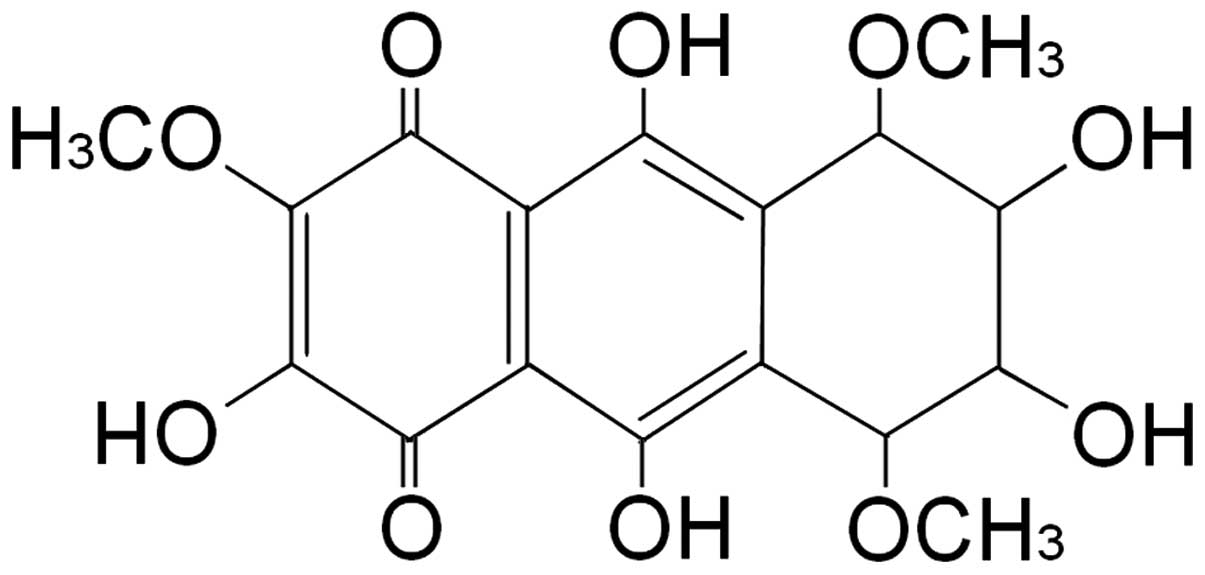
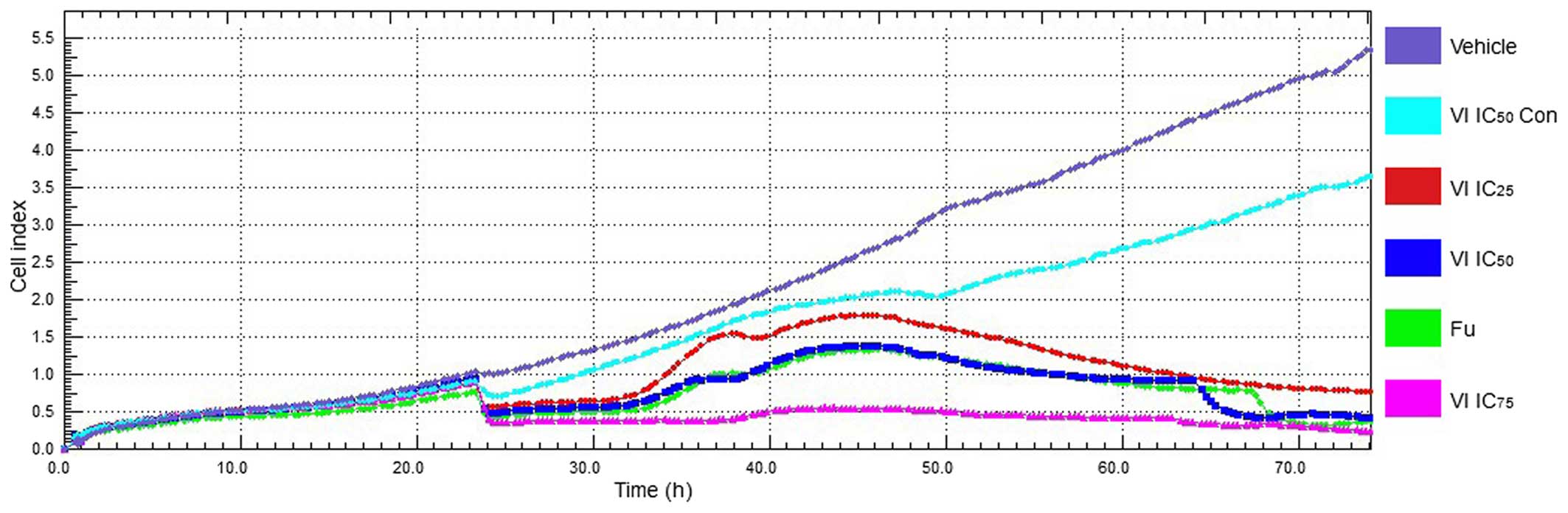
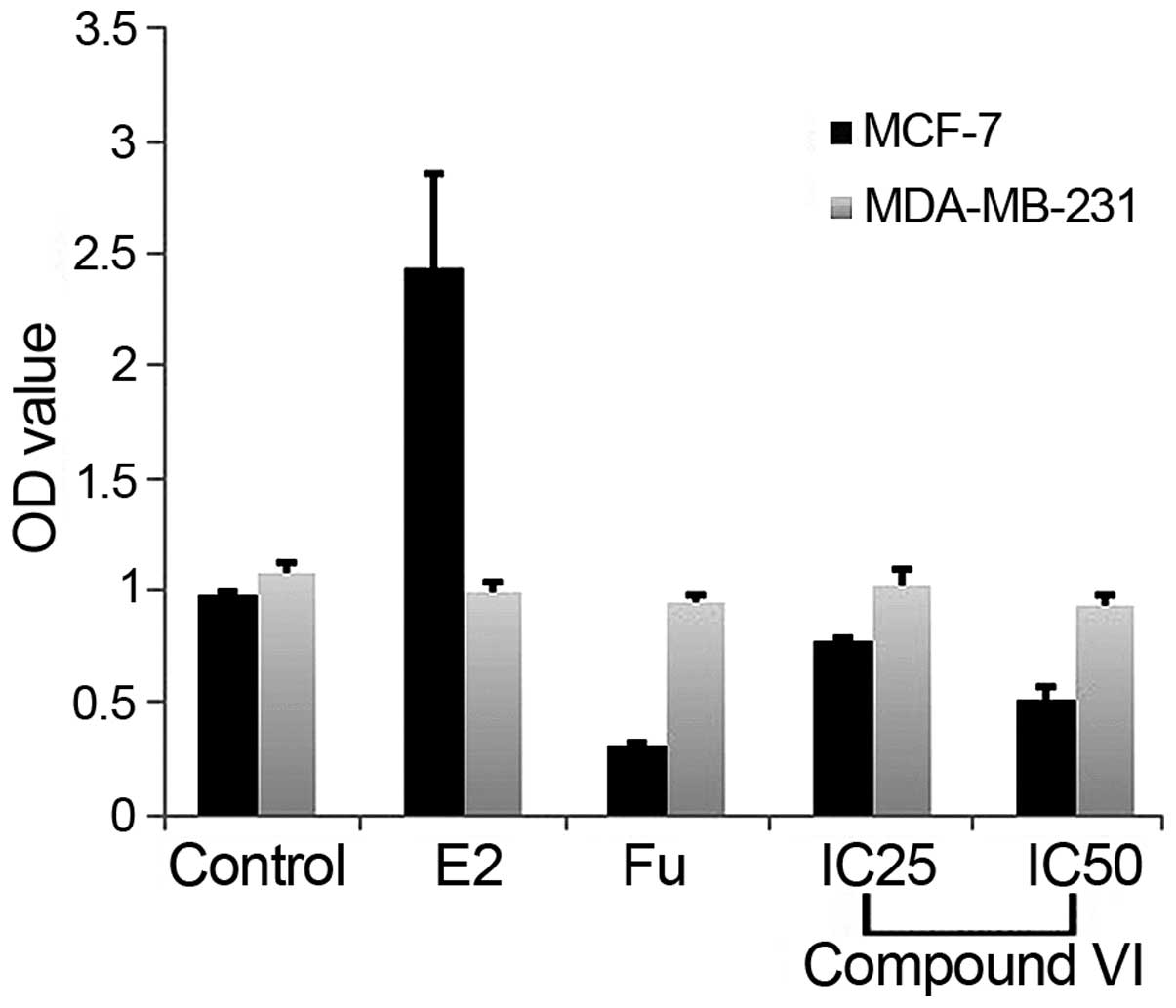
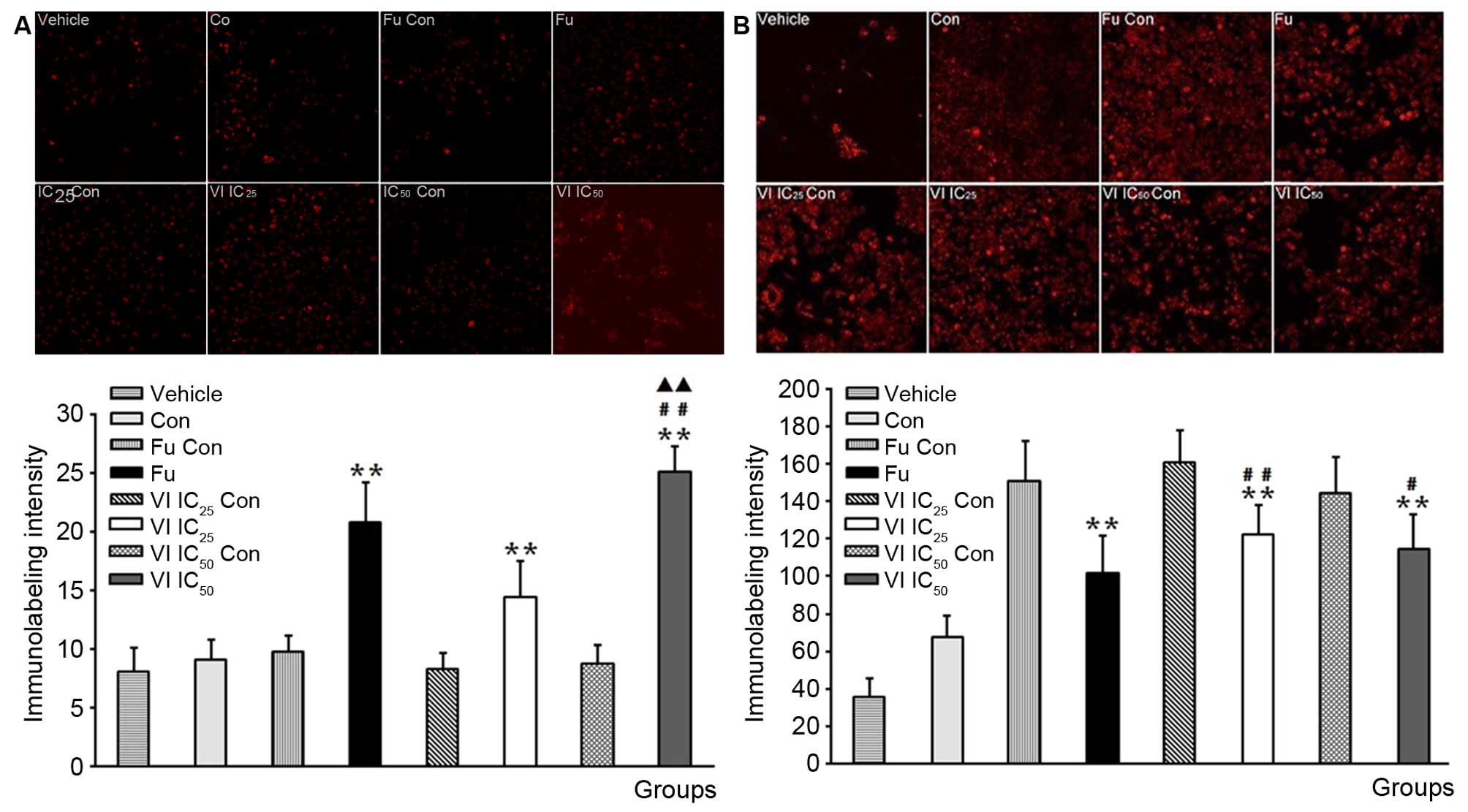
|
1
|
Mata-Gómez LC, Montañez JC, Méndez-Zavala
A and Aguilar CN: Biotechnological production of carotenoids by
yeasts: An overview. Microb Cell Fact. 13:122014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jackson H, Braun CL and Ernst H: The
chemistry of novel xanthophyll carotenoids. Am J Cardiol.
101:50D–57D. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kang B, Zhang X, Wu Z, Wang Z and Park S:
Production of citrinin-free Monascus pigments by submerged culture
at low pH. Enzyme Microb Technol. 55:50–57. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jomova K and Valko M: Health protective
effects of carotenoids and their interactions with other biological
antioxidants. Eur J Med Chem. 70:102–110. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hu W, Gao Q, Hamada MS, Dawood DH, Zheng
J, Chen Y and Ma Z: Potential of pseudomonas chlororaphis subsp.
aurantiaca strain Pcho10 as a biocontrol agent against Fusarium
graminearum. Phytopathology. 104:1289–1297. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Zeng XL, Cai YJ, Liao XR, Zeng XK, Li ZH
and Zhang DB: Extraction and physico-chemical properties of
pigments from liquid-cultured mycelia of Fusarium sp. B158. Food
Science. 33:131–135. 2012.In Chinese.
|
|
7
|
Reigan P, David S, Guo WC and Ross D: A
mechanistic and structural analysis of the inhibition of the 90-kDa
heat shock protein by the benzoquinone and hydroquinone ansamycins.
