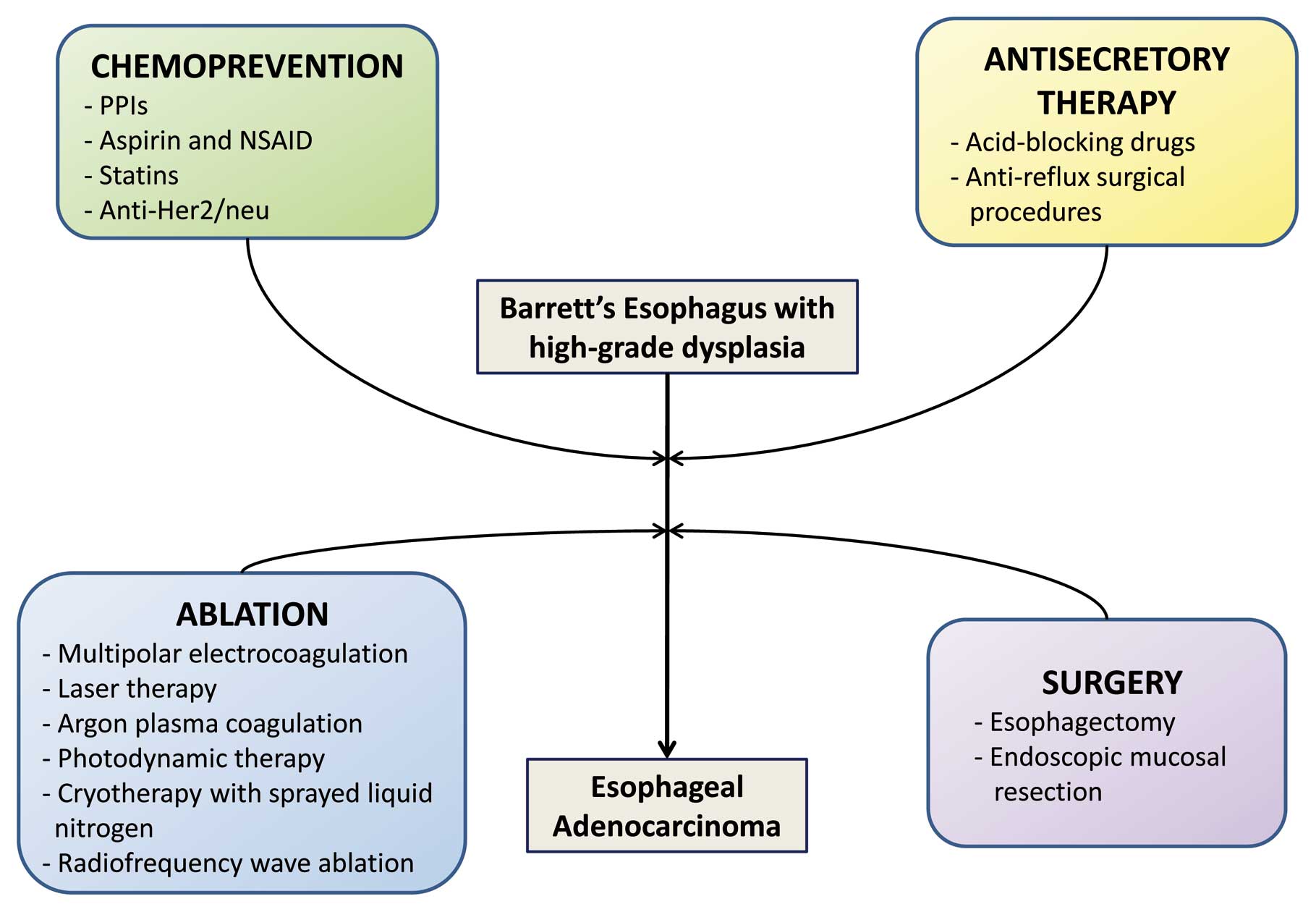
|
1
|
Enzinger P and Mayer R: Esophageal cancer.
N Engl J Med. 349:2241–2252. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ajani JA, Barthel JS, Bentrem DJ, et al:
Esophageal and esophago-gastric junction cancers. J Natl Compr Canc
Netw. 9:830–887. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Parkin DM: International variation.
Oncogene. 23:6329–6340. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Pohl H and Welch HG: The role of
overdiagnosis and reclassification in the marked increase of
esophageal adenocarcinoma incidence. J Natl Cancer Inst.
