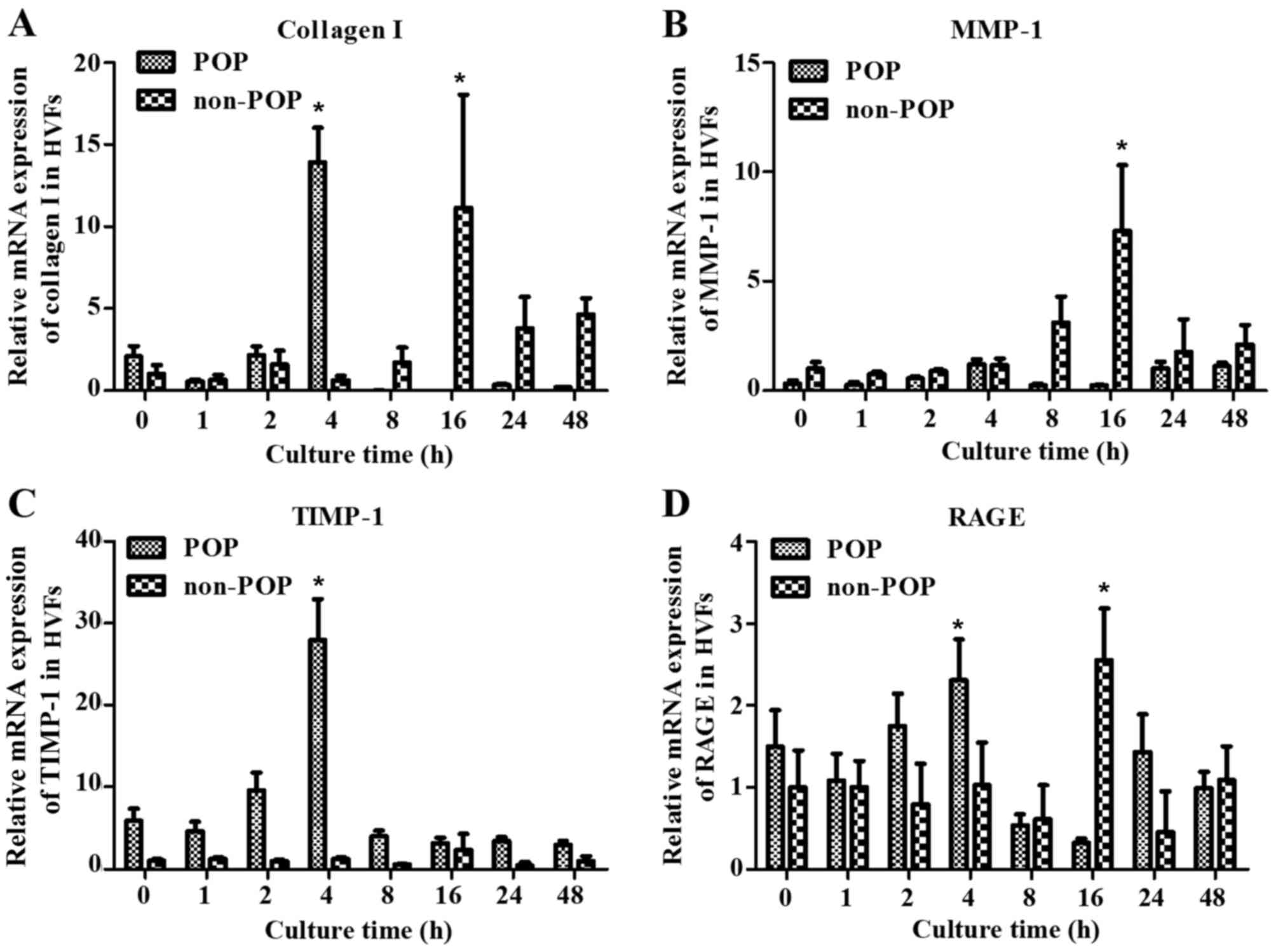
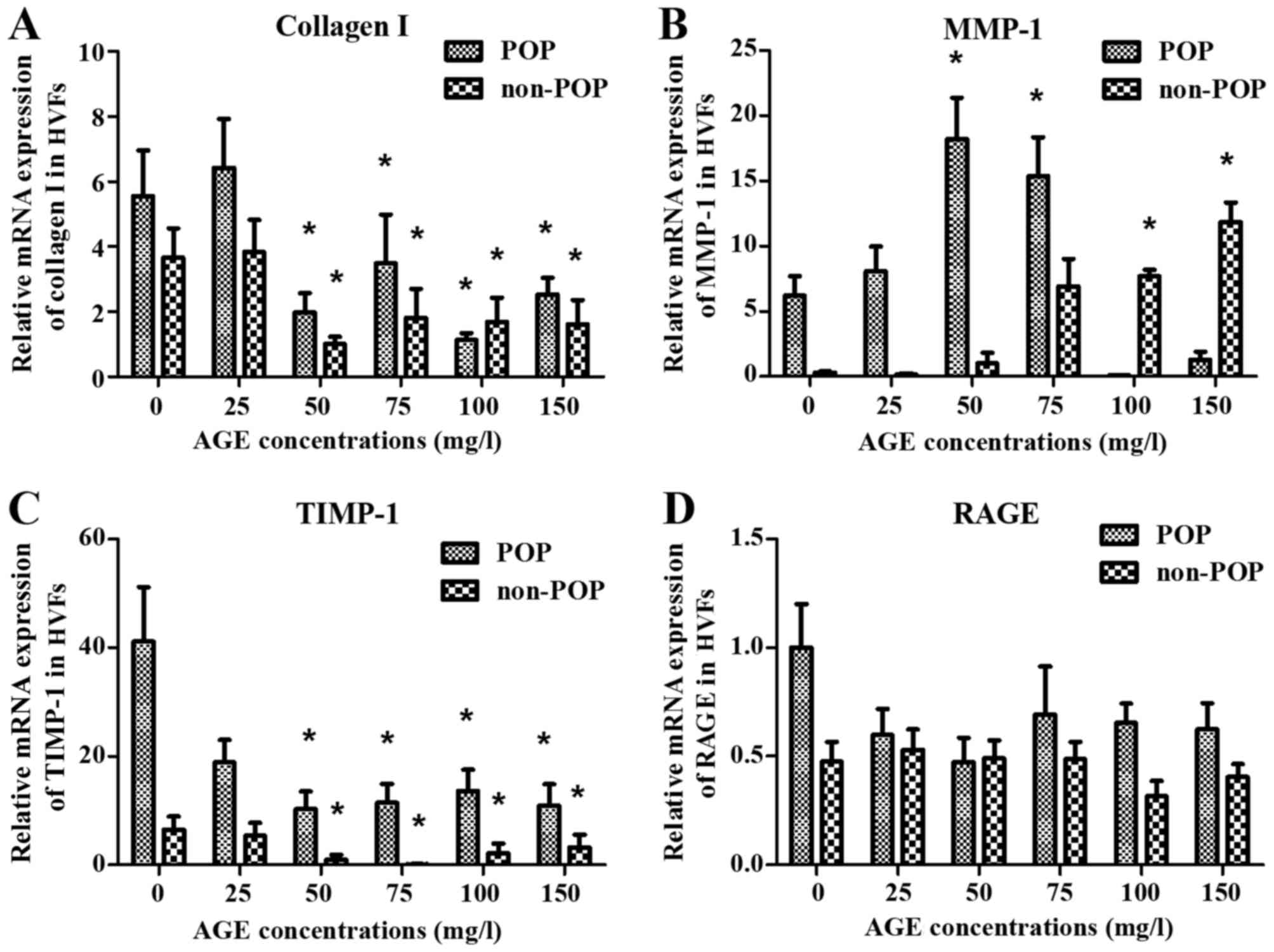
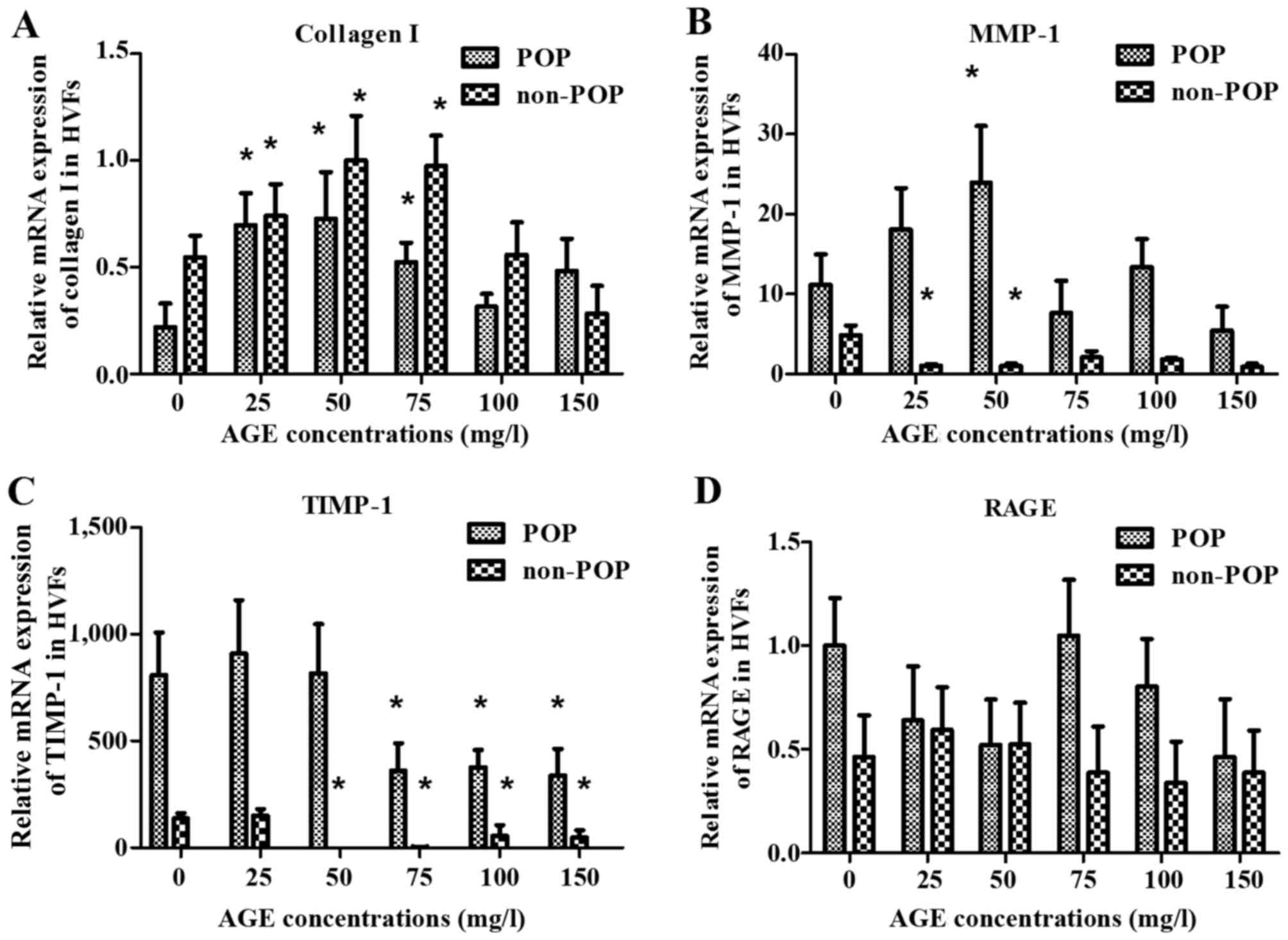
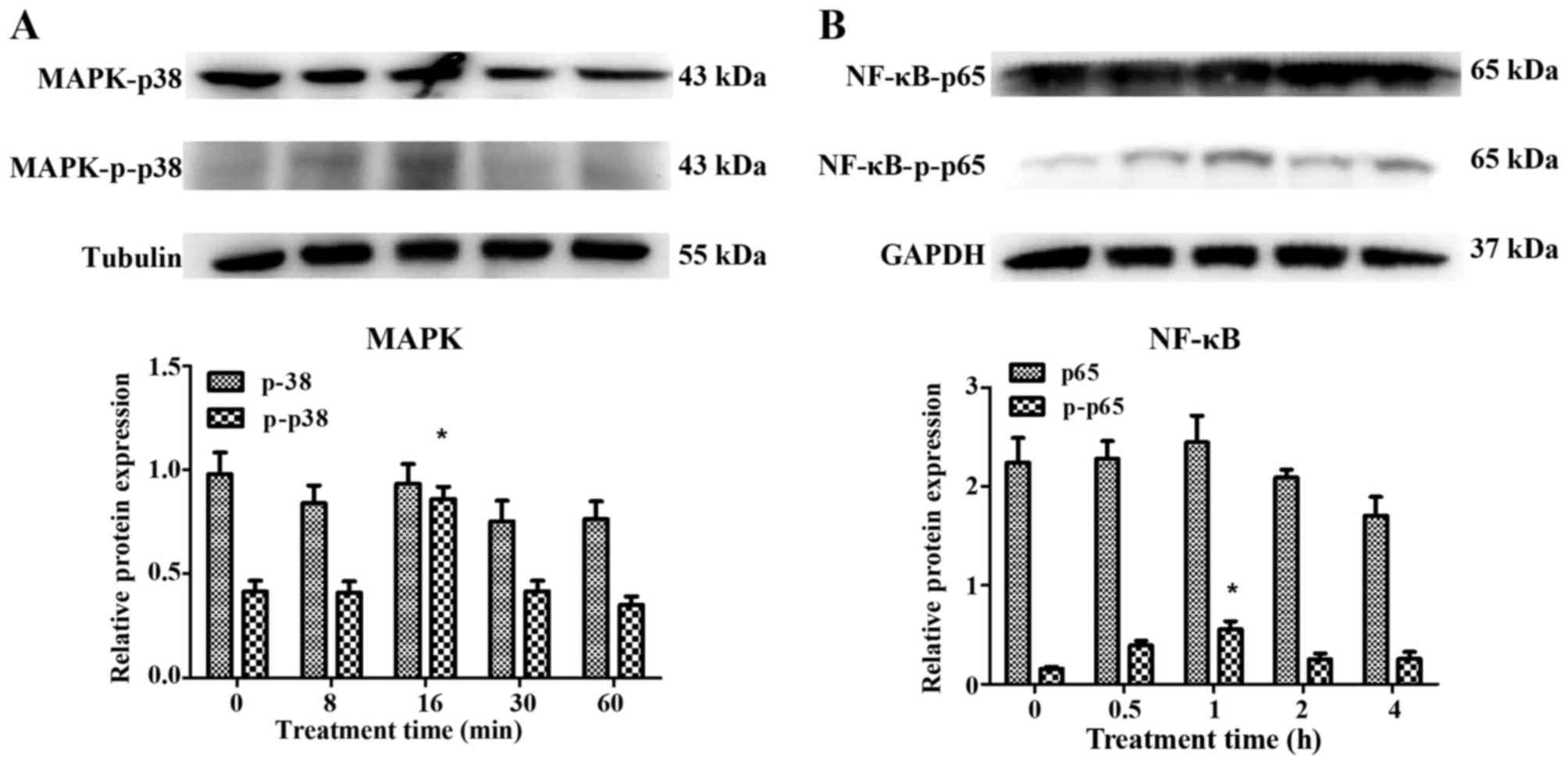
|
1
|
Chow D and Rodríguez LV: Epidemiology and
prevalence of pelvic organ prolapse. Curr Opin Urol. 23:293–298.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sun B, Zhou L, Wen Y, Wang C, Baer TM,
Pera RR and Chen B: Proliferative behavior of vaginal fibroblasts
from women with pelvic organ prolapse. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod
Biol. 183:1–4. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ruiz-Zapata AM, Kerkhof MH,
Zandieh-Doulabi B, Brölmann HA, Smit TH and Helder MN: Functional
characteristics of vaginal fibroblastic cells from premenopausal
women with pelvic organ prolapse. Mol Hum Reprod. 20:1135–1143.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chen HY, Lu Y, Qi Y, Bai WP and Liao QP:
Relationship between the expressions of mitofusin-2 and procollagen
in uterosacral ligament fibroblasts of postmenopausal patients with
pelvic organ prolapse. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol.
