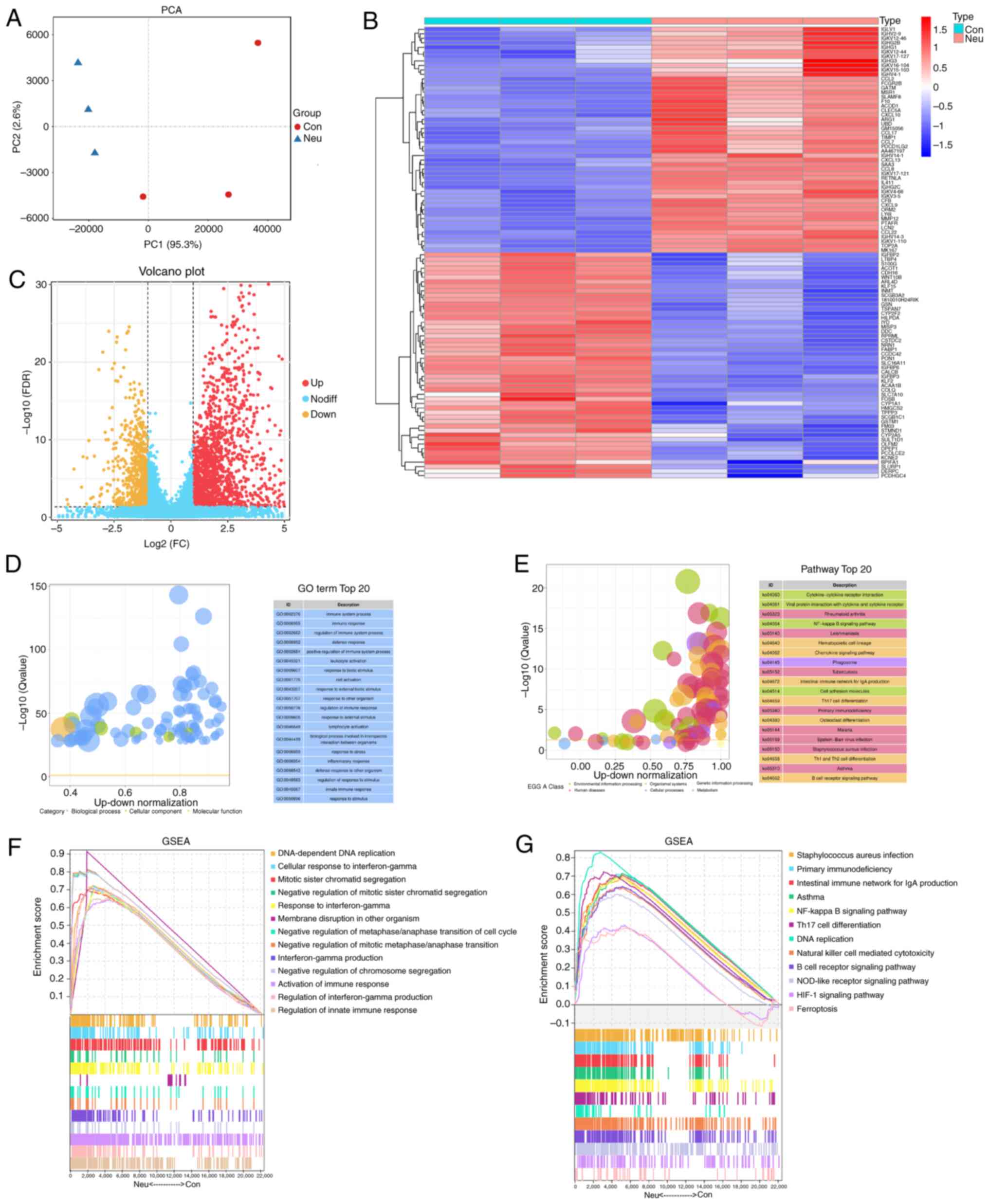
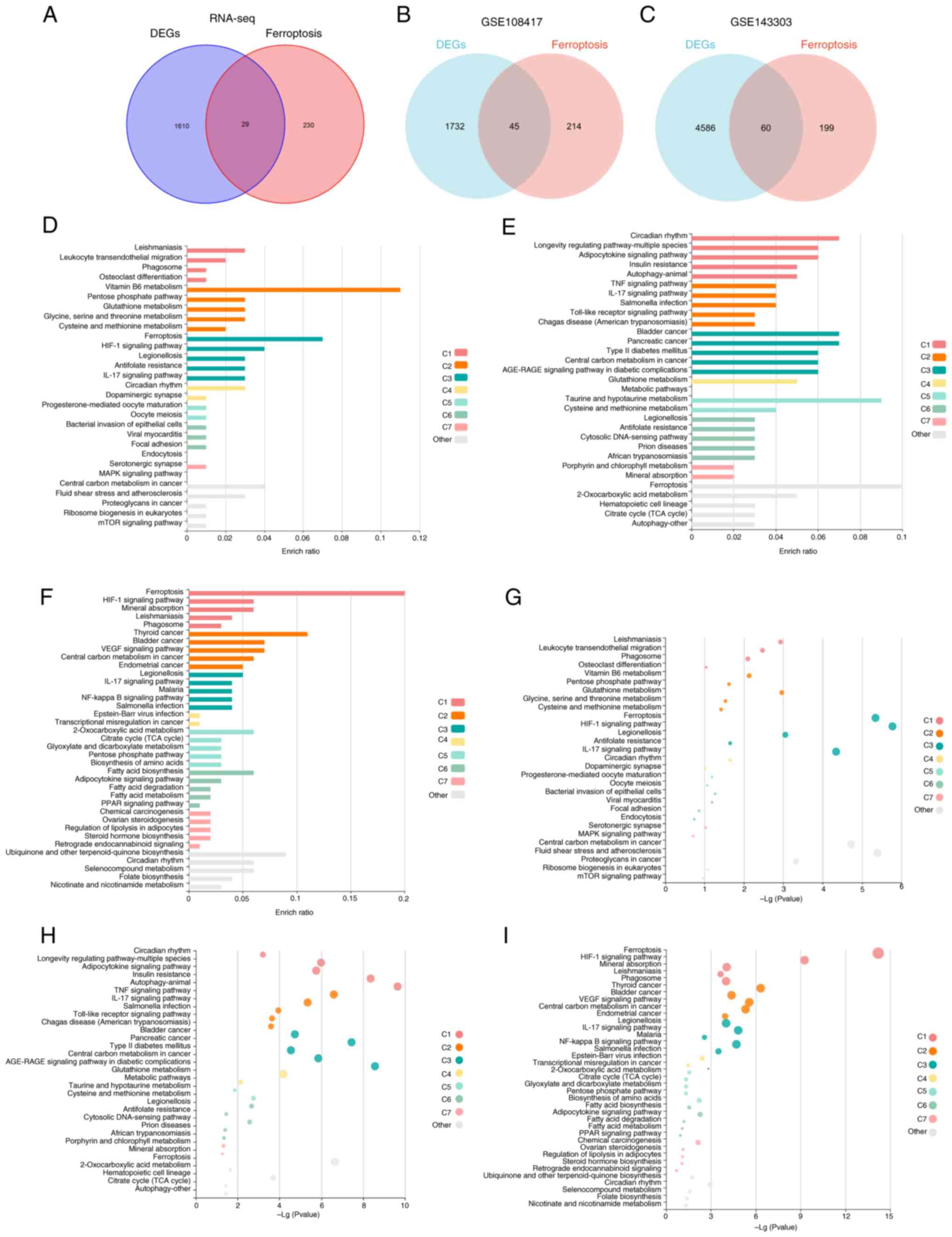
|
1
|
Hammad H and Lambrecht BN: The basic
immunology of asthma. Cell. 184:1469–1485. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ray A and Kolls JK: Neutrophilic
inflammation in asthma and association with disease severity.
Trends Immunol. 38:942–954. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhao L, Gao J, Chen G, Huang C, Kong W,
Feng Y and Zhen G: Mitochondria dysfunction in airway epithelial
cells is associated with type 2-low asthma. Front Genet.
