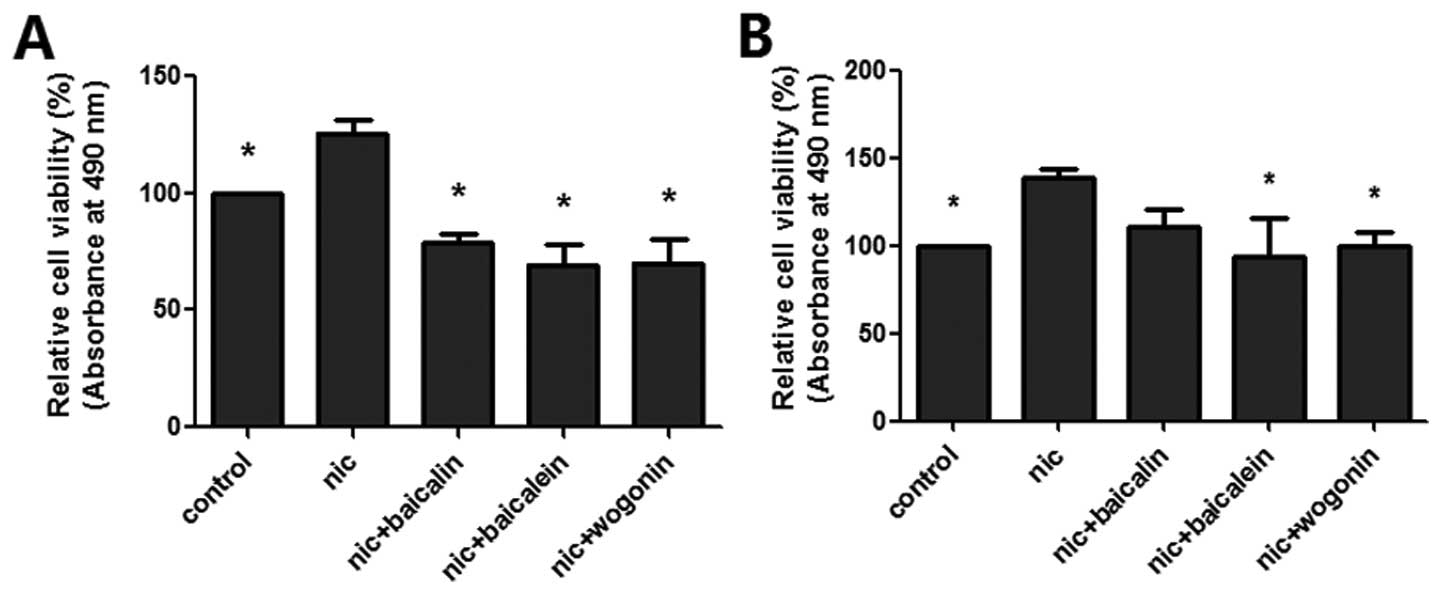
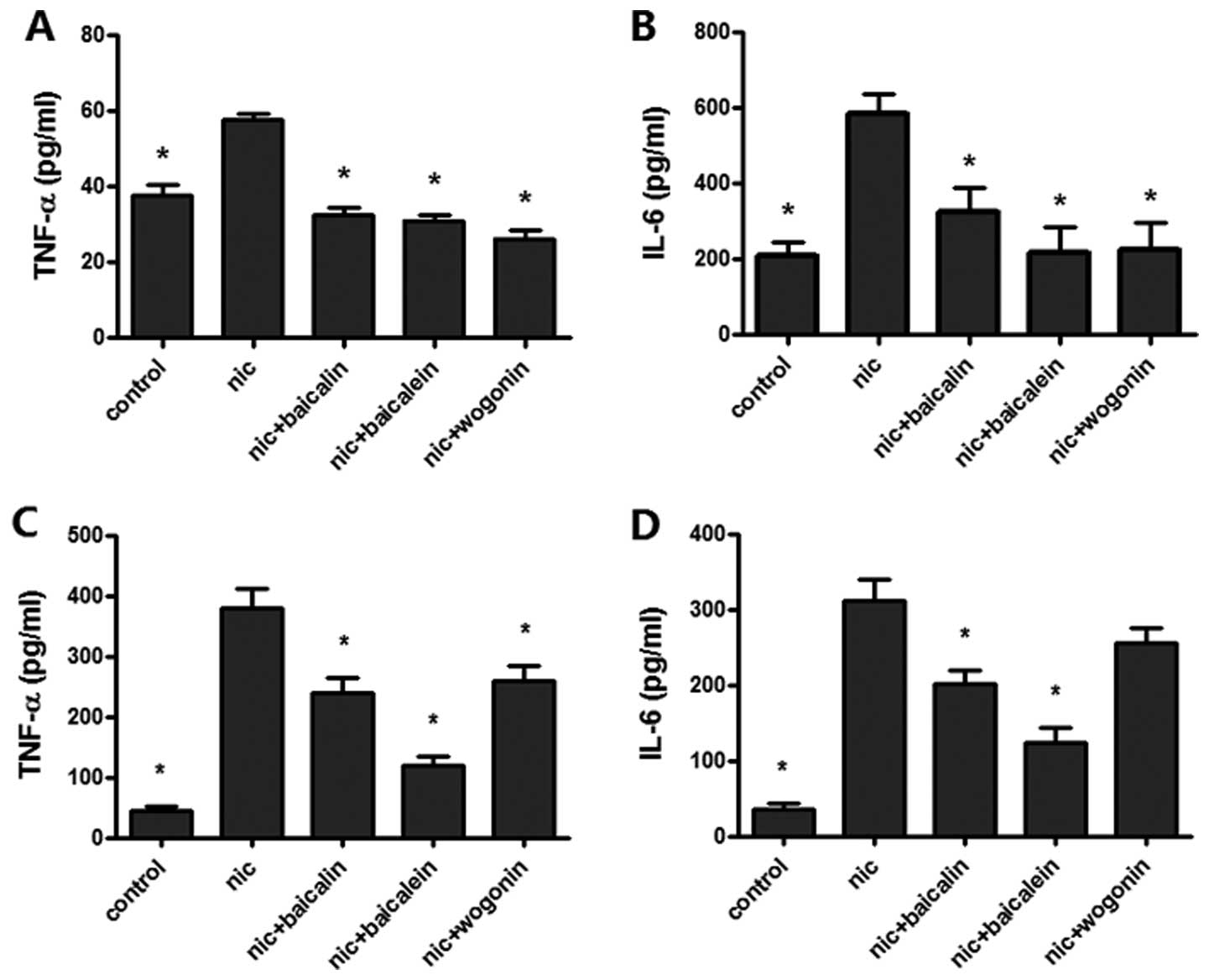
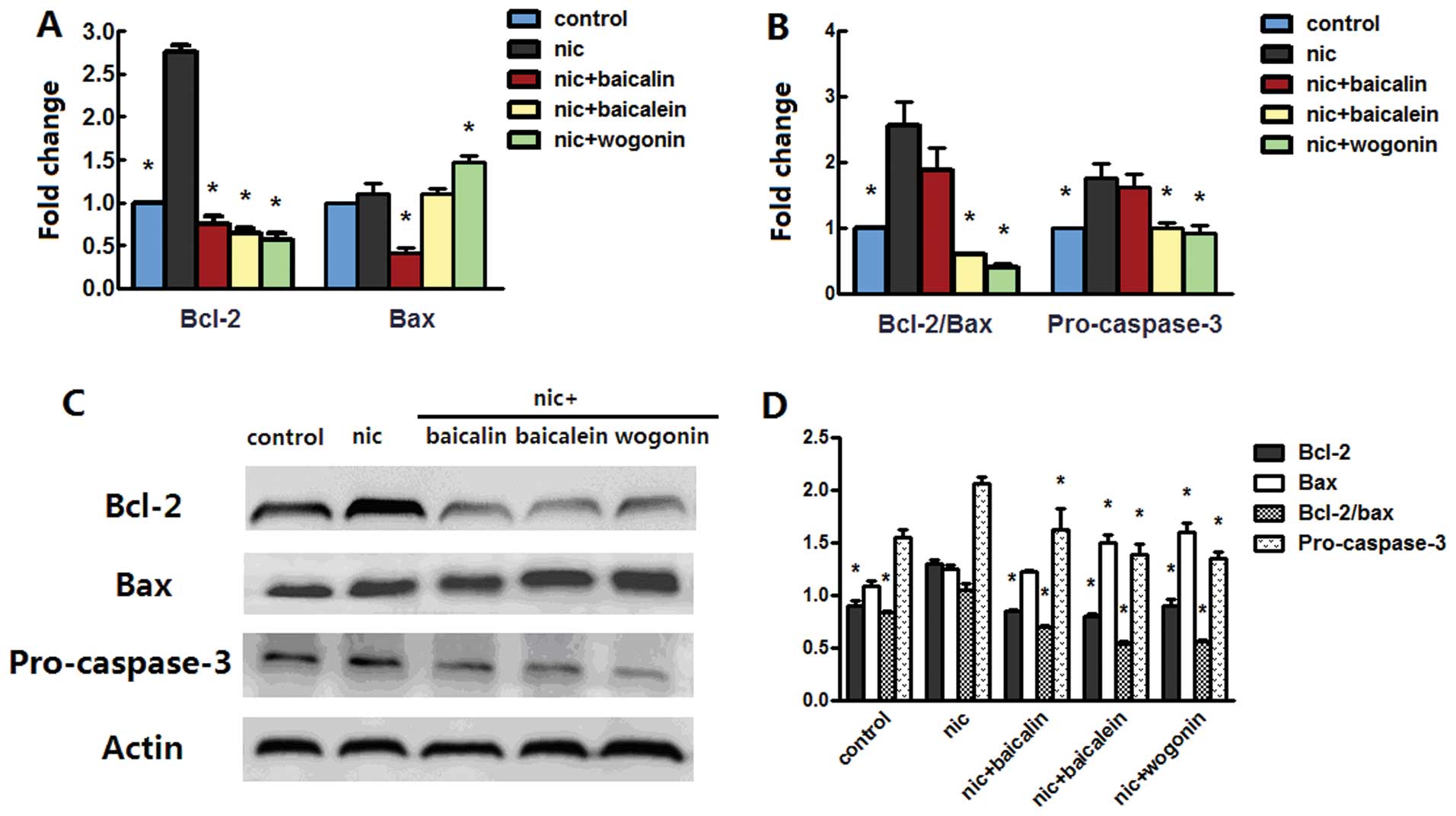
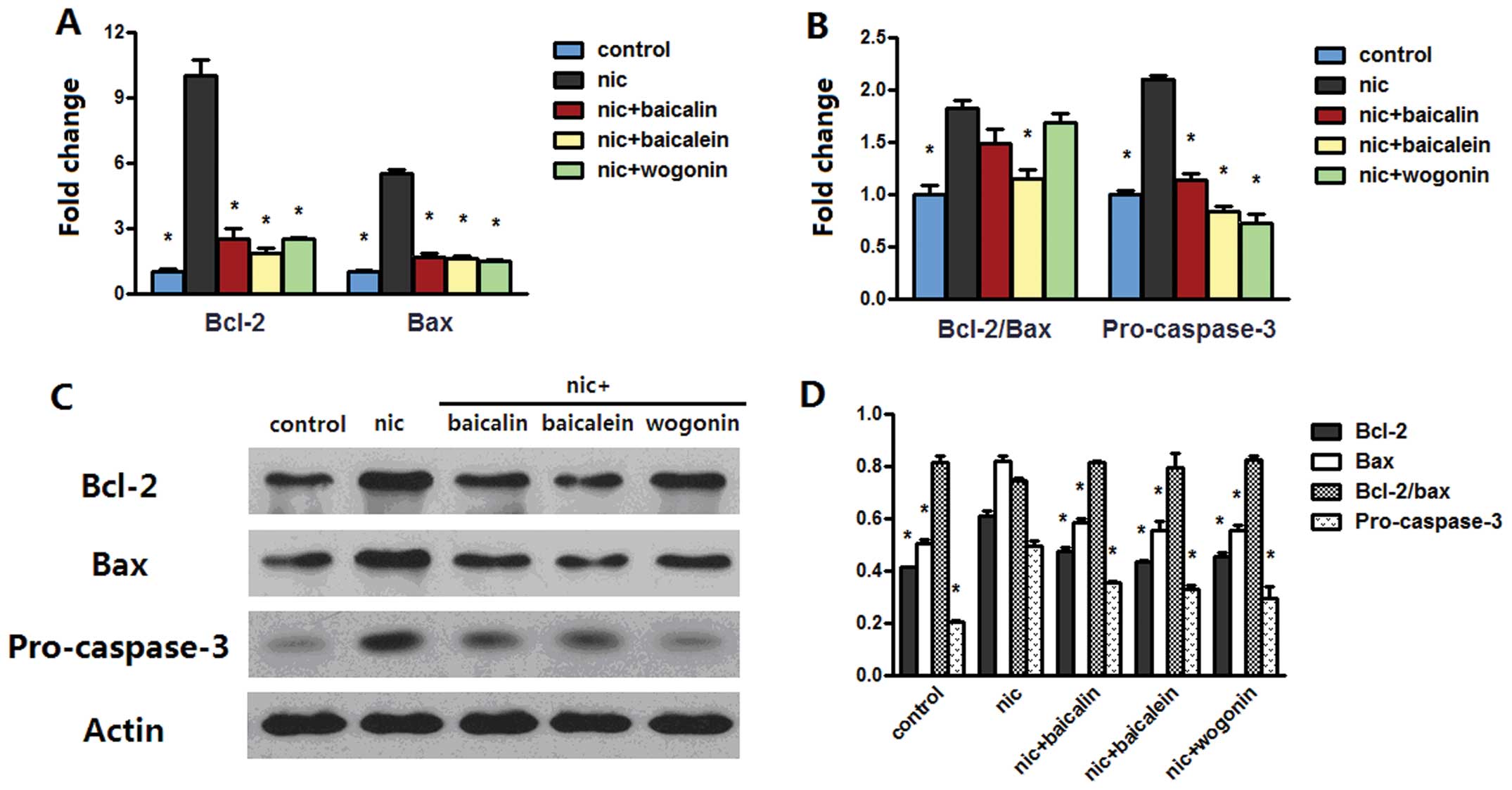
|
1.
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2.
|
Chen W, Zhang S and Zou X: Estimation and
projection of lung cancer incidence and mortality in China.
Zhongguo Fei Ai Za Zhi. 13:488–493. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
3.
|
Hecht SS: Cigarette smoking and lung
cancer: chemical mechanisms and approaches to prevention. Lancet
Oncol. 3:461–469. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4.
|
Zhang J, Ou JX and Bai CX: Tobacco smoking
in China: prevalence, disease burden, challenges and future
