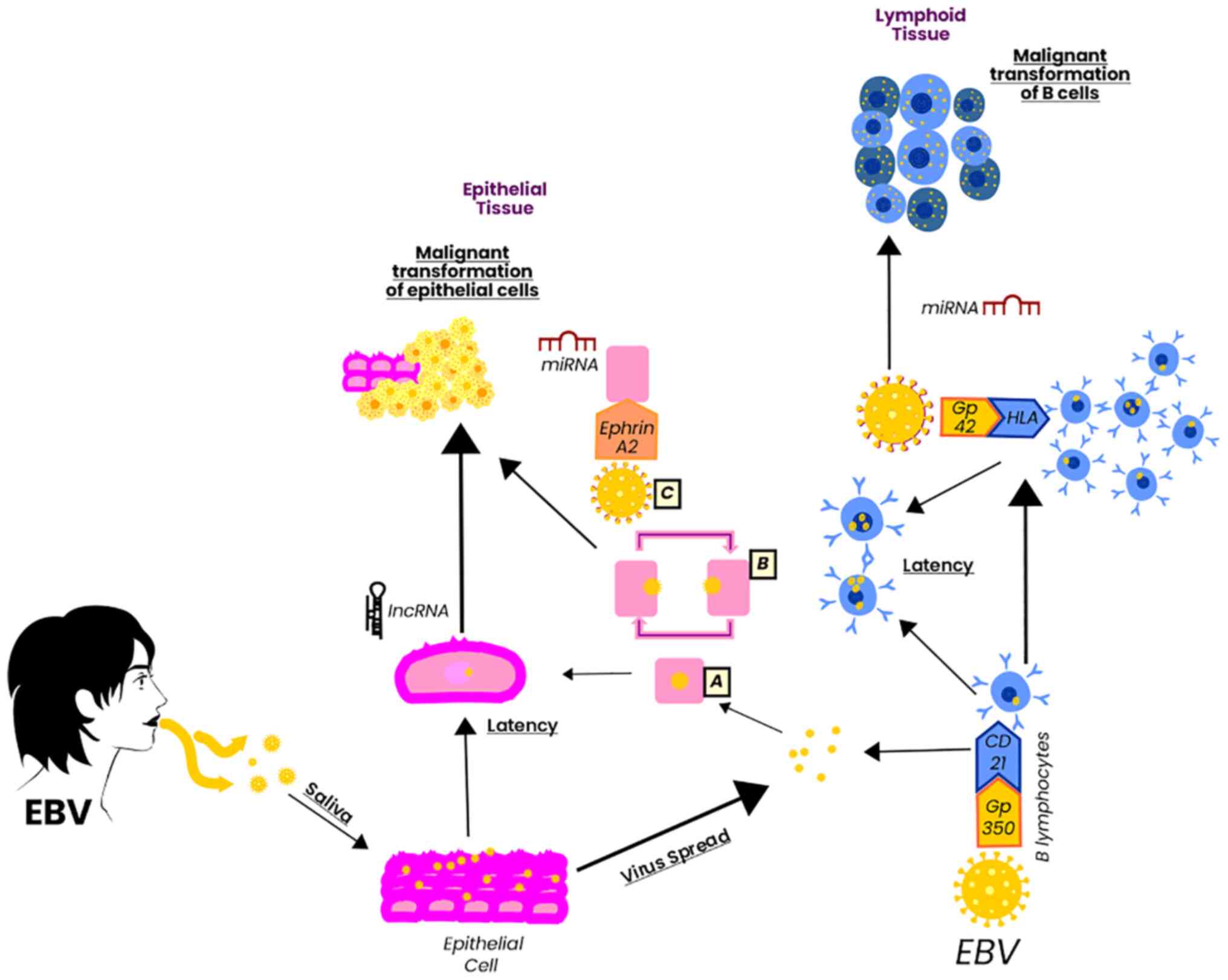
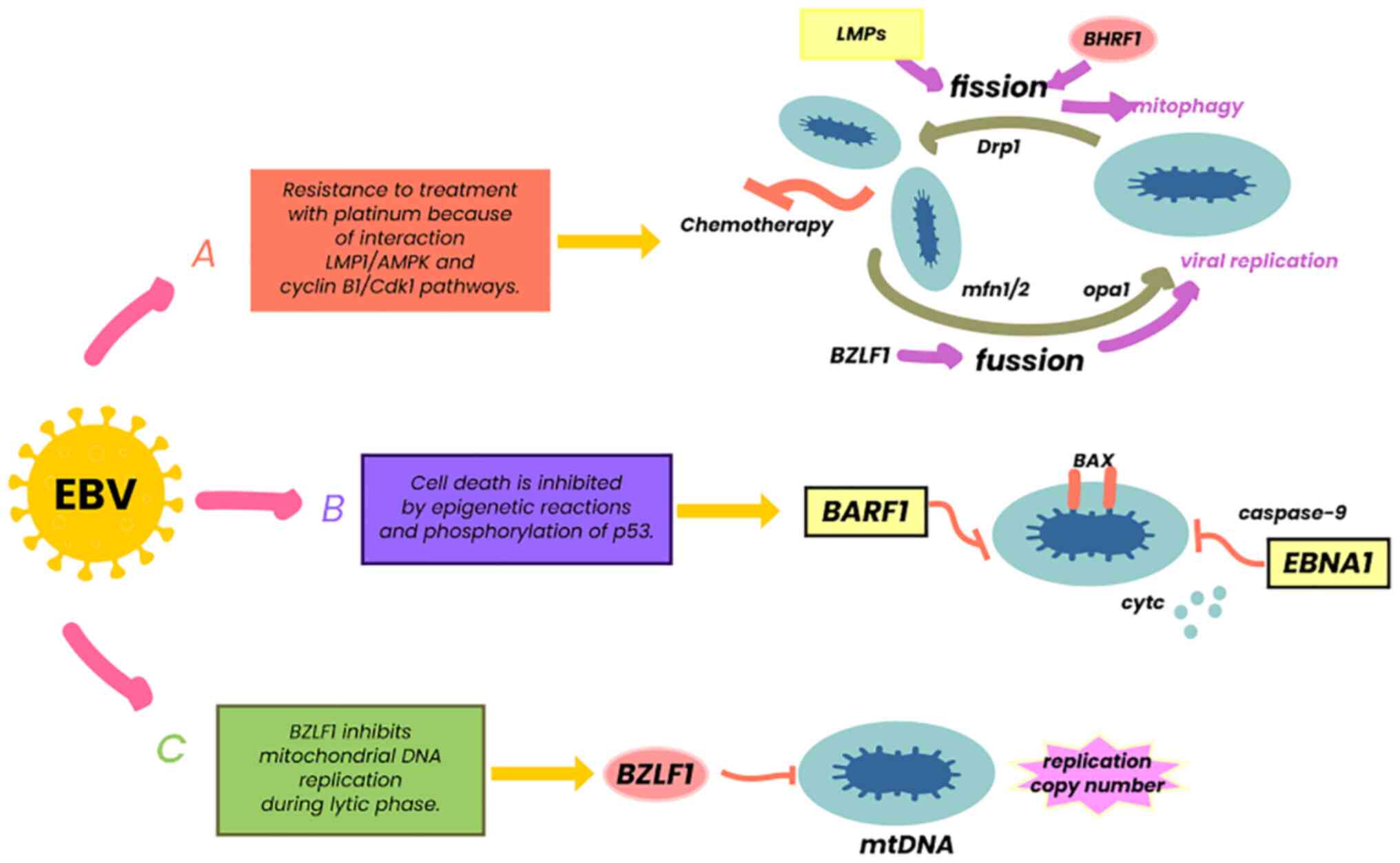
|
1
|
Bouvard V, Baan R, Straif K, Grosse Y,
Secretan B, El Ghissassi F, Benbrahim-Tallaa L, Guha N, Freeman C,
Galichet L, et al: A review of human carcinogens-Part B: biological
agents. Lancet Oncol. 10:321–322. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Muñoz N, Castellsagué X, Berrington de
González A and Gissmann L: Chapter 1: HPV in the etiology of human
cancer. Vaccine. 24(Suppl 3): S1–S10. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Bialecki ES and Di Bisceglie AM: Clinical
presentation and natural course of hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:485–489. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hermine O, Lefrère F, Bronowicki JP,
Mariette X, Jondeau K, Eclache-Saudreau V, Delmas B, Valensi F,
Cacoub P, Brechot C, et al: Regression of splenic lymphoma with
villous lymphocytes after treatment of hepatitis C virus infection.