14(1186317)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Doe C, Bafadhel M, Siddiqui S, Desai D,
Mistry V, Rugman P, McCormick M, Woods J, May R, Sleeman MA, et al:
Expression of the T helper 17-associated cytokines IL-17A and
IL-17F in asthma and COPD. Chest. 138:1140–1147. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Green RH, Brightling CE, Woltmann G,
Parker D, Wardlaw AJ and Pavord ID: Analysis of induced sputum in
adults with asthma: Identification of subgroup with isolated sputum
neutrophilia and poor response to inhaled corticosteroids. Thorax.
57:875–789. 2002.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR, Skouta
R, Zaitsev EM, Gleason CE, Patel DN, Bauer AJ, Cantley AM, Yang WS,
et al: Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell
death. Cell. 149:1060–1072. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Jiang YH, Wu SY, Wang Z, Zhang L, Zhang J,
Li Y, Liu C, Wu WZ and Xue YT: Bioinformatics analysis identifies
ferroptosis-related genes in the regulatory mechanism of myocardial
infarction. Exp Ther Med. 24(748)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Shao L, Fang Q, Ba C, Zhang Y, Shi C,
Zhang Y and Wang J: Identification of ferroptosis-associated genes
in chronic kidney disease. Exp Ther Med. 25(60)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hu T, Yu WP, Zou HX, Chai ZH, Le SY, Hu
FJ, Wang YC, Huang H, Lai SQ and Liu JC: Role of dysregulated
ferroptosis-related genes in cardiomyocyte ischemia-reperfusion
injury: Experimental verification and bioinformatics analysis. Exp
Ther Med. 26(534)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Zhou Q, Li T, Qin Q, Huang X and Wang Y:
Ferroptosis in lymphoma: Emerging mechanisms and a novel
therapeutic approach. Front Genet. 13(1039951)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang Q, Xiong Z, Wang B, Wang W and Zheng
H: Ferroptosis and preeclampsia: Genetic analysis of potential
biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Biochem Genet. 62:853–875.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Tang W, Dong M, Teng FZ, Cui J, Zhu X,
Wang W, Wuniqiemu T, Qin J, Yi L, Wang S, et al: Environmental
allergens house dust mite-induced asthma is associated with
ferroptosis in the lungs. Exp Ther Med. 22(1483)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Yang N and Shang Y: Ferrostatin-1 and
3-methyladenine ameliorate ferroptosis in OVA-induced asthma model
and in IL-13-challenged BEAS-2B cells. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2022(9657933)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Bao C, Liu C, Liu Q, Hua L, Hu J, Li Z and
Xu S: Liproxstatin-1 alleviates LPS/IL-13-induced bronchial
epithelial cell injury and neutrophilic asthma in mice by
inhibiting ferroptosis. Int Immunopharmacol.
109(108770)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Zhao X, Gao S, Ren H, Sun W, Zhang H, Sun
J, Yang S and Hao J: Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 promotes pancreatic
ductal adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis by activating
transcription of the actin-bundling protein fascin. Cancer Res.
74:2455–2464. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Gui D, Li Y, Chen X, Gao D, Yang Y and Li
X: HIF-1 signaling pathway involving iNOS, COX-2 and caspase-9
mediates the neuroprotection provided by erythropoietin in the
retina of chronic ocular hypertension rats. Mol Med Rep.
11:1490–1496. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fu X and Zhang F: Role of the HIF-1
signaling pathway in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Exp
Ther Med. 16:4553–4561. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Dong H, Zhang C, Shi D, Xiao X, Chen X,
Zeng Y, Li X and Xie R: Ferroptosis related genes participate in
the pathogenesis of spinal cord injury via HIF-1 signaling pathway.
Brain Res Bull. 192:192–202. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Qian JW, Wang C, Wang B, Yang J, Wang Y,
Luo F, Xu J, Zhao C, Liu R and Chu Y: The IFN-γ/PD-L1 axis between
T cells and tumor microenvironment: Hints for glioma
anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. J Neuroinflamm. 15(290)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Chen L, Hou W, Liu F, Zhu R, Lv A, Quan W
and Mao S: Blockade of NLRP3/caspase-1/IL-1β regulated Th17/treg
immune imbalance and attenuated the neutrophilic airway
inflammation in an ovalbumin-induced murine model of asthma. J
Immunol Res. 2022(9444227)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Bogaert P, Naessens T, De Koker S, Hennuy
B, Hacha J, Smet M, Cataldo D, Di Valentin E, Piette J, Tournoy KG
and Grooten J: Inflammatory signatures for eosinophilic vs
neutrophilic allergic pulmonary inflammation reveal critical
regulatory checkpoints. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol.
