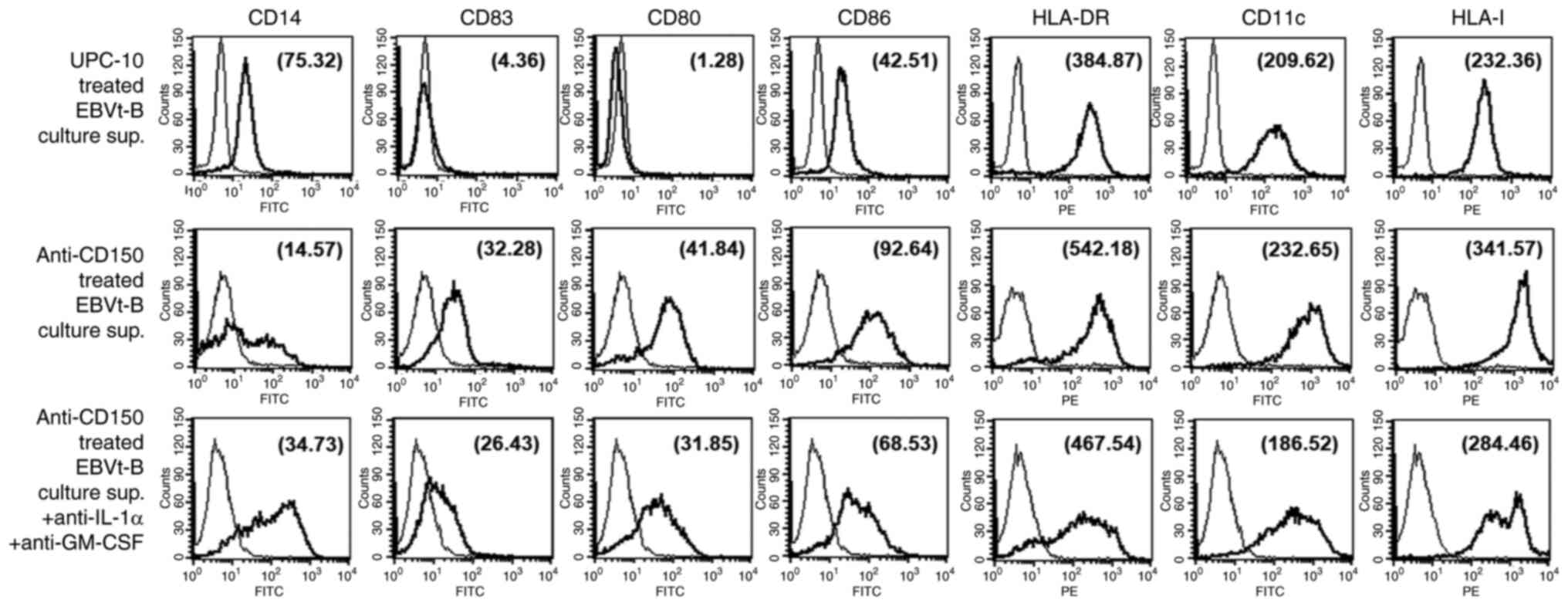
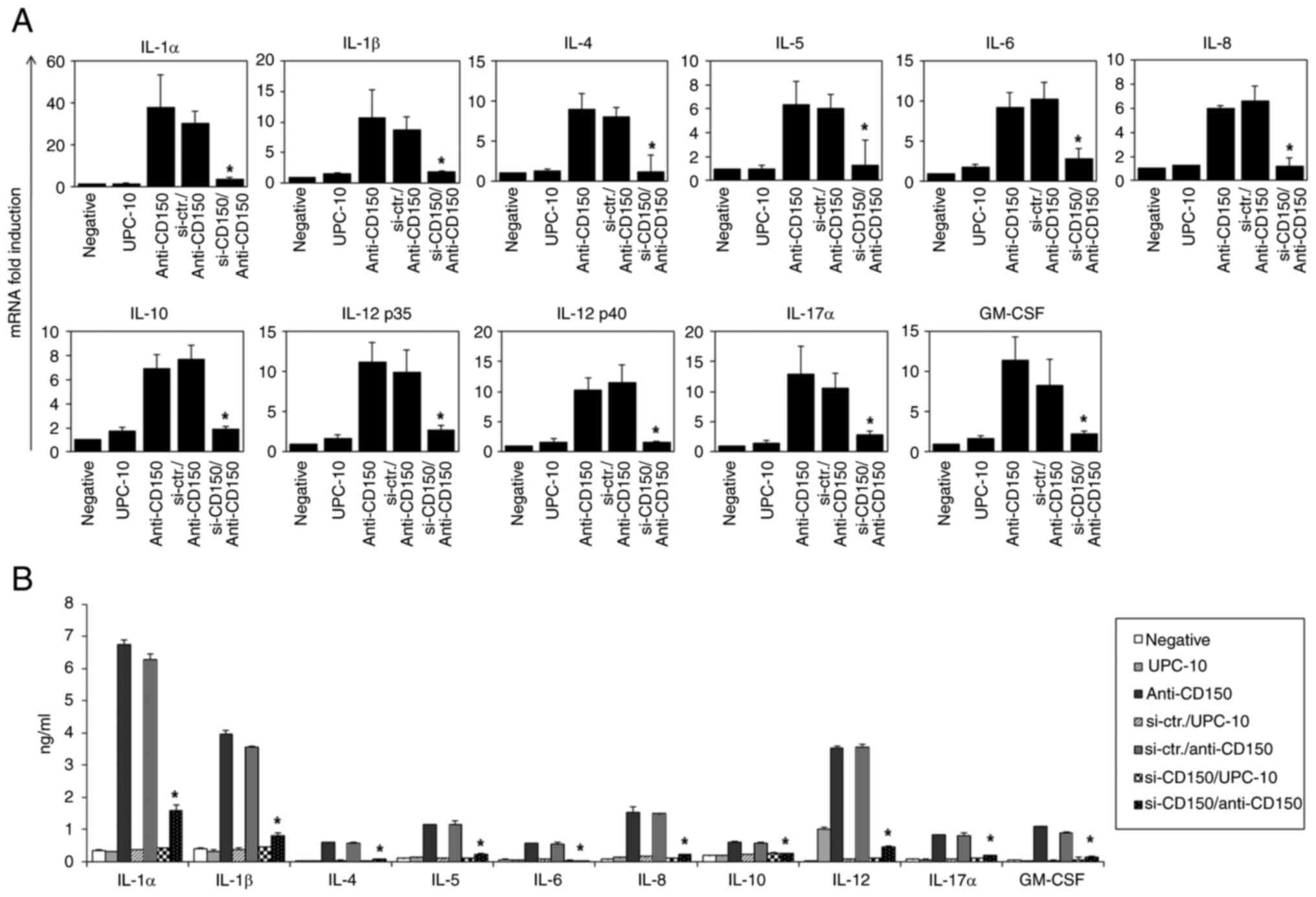
|
1
|
Cocks BG, Chang CC, Carballido JM, Yssel
H, de Vries JE and Aversa G: A novel receptor involved in T-cell
activation. Nature. 376:260–263. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Sidorenko SP and Clark EA: The
dual-function CD150 receptor subfamily: The viral attraction. Nat
Immunol. 4:19–24. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Farhangnia P, Ghomi SM, Mollazadehghomi S,
Nickho H, Akbarpour M and Delbandi AA: SLAM-family receptors come
of age as a potential molecular target in cancer immunotherapy.
