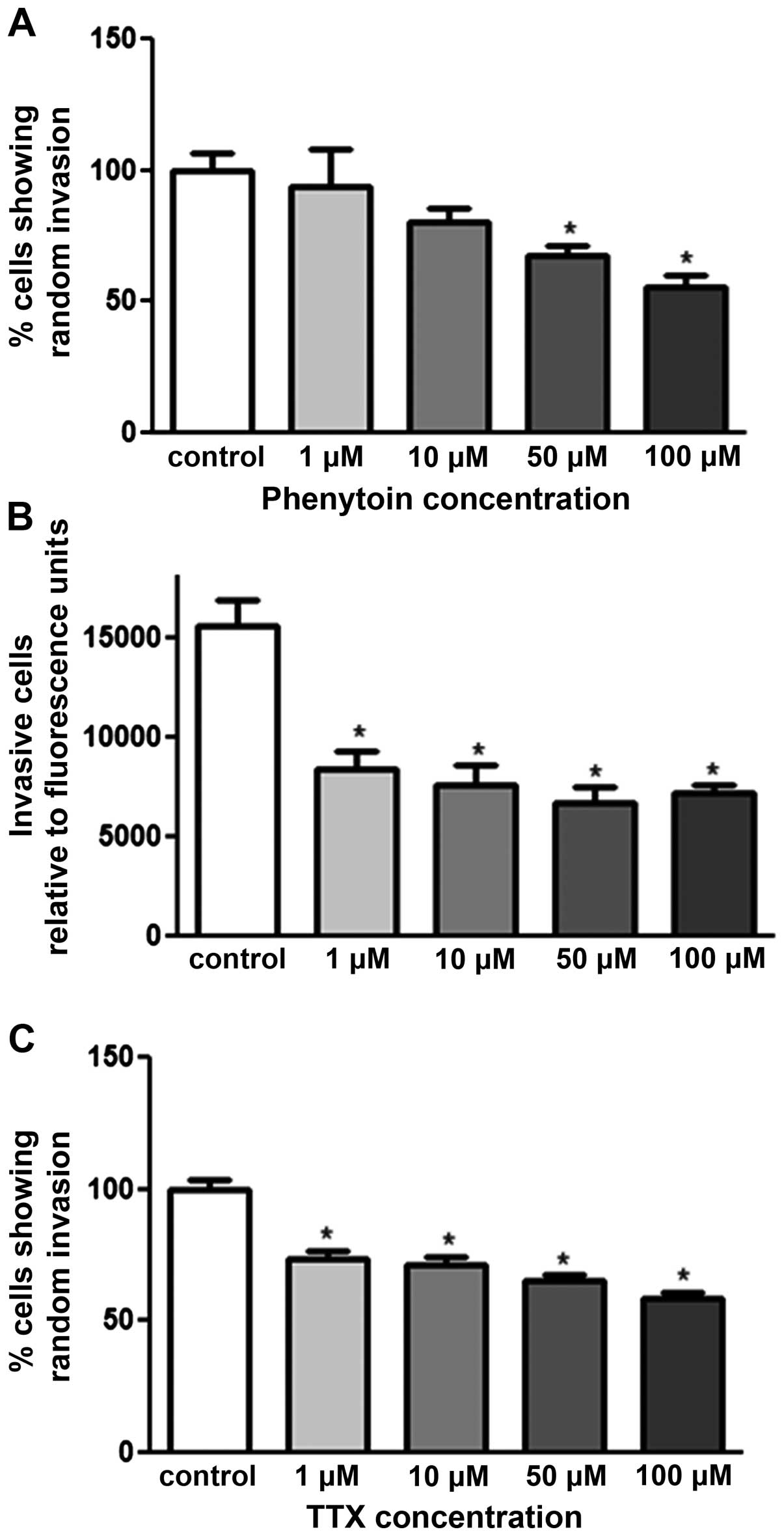
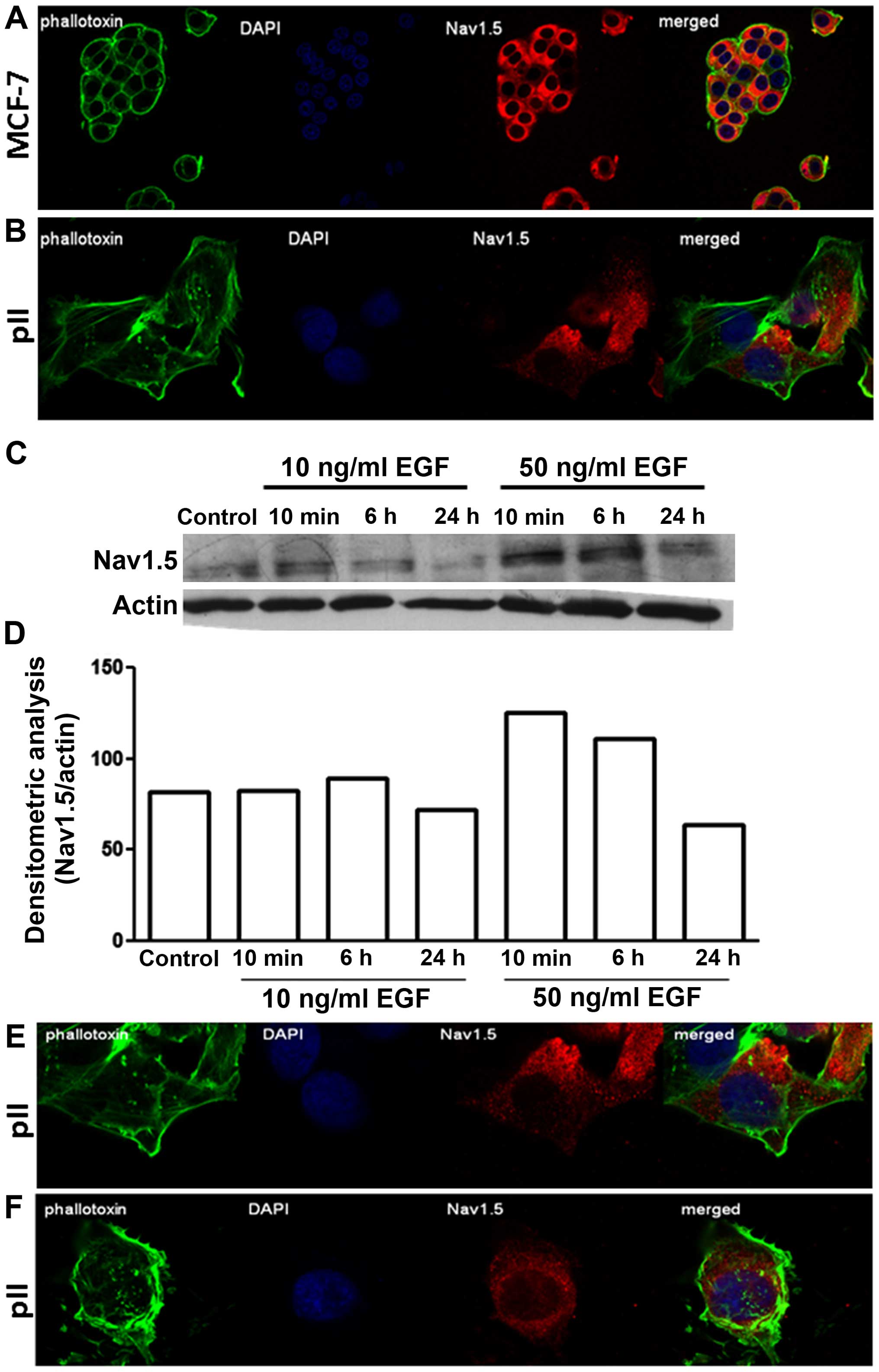
|
1
|
Yang LH, Tseng HS, Lin C, Chen LS, Chen
ST, Kuo SJ and Chen DR: Survival benefit of tamoxifen in estrogen
receptor-negative and progesterone receptor-positive low grade
breast cancer patients. J Breast Cancer. 15:288–295. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Al Saleh S, Sharaf LH and Luqmani YA:
Signalling pathways involved in endocrine resistance in breast
cancer and associations with epithelial to mesenchymal transition
(Review). Int J Oncol. 38:1197–1217. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yang M, Kozminski DJ, Wold LA, Modak R,
Calhoun JD, Isom LL and Brackenbury WJ: Therapeutic potential for
phenytoin: Targeting Na(v)1.5 sodium channels to reduce migration
and invasion in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat.
