Spandidos Publications style
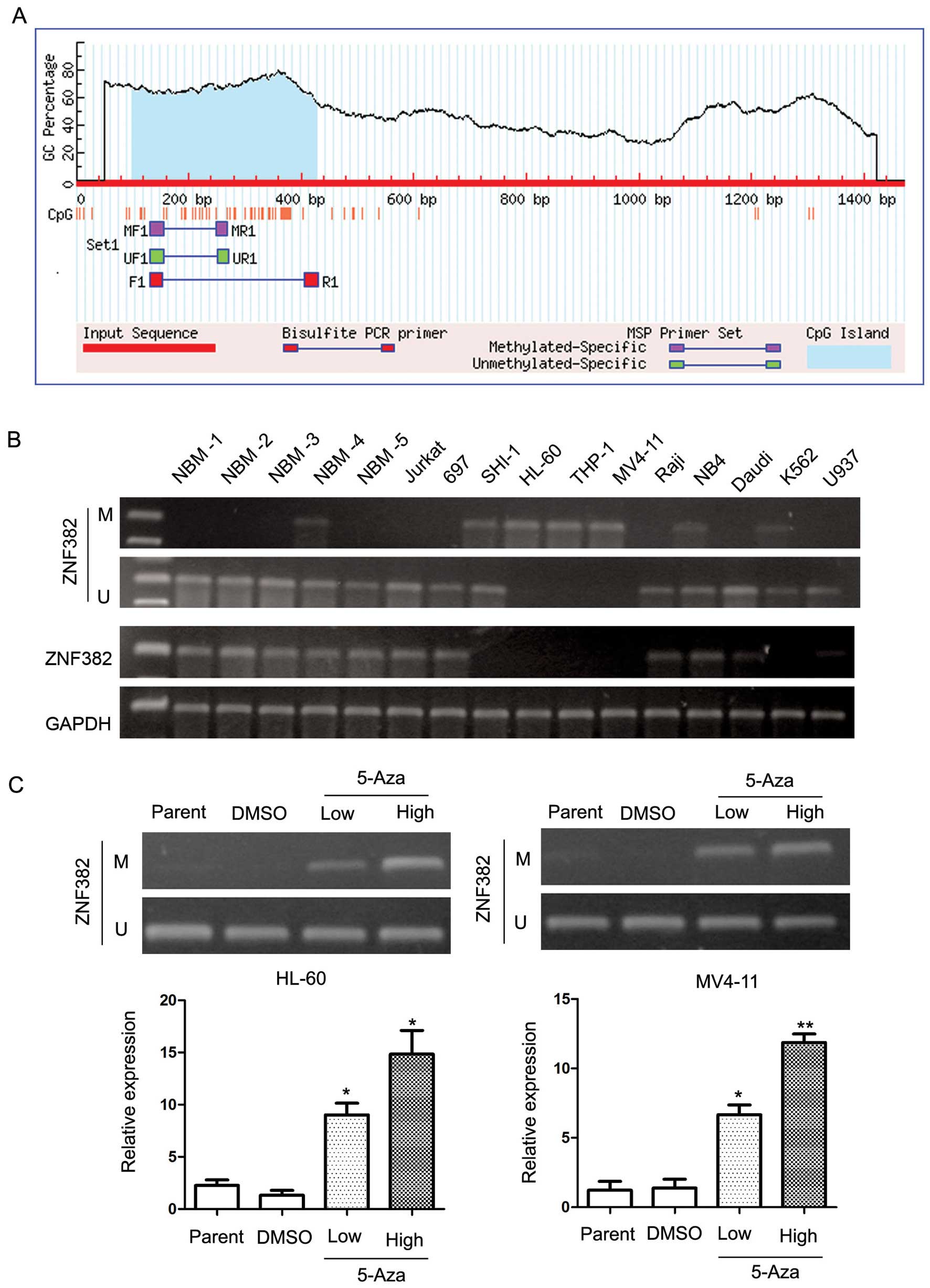
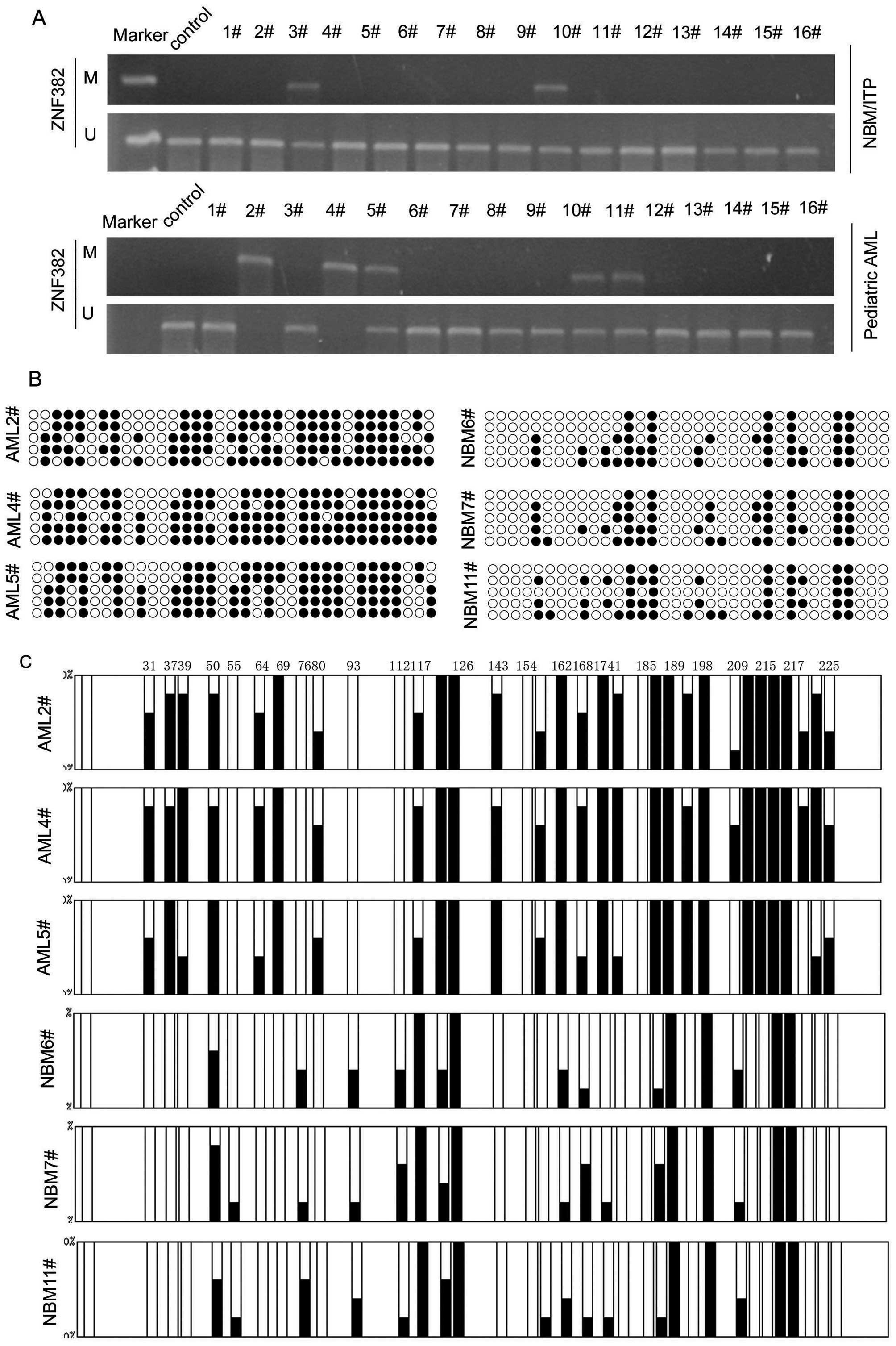
Tao Y, Hu S, Lu J, Cao L, Zhao W, Xiao P, Xu L, Li Z, Wang N, Du X, Du X, et al: Zinc finger protein 382 is downregulated by promoter hypermethylation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients. Int J Mol Med 34: 1505-1515, 2014.
APA
Tao, Y., Hu, S., Lu, J., Cao, L., Zhao, W., Xiao, P. ... Pan, J. (2014). Zinc finger protein 382 is downregulated by promoter hypermethylation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 34, 1505-1515. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2014.1966
MLA
Tao, Y., Hu, S., Lu, J., Cao, L., Zhao, W., Xiao, P., Xu, L., Li, Z., Wang, N., Du, X., Sun, L., Zhao, H., Fang, F., Su, G., Li, Y., Li, Y., Xu, Y., Ni, J., Wang, J., Feng, X., Pan, J."Zinc finger protein 382 is downregulated by promoter hypermethylation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 34.6 (2014): 1505-1515.
Chicago
Tao, Y., Hu, S., Lu, J., Cao, L., Zhao, W., Xiao, P., Xu, L., Li, Z., Wang, N., Du, X., Sun, L., Zhao, H., Fang, F., Su, G., Li, Y., Li, Y., Xu, Y., Ni, J., Wang, J., Feng, X., Pan, J."Zinc finger protein 382 is downregulated by promoter hypermethylation in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia patients". International Journal of Molecular Medicine 34, no. 6 (2014): 1505-1515. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2014.1966