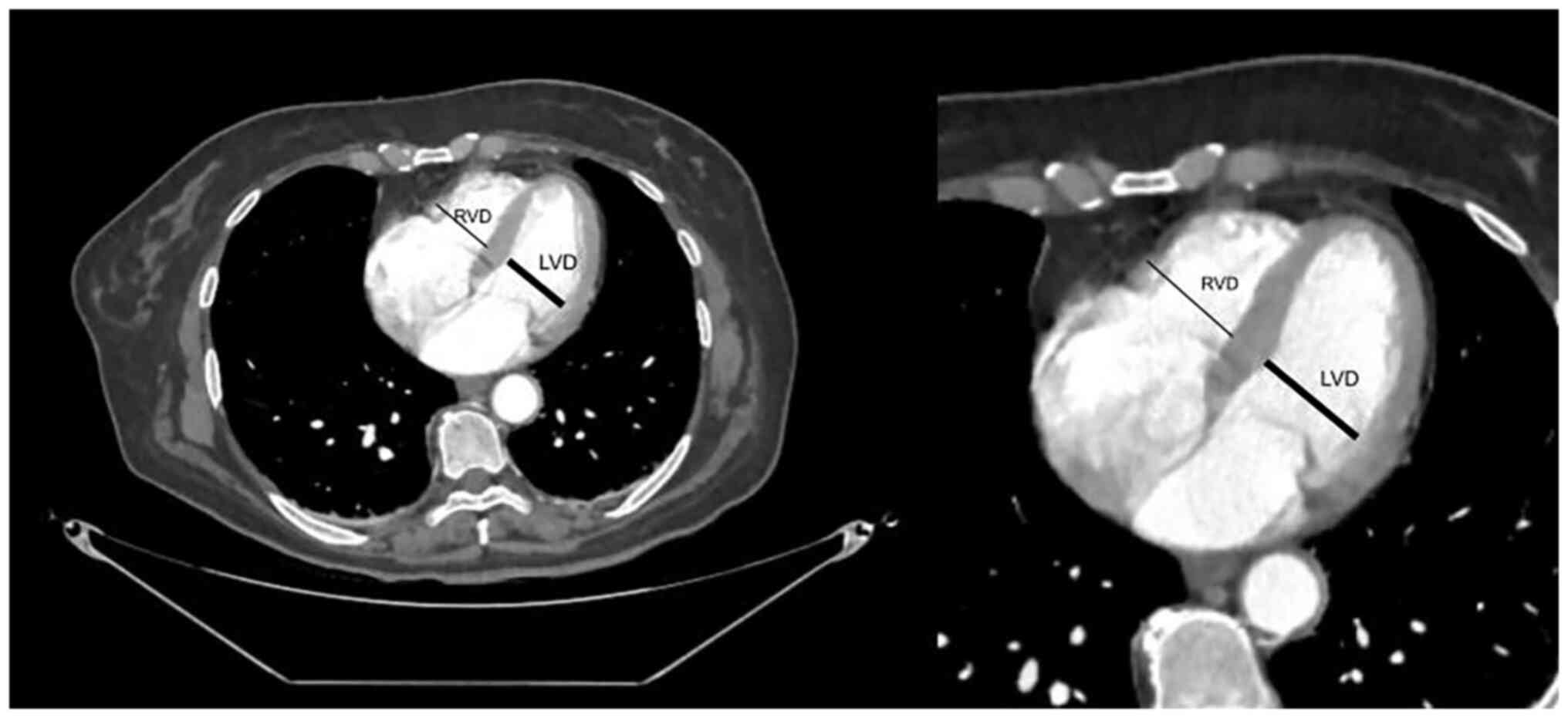
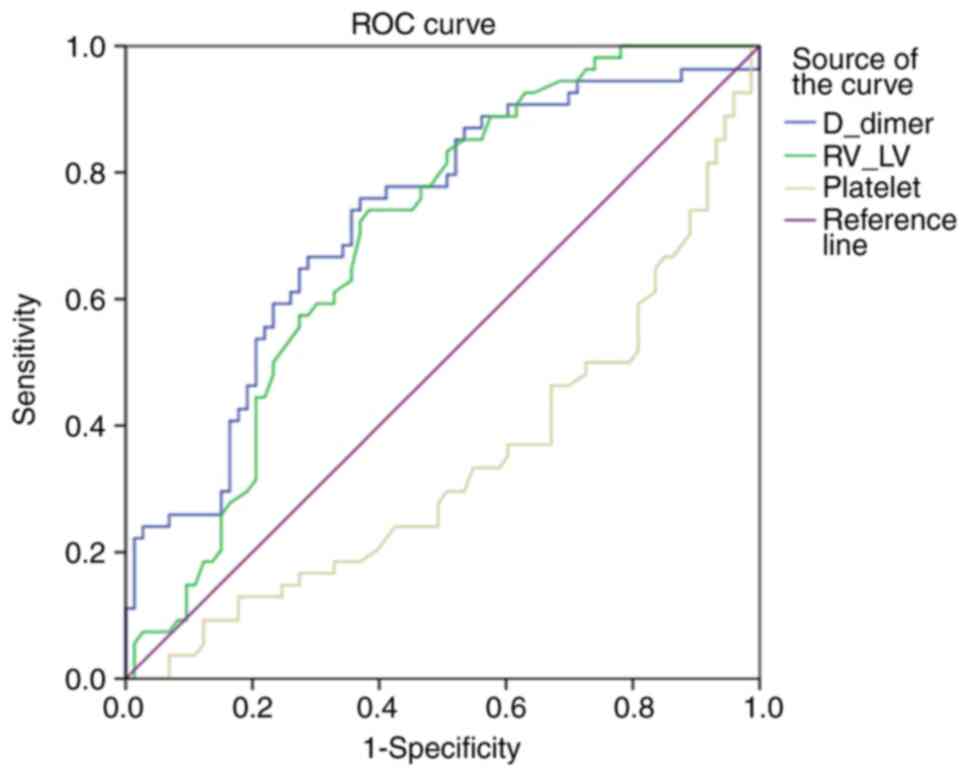
|
1
|
Konstantinides SV, Meyer G, Becattini C,
Bueno H, Geersing GJ, Harjola VP, Huisman MV, Humbert M, Jennings
CS, Jiménez D, et al: 2019 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and
management of acute pulmonary embolism developed in collaboration
with the European respiratory society (ERS). Eur Heart J.