97:142–146. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sharma P: Clinical practice. Barrett’s
esophagus. N Engl J Med. 361:2548–2556. 2009.
|
|
7
|
Ronkainen J, Aro P, Storskrubb T, et al:
Prevalence of Barrett’s esophagus in the general population: an
endoscopic study. Gastroenterology. 129:1825–1831. 2005.
|
|
8
|
Zou D, He J, Ma X, et al: Helicobacter
pylori infection and gastritis: the systematic investigation of
gastrointestinal diseases in China (SILC). J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
26:908–915. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bhat S, Coleman HG, Yousef F, Johnston BT,
McManus DT, Gavin AT and Murray LJ: Risk of malignant progression
in Barrett’s esophagus patients: results from a large
population-based study. J Natl Cancer Inst. 103:1049–1057.
2011.
|
|
10
|
Hvid-Jensen F, Pedersen L, Drewes AM,
Sørensen HT and Funch-Jensen P: Incidence of adenocarcinoma among
patients with Barrett’s esophagus. N Engl J Med. 365:1375–1383.
2011.
|
|
11
|
Shaheen NJ and Richter JE: Barrett’s
esophagus. Lancet. 373:850–861. 2009.
|
|
12
|
Kahrilas PJ: The problems with
surveillance of Barrett’s esophagus. N Engl J Med. 365:1437–1438.
2011.
|
|
13
|
Garud SS, Keilin S, Cai Q and Willingham
FF: Diagnosis and management of Barrett’s esophagus for the
endoscopist. Ther Adv Gastroenterol. 3:227–238. 2010.
|
|
14
|
Dent J, El-Serag HB, Wallander MA and
Johansson S: Epidemiology of gastro-oesophageal reflux disease: a
systematic review. Gut. 54:710–717. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Whiteman DC, Parmar P, Fahey P, et al:
Association of Helicobacter pylori infection with reduced
risk for esophageal cancer is independent of environmental and
genetic modifiers. Gastroenterol. 139:73–83. 2010.
|
|
16
|
Barrett NR: Chronic peptic ulcer of the
oesophagus and ‘oesophagitis’. Br J Surg. 38:175–182. 1950.
|
|
17
|
Allison PR and Johnstone AS: The
oesophagus lined with gastric mucous membrane. Thorax. 8:87–101.
1953. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Naef AP, Savary M and Ozzello L:
Columnar-lined lower esophagus: an acquired lesion with malignant
predisposition. Report on 140 cases of Barrett’s esophagus with 12
adenocarcinomas. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 70:826–835.
1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hamilton SR and Aaltonen LA; World Health
Organization of Tumours Classification: Pathology and Genetics of
Tumours of the Digestive System. IARC Press; Lyon: 2000
|
|
20
|
Schlemper RJ, Riddell RH, Kato Y, et al:
The Vienna classification of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasia.
Gut. 47:251–255. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lagergren J: Influence of obesity on the
risk of esophageal disorders. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol.
8:340–347. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
McElholm AR, McKnight AJ, Patterson CC,
Johnston BT, Hardie LJ and Murray LJ: A population-based study of
IGF axis polymorphisms and the esophageal inflammation, metaplasia,
adenocarcinoma sequence. Gastroenterology. 139:204–212. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kendall BJ, Macdonald GA, Hayward NK, et
al: Leptin and the risk of Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut. 57:448–454.
2008.
|
|
24
|
Rubenstein JH, Kao JY, Madanick RD, et al:
Association of adiponectin multimers with Barrett’s oesophagus.
Gut. 58:1583–1589. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Fletcher J, Wirz A, Henry E and McKoll KE:
Studies of acid exposure immediately above the gastro-oesophageal
squamocolumnar junction: evidence of short segment reflux. Gut.
53:168–173. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Farrè R, De Vos R, Geboes K, et al:
Critical role of stress in increased oesophageal mucosa
permeability and dilated inter-cellular spaces. Gut. 56:1191–1197.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Jovov B, Van Itallie CM, Shaheen NJ,
Carson JL, Gambling TM, Anderson JM and Orlando RC: Claudin-18: a
dominant tight junction protein in Barrett’s esophagus and likely
contributor to its acid resistance. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver
Physiol. 293:1106–1113. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Clemons NJ, McColl KE and Fitzgerald RC:
Nitric oxide and acid induce double-strand DNA breaks in Barrett’s
esophagus carcinogenesis via distinct mechanisms. Gastroenterology.
