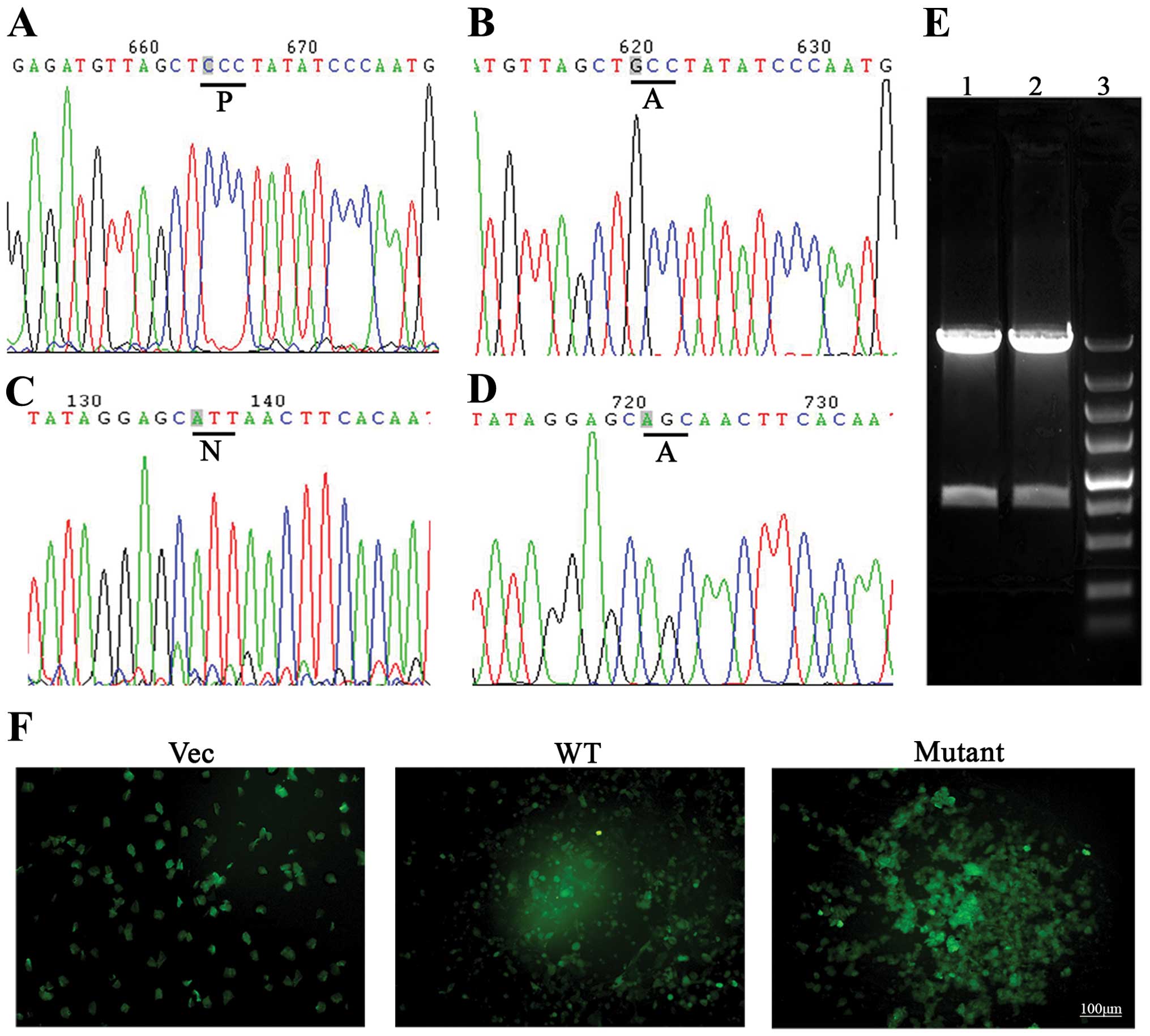
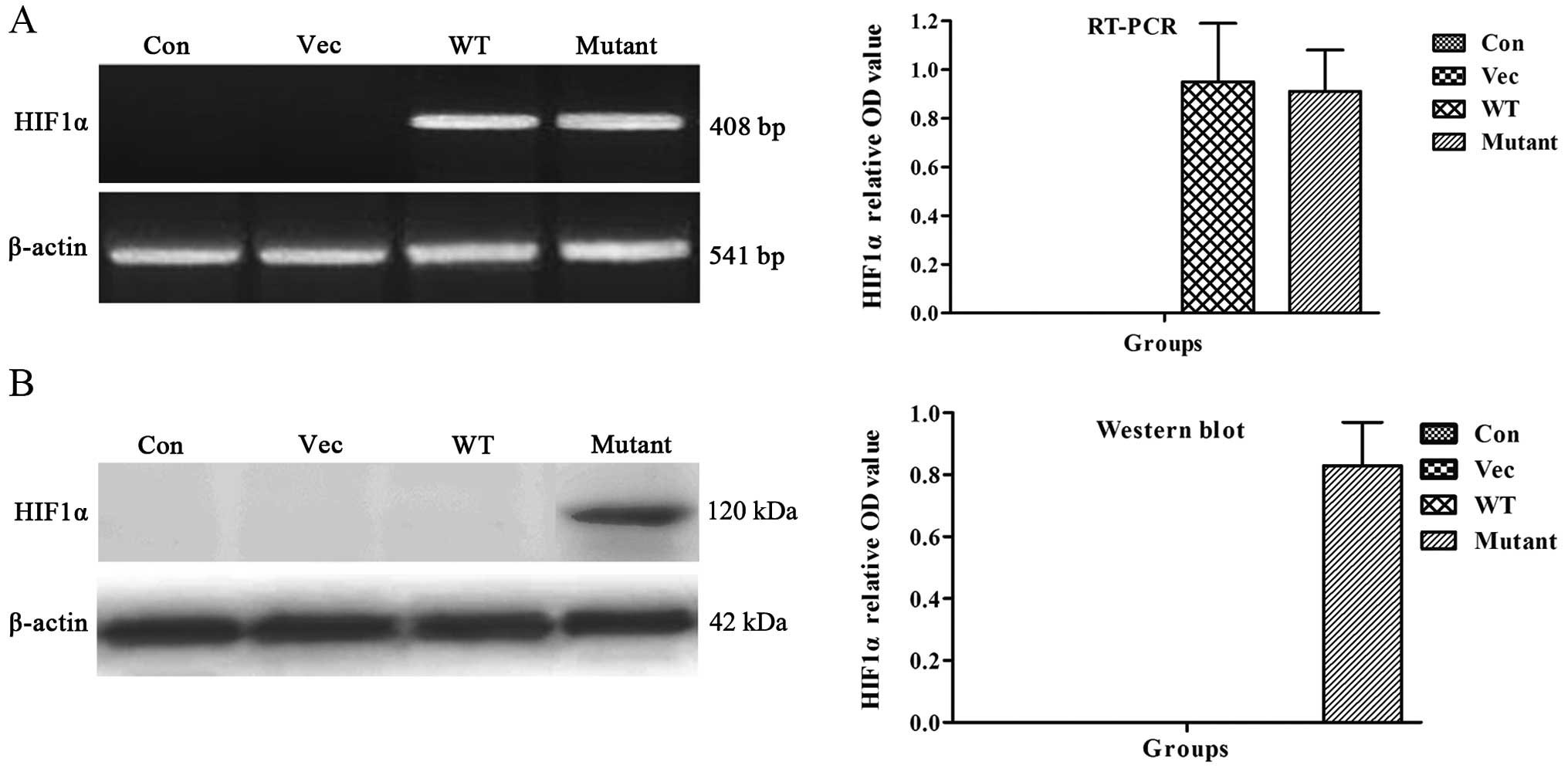
|
1
|
Giaccia A, Siim BG and Johnson RS: HIF-1
as a target for drug development. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2:803–811.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Khan TA, Sellke FW and Laham RJ: Gene
therapy progress and prospects: therapeutic angiogenesis for limb
and myocardial ischemia. Gene Ther. 10:285–291. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Semenza GL: Evaluation of HIF-1 inhibitors
as anticancer agents. Drug Discov Today. 12:853–859. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wan C, Gilbert SR, Wang Y, et al:
Activation of the hypoxia-inducible factor-1α pathway accelerates
bone regeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 105:686–691. 2008.
|
|
5
|
Pugh CW and Ratcliffe PJ: Regulation of
angiogenesis by hypoxia: role of the HIF system. Nat Med.
