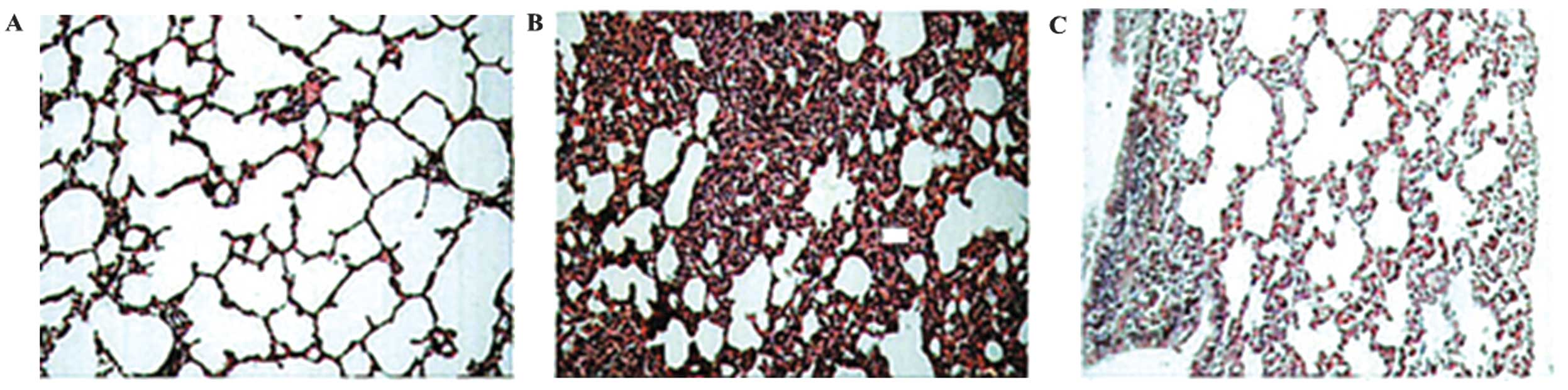
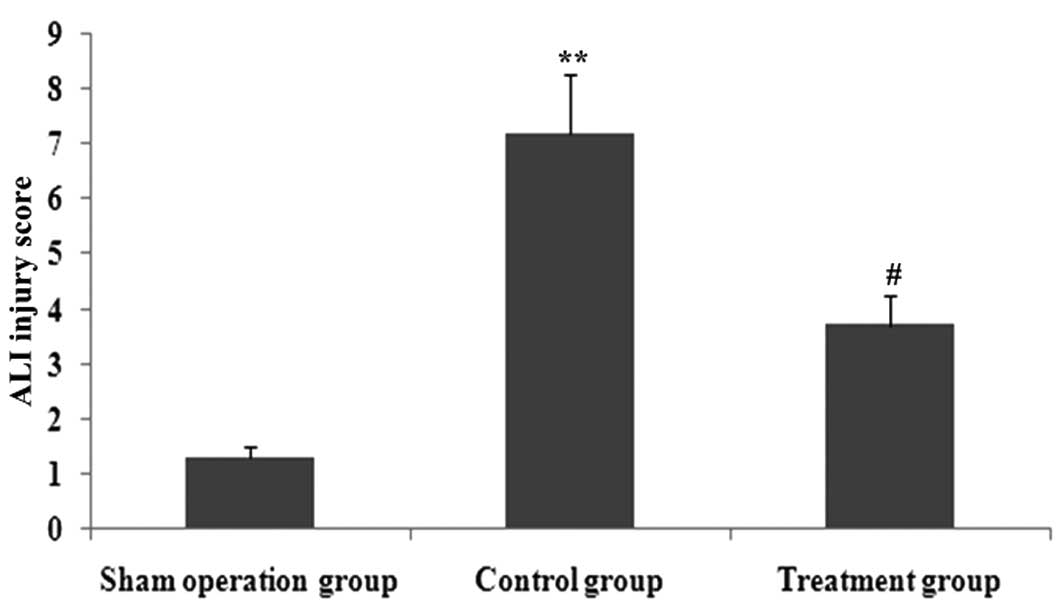
|
1
|
Ware LB and Matthay MA: The acute
respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med. 342:1334–1349. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rubenfeld GD, Caldwell E, Peabody E,
Weaver J, Martin DP, Neff M, Stern EJ and Hudson LD: Incidence and
outcomes of acute lung injury. N Engl J Med. 353:1685–1693. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Berthiaume Y, Folkesson HG and Matthay MA:
Lung edema clearance: 20 years of progress invited review: alveolar
edema fluid clearance in the injured lung. J Appl Physiol.