133:1198–1209. 2007.
|
|
29
|
Dvorak K, Payne CM, Chavarria M, et al:
Bile acids in combination with low pH induce oxidative stress and
oxidative DNA damage: relevance to the pathogenesis of Barrett’s
oesophagus. Gut. 56:763–771. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Sun X, Elston R, Barnholtz-Sloan J, et al:
A segregation analysis of Barrett’s esophagus and associated
adenocarcinomas. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 19:666–674.
2010.
|
|
31
|
Chak A, Ochs-Balcom H, Falk G, et al:
Familiality in Barrett’s esophagus, adenocarcinoma of the
esophagus, and adenocarcinoma of the gastroesophageal junction.
Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 15:1668–1673. 2006.
|
|
32
|
Croagh D, Phillips WA, Redvers R, Thomas
RJ and Kaur P: Identification of candidate murine esophageal stem
cells using a combination of cell kinetic studies and cell surface
markers. Stem Cells. 25:313–318. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Croagh D, Thomas RJ, Phillips WA and Kaur
P: Esophageal stem cells - a review of their identification and
characterization. Stem Cell Rev. 4:261–268. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Leedham SJ, Preston SL, McDonald SA, et
al: Individual crypt genetic heterogeneity and the origin of
metaplastic glandular epithelium in human Barrett’s oesophagus.
Gut. 57:1041–1408. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sarosi G, Brown G, Jaiswal K, et al: Bone
marrow progenitor cells contribute to esophageal regeneration and
metaplasia in a rat model of Barrett’s esophagus. Dis Esophagus.
21:43–50. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Yu WY, Slack JM and Tosh D: Conversion of
columnar to stratified squamous epithelium in the developing mouse
oesophagus. Dev Biol. 284:157–170. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Kong J, Crissey MA, Funakoshi S, Kreindler
JL and Lynch JP: Ectopic Cdx2 expression in murine esophagus models
an intermediate stage in the emergence of Barrett’s esophagus. PloS
One. 6:e182802011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Kosinski C, Stange DE, Xu C, et al: Indian
hedgehog regulates intestinal stem cell fate through
epithelial-mesenchymal interactions during development.
Gastroenterology. 139:893–903. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Kazumori H, Ishihara S and Kinoshita Y:
Roles of caudal-related homeobox gene Cdx1 in oesophageal
epithelial cells in Barrett’s epithelium development. Gut.
58:620–628. 2009.
|
|
40
|
Phillips WA, Lord RV, Nancarrow DJ, Watson
DJ and Whiteman DC: Barrett’s esophagus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
26:639–648. 2011.
|
|
41
|
Colleypriest BJ, Farrant JM, Slack JM and
Tosh D: The role of Cdx2 in Barrett’s metaplasia. Biochem Soc
Trans. 38:364–369. 2010.
|
|
42
|
Mutoh H, Sakurai S, Satoh K, Osaka H,
Hakamata Y, Takeuchi T and Sugano K: Cdx1 induced intestinal
metaplasia in the transgenic mouse stomach: comparative study with
Cdx2 transgenic mice. Gut. 53:1416–1423. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Barros R, da Costa LT, Pinto-de-Sousa J,
Duluc I, Freund JN, David L and Almeida R: CDX2 autoregulation in
human intestinal metaplasia of the stomach: impact on the stability
of the phenotype. Gut. 60:290–298. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Huo X, Zhang HY, Zhang XI, et al: Acid and
bile salt-induced CDX2 expression differs in esophageal squamous
cells from patients with and without Barrett’s esophagus.
Gastroenterology. 139:194–203. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Chen X, Qin R, Liu B, Ma Y, et al:
Multilayered epithelium in a rat model and human Barrett’s
esophagus: similar expression patterns of transcription factors and
differentiation markers. BMC Gastroenterol. 8:1–9. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Badreddine RJ and Wang KK: Barrett
esophagus: an update. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:369–378.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Wang DH, Clemons NJ, Miyashita T, et al:
Aberrant epithelialmesenchymal Hedgehog signaling characterizes
Barrett’s metaplasia. Gastroenterology. 138:1810–1822.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Liu W, Hahn H, Odze RD and Goyal RK:
Metaplastic esophageal columnar epithelium without goblet cells
shows DNA content abnormalities similar to goblet cell-containing
epithelium. Am J Gastroenterol. 104:816–824. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
49
|
Chaves P, Crespo M, Ribeiro C, et al:
Chromosomal analysis of Barrett’s cells: demonstration of
instability and detection of the metaplastic lineage involved. Mod
Pathol. 20:788–796. 2007.