300:L679–L690. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Chen X, Jiang X, Lu Y, Yao Y, Lu J, Zhi Q,
Lai L, Liang J and Li C: Aerosol inhalation of Mycobacterium bovis
can reduce the Th2 dominant immune response induced by ovalbumin
sensitization. Am J Transl Res. 14:3430–3438. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Li L, Sun Q, Xiao H, Zhang Q, Xu S, Lai L,
Li Z and Li C: Aerosol inhalation of heat-killed clostridium
butyricum CGMCC0313-1 alleviates allergic airway inflammation in
mice. J Immunol Res. 2022(8447603)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Xiao H, Zhang QN, Sun QX, Li LD, Xu SY and
Li CQ: Transcriptomic analysis reveals a link between hippo
signaling pathway and macrophages in lungs of mice with OVA-induced
allergic asthma. J Inflamm Res. 15:423–437. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dong L, Wang Y, Zheng T, Pu Y, Ma Y, Qi X,
Zhang W, Xue F, Shan Z, Liu J, et al: Hypoxic hUCMSC-derived
extracellular vesicles attenuate allergic airway inflammation and
airway remodeling in chronic asthma mice. Stem Cell Res Ther.
12(4)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Jia M, Fu H, Jiang X, Wang L, Xu J, Barnes
PJ, Adcock IM, Liu Y, He S, Zhang F, et al: DEL-1, as an
anti-neutrophil transepithelial migration molecule, inhibits airway
neutrophilic inflammation in asthma. Allergy. 79:1180–1194.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Pertea M, Pertea GM, Antonescu CM, Chang
TC, Mendell JT and Salzberg SL: StringTie enables improved
reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat
Biotechnol. 33:290–295. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Pertea M, Kim D, Pertea GM, Leek JT and
Salzberg SL: Transcript-level expression analysis of RNA-seq
experiments with HISAT, StringTie and ballgown. Nat Protoc.
11:1650–1667. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Love MI, Huber W and Anders S: Moderated
estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with
DESeq2. Genome Biol. 15(550)2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK,
Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub
TR, Lander ES and Mesirov JP: Gene set enrichment analysis: A
knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression
profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 102:15545–15550. 2005.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Ogata H, Goto S, Sato K, Fujibuchi W, Bono
H and Kanehisa M: KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes.
Nucleic Acids Res. 27:29–34. 1999.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Dusa A: venn: Draw Venn Diagrams R
package. R Core Team, Vienna, 2020.
|
|
33
|
von Mering C, Huynen M, Jaeggi D, Schmidt
S, Bork P and Snel B: STRING: A database of predicted functional
associations between proteins. Nucleic Acids Res. 31:258–261.
2003.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Ritchie ME, Phipson B, Wu D, Hu Y, Law CW,
Shi W and Smyth GK: limma powers differential expression analyses
for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res.
43(e47)2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Kassambara A: ggpubr: ‘ggplot2’ based
publication ready plots. R package version 0.4. 0, 2020. https://CRAN.R-project.org/package=ggpubr.
|
|
36
|
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, Tiberti N,
Lisacek F, Sanchez JC and Müller M: pROC: An open-source package
for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics.
12(77)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ginestet C: ggplot2: Elegant graphics for
data analysis. J R Stat Soc Ser A. 174:245. 2011.
|
|
38
|
Smoot ME, Ono K, Ruscheinski J, Wang PL
and Ideker T: Cytoscape 2.8: New features for data integration and
network visualization. Bioinformatics. 27:431–432. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Wong N and Wang X: miRDB: An online
resource for microRNA target prediction and functional annotations.
Nucleic Acids Res. 43 (Database Issue):D146–D152. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Dweep H, Sticht C, Pandey P and Gretz N:
miRWalk-database: Prediction of possible miRNA binding sites by
‘walking’ the genes of three genomes. J Biomed Inform. 44:839–847.
