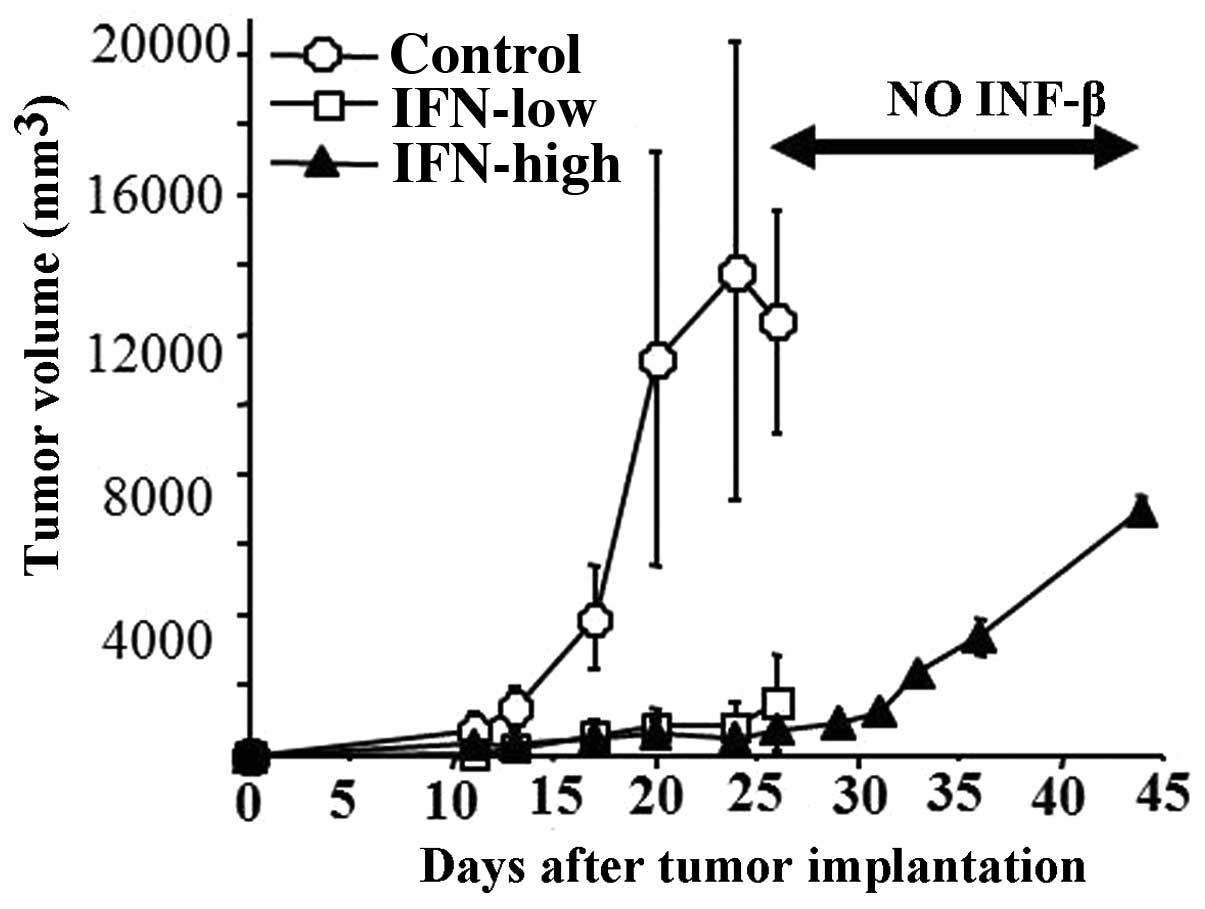
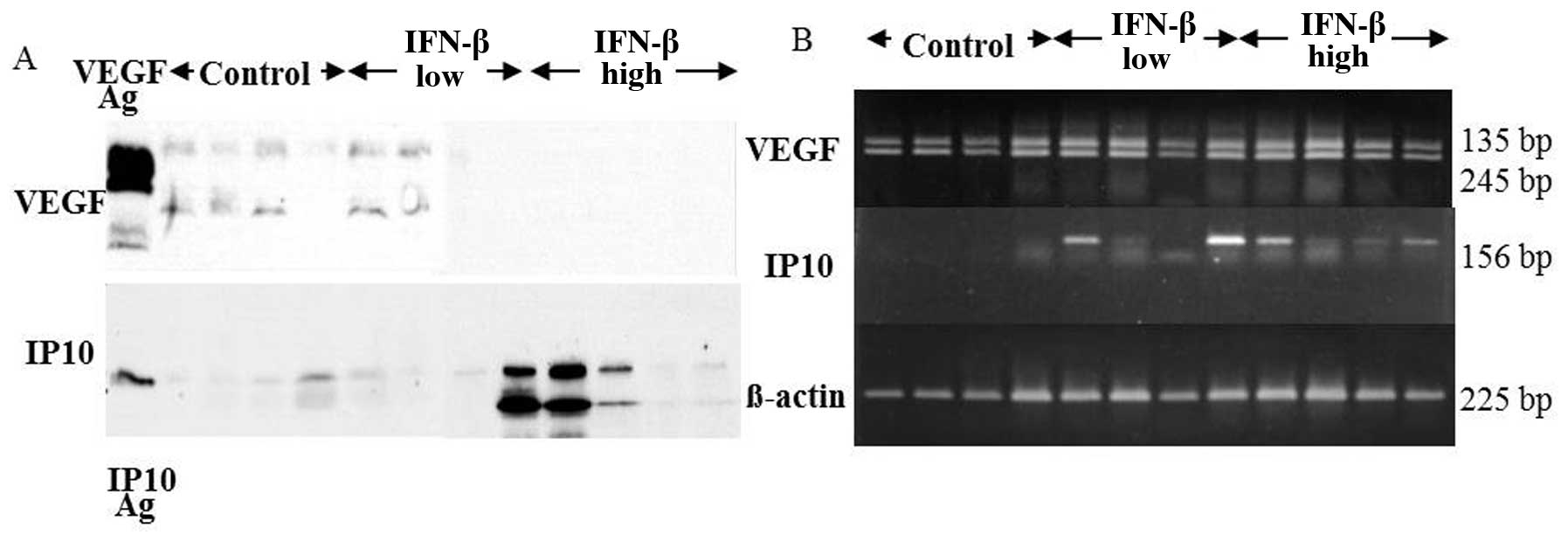
|
1
|
Fine HA, Wen PY, Robertson M, O’Neill A,
Kowal J, Loeffler JS and Black PML: A phase I trial of a new
recombinant human β-interferon (BG9015) for the treatment of
patients with recurrent gliomas. Clin Cancer Res. 3:381–387.
1997.
|
|
2
|
Natsume A, Ishii D, Wakabayashi T, Tsuno
T, Hatano H, Mizuno M and Yoshida J: IFN-beta down-regulates the
expression of DNA repair gene MGMT and sensitizes resistant glioma
cells to temozolomide. Cancer Res. 65:7573–7579. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yoshino A, Ogino A, Yachi K, Ohta T,
Fukushima T, Watanabe T, Katayama Y, Okamoto Y, Naruse N and Sano
E: Effect of IFN-beta on human glioma cell lines with temozolomide
resistance. Int J Oncol. 35:139–148. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Wakabayashi T, Kayama T, Nishikawa R,
Takahashi H, Hashimoto N, Takahashi J, Aoki T, Sugiyama K, Ogura M,
Natsume A and Yoshida J: A multicenter phase I trial of combination
therapy with interferon-beta and temozolomide for high-grade
gliomas (INTEGRA study): the final report. J Neurooncol.
104:573–577. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Colman H, Berkey BA, Maor MH, Groves MD,
Schultz CJ, Vermeulen S, Nelson DF, Mehta MP and Yung WK; Radiation
Therapy Oncology Group. Phase II Radiation Therapy Oncology Group
trial of conventional radiation therapy followed by treatment with
recombinant interferon-beta for supratentorial glioblastoma:
results of RTOG 9710. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 66:818–824.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Motomura K, Natsume A, Kishida Y, Higashi
H, Kondo Y, Nakasu Y, Abe T, Namb H, Wakai K and Wakabayashi T:
Benefits of interferon-beta and temozolomide combination therapy
for newly diagnosed primary glioblastoma with the unmethylated MGMT
promoter: a multicenter study. Cancer. 117:1721–1730. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brem S, Cotran R and Folkman J: Tumor
angiogenesis: a quantitative method for histologic grading. J Natl
Cancer Inst. 48:347–356. 1972.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Norden AD, Drappatz J and Wen PY: Novel
anti-angiogenic therapies for malignant gliomas. Lancet Neurol.
7:1152–1160. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nagane M, Nishikawa R, Narita Y, Kobayashi
H, Takano S, Shinoura N, Aoki T, Sugiyama K, Kuratsu J, Muragaki Y,
Sawamura Y and Matsutani M: Phase II study of single-agent
bevacizumab in Japanese patients with recurrent malignant glioma.
