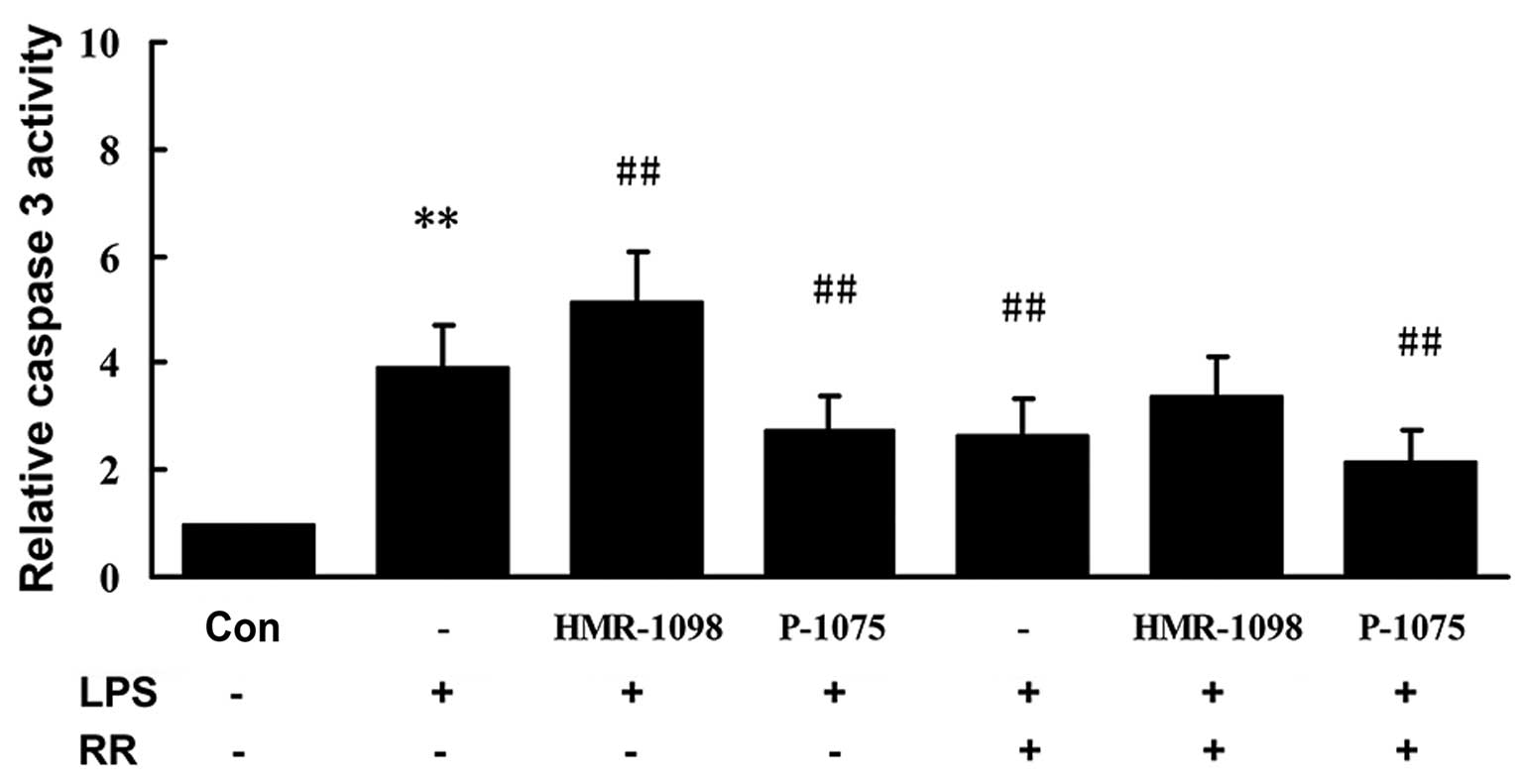
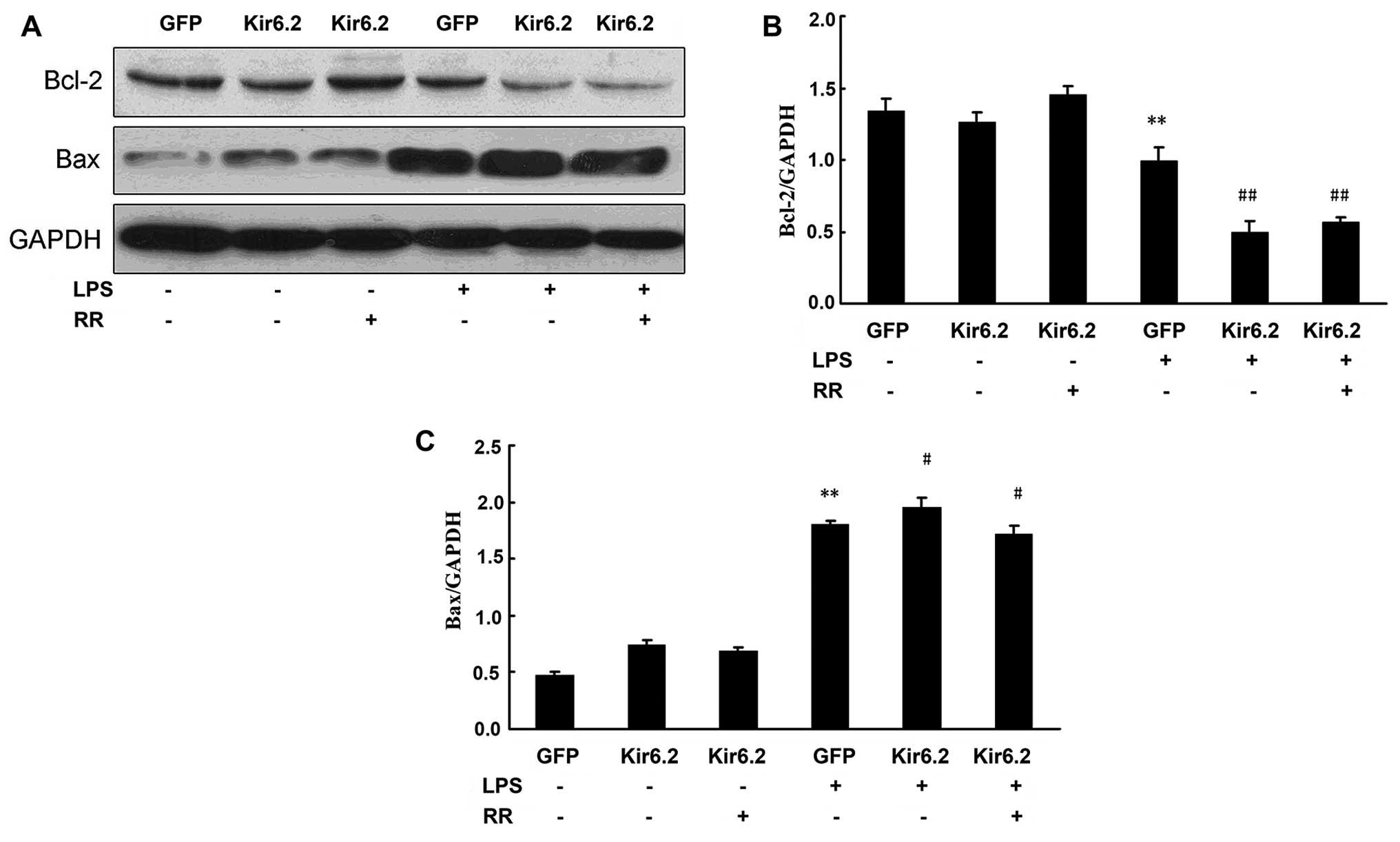
|
1
|
Merx MW and Weber C: Sepsis and the heart.
Circulation. 116:793–802. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zanotti-Cavazzoni SL and Hollenberg SM:
Cardiac dysfunction in severe sepsis and septic shock. Curr Opin
Crit Care. 15:392–397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lancel S, Joulin O, Favory R, Goossens JF,
Kluza J, Chopin C, Formstecher P, Marchetti P and Neviere R:
Ventricular myocyte caspases are directly responsible for
endotoxin-induced cardiac dysfunction. Circulation. 111:2596–2604.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Suzuki J, Bayna E, Dalle Molle E and Lew
WY: Nicotine inhibits cardiac apoptosis induced by
lipopolysaccharide in rats. J Am Coll Cardiol. 41:482–488. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Noma A: ATP-regulated K+
channels in cardiac muscle. Nature. 305:147–148. 1983. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zhou F, Yao HH, Wu JY, Ding JH, Sun T and
Hu G: Opening of microglial K(ATP) channels inhibits
rotenone-induced neuroinflammation. J Cell Mol Med. 12:1559–1570.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Liu H, Zhang HY, Zhu X, Shao Z and Yao Z:
Preconditioning blocks cardiocyte apoptosis: role of
K(ATP) channels and PKC-epsilon. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 282:H1380–H1386. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kane GC, Liu XK, Yamada S, Olson TM and
Terzic A: Cardiac KATP channels in health and disease. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 38:937–943. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Buckley JF, Singer M and Clapp LH: Role of
KATP channels in sepsis. Cardiovasc Res. 72:220–230.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yang ZW, Chen JK, Ni M, Zhao T, Deng YP,
Tao X, Jiang GJ and Shen FM: Role of Kir6.2 subunits of
ATP-sensitive potassium channels in endotoxemia-induced cardiac
dysfunction. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 12:752013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kuo JH, Chen SJ, Shih CC, Lue WM and Wu
CC: Abnormal activation of potassium channels in aortic smooth
muscle of rats with peritonitis-induced septic shock. Shock.