N Engl J Med. 347:89–94. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Thompson MP and Kurzrock R: Epstein-Barr
virus and cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:803–821. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mesri EA, Feitelson MA and Munger K: Human
viral oncogenesis: A cancer hallmarks analysis. Cell Host Microbe.
15:266–282. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Medina-Ortega AP, López-Valencia D,
Mosquera-Monje SL, Mora-Obando DL and Dueñas-Cuéllar RA:
Relationship between Epstein-Barr virus and cancer development.
Iatreia. 30:131–145. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Pietropaolo V, Prezioso C and Moens U:
Role of virus-induced host cell epigenetic changes in cancer. Int J
Mol Sci. 22:83462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hulse M, Caruso LB, Madzo J, Tan Y,
Johnson S and Tempera I: Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase 1 is necessary
for coactivating hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent gene
expression by Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1. PLoS
Pathog. 4:e10073942018. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Cao Y, Xie L, Shi F, Tang M, Li Y, Hu J,
Zhao L, Zhao L, Yu X, Luo X, et al: Targeting the signaling in
Epstein-Barr virus-associated diseases: Mechanism, regulation, and
clinical study. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 6:152021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
He B, Li W, Wu Y, Wei F, Gong Z, Bo H,
Wang Y, Li X, Xiang B, Guo C, et al: Epstein-Barr virus-encoded
miR-BART6-3p inhibits cancer cell metastasis and invasion by
targeting long non-coding RNA LOC553103. Cell Death Dis.
7:e23532016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hechter O, Sausen DG, Gallo ES, Dahari H
and Borenstein R: Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) epithelial associated
malignancies: Exploring pathologies and current treatments. Int J
Mol Sci. 23:143892022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Feng Y, Spezia M, Huang S, Yuan C, Zeng Z,
Zhang L, Ji X, Liu W, Huang B, Luo W, et al: Breast cancer
development and progression: Risk factors, cancer stem cells,
signaling pathways, genomics, and molecular pathogenesis. Genes
Dis. 5:77–106. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang M, Yu F, Wu W, Wang Y, Ding H and
Qian L: Epstein-Barr virus-encoded microRNAs as regulators in host
immune responses. Int J Biol Sci. 14:565–576. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
El-Sharkawy A, Al Zaidan L and Malki A:
Epstein-Barr virus-associated malignancies: Roles of viral
oncoproteins in carcinogenesis. Front Oncol. 8:2652018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shannon-Lowe C, Adland E, Bell A,
Delecluse H, Rickinson A and Rowe M: Features distinguishing
Epstein-Barr virus infections of epithelial cells and B cells:
viral genome expression, genome maintenance, and genome
amplification. J Virol. 83:7749–7760. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sinclair AJ, Moalwi MH and Amoaten T: Is
EBV associated with breast cancer in specific geographic locations?
Cancers (Basel). 13:8192021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shannon-Lowe C and Rowe M: Epstein Barr
virus entry; kissing and conjugation. Curr Opin Virol. 4:78–84.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Shannon-Lowe C and Rowe M: Epstein-Barr
virus infection of polarized epithelial cells via the basolateral
surface by memory B cell-mediated transfer infection. PLoS Pathog.
7:e10013382011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Imai S, Nishikawa J and Takada K:
Cell-to-cell contact as an efficient mode of Epstein-Barr virus
infection of diverse human epithelial cells. J Virol. 72:4371–4378.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tugizov SM, Berline JW and Palefsky JM:
Epstein-Barr virus infection of polarized tongue and nasopharyngeal
epithelial cells. Nat Med. 9:307–314. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen J, Sathiyamoorthy K, Zhang X,
Schaller S, Perez White BE, Jardetzky TS and Longnecker R: Ephrin
receptor A2 is a functional entry receptor for Epstein-Barr virus.