174:141–145. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Kanta J: Collagen matrix as a tool in
studying fibroblastic cell behavior. Cell Adh Migr. 9:308–316.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lim VF, Khoo JK, Wong V and Moore KH:
Recent studies of genetic dysfunction in pelvic organ prolapse: the
role of collagen defects. Aust N Z J Obstet Gynaecol. 54:198–205.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Jackson SR, Avery NC, Tarlton JF, Eckford
SD, Abrams P and Bailey AJ: Changes in metabolism of collagen in
genitourinary prolapsed. Lancet. 347:1658–1661. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Han L, Wang L, Wang Q, Li H and Zang H:
Association between pelvic organ prolapsed and stress urinary
incontinence with collagen. Exp Ther Med. 7:1337–1341. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kerkhof MH, Ruiz-Zapata AM, Bril H,
Bleeker MC, Belien JA, Stoop R and Helder MN: Changes in tissue
composition of the vaginal wall of premenopausal women with
prolapse. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 210:168.e1–9. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Vulic M, Strinic T, Tomic S, Capkun V,
Jakus IA and Ivica S: Difference in expression of collagen type I
and matrix metalloproteinase-1 in uterosacral ligaments of women
with and without pelvic organ prolapse. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod
Biol. 155:225–228. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dviri M, Leron E, Dreiher J, Mazor M and
Shaco-Levy R: Increased matrix metalloproteinases-1,-9 in the
uterosacral ligaments and vaginal tissue from women with pelvic
organ prolapse. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 156:113–117.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang X, Li Y, Chen J, Guo X, Guan H and Li
C: Differential expression profiling of matrix metalloproteinases
and tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases in females with or
without pelvic organ prolapse. Mol Med Rep. 10:2004–2008. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Willett TL, Pasquale J and Grynpas MD:
Collagen modifications in postmenopausal osteoporosis: Advanced
glycation endproducts may affect bone volume, structure and
quality. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 12:329–337. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ajith TA and Vinodkumar P: Advanced
glycation end products: Association with the pathogenesis of
diseases and the current therapeutic advances. Curr Clin Pharmacol.
11:118–127. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Yamagishi S, Fukami K and Matsui T:
Evaluation of tissue accumulation levels of advanced glycation end
products by skin autofluorescence: A novel marker of vascular
complications in high-risk patients for cardiovascular disease. Int
J Cardiol. 185:263–268. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hu H, Jiang H, Ren H, Hu X, Wang X and Han
C: AGEs and chronic subclinical inflammation in diabetes: Disorders
of immune system. Diabetes Metab Res Rev. 31:127–137. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Gkogkolou P and Böhm M: Advanced glycation
end products: Key players in skin aging? Dermatoendocrinol.
4:259–270. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen Y, Huang J, Hu C and Hua K:
Relationship of advanced glycation end products and their receptor
to pelvic organ prolapse. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 8:2288–2299.
2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
El Mourabit H, Loeuillard E, Lemoinne S,
Cadoret A and Housset C: Culture model of rat portal
myofibroblasts. Front Physiol. 7:1202016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Olszewski S, Olszewska E, Popko J,
Poskrobko E, Sierakowski S and Zwierz K: Fibroblast-like synovial
cells in rheumatoid arthritis - the impact of infliximab on
hexosaminidase activity. Adv Clin Exp Med. 24:807–813. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yong WK, Ho YF and Malek SN: Xanthohumol
induces apoptosis and S phase cell cycle arrest in A549 non-small
cell lung cancer cells. Pharmacogn Mag. 11(Suppl 2): S275–S283.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Nájera-Martínez M, García-Latorre EA and
Reyes-Maldonado E: Halomethane-induced cytotoxicity and cell
proliferation in human lung MRC-5 fibroblasts and NL20-TA
epithelial cells. Inhal Toxicol. 24:762–773. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Radia AM, Yaser AM, Ma X, Zhang J, Yang C,
Dong Q, Rong P, Ye B, Liu S and Wang W: Specific siRNA targeting
receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) decreases
proliferation in human breast cancer cell lines. Int J Mol Sci.