|
|
50
|
Li X, Galipeau PC, Sanchez CA, et al:
Single nucleotide polymorphism-based genome-wide chromosome copy
change, loss of heterozygosity, and aneuploidy in Barrett’s
esophagus neoplastic progression. Cancer Prev Res. 1:413–423.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wu IC, Zhao Y, Zhai R, et al: Association
between polymorphisms in cancer-related genes and early onset of
esophageal adenocarcinoma. Neoplasia. 13:386–392. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Galipeau PC, Li X, Blount PL, et al:
NSAIDs modulate CDKN2A, TP53, and DNA content risk for progression
to esophageal adenocarcinoma. PLoS Med. 4:e672007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Xing J, Ajani JA, Chen M, et al:
Constitutive short telomere length of chromosome 17p and 12q but
not 11q and 2p is associated with an increased risk for esophageal
cancer. Cancer Prev Res. 2:459–465. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Wang C, Yuan Y and Hunt RH:
Helicobacter pylori infection and Barrett’s esophagus: a
systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Gastroenterol.
104:492–500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
55
|
Anderson LA, Johnston BT, Watson RG, et
al: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the esophageal
inflammation-metaplasia-adenocarcinoma sequence. Cancer Res.
66:4975–4982. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Kubo A, Block G, Quesenberry CP, Buffler P
and Corley DA: Effects of dietary fiber, fats, and meat intakes on
the risk of Barrett’s esophagus. Nutr Cancer. 61:607–616.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
57
|
Kubo A, Levin TR, Block G, et al: Dietary
antioxidants, fruits, and vegetables and the risk of Barrett’s
esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 103:1614–1623. 2008.
|
|
58
|
Rossi E, Grisanti S, Villanacci V, et al:
HER-2 overexpression/amplification in Barrett’s oesophagus predicts
early transition from dysplasia to adenocarcinoma: a
clinico-pathologic study. J Cell Mol Med. 13:3826–3833. 2009.
|
|
59
|
Vakil N, van Zanten SV, Kahrilas P, Dent J
and Jones R: The Montreal definition and classification of
gastroesophageal reflux disease: a global evidence-based consensus.
Am J Gastroenterol. 101:1900–1920. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
60
|
Lundell LR, Dent J, Bennett JR, et al:
Endoscopic assessment of oesophagitis: clinical and functional
correlates and further validation of the Los Angeles
classification. Gut. 45:172–180. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
American Gastroenterological Association;
Spechler SJ, Sharma P, Souza RF, Inadomi JM and Shaheen NJ:
American Gastroenterological Association medical position statement
on the man agement of Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology.
140:1084–1091. 2011.
|
|
62
|
Voltaggio L, Montgomery EA and Lam-Himlin
D: A clinical and histopathologic focus on Barrett esophagus and
Barrett-related dysplasia. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 135:1249–1260.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Wang KK and Sampliner RE; Practice
Parameters Committee of the American College of Gastroenterology:
Updated guidelines 2008 for the diagnosis, surveillance and therapy
of Barrett’s esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 103:788–797.
2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
64
|
Playford RJ: New British Society of
Gastroenterology (BSG) guidelines for the diagnosis and management
of Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut. 55:4422006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
65
|
Sikkema M, Looman CWN, Steyerberg EW, et
al: Predictors for neoplastic progression in patients with
Barrett’s esophagus: a prospective cohort study. Am J
Gastroenterol. 106:1231–1238. 2011.
|
|
66
|
Sharma P, Dent J, Armstrong D, et al: The
development and validation of an endoscopic grading system for
Barrett’s esophagus: the Prague C & M Criteria.
Gastroenterology. 131:1392–1399. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
67
|
Wani S, Mathur S and Sharma P: How to
manage a Barrett’s esophagus patient with low-grade dysplasia. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:27–32. 2009.
|
|
68
|
Mannath J, Subramanian V, Hawkey CJ and
Raqunath K: Narrow band imaging for characterization of high grade
dysplasia and specialized intestinal metaplasia in Barrett’s
esophagus: a meta-analysis. Endoscopy. 42:351–359. 2010.
|
|
69
|
Wasielica-Berger J, Baniukiewicz A,
Wroblewski E, Chwiesko A and Dabrowski A: Magnification endoscopy
and chromoendoscopy in evaluation of specialized intestinal
metaplasia in Barrett’s esophagus. Dig Dis Sci. 56:1987–1995.