Nat Microbiol. 3:172–180. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zhang H, Li Y, Wang HB, Zhang A, Chen ML,
Fang ZX, Dong XD, Li SB, Du Y, Xiong D, et al: Ephrin receptor A2
is an epithelial cell receptor for Epstein-Barr virus entry. Nat
Microbiol. 3:164–171. 2018.
|
|
24
|
Ayee R, Ofori MEO, Wright E and Quaye O:
Epstein Barr Virus associated lymphomas and epithelia cancers in
humans. J Cancer. 11:1737–1750. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Al Moustafa AE, Al-Antary N, Aboulkassim
T, Akil N, Batist G and Yasmeen A: Co-prevalence of Epstein-Barr
virus and high-risk human papillomaviruses in Syrian women with
breast cancer. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 12:1936–1939. 2016.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lin JH, Tsai CH, Chu JS, Chen JY, Takada K
and Shew JY: Dysregulation of HER2/HER3 signaling axis in
Epstein-Barr virus-infected breast carcinoma cells. J Virol.
81:5705–5713. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Pal AD, Basak NP, Banerjee AS and Banerjee
S: Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-2A alters
mitochondrial dynamics promoting cellular migration mediated by
Notch signaling pathway. Carcinogenesis. 35:1592–1601. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Arias-Calvachi C, Blanco R, Calaf GM and
Aguayo F: Epstein-Barr virus association with breast cancer:
Evidence and perspectives. Biology (Basel). 11:7992022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Nasser F, Moussa N, Helmy MW and Haroun M:
Dual targeting of Notch and Wnt/β-catenin pathways: Potential
approach in triple-negative breast cancer treatment. Naunyn
Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol. 394:481–490. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Gómez-Archila JD, Espinosa-García AM,
Palacios-Reyes C, Trujillo-Cabrera Y, Mejía ALS, González AVA,
Rangel-López E, Alonso-Themann PG, Solís NDS, Hernández-Zavala A,
et al: NOTCH expression variability and relapse of breast cancer in
high-risk groups. Am J Med Sci. 364:583–594. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Shahi V, Agarwal P, Qayoom S, Kumar V,
Tewari S, Raghuvanshi S, Singh US and Goel MM: Detection of Epstein
Barr nuclear antigen-1 (EBNA-1), early antigen 1F, 2R (EA-1F,
EA-2R) along with Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 1
(LMP1) in breast cancer of Northern India: An interim analysis.
Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 23:3717–3723. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wang Z, Li Z, Wu Q, Li C, Li J, Zhang Y,
Wang C and Sun S and Sun S: DNER promotes epithelial-mesenchymal
transition and prevents chemosensitivity through the Wnt/β-catenin
pathway in breast cancer. Cell Death Dis. 11:6422020. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Zimber-Strobl U and Strobl LJ: EBNA2 and
Notch signalling in Epstein-Barr virus mediated immortalization of
B lymphocytes. Semin Cancer Biol. 11:423–434. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Anderson L and Longnecker R: An
auto-regulatory loop for EBV LMP2A involves activation of Notch.
Virology. 371:257–266. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Cyprian FS, Al-Farsi HF, Vranic S, Akhtar
S and Al Moustafa AE: Epstein-Barr virus and human papillomaviruses
interactions and their roles in the initiation of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer progression. Front
Oncol. 8:1112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zanella L, Riquelm I, Buchegger K, Abanto
M, Ili C and Brebi P: A reliable Epstein-Barr virus classification
based on phylogenomic and population analyses. Sci Rep. 9:98292019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zimber U, Adldinger HK, Lenoir GM,
Vuillaume M, Knebel-Doeberitz MV, Laux G, Desgranges C, Wittmann P,
Freese UK, Schneider U, et al: Geographical prevalence of two types
of Epstein-Barr virus. Virology. 154:56–66. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Smith NA, Baresel PC, Jackson CL, Ogolla
S, Toko EN, Heit S, Piriou E, Sumba OP, Middeldorp JM, Colborn KL
and Rochford R: Differences in the Epstein-Barr virus gp350 IgA
antibody response are associated with increased risk for
coinfection with a second strain of Epstein-Barr virus. J Infect
Dis. 219:955–963. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
39
|
Lung ML, Li SB and Chang RS: Study of
Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) transmission by EBV genotyping. J Infect
Dis. 164:213–214. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Golrokh Mofrad M, Kazeminezhad B and
Faghihloo E: Prevalence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) in Iranian
breast carcinoma patients. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 21:133–137.