134:603–615. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Onkal R and Djamgoz MBA: Molecular
pharmacology of voltage-gated sodium channel expression in
metastatic disease: Clinical potential of neonatal Nav1.5 in breast
cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 625:206–219. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chioni A-M, Brackenbury WJ, Calhoun JD,
Isom LL and Djamgoz MB: A novel adhesion molecule in human breast
cancer cells: Voltage-gated Na+ channel beta1 subunit.
Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 41:1216–1227. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
6
|
Brackenbury WJ, Djamgoz MBA and Isom LL:
An emerging role for voltage-gated Na+ channels in
cellular migration: Regulation of central nervous system
development and potentiation of invasive cancers. Neuroscientist.
14:571–583. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Brackenbury WJ, Davis TH, Chen C, Slat EA,
Detrow MJ, Dickendesher TL, Ranscht B and Isom LL: Voltage-gated
Na+ channel beta1 subunit-mediated neurite outgrowth
requires Fyn kinase and contributes to postnatal CNS development in
vivo. J Neurosci. 28:3246–3256. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Gillet L, Roger S, Bougnoux P, Le Guennec
J-Y and Besson P: Beneficial effects of omega-3 long-chain fatty
acids in breast cancer and cardiovascular diseases: Voltage-gated
sodium channels as a common feature? Biochimie. 93:4–6. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hernández-Plata E: Role of the
voltage-gated sodium channels in the metastatic capacity of cancer
cells. Rev Invest Clin. 64:567–575. 2012.(In Spanish).
|
|
10
|
Brackenbury WJ and Isom LL: Voltage-gated
Na channels: Potential for β subunits as therapeutic targets.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 12:1191–1203. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Roger S, Potier M, Vandier C, Besson P and
Le Guennec J-Y: Voltage-gated sodium channels: New targets in
cancer therapy? Curr Pharm Des. 12:3681–3695. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Potier M, Joulin V, Roger S, Besson P,
Jourdan ML, Leguennec JY, Bougnoux P and Vandier C: Identification
of SK3 channel as a new mediator of breast cancer cell migration.
Mol Cancer Ther. 5:2946–2953. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Goldin AL: Resurgence of sodium channel
research. Annu Rev Physiol. 63:871–894. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Goldin AL, Barchi RL, Caldwell JH, Hofmann
F, Howe JR, Hunter JC, Kallen RG, Mandel G, Meisler MH, Netter YB,
et al: Nomenclature of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron.
28:365–368. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Hernández-Plata E, Ortiz CS,
Marquina-Castillo B, Medina-Martinez I, Alfaro A, Berumen J, Rivera
M and Gomora JC: Overexpression of NaV 1.6 channels is associated
with the invasion capacity of human cervical cancer. Int J Cancer.
130:2013–2023. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Yildirim S, Altun S, Gumushan H, Patel A
and Djamgoz MBA: Voltage-gated sodium channel activity promotes
prostate cancer metastasis in vivo. Cancer Lett. 323:58–61. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Isom LL and Catterall WA: Na+
channel subunits and Ig domains. Nature. 383:307–308. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Diss JK, Archer SN, Hirano J, Fraser SP
and Djamgoz MB: Expression profiles of voltage-gated Na(+) channel
alpha-subunit genes in rat and human prostate cancer cell lines.
