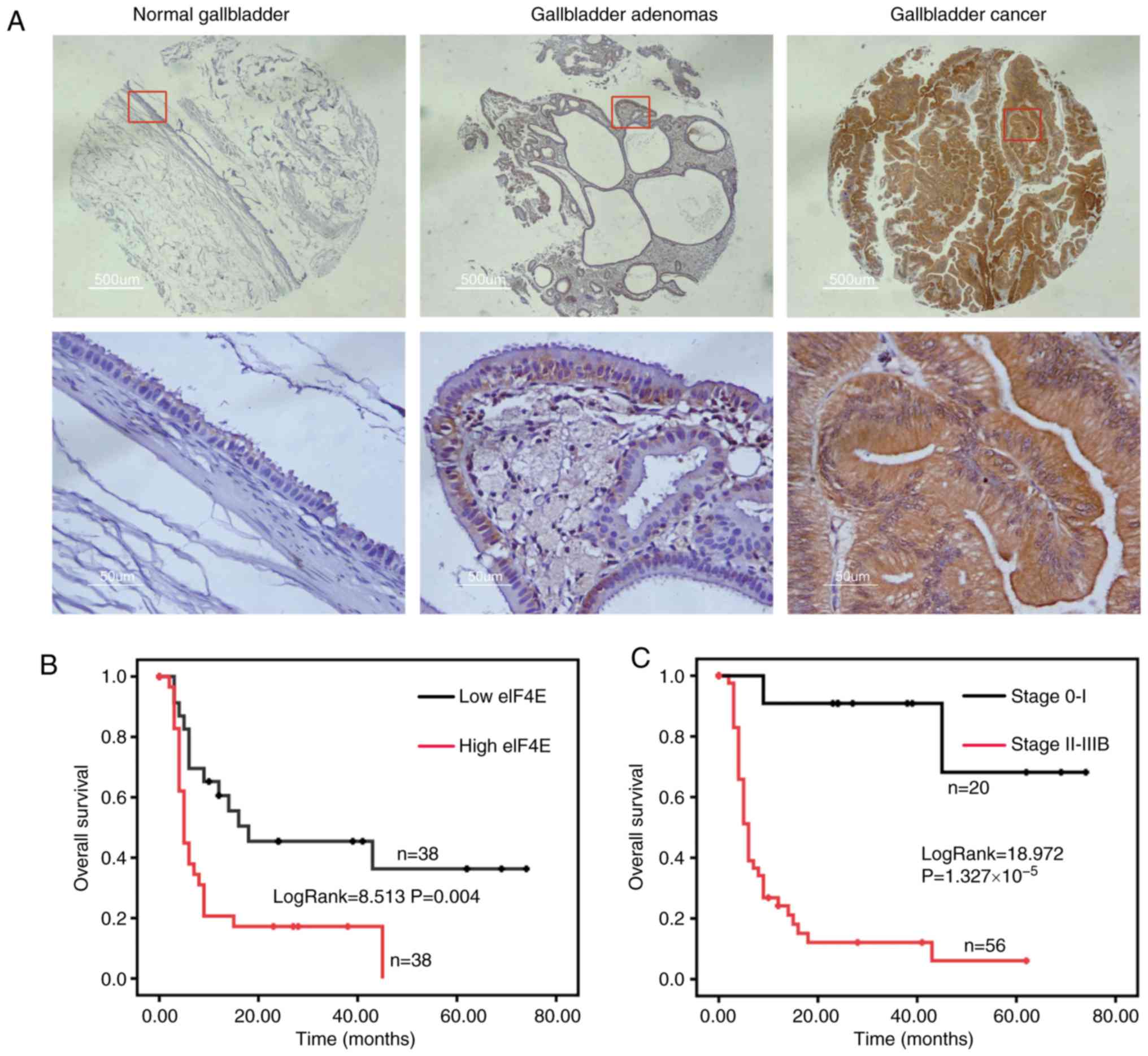
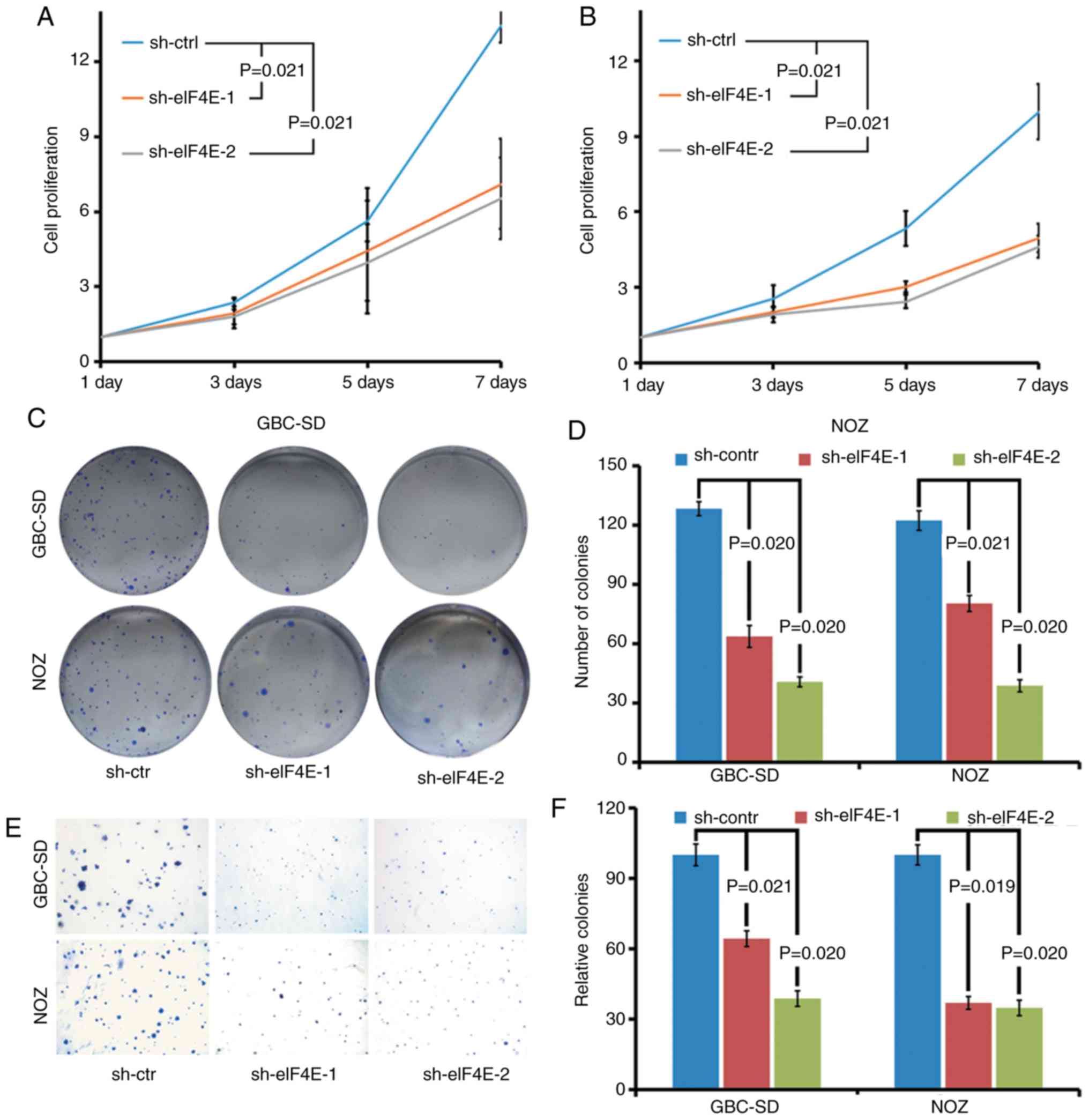
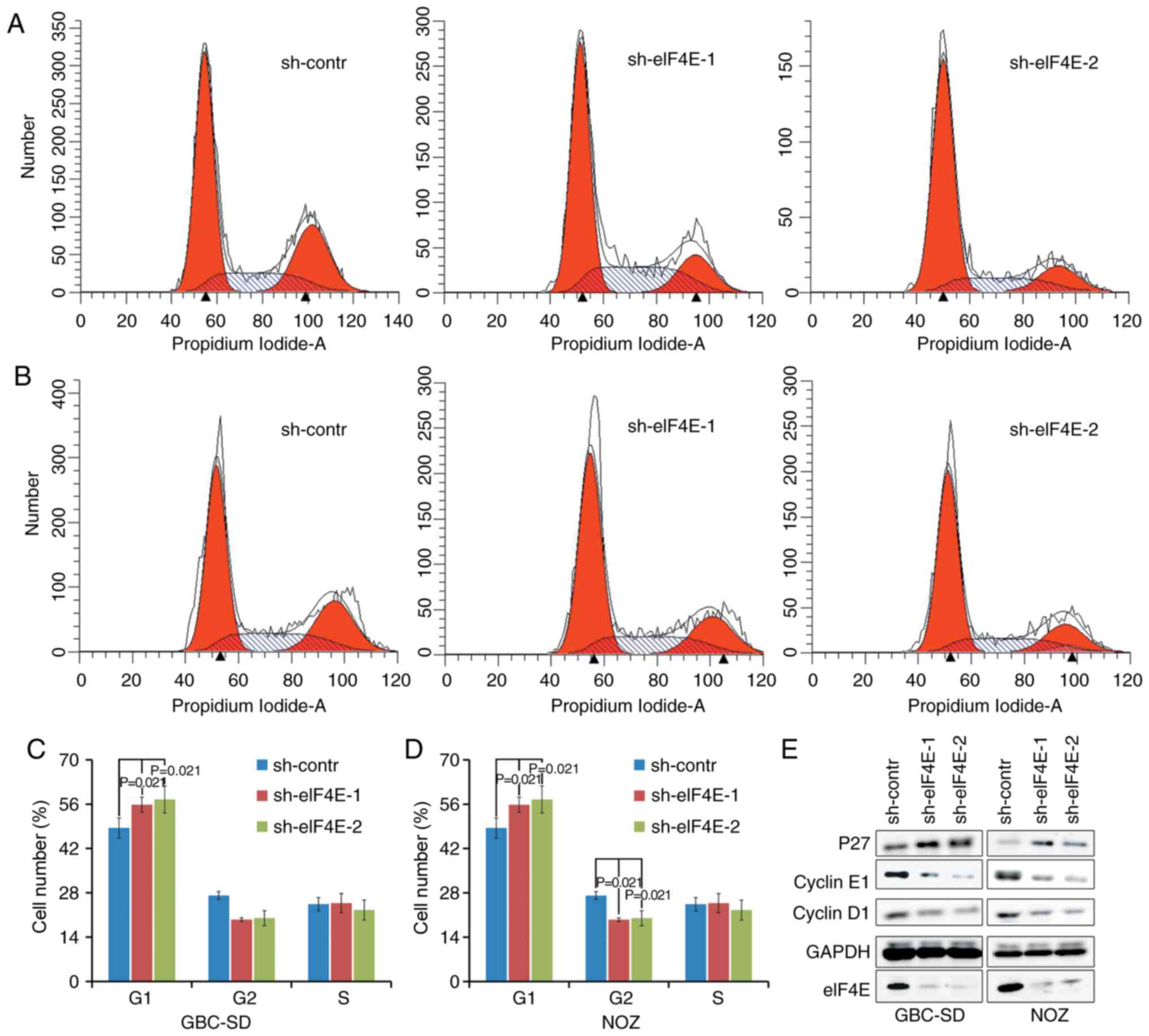
|
1
|
Randi G, Franceschi S and La Vecchia C:
Gallbladder cancer worldwide: Geographical distribution and risk
factors. Int J Cancer. 118:1591–1602. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Pitt SC, Jin LX, Hall BL, Strasberg SM and
Pitt HA: Incidental gallbladder cancer at cholecystectomy: When
should the surgeon be suspicious? Ann Surg. 260:128–133. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Elmasry M, Lindop D, Dunne DF, Malik H,
Poston GJ and Fenwick SW: The risk of malignancy in ultrasound
detected gallbladder polyps: A systematic review. Int J Surg. 33(Pt
A): 28–35. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dasari BVM, Ionescu MI, Pawlik TM, Hodson
J, Sutcliffe RP, Roberts KJ, Muiesan P, Isaac J, Marudanayagam R
and Mirza DF: Outcomes of surgical resection of gallbladder cancer
in patients presenting with jaundice: A systematic review and
meta-analysis. J Surg Oncol. 118:477–485. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aitken CE and Lorsch JR: A mechanistic
overview of translation initiation in eukaryotes. Nat Struct Mol
Biol. 19:568–576. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Pelletier J, Graff J, Ruggero D and
Sonenberg N: Targeting the eIF4F translation initiation complex: A
critical nexus for cancer development. Cancer Res. 75:250–263.
2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ramaswamy S, Ross KN, Lander ES and Golub
TR: A molecular signature of metastasis in primary solid tumors.
Nat Genet. 33:49–54. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Edge SB, Byrd DR, Compton CC, Fritz AG,
Greene FL and Trotti A: AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 7th ed.