Jpn J Clin Oncol. 42:887–895. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chinot OL, Wick W, Mason W, Henriksson R,
Saran F, Nishikawa R, Carpentier AF, Hoang-Xuan K, Kavan P, Cernea
D, Brandes AA, Hilton M, Abrey L and Cloughesy T: Bevacizumab plus
radiotherapy-temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma. N Engl
J Med. 370:709–722. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Singh RK, Gutman M, Bucana CD, Sanchez R,
Llansa N and Fidler IJ: Interferons α and β down-regulate the
expression of basic fibroblast growth factor in human carcinomas.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 92:4562–4566. 1995.
|
|
12
|
Dinney CPN, Bieleberg DR, Perrotte P,
Reich R, Eve BY, Bucana CD and Fidler IJ: Inhibition of basic
fibroblast growth factor expression, angiogenesis, and growth of
human bladder carcinoma in mice by systemic interferon-α
administration. Cancer Res. 58:808–814. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Gohji K, Fidler IJ, Tsan R, Radinsky R,
von Eschenbach AC, Tsuruo T and Nakajima M: Human recombinant
interferon-beta and -gamma decrease gelatinase production and
invasion by human KG-2 renal-carcinoma cells. Int J Cancer.
58:380–384. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Takano S, Gately S, Neville ME, Herblin
WF, Gross JL, Engelhard H, Perricone M, Eidsvoog K and Brem S:
Suramin, an anticancer and angiosuppressive agent, inhibits
endothelial cell binding of basic fibroblast growth factor,
migration, proliferation, and induction of urokinase-type
plasminogen activator. Cancer Res. 54:2654–2660. 1994.
|
|
15
|
Takano S, Tsuboi K, Matsumura A, Tomono Y,
Mistui Y and Nose T: Expression of the angiogenic factor thymidine
phosphorylase in human astrocytic tumors. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
126:145–152. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Boorsma DM, de Haan P, Willemze R and
Stoof TJ: Human growth factor (huGRO), interleukin-8 (IL-8) and
interferon-gamma-inducible protein (gamma-IP-10) gene expression in
cultured normal human keratinocytes. Arch Dermatol Res.
286:471–475. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Takano S, Yoshii Y, Kondo S, Maruno T,
Shirai S and Nose T: Concentration of vascular endothelial growth
factor in the serum and tumor tissue of brain tumor patients.
Cancer Res. 56:2185–2190. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Suzuki T, Yanagi K, Ookawa K, Hatakeyama K
and Ohshima N: Flow visualization of microcirculation in solid
tumor tissues: intravital microscopic observation of blood
circulation by use of a confocal laser microscope. Front Med Biol
Eng. 7:253–263. 1996.
|
|
19
|
Foltz RM, McLendon RE, Friedman HS, Dodge
RK, Bigner DD and Dewhirst MW: A pial window model for the
intracranial study of human glioma microvascular function.
Neurosurgery. 36:976–984. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ezekowitz RAB, Mulliken JB and Folkman J:
Interferon alfa 2a therapy for life-threatening hemangiomas in
infancy. N Engl J Med. 324:1456–1463. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Orchard PJ, Smith CM, Woods WG, Day DL,
Dehner LP and Shapiro R: Treatment of haemangio endotheliomas with
alpha interferon. Lancet. 2:565–567. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kirn DH and Kramer A: Long-term function
from disease progression with interferon alfa therapy in two
patients with malignant hemangiopericytoma. J Natl Cancer Inst.
88:764–765. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Real FX, Qettgen HF and Kroun SE: Kaposi’s
sarcoma and the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome: treatment with
high and low doses of recombinant leukocyte α interferon. J Clin
Oncol. 4:544–551. 1986.
|
|
24
|
Stout AJ, Gresser I and Thompson WD:
Inhibition of wound healing in mice by local interferon-β
injection. Int J Exp Pathol. 74:79–85. 1993.
|
|
25
|
Oliveira IC, Sciavolino PJ, Lee TH and
Vilcek J: Downregulation of interleukin 8 gene expression in human
fibroblasts: unique mechanism of transcriptional inhibition by
interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 89:9049–9053. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Boethius J, Blomgren H, Collins VP, Greitz
T and Strander H: The effect of human interferon-α administration
to patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Acta Neurochir.
68:239–251. 1983.
|
|
27
|
Rozera C, Carlei D, Lollini PL, De
Giovanni C, Musiani P, Di Carlo E, Belardelli F and Ferrantini M:
Interferon (IFN)-β gene transfer into TS/A adenocarcinoma cells and
comparison with IFN-α. Am J Pathol. 154:1211–1222. 1999.
|
|
28
|
Hong YK, Chung DS, Joe YA, Yang YJ, Kim
KM, Park YS, Yung WKA and Kang JK: Efficient inhibition of in vivo
human malignant glioma growth and angiogenesis by interferon-β
treatment at early stage of tumor development. Clin Cancer Res.
6:3354–3360. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zheng H, Qian J, Carbone CJ, Leu NA, Baker
DP and Fuchs SY: Vascular endothelial growth factor-induced
elimination of the type 1 interferon receptor is required for
efficient angiogenesis. Blood. 118:4003–4006. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xiao HB, Zhou WY, Chen XF, Mei J, Lv ZW,
Ding FB, Li GQ, Zhong H and Bao CR: Interferon-β efficiently
inhibited endothelial progenitor cell-induced tumor angiogenesis.