strategies. Respirology. 16:1165–1172. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5.
|
Egleton RD, Brown KC and Dasgupta P:
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors in cancer: multiple roles in
proliferation and inhibition of apoptosis. Trends Pharmacol Sci.
29:151–158. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6.
|
Thunnissen FB: Acetylcholine receptor
pathway and lung cancer. J Thorac Oncol. 4:943–946. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7.
|
Maneckjee R and Minna JD: Opioid and
nicotine receptors affect growth regulation of human lung cancer
cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 87:3294–3298. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8.
|
Tournier JM and Birembaut P: Nicotinic
acetylcholine receptors and predisposition to lung cancer. Curr
Opin Oncol. 23:83–87. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9.
|
Lam DC, Girard L, Ramirez R, et al:
Expression of nicotinic acetylcholine receptor subunit genes in
non-small-cell lung cancer reveals differences between smokers and
nonsmokers. Cancer Res. 67:4638–4647. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10.
|
Kelly PN and Strasser A: The role of Bcl-2
and its pro-survival relatives in tumourigenesis and cancer
therapy. Cell Death Differ. 18:1414–1424. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11.
|
Leber B, Geng F, Kale J and Andrews DW:
Drugs targeting Bcl-2 family members as an emerging strategy in
cancer. Expert Rev Mol Med. 12:e282010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12.
|
Xin M and Deng X: Nicotine inactivation of
the proapoptotic function of Bax through phosphorylation. J Biol
Chem. 280:10781–10789. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13.
|
Dasgupta P, Rizwani W, Pillai S, et al:
Nicotine induces cell proliferation, invasion and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in a variety of human cancer cell
lines. Int J Cancer. 124:36–45. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14.
|
Davis R, Rizwani W, Banerjee S, et al:
Nicotine promotes tumor growth and metastasis in mouse models of
lung cancer. PLoS One. 4:e75242009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15.