93:2207–2213. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Burns K, Clatworthy J, Martin L, Martinon
F, Plumpton C, Maschera B, Lewis A, Ray K, Tschopp J and Volpe F:
Tollip, a new component of the IL-1RI pathway, links IRAK to the
IL-1 receptor. Nat Cell Biol. 2:346–351. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Yamakami M and Yokosawa H: Tom1 (target of
Myb 1) is a novel negative regulator of interleukin-1- and tumor
necrosis factor-induced signaling pathways. Biol Pharm Bull.
27:564–566. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yamakami M, Yoshimori T and Yokosawa H:
Tom1, a VHS domain containing protein, interacts with Tollip,
ubiquitin, and clathrin. J Biol Chem. 278:52865–52872. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Katoh Y, Shiba Y, Mitsuhashi H, Yanagida
Y, Takatsu H and Nakayama K: Tollip and Tom1 form a complex and
recruit ubiquitin conjugated proteins onto early endosomes. J Biol
Chem. 279:24435–24443. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Brissoni B, Agostini L, Kropf M, Martinon
F, Swoboda Vl, et al: Intracellular trafficking of interleukin-1
receptor I requires Tollip. Curr Biol. 16:2265–2270. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang G and Ghosh S: Negative regulation
of Toll-like receptor mediated signaling by Tollip. J Biol Chem.
277:7059–7065. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Capelluto DG: Tollip: a multitasking
protein in innate immunity and protein trafficking. Microbes
Infect. 14:140–147. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sugi Y, Takahashi K, Nakano K, Hosono A
and Kaminogawa S: Transcription of the Tollip gene is elevated in
intestinal epithelial cells through impaired
O-GlcNAcylation-dependent nuclear translocation of the negative
regulator Elf-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 412:704–709. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Sun ML, Ma DH, Liu M, Yu YX, Cao DB, Ma C,
Wang X and Liu XL: Successful treatment of paraquat poisoning by
Xuebijing, an injection concocted from multiple Chinese medicinal
herbs: a case report. J Altern Complement Med. 15:1375–1378. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Celik S, Erdogan S and Tuzcu M: Caffeic
acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) exhibits significant potential as an
antidiabetic and liver-protective agent in streptozotocin-induced
diabetic rats. Pharmacol Res. 60:270–276. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL and
Randall RJ: Protein measurement with the folin phenol reagent. J
Biol Chem. 193:265–275. 1951.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kakkar P, Das B and Viswanathan PN: A
modified spectrophotometric assay of superoxide dismutase. Indian J
Biochem Biophys. 21:130–132. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Rokicki W, Zalejska-Fiolka J,
Mrukwa-Kominek E, Majewski W and Birkner E: Effect of selected
dietary compounds on extracellular superoxide dismutase in the
vitreous of chinchillas. Ophthalmic Res. 50:54–58. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
von Leitner EC, Klinke A, Atzler D, Slocum
JL, Lund N, Kielstein JT, Maas R, Schmidt-Haupt R, Pekarova M,
Hellwinkel O, Tsikas D, D’Alecy LG, Lau D, Willems S, Kubala L,
Ehmke H, Meinertz T, Blankenberg S, Schwedhelm E, Gadegbeku CA,
Böger RH, Baldus S and Sydow K: Pathogenic cycle between the
endogenous nitric oxide synthase inhibitor asymmetrical
dimethylarginine and the leukocyte-derived hemoprotein
myeloperoxidase. Circulation. 124:2735–2745. 2011.
|
|
18
|
Zhang B, Liu ZY, Li YY, Luo Y, Liu ML,
Dong HY, Wang YX, Liu Y, Zhao PT, Jin FG and Li ZC:
Antiinflammatory effects of matrine in LPS-induced acute lung
injury in mice. Eur J Pharm Sci. 44:573–579. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zhang L, Luo N, Liu J, Duan Z, Du G, Cheng
J, Lin H and Li Z: Emulsified isoflurane preconditioning protects
against liver and lung injury in rat model of hemorrhagic shock. J
Surg Res. 171:783–790. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Szapiel SV, Elson NA, Fulmer JD,
Hunninghake GW and Crystal RG: Bleomycin-induced interstitial
pulmonary disease in the nude, athymic mouse. Am Rev Respir Dis.