14:7959–7978. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Monden M, Koyama H, Otsuka Y, Morioka T,
Mori K, Shoji T, Mima Y, Motoyama K, Fukumoto S, Shioi A, et al:
Receptor for advanced glycation end products regulates adipocyte
hypertrophy and insulin sensitivity in mice: Involvement of
Toll-like receptor 2. Diabetes. 62:478–489. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Volz HC, Laohachewin D, Seidel C,
Lasitschka F, Keilbach K, Wienbrandt AR, Andrassy J, Bierhaus A,
Kaya Z, Katus HA, et al: S100A8/A9 aggravates post-ischemic heart
failure through activation of RAGE-dependent NF-κB signaling. Basic
Res Cardiol. 107:2502012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Angiolilli C, Kabala PA, Grabiec AM, Van
Baarsen IM, Ferguson BS, García S, Malvar Fernandez B, McKinsey TA,
Tak PP, Fossati G, et al: Histone deacetylase 3 regulates the
inflammatory gene expression programme of rheumatoid arthritis
fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis. 76:277–285. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Liu H, Liu A, Shi C and Li B: Curcumin
suppresses transforming growth factor-β1-induced cardiac fibroblast
differentiation via inhibition of Smad-2 and p38 MAPK signaling
pathways. Exp Ther Med. 11:998–1004. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Su C, Chen M, Huang H and Lin J:
Testosterone enhances lipopolysaccharide-induced interleukin-6 and
macrophage chemotactic protein-1 expression by activating the
extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2/nuclear factor-κB
signalling pathways in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Mol Med Rep. 12:696–704.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Marelli B, Le Nihouannen D, Hacking SA,
Tran S, Li J, Murshed M, Doillon CJ, Ghezzi CE, Zhang YL, Nazhat SN
and Barralet JE: Newly identified interfibrillar collagen
crosslinking suppresses cell proliferation and remodelling.
Biomaterials. 54:126–135. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Li W, Xu Q, Deng Y, Yang Z, Xing S, Zhao
X, Zhu P, Wang X, He Z and Gao Y: High-mobility group box 1
accelerates lipopolysaccharide-induced lung fibroblast
proliferation in vitro: Involvement of the NF-κB signaling pathway.
Lab Invest. 95:635–647. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kökçü A, Yanik F, Cetinkaya M, Alper T,
Kandemir B and Malatyalioglu E: Histopathological evaluation of the
connective tissue of the vaginal fascia and the uterine ligaments
inwomen with and without pelvic relaxation. Arch Gynecol Obstet.
266:75–78. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Niu Y, Xie T, Ge K, Lin Y and Lu S:
Effects of extracellular matrix glycosylation on proliferation and
apoptosis of human dermal fibroblasts via the receptor for advanced
glycosylated end products. Am J Dermatopathol. 30:344–351. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Abbass MM, Korany NS, Salama AH, Dmytryk
JJ and Safiejko-Mroczka B: The relationship between receptor for
advanced glycation end products expression and the severity of
periodontal disease in the gingiva of diabetic and non diabetic
periodontitis patients. Arch Oral Biol. 57:1342–1354. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Matsui T, Nakashima S, Nishino Y, Ojima A,
Nakamura N, Arima K, Fukami K, Okuda S and Yamagishi S: Dipeptidyl
peptidase-4 deficiency protects against experimental diabetic
nephropathy partly by blocking the advanced glycation end
products-receptor axis. Lab Invest. 95:525–533. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Giridharan VV, Thandavarayan RA, Arumugam
S, Mizuno M, Nawa H, Suzuki K, Ko KM, Krishnamurthy P, Watanabe K
and Konishi T: Schisandrin B ameliorates ICV-infused amyloid β
induced oxidative stress and neuronal dysfunction through
inhibiting RAGE/NF-κB/MAPK and up-regulating HSP/Beclin expression.
PLoS One. 10:e01424832015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Wu Q, Li S, Li X, Sui Y, Yang Y, Dong L,
Xie B and Sun Z: Inhibition of advanced glycation endproduct
formation by lotus seedpod oligomeric procyanidins through
RAGE-MAPK signaling and NF-κB activation in high-fat-diet rats. J
Agric Food Chem. 63:6989–6998. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Medeiros MC, Frasnelli SC, Bastos AS,
Orrico SR and Rossa C Jr: Modulation of cell proliferation,
survival and gene expression by RAGE and TLR signaling in cells of
the innate and adaptive immune response: Role of p38 MAPK and
NF-κB. J Appl Oral Sci. 22:185–193. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
He ZW, Qin YH, Wang ZW, Chen Y, Shen Q and
Dai SM: HMGB1 acts in synergy with lipopolysaccharide in activating
rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts via p38 MAPK and NF-κB signaling
pathways. Mediators Inflamm. 2013:5967162013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
de Bittencourt Pasquali MA, Gelain DP,
Zeidán-Chuliá F, Pires AS, Gasparotto J, Terra SR and Moreira JC:
Vitamin A (retinol) downregulates the receptor for advanced
glycation endproducts (RAGE) by oxidant-dependent activation of p38
MAPK and NF-κB in human lung cancer A549 cells. Cell Signal.
25:939–954. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|