2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Furió-Tarí P, Tarazona S, Gabaldón T,
Enright AJ and Conesa A: spongeScan: A web for detecting microRNA
binding elements in lncRNA sequences. Nucleic Acids Res. 44
(W1):W176–W180. 2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Yoo M, Shin J, Kim J, Ryall KA, Lee K, Lee
S, Jeon M, Kang J and Tan AC: DSigDB: Drug signatures database for
gene set analysis. Bioinformatics. 31:3069–3071. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Morris GM, Goodsell DS, Halliday RS, Huey
R, Hart WE, Belew RK and Olson AJ: Automated docking using a
Lamarckian genetic algorithm and an empirical binding free energy
function. J Comput Chem. 19:1639–1662. 1998.
|
|
44
|
Wishart DS, Feunang YD, Guo AC, Lo EJ,
Marcu A, Grant JR, Sajed T, Johnson D, Li C, Sayeeda Z, et al:
DrugBank 5.0: A major update to the DrugBank database for 2018.
Nucleic Acids Res. 46 (D1):D1074–D1082. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Berman HM, Westbrook J, Feng Z, Gilliland
G, Bhat TN, Weissig H, Shindyalov IN and Bourne PE: The protein
data bank. Nucleic Acids Res. 28:235–242. 2000.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Tian YN, Zhou YH, Li L, Huang C, Lin L, Li
C and Ye Y: Effect of substrate composition on physicochemical
properties of the medium-long-medium structured triacylglycerol. J
Sci Food Agric. 104:942–955. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408.
2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Raundhal M, Morse C, Khare A, Oriss TB,
Milosevic J, Trudeau J, Huff R, Pilewski J, Holguin F, Kolls J, et
al: High IFN-γ and low SLPI mark severe asthma in mice and humans.
J Clin Invest. 125:3037–3050. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
McKinley L, Alcorn JF, Peterson A, Dupont
RB, Kapadia S, Logar A, Henry A, Irvin CG, Piganelli JD, Ray A and
Kolls JK: TH17 cells mediate steroid-resistant airway inflammation
and airway hyperresponsiveness in mice. J Immunol. 181:4089–4097.
2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
50
|
Zeng Z, Huang H, Zhang J, Liu Y, Zhong W,
Chen W, Lu Y, Qiao Y, Zhao H, Meng X, et al: HDM induce airway
epithelial cell ferroptosis and promote inflammation by activating
ferritinophagy in asthma. FASEB J. 36(e22359)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
51
|
Deng B, Liao F, Liu Y, He P, Wei S, Liu C
and Dong W: Comprehensive analysis of endoplasmic reticulum
stress-associated genes signature of ulcerative colitis. Front
Immunol. 14(1158648)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
52
|
Choi W, Wu Y, Li Y and Dong J: Network
pharmacology prediction and molecular docking analysis reveal the
mechanism of modified Bushen Yiqi formulas on chronic obstructive
pulmonary disease. J Gene Med. 26(e3607)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Cao F, Luo A and Yang C: G6PD inhibits
ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting cytochrome
P450 oxidoreductase. Cell Signal. 87(110098)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Wang S, Song Y, Xu F, Liu H, Shen Y, Hu L,
Fu Y and Zhu L: Identification and validation of
ferroptosis-related genes in lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung
injury. Cell Signal. 108(110698)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Chen D, Li Z, Bao P, Chen M, Zhang M, Yan
F, Xu Y, Ji C, Hu X, Sanchis D, et al: Nrf2 deficiency aggravates
angiotensin II-induced cardiac injury by increasing hypertrophy and
enhancing IL-6/STAT3-dependent inflammation. Biochim Biophys Acta
Mol Basis Dis. 1865:1253–1264. 2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Zhang Z, Tang J, Song J, Xie M, Liu Y,
Dong Z, Liu X, Li X, Zhang M, Chen Y, et al: Elabela alleviates
ferroptosis, myocardial remodeling, fibrosis and heart dysfunction
in hypertensive mice by modulating the IL-6/STAT3/GPX4 signaling.