32:74–79. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Shi W, Cui N, Wu Z, Yang Y, Zhang S, Gai
H, Zhu D and Jiang C: Lipopolysaccharides up-regulate Kir6.1/SUR2B
channel expression and enhance vascular KATP channel
activity via NF-kappaB-dependent signaling. J Biol Chem.
285:3021–3029. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Charalambous BM, Stephens RC, Feavers IM
and Montgomery HE: Role of bacterial endotoxin in chronic heart
failure: the gut of the matter. Shock. 28:15–23. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Shen M, Wu RX, Zhao L, Li J, Guo HT, Fan
R, Cui Y, Wang YM, Yue SQ and Pei JM: Resveratrol attenuates
ischemia/reperfusion injury in neonatal cardiomyocytes and its
underlying mechanism. PLoS One. 7:e512232012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Nichols CG: KATP channels as
molecular sensors of cellular metabolism. Nature. 440:470–476.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sellitto AD, Al-Dadah AS, Schuessler RB,
Nichols CG and Lawton JS: An open sarcolemmal adenosine
triphosphate-sensitive potassium channel is necessary for
detrimental myocyte swelling secondary to stress. Circulation.
124(Suppl 11): S70–S74. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Suzuki M, Sasaki N, Miki T, Sakamoto N,
Ohmoto-Sekine Y, Tamagawa M, Seino S, Marbán E and Nakaya H: Role
of sarcolemmal K(ATP) channels in cardioprotection against
ischemia/reperfusion injury in mice. J Clin Invest. 109:509–516.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Zingman LV, Hodgson DM, Bast PH, Kane GC,
Perez-Terzic C, Gumina RJ, Pucar D, Bienengraeber M, Dzeja PP, Miki
T, et al: Kir6.2 is required for adaptation to stress. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 99:13278–13283. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gumina RJ, Pucar D, Bast P, Hodgson DM,
Kurtz CE, Dzeja PP, Miki T, Seino S and Terzic A: Knockout of
Kir6.2 negates ischemic preconditioning-induced protection of
myocardial energetics. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
284:H2106–H2113. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rainbow RD, Lodwick D, Hudman D, Davies
NW, Norman RI and Standen NB: SUR2A C-terminal fragments reduce
KATP currents and ischaemic tolerance of rat cardiac
myocytes. J Physiol. 557:785–794. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Marinovic J, Ljubkovic M, Stadnicka A,
Bosnjak ZJ and Bienengraeber M: Role of sarcolemmal ATP-sensitive
potassium channel in oxidative stress-induced apoptosis:
mitochondrial connection. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
294:H1317–H1325. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ohmasa F, Saito M, Oiwa H, Tsounapi P,
Shomori K, Kitatani K, Dimitriadis F, Kinoshita Y and Satoh K:
Pharmacological preconditioning of ATP-sensitive potassium channel
openers on acute urinary retention-induced bladder dysfunction in
the rat. BJU Int. 110:E245–E252. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tsounapi P, Saito M, Dimitriadis F,
Kitatani K, Kinoshita Y, Shomori K, Takenaka A and Satoh K: The
role of K ATP channels on ischemia-reperfusion injury in the rat
testis. Life Sci. 90:649–656. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Dorn GW II: Apoptotic and non-apoptotic
programmed cardiomyocyte death in ventricular remodelling.
Cardiovasc Res. 81:465–473. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Nishida K, Yamaguchi O and Otsu K:
Crosstalk between autophagy and apoptosis in heart disease. Circ
Res. 103:343–351. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hassoun SM, Marechal X, Montaigne D,
Bouazza Y, Decoster B, Lancel S and Neviere R: Prevention of
endotoxin-induced sarcoplasmic reticulum calcium leak improves
mitochondrial and myocardial dysfunction. Crit Care Med.
36:2590–2596. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|