9:677–684. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Majmundar AJ, Wong WJ and Simon MC:
Hypoxia-inducible factors and the response to hypoxic stress. Mol
Cell. 40:294–309. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang GL, Jiang BH, Rue EA and Semenza GL:
Hypoxia-inducible factor 1 is a basic-helix-loop-helix-PAS
heterodimer regulated by cellular O2 tension. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 92:5510–5514. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Fiorenzo P, Mongiardi MP, Dimitri D, et
al: HIF1-positive and HIF1-negative glioblastoma cells compete
in vitro but cooperate in tumor growth in vivo. Int J
Oncol. 36:785–791. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Giatromanolaki A, Fiska A, Pitsiava D,
Kartalis G, Kouourakis MI and Sivridis E: Erythropoietin receptors
in endometrial carcinoma as related to HIF1α and VEGF expression.
In vivo. 23:699–703. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rey S and Semenza GL: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1-dependent mechanisms of vascularization and vascular
remodelling. Cardiovasc Res. 86:236–242. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bruick RK and McKnight SL: A conserved
family of prolyl-4-hydroxylases that modify HIF. Science.
294:1337–1340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dang EV, Barbi J, Yang HY, et al: Control
of T(H)17/T(reg) balance by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Cell.
146:772–784. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Evans CE, Humphries J, Mattock K, et al:
Hypoxia and upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1α stimulate
venous thrombus recanalization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
30:2443–2451. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Kazi AA, Molitoris KH and Koos RD:
Estrogen rapidly activates the PI3K/AKT pathway and
hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and induces vascular endothelial growth
factor A expression in luminal epithelial cells of the rat uterus.
Biol Reprod. 81:378–387. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Lando D, Peet DJ, Whelan DA, Gorman JJ and
Whitelaw ML: Asparagine hydroxylation of the HIF transactivation
domain a hypoxic switch. Science. 295:858–861. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ralph GS, Parham S, Lee SR, et al:
Identification of potential stroke targets by lentiviral vector
mediated overexpression of HIF-1α and HIF-2α in a primary neuronal
model of hypoxia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 24:245–258.
2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins
R, et al: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Liu N, Zhang Y, Fan L, et al: Effects of
transplantation with bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells
modified by Survivin on experimental stroke in rats. J Transl Med.
9:1052011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Boltze J, Kowalski I, Geiger K, et al:
Experimental treatment of stroke in spontaneously hypertensive rats
by CD34+ and CD34− cord blood cells. Ger Med
Sci. 3:Doc092005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Neumann-Haefelin T, Kastrup A, de
Crespigny A, Yenari MA, Ringer T, Sun GH and Moseley ME: Serial MRI
after transient focal cerebral ischemia in rats: dynamics of tissue
injury, blood-brain barrier damage, and edema formation. Stroke.
31:1965–1972. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR and Folkman
J: Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis-correlation in invasive breast
carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 324:1–8. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Mustafa AK, Ahmad AS, Zeynalov E, et al:
Serine racemase deletion protects against cerebral ischemia and
excitotoxicity. J Neurosci. 30:1413–1416. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ruiz-Crespo S, Trejo-Gabriel-Galán JM and
Coma-del-Corral MJ: Localizing coordinates of cerebral ischemic
tissue without the need of staining in a rat model of focal
cerebral infarct. Metab Brain Dis. 28:21–24. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yu J, Zhu H, Ko D and Kindy MS:
Motoneuronotrophic factor analog GM6 reduces infarct volume and
behavioral deficits following transient ischemia in the mouse.
Brain Res. 1238:143–153. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Elson DA, Thurston G, Huang LE, Ginzinger
DG, McDonald DM, Johnson RS and Arbeit JM: Induction of
hypervascularity without leakage or inflammation in transgenic mice
overexpressing hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Genes Dev.
15:2520–2532. 2001.
|
|
26
|
Menge T, Zhao Y, Zhao J, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells regulate blood-brain barrier integrity
through TIMP3 release after traumatic brain injury. Sci Transl Med.
4:161ra1502012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pati S, Khakoo AY, Zhao J, et al: Human
mesenchymal stem cells inhibit vascular permeability by modulating
vascular endothelial cadherin/β-catenin signaling. Stem Cells Dev.
20:89–101. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Warach S and Latour LL: Evidence of
reperfusion injury, exacerbated by thrombolytic therapy, in human
focal brain ischemia using a novel imaging marker of early
blood-brain barrier disruption. Stroke. 35:2659–2661. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Zacharek A, Chen J, Cui X, et al:
Angiopoietin1/Tie2 and VEGF/Flk1 induced by MSC treatment amplifies
angiogenesis and vascular stabilization after stroke. J Cereb Blood
Flow Metab. 27:1684–1691. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|