2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Gupta I, Jabeen A, Al-Sarraf R, Farghaly
H, Vranic S, Sultan AA, Al Moustafa AE and Al-Thawadi H: The
co-presence of high-risk human papillomaviruses and Epstein-Barr
virus is linked with tumor grade and stage in Qatari women with
breast cancer. Hum Vaccin Immunother. 17:982–989. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
42
|
Aboulkassim T, Yasmeen A, Akil N, Batist G
and Al Moustafa AE: Incidence of Epstein-Barr virus in Syrian women
with breast cancer: A tissue microarray study. Hum Vaccin
Immunother. 11:951–955. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Fessahaye G, Elhassan AM, Elamin EM, Adam
AAM, Ghebremedhin A and Ibrahim ME: Association of Epstein-Barr
virus and breast cancer in Eritrea. Infect Agents Cancer.
12:622017. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Nwagu GC, Bhattarai S, Swahn M, Ahmed S
and Aneja R: Prevalence and mortality of triple-negative breast
cancer in West Africa: Biologic and sociocultural factors. JCO Glob
Oncol. 7:1129–1140. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Acheampong T, Kehm RD, Terry MB, Argov EL
and Tehranifar P: Incidence trends of breast cancer molecular
subtypes by age and race/ethnicity in the US from 2010 to 2016.
JAMA Netw Open. 3:e20132262020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Siddharth S and Sharma D: Racial disparity
and triple-negative breast cancer in African-American women: A
multifaceted affair between obesity, biology, and socioeconomic
determinants. Cancers (Basel). 10:5142018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Ibrahim SA, Hassan H, Vilardo L, Kumar SK,
Kumar AV, Kelsch R, Schneider C, Kiesel L, Eich HT, Zucchi I, et
al: Syndecan-1 (CD138) modulates triple-negative breast cancer stem
cell properties via regulation of LRP-6 and IL-6-mediated STAT3
signaling. PLoS One. 8:e857372013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Rahim A, Afzal M and Naveed AK: Genetic
polymorphism of miRNA-196a and its target gene annexin-A1
expression based on ethnicity in Pakistani female breast cancer
patients. Pak J Med Sci. 35:1598–1604. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Treece AL, Duncan DL, Tang W, Elmore S,
Morgan DR and Gulley ML, Speck O, Meyers MO and Gulley ML: Gastric
adenocarcinoma microRNA profiles in fixed tissue and in plasma
reveal cancer-associated and Epstein-Barr virus-related expression
patterns. Lab Invest. 96:661–671. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Ramanto KN, Widianto KJ, Wibowo SSH and
Agustriawan D: The regulation of microRNA in each of cancer stage
from two different ethnicities as potential biomarker for breast
cancer. Comput Biol Chem. 93:1074972021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
GLOBOCAN 2020: International Agency for
Research of Cancer 2022. Available in: http://gco.iarc.fr/. Accessed May 5, 2022
|
|
52
|
Mexican consensus on diagnosis and breast
cancer treatment. GAMO. 7(Supl 2)2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Smatti MK, Al-Sadeq DW, Ali NH, Pintus G,
Abou-Saleh H and Nasrallah GK: Epstein-Barr virus epidemiology,
serology, and genetic variability of LMP-1 oncogene among healthy
population: An update. Front Oncol. 8:2112018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Fierti AO, Yakass MB, Okertchiri EA,
Adadey SM and Quay O: The role of Epstein-Barr virus in modulating
key tumor suppressor genes in associated malignancies: Epigenetics,
transcriptional, and post-translational modifications.
