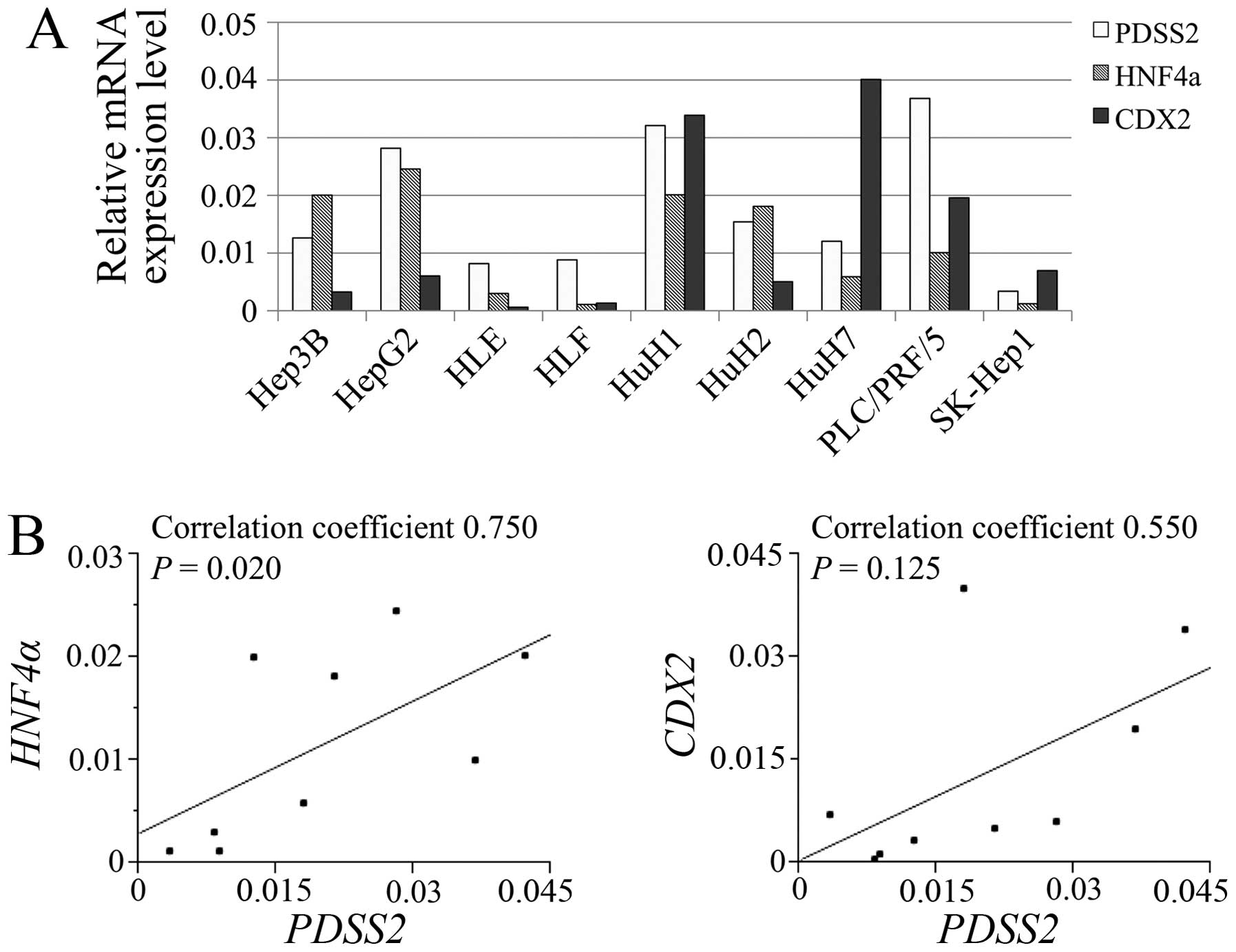
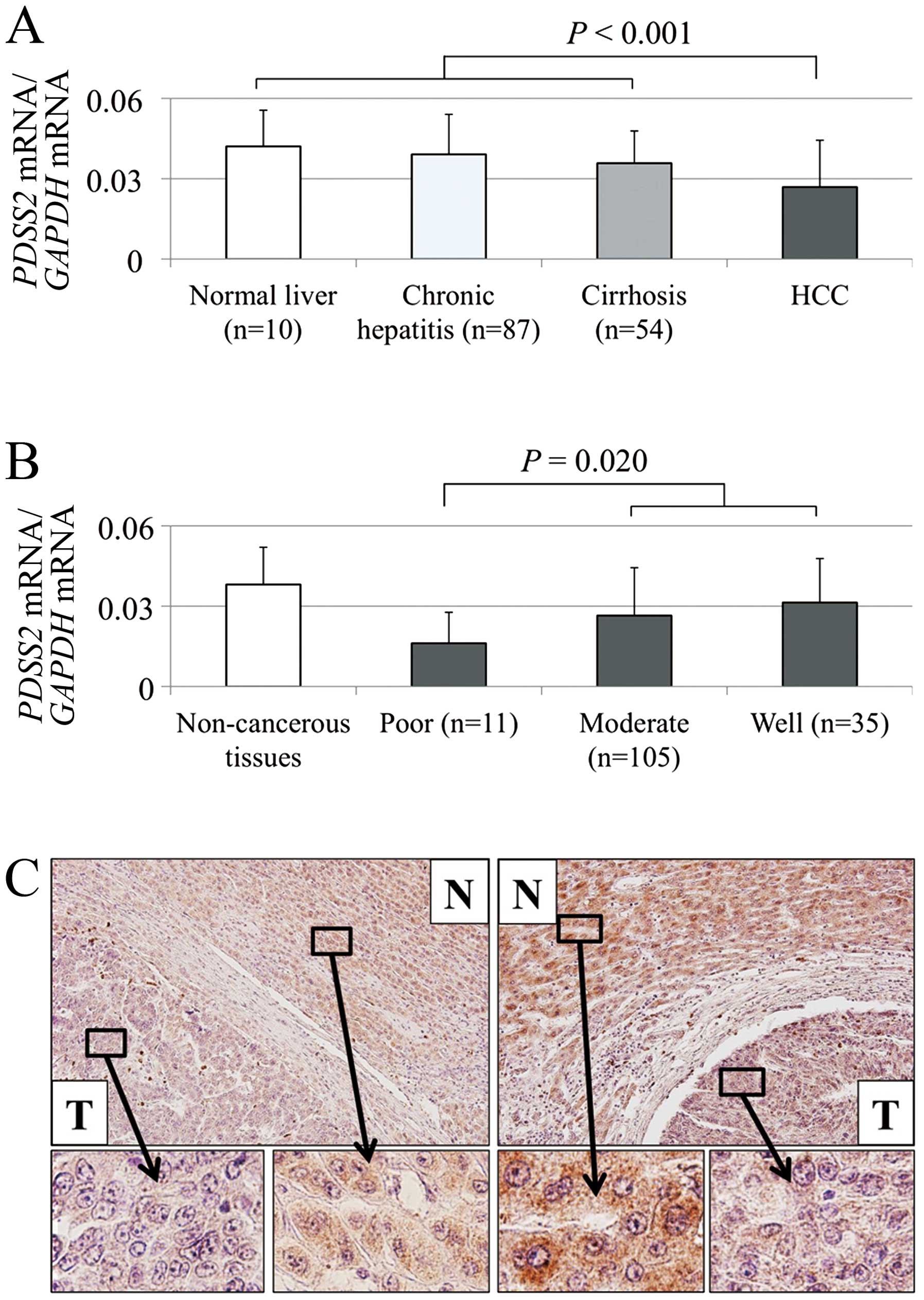
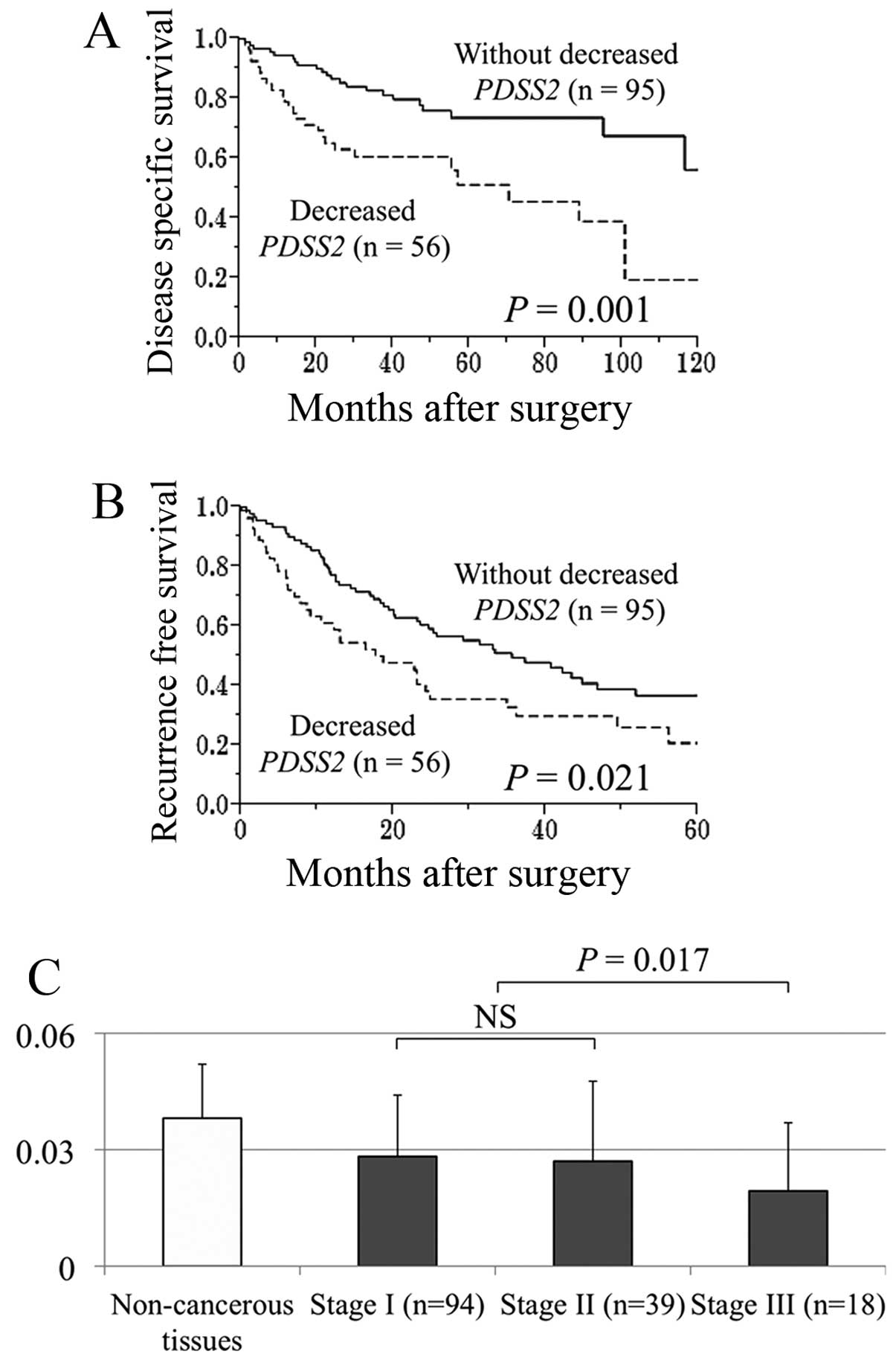
|
1
|
Minguez B and Lachenmayer A: Diagnostic
and prognostic molecular markers in hepatocellular carcinoma. Dis
Markers. 31:181–190. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Oya H, et al:
Downregulation of DENND2D by promoter hypermethylation is
associated with early recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J
Oncol. 44:44–52. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Shiraha H, Yamamoto K and Namba M: Human
hepatocyte carcinogenesis (review). Int J Oncol. 42:1133–1138.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
El-Serag HB: Hepatocellular carcinoma:
recent trends in the United States. Gastroenterology. 127:S27–S34.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Nishikawa Y, et al:
Correlations of the expression of vascular endothelial growth
factor B and its isoforms in hepatocellular carcinoma with
clinico-pathological parameters. J Surg Oncol. 98:190–196. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Llovet JM, Burroughs A and Bruix J:
Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 362:1907–1917. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Okamura Y, et al:
Promoter hypermethylation of fibulin 1 gene is associated with
tumor progression in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mol Carcinog.
50:571–579. 2011. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
El-Serag HB and Mason AC: Rising incidence
of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States. N Engl J Med.