|
Nelson AR, Fingleton B, Rothenberg ML and
Matrisian LM: Matrix metalloproteinases: biologic activity and
clinical implications. J Clin Oncol. 18:1135–1149. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16.
|
Bayramoglu A, Gunes HV, Metintas M,
Degirmenci I, Mutlu F and Alatas F: The association of MMP-9 enzyme
activity, MMP-9 C1562T polymorphism, and MMP-2 and -9 and TIMP-1,
-2, -3, and -4 gene expression in lung cancer. Genet Test Mol
Biomarkers. 13:671–678. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17.
|
Herbst RS, Yano S, Kuniyasu H, et al:
Differential expression of E-cadherin and type IV collagenase genes
predicts outcome in patients with stage I non-small cell lung
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 6:790–797. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18.
|
Klein G, Vellenga E, Fraaije MW, Kamps WA
and de Bont ES: The possible role of matrix metalloproteinase
(MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in cancer, e.g. acute leukemia. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 50:87–100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19.
|
Zong Y, Zhang ST and Zhu ST: Nicotine
enhances migration and invasion of human esophageal squamous
carcinoma cells which is inhibited by nimesulide. World J
Gastroenterol. 15:2500–2505. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20.
|
Lee HZ, Leung HW, Lai MY and Wu CH:
Baicalein induced cell cycle arrest and apoptosis in human lung
squamous carcinoma CH27 cells. Anticancer Res. 25:959–964.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21.
|
Leung HW, Yang WH, Lai MY, Lin CJ and Lee
HZ: Inhibition of 12-lipoxygenase during baicalein-induced human
lung nonsmall carcinoma H460 cell apoptosis. Food Chem Toxicol.
45:403–411. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22.
|
Du G, Han G, Zhang S, et al: Baicalin
suppresses lung carcinoma and lung metastasis by SOD mimic and
HIF-1alpha inhibition. Eur J Pharmacol. 630:121–130. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23.
|
Li-Weber M: New therapeutic aspects of
flavones: the anti-cancer properties of Scutellaria and its main
active constituents Wogonin, Baicalein and Baicalin. Cancer Treat
Rev. 35:57–68. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24.
|
Lixuan Z, Jingcheng D, Wenqin Y, Jianhua
H, Baojun L and Xiaotao F: Baicalin attenuates inflammation by
inhibiting NF-kappaB activation in cigarette smoke induced
inflammatory models. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 23:411–419. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25.
|
Li L, Bao H, Wu J, et al: Baicalin is
anti-inflammatory in cigarette smoke-induced inflammatory models in
vivo and in vitro: a possible role for HDAC2 activity. Int
Immunopharmacol. 13:15–22. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26.
|
Petty TL: Are COPD and lung cancer two
manifestations of the same disease? Chest. 128:1895–1897. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27.
|
Yang IA, Relan V, Wright CM, et al: Common
pathogenic mechanisms and pathways in the development of COPD and
lung cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 15:439–456. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28.
|
Takahashi H, Ogata H, Nishigaki R, Broide
DH and Karin M: Tobacco smoke promotes lung tumorigenesis by
triggering IKKbeta- and JNK1-dependent inflammation. Cancer Cell.
17:89–97. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29.
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
30.
|
Karunagaran D, Joseph J and Kumar TR: Cell
growth regulation. Adv Exp Med Biol. 595:245–268. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31.
|
Fennell DA: Caspase regulation in
non-small cell lung cancer and its potential for therapeutic
exploitation. Clin Cancer Res. 11:2097–2105. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32.
|
Steeg PS: Tumor metastasis: mechanistic
insights and clinical challenges. Nat Med. 12:895–904. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33.
|
Chandrashekar N, Selvamani A, Subramanian
R, Pandi A and Thiruvengadam D: Baicalein inhibits pulmonary
carcinogenesis-associated inflammation and interferes with COX-2,
MMP-2 and MMP-9 expressions in-vivo. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
261:10–21. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34.
|
Tauler J and Mulshine JL: Lung cancer and
inflammation: interaction of chemokines and hnRNPs. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 9:384–388. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35.
|
Puliyappadamba VT, Cheriyan VT,
Thulasidasan AK, et al: Nicotine-induced survival signaling in lung
cancer cells is dependent on their p53 status while its
downregulation by curcumin is independent. Mol Cancer. 9:2202010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|