Front Immunol. 14:11741382023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kis LL, Nagy N, Klein G and Klein E:
Expression of SH2D1A in five classical Hodgkin's disease-derived
cell lines. Int J Cancer. 104:658–661. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sayos J, Wu C, Morra M, Wang N, Zhang X,
Allen D, van Schaik S, Notarangelo L, Geha R, Roncarolo MG, et al:
The X-linked lymphoproliferative-disease gene product SAP regulates
signals induced through the co-receptor SLAM. Nature. 395:462–469.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Shcherbina V, Gordiienko I, Shlapatska L,
Gluzman D and Sidorenko S: CD150 and CD180 are negative regulators
of IL-10 expression and secretion in chronic lymphocytic leukemia B
cells. Neoplasma. 68:760–769. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Sidorenko SP and Clark EA:
Characterization of a cell surface glycoprotein IPO-3, expressed on
activated human B and T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 151:4614–4624.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Aversa G, Chang CC, Carballido JM, Cocks
BG and de Vries JE: Engagement of the signaling lymphocytic
activation molecule (SLAM) on activated T cells results in
IL-2-independent, cyclosporin A-sensitive T cell proliferation and
IFN-gamma production. J Immunol. 158:4036–4044. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Howie D, Okamoto S, Rietdijk S, Clarke K,
Wang N, Gullo C, Bruggeman JP, Manning S, Coyle AJ, Greenfield E,
et al: The role of SAP in murine CD150 (SLAM)-mediated T-cell
proliferation and interferon gamma production. Blood.
100:2899–2907. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Farina C, Theil D, Semlinger B, Hohlfeld R
and Meinl E: Distinct responses of monocytes to Toll-like receptor
ligands and inflammatory cytokines. Int Immunol. 16:799–809. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chapuis F, Rosenzwajg M, Yagello M, Ekman
M, Biberfeld P and Gluckman JC: Differentiation of human dendritic
cells from monocytes in vitro. Eur J Immunol. 27:431–441. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Randolph GJ, Beaulieu S, Lebecque S,
Steinman RM and Muller WA: Differentiation of monocytes into
dendritic cells in a model of transendothelial trafficking.
Science. 282:480–483. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tatsuo H, Ono N and Yanagi Y:
Morbilliviruses use signaling lymphocyte activation molecules
(CD150) as cellular receptors. J Virol. 75:5842–5850. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
de Swart RL, Ludlow M, de Witte L, Yanagi
Y, van Amerongen G, McQuaid S, Yüksel S, Geijtenbeek TB, Duprex WP
and Osterhaus AD: Predominant infection of CD150+ lymphocytes and
dendritic cells during measles virus infection of macaques. PLoS
Pathog. 3:e1782007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Amurri L, Reynard O, Gerlier D, Horvat B
and Iampietro M: Measles virus-induced host immunity and mechanisms
of viral evasion. Viruses. 14:26412022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hirsch RL, Griffin DE, Johnson RT, Cooper
SJ, Lindo de Soriano I, Roedenbeck S and Vaisberg A: Cellular
immune responses during complicated and uncomplicated measles virus
infections of man. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 31:1–12. 1984.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ward BJ, Johnson RT, Vaisberg A, Jauregui
E and Griffin DE: Cytokine production in vitro and the
lymphoproliferative defect of natural measles virus infection. Clin
Immunol Immunopathol. 61:236–248. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Allen CDC, Okada T and Cyster JG:
Germinal-center organization and cellular dynamics. Immunity.
27:190–202. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Garside P, Ingulli E, Merica RR, Johnson
JG, Noelle RJ and Jenkins MK: Visualization of specific B and T
lymphocyte interactions in the lymph node. Science. 281:96–99.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yin X, Chen S and Eisenbarth SC: Dendritic
cell regulation of T helper cells. Annu Rev Immunol. 39:759–790.
2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Crotty S, Kersh EN, Cannons J,
Schwartzberg PL and Ahmed R: SAP is required for generating
long-term humoral immunity. Nature. 421:282–287. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Park GB, Kim YS, Lee HK, Song H, Kim S,
Cho DH and Hur DY: Reactive oxygen species and p38 MAPK regulate
Bax translocation and calcium redistribution in salubrinal-induced
apoptosis of EBV-transformed B cells. Cancer Lett. 313:235–248.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
24
|
Ottaviani E, Malagoli D and Franchini A:
Invertebrate humoral factors: Cytokines as mediators of cell
survival. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 34:1–25. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hur DY, Park GB, Kim YS, Lee HK and Kim
DJ: Composition containing complex cytokines derived from
EBV-infected B cells for inducing the maturation of dendritic
cells. US Patent US9845456B2. Filed March 20, 2014; issued December
19, 2017.