2011.
|
|
70
|
Prasad GA, Wu TT, Wigle DA, et al:
Endoscopic and surgical treatment of mucosal (T1a) esophageal
adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s esophagus. Gastroenterology.
137:815–823. 2009.
|
|
71
|
Yachimski P, Nishioka NS, Richards E and
Hur C: Treatment of Barrett’s esophagus with high-grade dysplasia
or cancer: predictor of surgical versus endoscopic therapy. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:1206–1211. 2008.
|
|
72
|
Fleischer DE, Overholt BF, Sharma P, et
al: Endoscopic ablation of Barrett’s esophagus: a multicenter study
with 2.5-year follow-up. Gastrointest Endosc. 68:867–876. 2008.
|
|
73
|
Pech O, Behrens A, May A, et al: Long-term
results and risk factor analysis for recurrence after curative
endoscopic therapy in 349 patients with high-grade intraepithelial
neoplasia and mucosal adenocarcinoma in Barrett’s oesophagus. Gut.
57:1200–1206. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
74
|
Gaddam S and Sharma P: Advances in
endoscopic diagnosis and treatment of Barrett’s esophagus. J Dig
Dis. 11:323–333. 2010.
|
|
75
|
Nealis TB, Washington K and Keswani RN:
Endoscopic therapy of esophageal premalignancy and early
malignancy. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw. 9:890–899. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
76
|
Yachimski P, Puricelli WP and Nishioka NS:
Patient predictors of esophageal stricture development after
photodynamic therapy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 6:302–308. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
77
|
Ulsiewicz WJ and Shaheen NJ: The role of
radiofrequency ablation in the management of Barrett’s esophagus.
Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 21:95–109. 2011.
|
|
78
|
Shaheen NJ, Overholt BF, Sampliner RE, et
al: Durability of radiofrequency ablation in Barrett’s esophagus
with dysplasia. Gastroenterology. 141:460–468. 2011.
|
|
79
|
Shaheen NJ, Sharma P, Overholt BF, et al:
Radiofrequency ablation in Barrett’s esophagus with dysplasia. N
Engl J Med. 360:2277–2288. 2009.
|
|
80
|
Dent J: Barrett’s esophagus: A historical
perspective, an update on core practicalities and predictions on
future evolutions of management. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 26:11–30.
2011.
|
|
81
|
El-Serag HB, Aguirre TV, Davis S, Kuebeler
M, Bhattacharyya A and Sampliner RE: Proton pump inhibitors are
associated with reduced incidence of dysplasia in Barrett’s
esophagus. Am J Gastroenterol. 99:1877–1883. 2004.
|
|
82
|
Nguyen DM, El-Serag HB, Henderson L, Stein
D, Bhattacharyya A and Sampliner RE: Medication usage and the risk
of neoplasia in patients with Barrett’s esophagus. Clin
Gastroenterol Hepatol. 7:1299–1304. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
83
|
Jankowski JA and Hooper PA:
Chemoprevention in Barrett’s esophagus: A pill a day? Gastrointest
Endosc Clin N Am. 21:155–170. 2011.
|
|
84
|
Neumann H, Mönkemüller K, Vieth M and
Malfertheiner P: Chemoprevention of adenocarcinoma associated with
Barrett’s esophagus: potential options. Dig Dis. 27:18–23.
2009.
|
|
85
|
Heath EI, Canto MI, Piantadosi S, et al:
Secondary chemo-prevention of Barrett’s esophagus with celecoxib:
results of a randomized trial. J Natl Cancer Inst. 99:545–557.
2007.
|
|
86
|
Das D, Chilton AP and Jankowski JA:
Chemoprevention of oesophageal cancer and the AspECT trial. Recent
Results Cancer Res. 181:161–169. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
87
|
Ong CA, Lao-Sirieix P and Fitzgerald RC:
Biomarkers in Barrett’s esophagus and esophageal adenocarcinoma:
Predictors of progression and prognosis. World J Gastroenterol.
16:5669–5681. 2010.
|