Biomolecules. 12:1272022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Mátyási B, Farkas Z, Kopper L, Sebestyén
A, Boissan M, Mehta A and Takács-Vellai K: The function of
NM23-H1/NME1 and its homologs in major processes linked to
metastasis. Pathol Oncol Res. 26:49–61. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Cheerathodi MR and Meckes DG Jr: The
Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 interactome: Biological implications and
therapeutic targets. Future Virol. 13:863–887. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Longnecker R and Kieff E: A second
Epstein-Barr virus membrane protein (LMP2) is expressed in latent
infection and colocalizes with LMP1. J Virol. 64:2319–2326. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Wasil LR and Shair KHY: Modified anoikis
assay that functionally segregates Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 strains
into two groups. J Virol. 92:e00557–18. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Xie L, Shi F, Li Y, Li W, Yu X, Zhao L,
Zhou M, Hu J, Luo X, Tang M, et al: Drp1-dependent remodeling of
mitochondrial morphology triggered by EBV-LMP1 increases cisplatin
resistance. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 5:562020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Pratt ZL, Kuzembayeva M, Sengupta S and
Sugden B: The microRNAs of Epstein-Barr virus are expressed at
dramatically differing levels among cell lines. Virology.
386:387–397. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wang M, Gu B, Chen X, Wang Y, Li P and
Wang K: The function and therapeutic potential of Epstein-Barr
virus-encoded MicroRNAs in cancer. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids.
17:657–668. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
62
|
Liu Y, Hu Z, Zhang Y and Wang C: Long
non-coding RNAs in Epstein-Barr virus-related cancer. Cancer Cell
Int. 21:2782021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Kang MS and Kieff E: Epstein-Barr virus
latent genes. Exp Mol Med. 47:e1312015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Houmani JL, Davis CI and Ruf IK:
Growth-promoting properties of Epstein-Barr virus EBER-1 RNA
correlate with ribosomal protein L22 binding. J Virol.
83:9844–9853. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Samanta M, Iwakiri D, Kanda T, Imaizumi T
and Takada K: EB virus-encoded RNAs are recognized by RIG-I and
activate signaling to induce type I IFN. EMBO J. 25:4207–4214.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
66
|
Yang GD, Huang TJ, Peng LX, Yang CF, Liu
RY, Huang HB, Chu QQ, Yang HJ, Huang JL, Zhu ZY, et al:
Epstein-Barr virus_encoded LMP1 upregulates microRNA-21 to promote
the resistance of nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells to
cisplatin-induced apoptosis by suppressing PDCD4 and Fas-L. PLoS
One. 8:e783552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Sales ACV, Gomes da Silva IIF, Leite MCB,
Coutinho LL, Reis RBAC, Castoldi A, Bg Martins D, Lima-Filho JL and
Souto FO: Mirna21 expression in the breast cancer tumor tissue is
independent of neoadjuvant chemotherapy. Breast Cancer (Dove Med
Press). 12:141–151. 2020.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
68
|
Zhu K, Wu Y, He P, Fan Y, Zhong X, Zheng H
and Luo T: PI3K/AKT/mTOR-targeted therapy for breast cancer. Cells.
11:25082022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
69
|
Tankova T, Senkus E, Beloyartseva M,
Borštnar S, Catrinoiu D, Frolova M, Hegmane A, Janež A, Krnić M,
Lengyel Z, et al: Management strategies for hyperglycemia
associated with the α-selective PI3K inhibitor alpelisib for the
treatment of breast cancer. Cancers (Basel). 14:15982022.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
70
|
Mostafaei S, Kazemnejad A, Norooznezhad
AH, Mahaki B and Moghoofei M: Simultaneous effects of viral factors
of human papilloma virus and Epstein-Barr virus on progression of
breast and thyroid cancers: Application of structural equation
modeling. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 21:1431–1439. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
71
|
Tsai JH, Tsai CH, Cheng MH, Lin SJ, Xu FL
and Yang CC: Association of viral factors with non-familial breast
cancer in Taiwan by comparison with non-cancerous, fibroadenoma,
and thyroid tumor tissues. J Med Virol. 75:276–281. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
72
|
Tsai JH, Hsu CS, Tsai CH, Su JM, Liu YT,
Cheng MH, Wei JC, Chen FL and Yang CC: Relationship between viral
factors, axillary lymph node status and survival in breast cancer.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 133:13–21. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
73
|
Klein G: Tumor associations of
EBV-historical perspectives. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 390:17–22.
