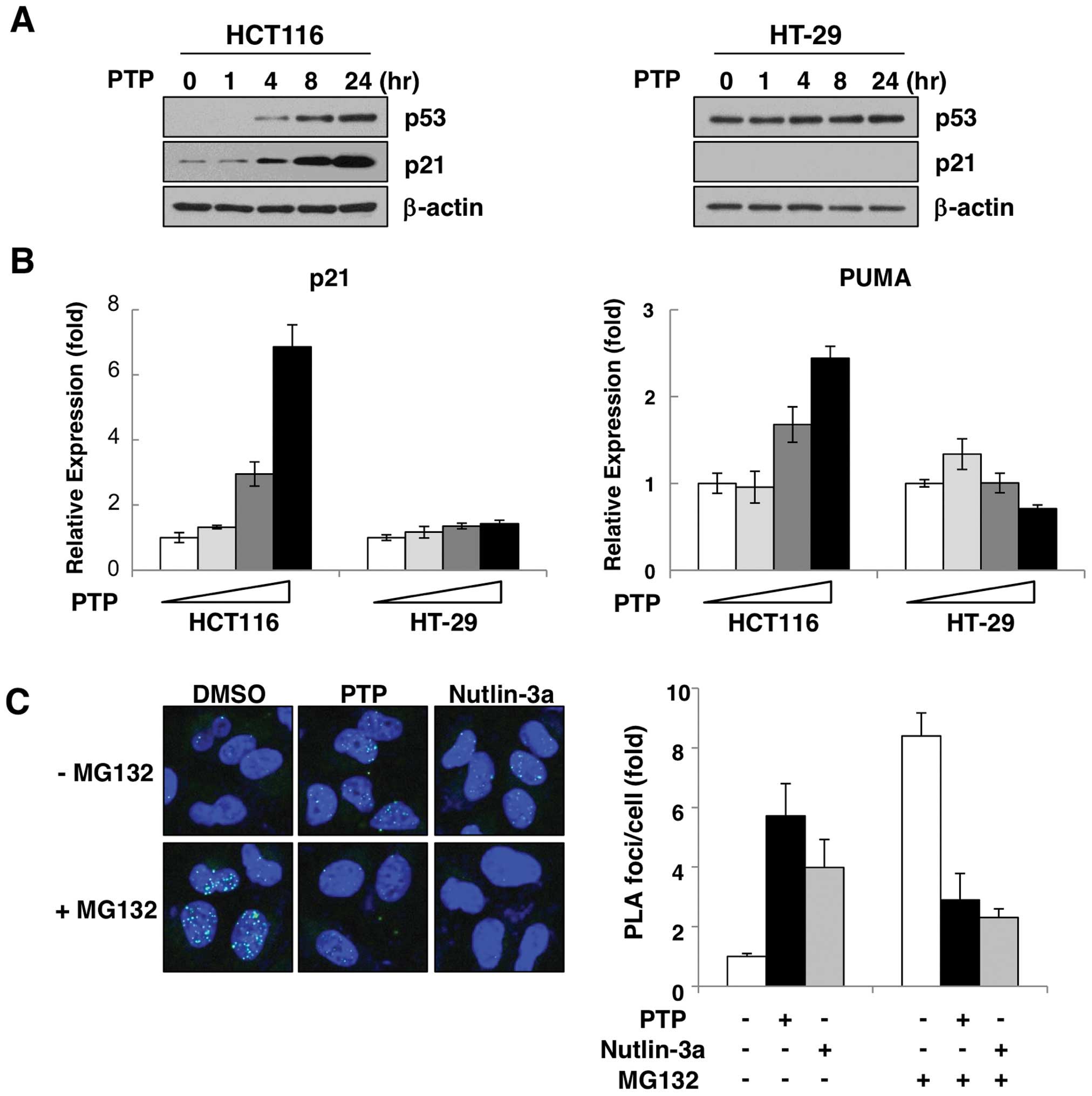
|
1
|
Vousden KH: p53: Death Star. Cell.
103:691–694. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Vogelstein B, Lane D and Levine AJ:
Surfing the p53 network. Nature. 408:307–310. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Juven T, Barak Y, Zauberman A, George DL
and Oren M: Wild type p53 can mediate sequence-specific
transactivation of an internal promoter within the mdm2 gene.
Oncogene. 8:3411–3416. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Barak Y, Juven T, Haffner R and Oren M:
mdm2 expression is induced by wild type p53 activity. EMBO J.
12:461–468. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Miyashita T, Harigai M, Hanada M and Reed
JC: Identification of a p53-dependent negative response element in
the bcl-2 gene. Cancer Res. 54:3131–3135. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Banin S, Moyal L, Shieh SY, Anderson CW,
Chessa L, Smorodinsky NI, Prives C, Reiss Y, Shiloh Y and Ziv Y:
Enhanced phosphorylation of p53 by ATM in response to DNA damage.
Science. 281:1674–1677. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Tibbetts RS, Brumbaugh KM, Williams JM,
Sarkaria JN, Cliby WA, Shieh SY, Taya Y, Prives C and Abraham RT: A
role for ATR in the DNA damage-induced phosphorylation of p53.