Free Radical Bio Med. 181:130–142. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Han F, Li S, Yang Y and Bai Z:
Interleukin-6 promotes ferroptosis in bronchial epithelial cells by
inducing reactive oxygen species-dependent lipid peroxidation and
disrupting iron homeostasis. Bioengineered. 12:5279–5288.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
58
|
Yi Q, Liang Q, Liu Y, Gong Z and Yan Y:
Application of genomic selection and experimental techniques to
predict cell death and immunotherapeutic efficacy of
ferroptosis-related CXCL2 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol.
12(998736)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Jin R, Yang R, Cui C, Zhang H, Cai J, Geng
B and Chen Z: Ferroptosis due to cystathionine γ Lyase/hydrogen
sulfide downregulation under high hydrostatic pressure exacerbates
VSMC dysfunction. Front Cell Dev Biol. 10(829316)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
60
|
Hayashi K, Saeki M, Miura K, Yamasaki N,
Matsuda M, Shimora H, Nabe T, Shimizu Y, Fujita T, Endou H and
Kaminuma O: JPH203, a LAT1 inhibitor, alleviates steroid-resistant
murine airway inflammation mediated by Th17 cells. Allergy.
78:2780–2783. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
61
|
Törnroos R, Tina E and Eremo AG: SLC7A5 is
linked to increased expression of genes related to proliferation
and hypoxia in estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. Oncol Rep.
47(17)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
62
|
Consoli V, Sorrenti V, Grosso S and
Vanella L: Heme oxygenase-1 signaling and redox homeostasis in
physiopathological conditions. Biomolecules. 11(589)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
63
|
Kwon MY, Park E, Lee SJ and Chung SW: Heme
oxygenase-1 accelerates erastin-induced ferroptotic cell death.
Oncotarget. 6:24393–24403. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
64
|
Tang Z, Ju Y, Dai X, Ni N, Liu Y, Zhang D,
Gao H, Sun H, Zhang J and Gu P: HO-1-mediated ferroptosis as a
target for protection against retinal pigment epithelium
degeneration. Redox Bio. 43(101971)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
65
|
Wong TH, Chen HA, Gau RJ, Yen JH and Suen
JL: Heme oxygenase-1-expressing dendritic cells promote Foxp3+
regulatory T cell differentiation and induce less severe airway
inflammation in murine models. PLoS One.
11(e0168919)2016.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
66
|
Feng FH, He SS, Li XL, He JK and Luo LX:
Mitochondria-mediated ferroptosis in diseases therapy: From
molecular mechanisms to implications. Aging Dis. 15:714–738.
2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
67
|
McGettrick AF and O'Neill LAJ: The role of
HIF in immunity and inflammation. Cell Metab. 32:524–536.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
68
|
Zhongyin Z, Wei W, Juan X and Guohua F:
Isoliquiritin apioside relieves intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion-induced acute lung injury by blocking
Hif-1α-mediated ferroptosis. Int Immunopharmacol.
108(108852)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
69
|
Wu Y, Wang J, Zhao T, Chen J, Kang L, Wei
Y, Han L, Shen L, Long C, Wu S and Wei G: Di-(2-ethylhexyl)
phthalate exposure leads to ferroptosis via the HIF-1α/HO-1
signaling pathway in mouse testes. J Hazard Mater.
426(127807)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Feng X, Wang S, Sun Z, Dong H, Yu H, Huang
M and Gao X: Ferroptosis enhanced diabetic renal tubular injury via
HIF-1α/HO-1 Pathway in db/db mice. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne).
12(526390)2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
71
|
Huerta-Yepez S, Baay-Guzman GJ, Bebenek
IG, Hernandez-Pando R, Vega MI, Chi L, Riedl M, Diaz-Sanchez D,
Kleerup E, Tashkin DP, et al: Hypoxia inducible factor promotes
murine allergic airway inflammation and is increased in asthma and
rhinitis. Allergy. 66:909–918. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Chen T, Chen X, Zhang S, Zhu J, Tang B,
Wang A, Dong L, Zhang Z, Yu C, Sun Y, et al: The genome sequence
archive family: Toward explosive data growth and diverse data
types. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 19:578–583.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
National Genomics Data Center Members and
Partners. Database resources of the national genomics data center
in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 48 (D1):D24–D33. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|