2015.
|
|
74
|
Yates J, Warren N, Reisman D and Sugden B:
A cis-acting element from the Epstein-Barr viral genome that
permits stable replication of recombinant plasmids in latently
infected cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USa. 81:3806–3810. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
75
|
Naushad W, Surriya O and Sadia H:
Prevalence of EBV, HPV and MMTV in Pakistani breast cancer
patients: A possible etiological role of viruses in breast cancer.
Infect Genet Evol. 54:230–237. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Corbex M, Bouzbid S, Traverse-Glehen A,
Aouras H, McKay-Chopin S, Carreira C, Lankar A, Tommasino M and
Gheit T: Prevalence of papillomaviruses, polyomaviruses, and
herpesviruses in triple-negative and inflammatory breast tumors
from Algeria compared with other types of breast cancer tumors.
PLoS One. 9:e1145592014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
McKenzie J and El-Guindy A: Epstein-Barr
virus lytic cycle reactivation. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol.
391:237–261. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
78
|
Murata T, Sugimoto A, Inagaki T, Yanagi Y,
Watanabe T, Sato Y and Kimura H: Molecular basis of Epstein-Barr
virus latency establishment and lytic reactivation. Viruses.
13:23442021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
79
|
Chéne A, Donati D, Guerreiro-Cacais AO,
Levitsky V, Chen Q, Falk KI, Orem J, Kironde F, Wahlgren M and
Bejarano MT: A molecular link between malaria and Epstein-Barr
virus reactivation. PLoS Pathog. 3:e802007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
80
|
Gold JE, Okyay RA, Licht WE and Hurley DJ:
Investigation of long COVID prevalence and its relationship to
Epstein-Barr virus reactivation. Pathogens. 10:7632021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
81
|
Hu J, Li Y, Li H, Shi F, Xie L, Zhao L,
Tang M, Luo X, Jia W, Fan J, et al: Targeting Epstein-Barr virus
oncoprotein LMP1-mediated high oxidative stress suppresses EBV
lytic reactivation and sensitizes tumors to radiation therapy.
Theranostics. 10:11921–11937. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
82
|
Mehta SK, Bloom DC, Plante I, Stowe R,
Feiveson AH, Renner A, Dhummakupt A, Markan D, Zhang Y, Wu H, et
al: Reactivation of latent Epstein-Barr virus: A comparison after
exposure to gamma, proton, carbon, and iron radiation. Int J Mol
Sci. 19:29612018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Sausen DG, Bhutta MS, Gallo ES, Dahari H
and Borenstein R: Stress-induced Epstein-Barr virus reactivation.
Biomolecules. 11:13802021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
84
|
Anderson NM and Simon MC: The tumor
microenvironment. Curr Biol. 30:R921–R925. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
85
|
Kluwe J, Mencin A and Schwabe RF:
Toll-like receptors, wound healing, and carcinogenesis. J Mol Med
(Berl). 87:125–138. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
86
|
Pedroza-Gonzalez A, Xu K, Wu TC, Aspord C,
Tindle S, Marches F, Gallegos M, Burton EC, Savino D, Hori T, et
al: Thymic stromal lymphopoietin fosters human breast tumor growth
by promoting type 2 inflammation. J Exp Med. 208:479–490. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
DeNardo DG, Barreto JB, Andreu P, Vasquez
L, Tawfik D, Kolhatkar N and Coussens LM: CD4(+) T cells regulate
pulmonary metastasis of mammary carcinomas by enhancing protumor
properties of macrophages. Cancer Cell. 16:91–102. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
88
|
Kuan EL and Ziegler SF: A tumor-myeloid
cell axis, mediated via the cytokines IL-1α and TSLP, promotes the
progression of breast cancer. Nat Immunol. 19:366–374. 2018.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
89
|
Wu TC, Xu K, Martinek J, Young RR,
Banchereau R, George J, Turner J, Kim KI, Zurawski S, Wang X, et
al: IL1 receptor antagonist controls transcriptional signature of
inflammation in patients with metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Res.
78:5243–5258. 2018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
90
|
Sheikhpour E, Noorbakhsh P, Foroughi E,
Farahnak S, Nasiri R and Neamatzadeh H: A survey on the role of
interleukin-10 in breast cancer: A narrative. Rep Biochem Mol Biol.