Gene Ther. 19:1030–1034. 2012.
|
|
31
|
Björndahl M, Cao R, Eriksson A and Cao Y:
Blockage of VEGF-induced angiogenesis by preventing VEGF secretion.
Circ Res. 94:1443–1450. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Von Marschall A, Scholz A, Cramer T,
Schafer G, Schirner M, Oberg K, Wiedenmann B, Hocker M and Rosewicz
S: Effects of interferon alpha on vascular endothelial growth
factor gene transcription and tumor angiogenesis. J Natl Cancer
Inst. 95:421–437. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bedogni B, O’Neill MS, Welford SM, Bouley
DM, Giaccia AJ, Denko NC and Powell MB: Topical treatment with
inhibitors of the phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase/Akt and
Raf/mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase/extracellular
signal-regulated kinase pathways reduces melanoma development in
severe combined immunodeficient mice. Cancer Res. 64:2552–2560.
2004.
|
|
34
|
Raig ET, Jones NB, Varker KA, Benniger K,
Go MR, Biber JL, Lesinski GB and Carson WE III: VEGF secretion is
inhibited by interferon-alpha in several melanoma cell lines. J
Interferon Cytokine Res. 28:553–561. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Yoshino A, Tashiro S, Ogino A, Yachi K,
Ohta T, Fukushima T, Watanabe T, Katayama Y, Okamoto Y, Sano E and
Tsumoto K: Gene expression profiles predicting the response to
IFN-β and a combination of temozolomide and IFN-β in malignant
gliomas. Int J Oncol. 39:529–542. 2011.
|
|
36
|
Keane MP, Arenberg DA, Moore BB, Addison
CL and Strieter RM: CXC chemokines and angiogenesis/angiostasis.
Proc Assoc Am Physicians. 110:288–296. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Arenberg DA, Kunkel SL, Polverini PJ,
Morris SB, Burdick MD, Glass MC, Taub DT, Iamettoni MD, Whyte RI
and Strieter RM: Interferon-γ-inducible protein 10 (IP-10) is an
angiostatic factor that inhibits human non-small cell lung cancer
(NSCLC) tumorigenesis and spontaneous metastases. J Exp Med.
184:981–982. 1996.
|
|
38
|
Sato E, Fujimoto J and Tamaya T:
Expression of interferon-gamma-inducible protein 10 related to
angiogenesis in uterine endometrial cancers. Oncology. 73:246–251.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu M, Guo S and Stiles JK: The emerging
role of CXCL10 in cancer (Review). Oncol Lett. 2:583–589.
2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Yuan F, Salehi HA, Boucher Y, Vasthrae US,
Tuma RF and Jain RK: Vascular permeability and microcirculation of
gliomas and mammary carcinomas transplanted in rat and mouse
cranial windows. Cancer Res. 54:4564–4568. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Fatterpekar GM, Galheigo D, Narayana A,
Johnson G and Knopp E: Treatment-related change versus tumor
recurrence in high-grade gliomas: a diagnostic conundrum - use of
dynamic susceptibility contrast-enhanced (DSC) perfusion MRI. AJR
Am J Roentgenol. 198:19–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Emblem KE, Mouridsen K, Bjornerud A,
Farrar CT, Jennings D, Borra RJ, Wen PY, Ivy P, Batchelor TT, Rosen
BR, Jain RK and Sorensen AG: Vessel architectural imaging
identifies cancer patient responders to anti-angiogenic therapy.
Nat Med. 19:1178–1183. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Lou J, Gasche Y, Zheng L, Giroud C, Morel
P, Clements J, Ythier A and Grau GE: Interferon-β inhibits
activated leukocyte migration through human brain microvascular
endothelial cell monolayer. Lab Invest. 79:1015–1025. 1999.
|
|
44
|
Kallmann B, Hummel V, Lindenlaub T,
Ruprecht K, Toyka KV and Rieckmann P: Cytokine-induced modulation
of cellular adhesion to human cerebral endothelial cells is
mediated by soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1. Brain.
123:687–697. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Cindrova-Davies T, Sanders DA, Burton GJ
and Charnock-Jones DS: Soluble FLT1 sensitizes endothelial cells to
inflammatory cytokines by antagonizing VEGF receptor-mediated
signalling. Cardiovasc Res. 89:671–679. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Goel S, Wong AH and Jain RK: Vascular
normalization as a therapeutic strategy for malignant and
nonmalignant disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med. 2:a0064862012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Boucher E, Unemori B, Seed B and Jain RK:
Relaxin increases the transport of large molecules in high collagen
content tumors. Proc Am Assoc Cancer Res. 41:abs 642000.
|