Genes Dev. 13:152–157. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bykov VJ, Issaeva N, Shilov A, Hultcrantz
M, Pugacheva E, Chumakov P, Bergman J, Wiman KG and Selivanova G:
Restoration of the tumor suppressor function to mutant p53 by a
low-molecular-weight compound. Nat Med. 8:282–288. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Miyachi M, Kakazu N, Yagyu S, Katsumi Y,
Tsubai-Shimizu S, Kikuchi K, Tsuchiya K, Iehara T and Hosoi H:
Restoration of p53 pathway by nutlin-3 induces cell cycle arrest
and apoptosis in human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Clin Cancer Res.
15:4077–4084. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Dai F, Chen Y, Song Y, Huang L, Zhai D,
Dong Y, Lai L, Zhang T, Li D, Pang X, Liu M and Yi Z: A natural
small molecule Harmine inhibits angiogenesis and suppresses tumour
growth through activation of p53 in endothelial cells. PLoS One.
7:e521622012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhang Q, Zeng SX, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Ding
D, Ye Q, Meroueh SO and Lu H: A small molecule Inauhzin inhibits
SIRT1 activity and suppresses tumour growth through activation of
p53. EMBO Mol Med. 4:298–312. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jain KS, Chitre TS, Miniyar PB, Kathiravan
MK, Bendre VS, Veer VS, Shahane SR and Shishoo CJ: Biological and
medicinal significance of pyrimidines. Curr Sci. 90:793–803.
2006.
|
|
13
|
Zhang N, Ayral-Kaloustian S, Nguyen T,
Hernandez R and Beyer C: 2-Cyanoaminopyrimidines as a class of
antitumor agents that promote tubulin polymerization. Bioorg Med
Chem Lett. 17:3003–3005. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Cocco MT, Congiu C, Lilliu V and Onnis V:
Synthesis and in vitro antitumoral activity of new
hyrazinopyriminide-5-carbonitrile derivatives. Bioorg Med Chem.
14:366–372. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cocco MT, Congiu C, Lilliu V and Onnis V:
Synthesis of new N-(2-(trifluoromethyl)pyridine-yl)anthranilic acid
derivatives and their evaluation as anticancer agents. Bioorg Med
Chem Lett. 14:5787–5791. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Longley DB, Harkin DP and Johnston PG:
5-Fluorouracil: mechanisms of action and clinical stratagies. Nat
Rev Cancer. 3:330–338. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lim MJ, Ahn JY, Han Y, Yu CH, Kim MH, Lee
SL, Lim DS and Song JY: Acriflavine enhances radiosensitivity of
colon cancer cells through endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated
apoptosis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 44:1214–1222. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Harris SL and Levine AJ: The p53 pathway:
positive and negative feedback loops. Oncogene. 24:2899–2908. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Haupt Y, Maya R, Kazaz A and Oren M: Mdm2
promotes the rapid degradation of p53. Nature. 387:296–299. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Demidenko ZN, Korotchkina LG, Gudkov AV
and Blagosklonny MV: Paradoxical suppression of cellular senescence
by p53. Proc Natl Acd Sci USA. 107:9660–9664. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hofseth LJ, Hussain SP and Harris CC: p53:
25 years after its discovery. Trends Pharmacol. 25:177–181.
2004.
|
|
22
|
Korotchkina LG, Leontieva OV, Bukreeva EI,
Demidenko ZN, Gudkov AV and Blagosklonny MV: The choice between
p53-induced senescence and quiescence is determined in part by the
mTOR pathway. Aging (Albany, NY). 2:344–352. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Melnikova VO, Santamaria AB, Bolshakov SV
and Ananthaswamy HN: Mutant p53 is constitutively phosphorylated at
Serine 15 in UV-induced mouse skin tumors: involvement of ERK1/2
MAP kinase. Oncogene. 22:5958–5966. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Persons DL, Yazlovitskaya EM and Pelling
JC: Effect of extra-cellular signal-regulated kinase on p53
accumulation in response to cisplatin. J Biol Chem.
275:35778–35785. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
She QB, Chen N and Dong Z: ERKs and p38
kinase phosphorylate p53 protein at serine 15 in response to UV
radiation. J Biol Chem. 275:20444–20449. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Kubbutat MH, Jones SN and Vousden KH:
Regulation of p53 stability by Mdm2. Nature. 387:299–303. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Maltzman W and Czyzyk L: UV irradiation
stimulates levels of p53 cellular tumor antigen in nontransformed
mouse cells. Mol Cell Biol. 4:1689–1694. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ashcroft M, Taya Y and Vousden KH: Stress
signals utilize multiple pathways to stabilize p53. Mol Cell Biol.
20:3224–3233. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ito A, Lai CH, Zhao X, Saito S, Hamilton
MH, Appella E and Yao TP: p300/CBP-mediated p53 acetylation is
commonly induced by p53-activating agents and inhibited by MDM2.
EMBO J. 20:1331–1340. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Kuroda T, Murayama A, Katagiri N, Ohta Y,
Fujita E, Masumoto H, Ema M, Takahashi S, Kimura K and Yanagisawa
J: RNA content in the nucleolus alters p53 acetylation via MYBBP1A.
EMBO J. 30:1054–1066. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Barneda-Zahonero B and Parra M: Histone
deacetylases and cancer. Mol Oncol. 6:579–589. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Vaziri H, Dessain SK, Eaton EN, Imai SI,
Frye RA, Pandita TK, Guarente L and Weinberg RA:
hSIR2SIRT1 functions as an NAD-dependent p53
deacetylation. Cell. 107:149–159. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|