7:30–37. 2018.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
91
|
Azuma K, Ikeda K, Suzuki T, Aogi K,
Horie-Inoue K and Inoue S: TRIM47 activates NF-κB signaling via
PKC-ε/PKD3 stabilization and contributes to endocrine therapy
resistance in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
118:e21007841182021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
92
|
Omokehinde T and Johnson RW: GP130
cytokines in breast cancer and bone. Cancers (Basel). 12:3262020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
93
|
Wang L, Simons DL, Lu X, Tu TY, Avalos C,
Chang AY, Dirbas FM, Yim JH, Waisman J and Lee PP: Breast cancer
induces systemic immune changes on cytokine signaling in peripheral
blood monocytes and lymphocytes. EBioMedicine. 52:1026312020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
94
|
Crake RLI, Strother MR, Phillips E, Doogue
MP, Zhang M, Frampton CMA, Robinson BA and Currie MJ: Influence of
serum inflammatory cytokines on cytochrome P450 drug metabolising
activity during breast cancer chemotherapy: A patient feasibility
study. Sci Rep. 11:56482021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
95
|
Sparano JA, O'Neill A, Graham N, Northfelt
DW, Dang CT, Wolff AC, Sledge GW and Miller KD: Inflammatory
cytokines and distant recurrence in HER2-negative early breast
cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer. 8:162022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
96
|
Chen W, Qin Y and Liu S: Cytokines, breast
cancer stem cells (BCSCs) and chemoresistance. Clin Transl Med.
7:272018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
97
|
Liu F, Li L, Lan M, Zou T, Kong Z, Cai T,
Wu XY and Cai Y: Key factor regulating inflammatory
microenvironment, metastasis, and resistance in breast cancer:
Interleukin-1 signaling. Mediators Inflamm. 2021:77858902021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
98
|
Cierna Z, Smolkova B, Cholujova D,
Gronesova P, Miklikova S, Cihova M, Plava J and Mego M: Decreased
levels of circulating cytokines VEGF, TNF-β and IL-15 indicate
PD-L1 overexpression in tumours of primary breast cancer patients.
Sci Rep. 11:12942021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
99
|
Figenschau SL, Knutsen E, Urbarova I,
Fenton C, Elston B, Perander M, Mortensen ES and Fenton KA: ICAM1
expression is induced by proinflammatory cytokines and associated
with TLS formation in aggressive breast cancer subtypes. Sci Rep.
8:117202018. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
100
|
Jurisic V: Multiomic analysis of cytokines
in immuno-oncology. Expert Rev Proteomics. 17:663–674. 2020.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
101
|
Farahmand M, Monavari SH, Shoja Z,
Ghaffari H, Tavakoli M and Tavakoli A: Epstein-Barr virus and risk
of breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Future
Oncol. 15:2873–2885. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
102
|
Jin Q, Su J, Yan D and Wu S: Epstein-Barr
virus infection and increased sporadic breast carcinoma risk: A
meta-analysis. Med Princ Pract. 29:195–200. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
103
|
Morales-Sánchez A, Molina-Muñoz T,
Martínez-López JL, Hernández-Sancén P, Mantilla A, Leal YA, Torres
J and Fuentes-Pananá EM: No association between Epstein-Barr virus
and mouse mammary tumor virus with breast cancer in Mexican women.
Sci Rep. 3:29702013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
104
|
Palser AL, Grayson NE, White RE, Corton C,
Correia S, Ba Abdullah MM, Watson SJ, Cotton M, Arrand JR, Murray
PG, et al: Genome diversity of Epstein-Barr virus from multiple
tumor types and normal infection. J Virol. 89:5222–5237. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
105
|
Ba Abdullah MM, Palermo RD, Palser AL,
Grayson NE, Kellam P, Correia S, Szymula A and White RE:
Heterogeneity of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) major internal repeat
reveals evolutionary mechanisms of EBV and a functional defect in
the prototype EBV strain B95-8. J Virol. 91:e00920–17. 2017.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
106
|
Farrell PJ and White RE: Do Epstein-Barr
virus mutations and natural genome sequence variations contribute
to disease? Biomolecules. 12:172021. View Article : Google Scholar
|