Mol Pharmacol. 79:823–832. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Pedrini N, Ortiz-Urquiza A, Huarte-Bonnet
C, Fan Y, Juárez MP and Keyhani NO: Tenebrionid secretions and a
fungal benzoquinone oxidoreductase form competing components of an
arms race between a host and pathogen. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
112:231–240. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Gaascht F, Dicato M and Diederich M: Venus
flytrap (Dionaea muscipula Solander ex Ellis) contains powerful
compounds that prevent and cure cancer. Front Oncol. 3:202–210.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Boopalan T, Arumugam A, Parada J,
Saltzstein E and Lakshmanaswamy R: Receptor activator for nuclear
factor-κB ligand signaling promotes progesterone-mediated
estrogen-induced mammary carcinogenesis. Cancer Sci. 106:25–33.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
11
|
King AE, Collins F, Klonisch T, Sallenave
JM, Critchley HO and Saunders PT: An additive interaction between
the NFkappaB and estrogen receptor signalling pathways in human
endometrial epithelial cells. Hum Reprod. 25:510–518. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Ashcroft KJ, Syed F and Bayat A:
Site-specific keloid fibroblasts alter the behaviour of normal skin
and normal scar fibroblasts through paracrine signalling. PLoS One.
8:e756002013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kim JH, Jekarl DW, Kim M, Oh EJ, Kim Y,
Park IY and Shin JC: Effects of ECM protein mimetics on adhesion
and proliferation of chorion derived mesenchymal stem cells. Int J
Med Sci. 11:298–308. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Marconett CN, Sundar SN, Poindexter KM,
Stueve TR, Bjeldanes LF and Firestone GL: Indole-3-Carbinol
triggers aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent estrogen receptor
(ER)α protein degradation in breast cancer cells disrupting an
ERα-GATA3 transcriptional cross-regulatory loop. Mol Biol Cell.
21:1166–1177. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Mezzanotte L, An N, Mol IM, Löwik CW and
Kaijzel EL: A new multicolor bioluminescence imaging platform to
investigate NF-κB activity and apoptosis in human breast cancer
cells. PLoS One. 9:e855502014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Tozawa K, Sagawa M and Kizaki M: Quinone
methide tripterine, celastrol, induces apoptosis in human myeloma
cells via NF-κB pathway. Int J Oncol. 39:1117–1122. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Kruk J: Overweight, obesity, oxidative
stress and the risk of breast cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:9579–9586. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schiavano GF, De Santi M, Brandi G,
Fanelli M, Bucchini A, Giamperi L and Giomaro G: Inhibition of
breast cancer cell proliferation and in vitro tumorigenesis by a
new red apple cultivar. PLoS One. 10:e01358402015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ahmadian M and Samah AA: Application of
health behavior theories to breast cancer screening among Asian
women. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 14:4005–4013. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gordaliza M: Synthetic strategies to
terpene quinones/hydroquinones. Mar Drugs. 10:358–402. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bertanha CS, Januário AH, Alvarenga TA,
Pimenta LP, Silva ML, Cunha WR and Pauletti PM: Quinone and
hydroquinone metabolites from the ascidians of the genus Aplidium.
Mar Drugs. 12:3608–3633. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Magnani L, Ballantyne EB, Zhang X and
Lupien M: PBX1 genomic pioneer function drives ERα signaling
underlying progression in breast cancer. PLoS Genet.
7:e10023682011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Shanle EK and Xu W: Endocrine disrupting
chemicals targeting estrogen receptor signaling: Identification and
mechanisms of action. Chem Res Toxicol. 24:6–19. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
24
|
Condon JC, Hardy DB, Kovaric K and
Mendelson CR: Up-regulation of the progesterone receptor (PR)-C
isoform in laboring myometrium by activation of nuclear
factor-kappaB may contribute to the onset of labor through
inhibition of PR function. Mol Endocrinol. 20:764–775. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Dai XL, Zhou SL, Qiu J, Liu YF and Hua H:
Correlated expression of Fas, NF-kappaB, and VEGF-C in infiltrating
ductal carcinoma of the breast. Eur J Gynaecol Oncol. 33:633–639.
2012.
|
|
26
|
Reuter S, Prasad S, Phromnoi K, Ravindran
J, Sung B, Yadav VR, Kannappan R, Chaturvedi MM and Aggarwal BB:
Thiocolchicoside exhibits anticancer effects through
down-regulation of NF-κB pathway and its regulated gene products
linked to inflammation and cancer. Cancer Prev Res (Phila).
3:1462–1472. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Miller Susanne C, Huang RL and Sakamuru S:
Identification of known drugs that act as inhibitors of NF-κB
signaling and their mechanism of action. Biochem Pharmacol.
9:1272–1280. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|