41:543–603. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Balakrishna AM, Reddi V, Belford PM,
Alvarez M, Jaber WA, Zhao DX and Vallabhajosyula S:
Intermediate-Risk pulmonary embolism: A review of contemporary
diagnosis, risk stratification and management. Medicina (Kaunas).
58(1186)2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zimmermann L, Laufs U, Petros S and Lenk
K: Outcome after thrombolysis in patients with intermediate
high-risk pulmonary embolism: A propensity score analysis. J Emerg
Med. 62:378–389. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Meyer G, Vicaut E, Danays T, Agnelli G,
Becattini C, Beyer-Westendorf J, Bluhmki E, Bouvaist H, Brenner B,
Couturaud F, et al: Fibrinolysis for patients with
intermediate-risk pulmonary embolism. N Engl J Med. 370:1402–1411.
2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kagima J, Stolbrink M, Masheti S, Mbaiyani
C, Munubi A, Joekes E, Mortimer K, Rylance J and Morton B:
Diagnostic accuracy of combined thoracic and cardiac sonography for
the diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. PLoS One. 15(e0235940)2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Thomas SE, Weinberg I, Schainfeld RM,
Rosenfield K and Parmar GM: Diagnosis of pulmonary embolism: A
review of evidence-based approaches. J Clin Med.
13(3722)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Kang DK, Thilo C, Schoepf UJ, Barraza JM
Jr, Nance JW Jr, Bastarrika G, Abro JA, Ravenel JG, Costello P and
Goldhaber SZ: CT signs of right ventricular dysfunction: Prognostic
role in acute pulmonary embolism. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging.
4:841–849. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Miyagawa M, Okumura Y, Fukamachi D, Fukuda
I, Nakamura M, Yamada N, Takayama M, Maeda H, Yamashita T, Ikeda T,
et al: Clinical implication of the right ventricular/left
ventricular diameter ratio in patients with pulmonary
thromboembolism. Int Heart J. 63:255–263. 2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang J, Guan W, Chen D, Han Y, Xu Z, Qiang
J, Chen W, Li N and Gao W: The value of CTPA for diagnosing acute
pulmonary thromboembolism and the ensuing right ventricular
dysfunction. Cell Biochem Biophys. 69:517–522. 2014.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Pastré J, Sanchis-Borja M and Benlounes M:
Risk stratification and treatment of pulmonary embolism with
intermediate-risk of mortality. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 28:375–383.
2022.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Tapson VF: Thrombolytic therapy in acute
pulmonary embolism. Curr Opin Cardiol. 27:585–591. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Keller K, Beule J, Balzer JO and Dippold
W: D-Dimer and thrombus burden in acute pulmonary embolism. Am J
Emerg Med. 36:1613–1618. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Hu J, Tian X, Liu XW, Liu YZ, Gao BL and
Li CY: Markers of right ventricular dysfunction predict 30-day
adverse prognosis of pulmonary embolism on pulmonary computed
tomographic angiography. Medicine (Baltimore).
102(e34304)2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Brunton N, McBane R, Casanegra AI,
Houghton DE, Balanescu DV, Ahmad S, Caples S, Motiei A and Henkin
S: Risk stratification and management of intermediate-risk acute
pulmonary embolism. J Clin Med. 13(257)2024.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Park JR, Chang SA, Jang SY, No HJ, Park
SJ, Choi SH, Park SW, Kim H, Choe YH, Lee KS, et al: Evaluation of
right ventricular dysfunction and prediction of clinical outcomes
in acute pulmonary embolism by chest computed tomography:
Comparisons with echocardiography. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging.
28:979–987. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ayöz S, Erol S, Kul M, Kaya AG, Çoruh AG,
Savaş İ, Aydın Ö and Kaya A: Using RV/LV ratio and cardiac
biomarkers to define the risk of mortality from pulmonary embolism.
Tuberk Toraks. 69:297–306. 2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Ammari Z, Hasnie AA, Ruzieh M, Dasa O,
Al-Sarie M, Shastri P, Ashcherkin N, Brewster PS, Cooper CJ and
Gupta R: Prognostic value of computed tomography versus
echocardiography derived right to left ventricular diameter ratio
in acute pulmonary embolism. Am J Med Sci. 361:445–450.
2021.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Moore AJE, Wachsmann J, Chamarthy MR,
Panjikaran L, Tanabe Y and Rajiah P: Imaging of acute pulmonary
embolism: An update. Cardiovasc Diagn Ther. 8:225–243.
2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Nasser MF, Jabri A, Limaye S, Sharma S,
Hamade H, Mhanna M, Aneja A and Gandhi S: Echocardiographic
evaluation of pulmonary embolism: A review. J Am Soc Echocardiogr.
36:906–912. 2023.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yamashita Y, Morimoto T, Amano H, Takase
T, Hiramori S, Kim K, Oi M, Akao M, Kobayashi Y, Toyofuku M, et al:
Validation of simplified PESI score for identification of low-risk
patients with pulmonary embolism: From the COMMAND VTE registry.
Eur Heart J Acute Cardiovasc Care. 9:262–270. 2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|