120:893–899. 1979.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Risøe PK, Ryg U, Wang YY, Rutkovskiy A,
Smedsrød B, Valen G and Dahle MK: Cecal ligation and puncture
sepsis is associated with attenuated expression of adenylyl cyclase
9 and increased miR142–3p. Shock. 36:390–395. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li HF, Sun MG, Yu YX and Liu XL: Xuebijing
alters tumor necrosis factor-alpha, interleukin-1beta and p38
mitogen activated protein kinase content in a rat model of cardiac
arrest following cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Neural Regen Res.
6:2573–2576. 2011.
|
|
23
|
Chen Y, Tong HS, Zhang XQ, Tang LQ, Pan
ZG, Liu ZF, Duan PK and Su L: Xuebijing injection alleviates liver
injury by inhibiting secretory function of Kupffer cells in heat
stroke rats. J Tradit Chin Med. 33:243–249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qi F, Liang ZX, She DY, Yan GT and Chen
LA: A clinical study on the effects and mechanism of xuebijing
injection in severe pneumonia patients. J Tradit Chin Med.
31:46–49. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Shao M, Liu B, Wang JQ, Tao XG, Zhou SS,
Jin K and Zhang CP: Effect of Xuebijing injection on T helper 17
and CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells in patients
with sepsis. Zhongguo Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 23:430–434.
2011.(In Chinese).
|
|
26
|
Sun J, Xue Q, Guo L, Cui L and Wang J:
Xuebijing protects against lipopolysaccharide-induced lung injury
in rabbits. Exp Lung Res. 36:211–218. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou G, Kamenos G, Pendem S, Wilson JX and
Wu F: Ascorbate protects against vascular leakage in cecal ligation
and puncture-induced septic peritonitis. Am J Physiol Regul Integr
Comp Physiol. 302:R409–R416. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Nan YH, Park IS, Hahm KS and Shin SY:
Antimicrobial activity, bactericidal mechanism and LPS-neutralizing
activity of the cell-penetrating peptide pVEC and its analogs. J
Pept Sci. 17:812–817. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hukkanen RR, Liggitt HD, Murnane RD and
Frevert CW: Systemic inflammatory response syndrome in nonhuman
primates culminating in multiple organ failure, acute lung injury,
and disseminated intravascular coagulation. Toxicol Pathol.
37:799–804. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Moncada-Pazos A, Obaya AJ, Llamazares M,
Heljasvaara R, Suárez MF, Colado E, Noël A, Cal S and López-Otín C:
ADAMTS-12 metalloprotease is necessary for normal inflammatory
response. J Biol Chem. 287:39554–39563. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ghosh S and Hayden MS: Newregulators of
NF-κB in inflammation. Nat Rev Immunol. 8:837–848. 2008.
|
|
32
|
Zhao D, Ding R, Mao Y, Wang L, Zhang Z and
Ma X: Heparin rescues sepsis-associated acute lung injury and
lethality through the suppression of inflammatory responses.
Inflammation. 35:1825–1832. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Ji MH, Zhu XL, Liu FF, Li GM, Tian M, Wu
J, Fan YX, Li N and Yang JJ: Alpha 2A-adrenoreceptor blockade
improves sepsis-induced acute lung injury accompanied with
depressed high mobility group box-1 levels in rats. Cytokine.
60:639–645. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Li X, Zheng Z, Li X and Ma X:
Unfractionated heparin inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammatory response through blocking p38 MAPK and NF-κB
activation on endothelial cell. Cytokine. 60:114–121.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Biswas A, Wilmanski J, Forsman H, Hrncir
T, Hao L, Tlaskalova-Hogenova H and Kobayashi KS: Negative
regulation of Toll-like receptor signaling plays an essential role
in homeostasis of the intestine. Eur J Immunol. 41:182–194. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ostuni R, Zanoni I and Granucci F:
Deciphering the complexity of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell
Mol Life Sci. 67:4109–4134. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liew FY, Xu D, Brint EK and O’Neill LA:
Negative regulation of toll-like receptor-mediated immune
responses. Nat Rev Immunol. 5:446–458. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Oshima N, Ishihara S, Rumi MAK, Aziz MM,
Mishima Y, Kadota C, Moriyama I, Ishimura N, Amano Y and Kinoshita
Y: A20 is an early responding negative regulator of Toll-like
receptor 5 signalling in intestinal epithelial cells during
inflammation. Clin Exp Immunol. 159:185–198. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wald D, Qin J, Zhao Z, Qian Y, Naramura M,
Tian L, Towne J, Sims JE, Stark GR and Li X: SIGIRR, a negative
regulator of Toll-like receptor-interleukin 1 receptor signaling.