Springer; New York, NY: 2010
|
|
9
|
Lu Li M, Zhang J, Li F, Zhang H, Wu B, Tan
X, Zhang Z, Gao L, Mu GJ, et al: Yes-associated protein 1 (YAP1)
promotes human gallbladder tumor growth via activation of the
AXL/MAPK pathway. Cancer Lett. 355:201–209. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Yin X, Kim RH, Sun G, Miller JK and Li BD:
Overexpression of eukaryotic initiation factor 4E is correlated
with increased risk for systemic dissemination in node-positive
breast cancer patients. J Am Coll Surg. 218:663–671. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Khosravi S, Tam KJ, Ardekani GS, Martinka
M, McElwee KJ and Ong CJ: eIF4E is an adverse prognostic marker of
melanoma patient survival by increasing melanoma cell invasion. J
Invest Dermatol. 135:1358–1367. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kwegyir-Afful AK, Bruno RD,
Purushottamachar P, Murigi FN and Njar VC: Galeterone and VNPT55
disrupt Mnk-eIF4E to inhibit prostate cancer cell migration and
invasion. FEBS J. 283:3898–3918. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Liu F, Wang X, Li J, Gu K, Lv L, Zhang S,
Che D, Cao J, Jin S and Yu Y: miR-34c-3p functions as a tumour
suppressor by inhibiting eIF4E expression in non-small cell lung
cancer. Cell Prolif. 48:582–592. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wiegering A, Uthe FW, Jamieson T, Ruoss Y,
Hüttenrauch M, Küspert M, Pfann C, Nixon C, Herold S, Walz S, et
al: Targeting translation initiation bypasses signaling crosstalk
mechanisms that maintain high MYC levels in colorectal cancer.
Cancer Discov. 5:768–781. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sonenberg N and Hinnebusch AG: Regulation
of translation initiation in eukaryotes: Mechanisms and biological
targets. Cell. 136:731–745. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Siddiqui N and Sonenberg N: Signalling to
eIF4E in cancer. Biochem Soc Trans. 43:763–772. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wan J, Shi F, Xu Z and Zhao M: Knockdown
of eIF4E suppresses cell proliferation, invasion and enhances
cisplatin cytotoxicity in human ovarian cancer cells. Int J Oncol.
47:2217–2225. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Chen B, Zhang B, Xia L, Zhang J, Chen Y,
Hu Q and Zhu C: Knockdown of eukaryotic translation initiation
factor 4E suppresses cell growth and invasion, and induces
apoptosis and cell cycle arrest in a human lung adenocarcinoma cell
line. Mol Med Rep. 13:33842016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Truitt ML, Conn CS, Shi Z, Pang X,
Tokuyasu T, Coady AM, Seo Y, Barna M and Ruggero D: Differential
requirements for eIF4E dose in normal development and cancer. Cell.
162:59–71. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Robichaud N, del Rincon SV, Huor B, Alain
T, Petruccelli LA, Hearnden J, Goncalves C, Grotegut S, Spruck CH,
Furic L, et al: Phosphorylation of eIF4E promotes EMT and
metastasis via translational control of SNAIL and MMP-3. Oncogene.
34:2032–2042. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
D'Abronzo LS, Bose S, Crapuchettes ME,
Beggs RE, Vinall RL, Tepper CG, Siddiqui S, Mudryj M, Melgoza FU,
Durbin-Johnson BP, et al: The androgen receptor is a negative
regulator of eIF4E phosphorylation at S209: Implications for the
use of mTOR inhibitors in advanced prostate cancer. Oncogene.
36:6359–6373. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Duffy AG, Makarova-Rusher OV, Ulahannan
SV, Rahma OE, Fioravanti S, Walker M, Abdullah S, Raffeld M,
Anderson V, Abi-Jaoudeh N, et al: Modulation of tumor eIF4E by
antisense inhibition: A phase I/II translational clinical trial of
ISIS 183750-an antisense oligonucleotide against eIF4E-in
combination with irinotecan in solid tumors and
irinotecan-refractory colorectal cancer. Int J Cancer.
139:1648–1657. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Robichaud N, Hsu BE, Istomine R, Alvarez
F, Blagih J, Ma EH, Morales SV, Dai DL, Li G, Souleimanova M, et
al: Translational control in the tumor microenvironment promotes
lung metastasis: Phosphorylation of eIF4E in neutrophils. Proc Natl
Acad Sci USA. 115:E2202–E2209. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|