|
|
26
|
Zou GM and Tam YK: Cytokines in the
generation and maturation of dendritic cells: Recent advances. Eur
Cytokine Netw. 13:186–199. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Fricke I, Mitchell D, Petersen F, Böhle A,
Bulfone-Paus S and Brandau S: Platelet factor 4 in conjunction with
IL-4 directs differentiation of human monocytes into specialized
antigen-presenting cells. FASEB J. 18:1588–1590. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Isomäki P, Aversa G, Cocks BG, Luukkainen
R, Saario R, Toivanen P, de Vries JE and Punnonen J: Increased
expression of signaling lymphocytic activation molecule in patients
with rheumatoid arthritis and its role in the regulation of
cytokine production in rheumatoid synovium. J Immunol.
159:2986–2993. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Minagawa H, Tanaka K, Ono N, Tatsuo H and
Yanagi Y: Induction of the measles virus receptor SLAM (CD150) on
monocytes. J Gen Virol. 82:2913–2917. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bleharski JR, Niazi KR, Sieling PA, Cheng
G and Modlin RL: Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule is
expressed on CD40 ligand-activated dendritic cells and directly
augments production of inflammatory cytokines. J Immunol.
167:3174–3181. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Tojjari A, Giles FJ, Vilbert M, Saeed A
and Cavalcante L: SLAM modification as an immune-modulatory
therapeutic approach in cancer. Cancers (Basel).
15:48082023.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mavaddat N, Mason DW, Atkinson PD, Evans
EJ, Gilbert RJ, Stuart DI, Fennelly JA, Barclay AN, Davis SJ and
Brown MH: Signaling lymphocytic activation molecule (CDw150) is
homophilic but self-associates with very low affinity. J Biol Chem.
275:28100–28109. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sidorenko SP, Vetrova EP, Yurchenko OV,
Berdova AG, Shlapatskaya LN and Gluzman DF: Monoclonal antibodies
of IPO series against B cell differentiation antigens in leukemia
and lymphoma immunophenotyping. Neoplasma. 39:3–9. 1992.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yurchenko MY, Kovalevska LM, Shlapatska
LM, Berdova GG, Clark EA and Sidorenko SP: CD150 regulates JNK1/2
activation in normal and Hodgkin's lymphoma B cells. Immunol Cell
Biol. 88:565–574. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Burdin N, Péronne C, Banchereau J and
Rousset F: Epstein-Barr virus transformation induces B lymphocytes
to produce human interleukin 10. J Exp Med. 177:295–304. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Tatsuo H, Ono N, Tanaka K and Yanagi Y:
SLAM (CDw150) is a cellular receptor for measles virus. Nature.
406:893–897. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Nédellec P, Dveksler GS, Daniels E,
Turbide C, Chow B, Basile AA, Holmes KV and Beauchemin N: Bgp2, a
new member of the carcinoembryonic antigen-related gene family,
encodes an alternative receptor for mouse hepatitis viruses. J
Virol. 68:4525–4537. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rowe JM and Rapoport AP: Hemopoietic
growth factors: A review. J Clin Pharmacol. 32:486–501. 1992.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Vellenga E, Young DC, Wagner K, Wiper D,
Ostapovicz D and Griffin JD: The effects of GM-CSF and G-CSF in
promoting growth of clonogenic cells in acute myeloblastic
leukemia. Blood. 69:1771–1776. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Gasson JC, Kaufman SE, Weisbart RH,
Tomonaga M and Golde DW: High-affinity binding of
granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor to normal and
leukemic human myeloid cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 83:669–673.
1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Dauer M, Obermaier B, Herten J, Haerle C,
Pohl K, Rothenfusser S, Schnurr M, Endres S and Eigler A: Mature
dendritic cells derived from human monocytes within 48 h: A novel
strategy for dendritic cell differentiation from blood precursors.
J Immunol. 170:4069–4076. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Hanazawa S, Hanaizumi C, Amano S, Hirose
K, Ohmori Y, Kumegawa M, Yamaura K and Kitano S: Inductive effect
of recombinant human interleukin-1 alpha and beta on
differentiation of macrophage-like tumor cell line P388D1. J Cell
Physiol. 136:543–546. 1988.PubMed/NCBI
|