Nat Immunol. 4:920–927. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kobayashi K, Hernandez LD, Galan JE,
Janeway CA Jr, Medzhitov R and Flavell RA: IRAK-M is a negative
regulator of Toll-like receptor signaling. Cell. 110:191–202. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Bulut Y, Faure E, Thomas L, Equils O and
Arditi M: Cooperation of toll-like receptor 2 and 6 for cellular
activation by soluble tuberculosis factor and Borrelia
burgdorferi outer surface protein a lipoprotein: role of toll
interacting protein and IL-1 receptor signaling molecules in
toll-like receptor 2 signaling. J Immunol. 167:987–994.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Burns K, Janssens S, Brissoni B, Olivos N,
Beyaert R and Tschopp J: Inhibition of interleukin 1
receptor/toll-like receptor signaling through the alternatively
spliced, short form of MyD88 is due to its failure to recruit
IRAK-4. J Exp Med. 197:263–268. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Neumann D, Lienenklaus S, Rosati O and
Martin MU: IL-1β-induced phosphorylation of PKB/Akt depends on the
presence of IRAK-1. Eur J Immunol. 32:3689–3698. 2002.
|
|
44
|
Shimizu K, Taniyama Y, Sanada F, Azuma J,
Iwabayashi M, Iekushi K, Rakugi H and Morishita R: Hepatocyte
growth factor inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced oxidative stress
via epithelial growth factor receptor degradation. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 32:2687–2693. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Bastarache JA, Sebag SC, Clune JK, Grove
BS, Lawson WE, Janz DR, Roberts LJ, Dworski R, Mackman N and Ware
LB: Low levels of tissue factor lead to alveolar haemorrhage,
potentiating murine acute lung injury and oxidative stress. Thorax.
67:1032–1039. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Bedirli N, Demirtas CY, Akkaya T, Salman
B, Alper M, Bedirli A and Pasaoglu H: Volatile anesthetic
preconditioning attenuated sepsis induced lung inflammation. J Surg
Res. 178:e17–e23. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Yageta Y, Ishii Y, Morishima Y, Masuko H,
Ano S, Yamadori T, Itoh K, Takeuchi K, Yamamoto M and Hizawa N:
Role of Nrf2 in host defense against influenza virus in cigarette
smoke-exposed mice. J Virol. 85:4679–4690. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Boutten A, Goven D, Boczkowski J and Bonay
M: Oxidative stress targets in pulmonary emphysema: focus on the
Nrf2 pathway. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:329–346. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Cho HY, Imani F, Miller-DeGraff L, Walters
D, Melendi GA, Yamamoto M, Polack FP and Kleeberger SR: Antiviral
activity of Nrf2 in a murine model of respiratory syncytial virus
disease. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 179:138–150. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Jeong SJ, Han SH, Kim CO, Choi JY and Kim
JM: Anti-vascular endothelial growth factor antibody attenuates
inflammation and decreases mortality in an experimental model of
severe sepsis. Crit Care. 17:R97–R98. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Qiu Y, Ferguson J, Oltean S, Neal CR,
Kaura A, Bevan H, Wood E, Sage LM, Lanati S, Nowak DG, Salmon AH,
Bates D and Harper SJ: Overexpression of VEGF165b in podocytes
reduces glomerular permeability. J Am Soc Nephrol. 21:1498–1509.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Jezovnik MK and Poredos P: Idiopathic
venous thrombosis is related to systemic inflammatory response and
to increased levels of circulating markers of endothelial
dysfunction. Int Angiol. 29:226–231. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Hack CE and Zeerleder S: The endothelium
in sepsis: source of and a target for inflammation. Crit Care Med.
29:S21–S27. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Reinhart K, Bayer O, Brunkhorst F and
Meisner M: Markers of endothelial damage in organ dysfunction and
sepsis. Crit Care Med. 30:S302–S312. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Lucas R, Sridhar S, Rick FG, Gorshkov B,
Umapathy NS, Yang G, Oseghale A, Verin AD, Chakraborty T, Matthay
MA, Zemskov EA, White R, Block NL and Schally AV: Agonist of growth
hormone-releasing hormone reduces pneumolysin-induced pulmonary
permeability edema. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 303:F1026–F1036.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|