340:745–750. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Villanueva A, Newell P, Chiang DY,
Friedman SL and Llovet JM: Genomics and signaling pathways in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Semin Liver Dis. 27:55–76. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Miki D, Ochi H, Hayes CN, Aikata H and
Chayama K: Hepatocellular carcinoma: towards personalized medicine.
Cancer Sci. 103:846–850. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kanda M, Nomoto S, Okamura Y, et al:
Detection of metallothionein 1G as a methylated tumor suppressor
gene in human hepatocellular carcinoma using a novel method of
double combination array analysis. Int J Oncol. 35:477–483.
2009.
|
|
14
|
Herath NI, Leggett BA and MacDonald GA:
Review of genetic and epigenetic alterations in
hepatocarcinogenesis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:15–21. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Saiki R, Nagata A, Kainou T, Matsuda H and
Kawamukai M: Characterization of solanesyl and decaprenyl
diphosphate synthases in mice and humans. FEBS J. 272:5606–5622.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Fung JM, Smith R, Brown MA, et al:
Identification and characterization of a novel melanoma tumor
suppressor gene on human chromosome 6q21. Clin Cancer Res.
15:797–803. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Turunen M, Olsson J and Dallner G:
Metabolism and function of coenzyme Q. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1660:171–199. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Quinzii CM, DiMauro S and Hirano M: Human
coenzyme Q10 deficiency. Neurochem Res. 32:723–727. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
DiMauro S, Quinzii CM and Hirano M:
Mutations in coenzyme Q10 biosynthetic genes. J Clin Invest.
117:587–589. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Chen P, Yu J, Knecht J and Chen Q:
Decrease of PDSS2 expression, a novel tumor suppressor, in
non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Epidemiol. 37:166–171. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Takami H, Kanda M, Oya H, et al:
Evaluation of MAGE-D4 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma in
Japanese patients. J Surg Oncol. 108:557–562. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Sobin LH, Gospodarowicz MK and Wittekind
Ch: International Union Against Cancer: TNM Classification of
Malignant Tumors. 7th edition. Wiley-Blackwell; New York: 2009
|
|
23
|
Oya H, Kanda M, Takami H, et al:
Overexpression of melanomaassociated antigen D4 is an independent
prognostic factor in squamous cell carcinoma of the esophagus. Dis
Esophagus. Oct 2–2013.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Kanda M, Shimizu D, Nomoto S, et al:
Prognostic impact of expression and methylation status of DENN/MADD
domaincontaining protein 2D in gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. Apr
3–2014.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
25
|
Shimizu D, Kanda M, Nomoto S, et al:
Identification of intragenic methylation in the TU SC1 gene as a
novel prognostic marker of hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Rep.
31:1305–1313. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takai D and Jones PA: The CpG island
searcher: a new WWW resource. In Silico Biol. 3:235–240.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hibino S, Kanda M, Oya H, et al: Reduced
expression of DENND2D through promoter hypermethylation is an
adverse prognostic factor in squamous cell carcinoma of the
esophagus. Oncol Rep. 31:693–700. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Saandi T, Baraille F, Derbal-Wolfrom L, et
al: Regulation of the tumor suppressor homeogene Cdx2 by HNF4alpha
in intestinal cancer. Oncogene. 32:3782–3788. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kanda M, Shimizu D, Nomoto S, et al:
Clinical significance of expression and epigenetic profiling of TU
SC1 in gastric cancer. J Surg Oncol. 110:136–144. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Nagai H, Pineau P, Tiollais P, Buendia MA
and Dejean A: Comprehensive allelotyping of human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Oncogene. 14:2927–2933. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li SP, Wang HY, Li JQ, et al: Genome-wide
analyses on loss of heterozygosity in hepatocellular carcinoma in
Southern China. J Hepatol. 34:840–849. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Walesky C, Edwards G, Borude P, et al:
Hepatocyte nuclear factor 4 alpha deletion promotes
diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma in rodents.
Hepatology. 57:2480–2490. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Ehehalt F, Rummele P, Kersting S, et al:
Hepatocyte nuclear factor (HNF) 4alpha expression distinguishes
ampullary cancer subtypes and prognosis after resection. Ann Surg.
254:302–310. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|