Prostate. 48:165–178. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Djamgoz MB and Onkal R: Persistent current
blockers of voltage-gated sodium channels: A clinical opportunity
for controlling metastatic disease. Recent Patents Anticancer Drug
Discov. 8:66–84. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Laniado ME, Lalani EN, Fraser SP, Grimes
JA, Bhangal G, Djamgoz MB and Abel PD: Expression and functional
analysis of voltage-activated Na+ channels in human
prostate cancer cell lines and their contribution to invasion in
vitro. Am J Pathol. 150:1213–1221. 1997.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Nelson M, Millican-Slater R, Forrest LC
and Brackenbury WJ: The sodium channel β1 subunit mediates
outgrowth of neurite-like processes on breast cancer cells and
promotes tumour growth and metastasis. Int J Cancer. 135:2338–2351.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Fraser SP, Diss JKJ, Chioni A-M, Mycielska
ME, Pan H, Yamaci RF, Pani F, Siwy Z, Krasowska M, Grzywna Z, et
al: Voltage-gated sodium channel expression and potentiation of
human breast cancer metastasis. Clin Cancer Res. 11:5381–5389.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Brisson L, Gillet L, Calaghan S, Besson P,
Le Guennec JY, Roger S and Gore J: Na(V)1.5 enhances breast cancer
cell invasiveness by increasing NHE1-dependent H(+) efflux in
caveolae. Oncogene. 30:2070–2076. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gillet L, Roger S, Besson P, Lecaille F,
Gore J, Bougnoux P, Lalmanach G and Le Guennec JY: Voltage-gated
sodium channel Activity promotes cysteine cathepsin-dependent
invasiveness and colony growth of human cancer cells. J Biol Chem.
284:8680–8691. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Luqmani YA, Al Azmi A, Al Bader M, Abraham
G and El Zawahri M: Modification of gene expression induced by
siRNA targeting of estrogen receptor alpha in MCF7 human breast
cancer cells. Int J Oncol. 34:231–242. 2009.
|
|
26
|
Khajah MA, Al Saleh S, Mathew PM and
Luqmani YA: Differential effect of growth factors on invasion and
proliferation of endocrine-resistant breast cancer cells. PLoS One.
7:e418472012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Al Saleh S, Al Mulla F and Luqmani YA:
Estrogen receptor silencing induces epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in human breast cancer cells. PLoS One. 6:e206102011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brackenbury WJ, Calhoun JD, Chen C,
Miyazaki H, Nukina N, Oyama F, Ranscht B and Isom LL: Functional
reciprocity between Na+ channel Nav1.6 and beta1
subunits in the coordinated regulation of excitability and neurite
outgrowth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 107:2283–2288. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Brackenbury WJ and Djamgoz MBA:
Activity-dependent regulation of voltage-gated Na+
channel expression in Mat-LyLu rat prostate cancer cell line. J
Physiol. 573:343–356. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
House CD, Vaske CJ, Schwartz AM, Obias V,
Frank B, Luu T, Sarvazyan N, Irby R, Strausberg RL, Hales TG, et
al: Voltage-gated Na+ channel SCN5A is a key regulator
of a gene transcriptional network that controls colon cancer
invasion. Cancer Res. 70:6957–6967. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
House CD, Wang BD, Ceniccola K, Williams
R, Simaan M, Olender J, Patel V, Baptista-Hon DT, Annunziata CM,
Gutkind JS, et al: Voltage-gated Na+ channel activity
increases colon cancer transcriptional activity and invasion via
persistent MAPK signaling. Sci Rep. 5:115412015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Carrithers MD, Chatterjee G, Carrithers
LM, Offoha R, Iheagwara U, Rahner C, Graham M and Waxman SG:
Regulation of podosome formation in macrophages by a splice variant
of the sodium channel SCN8A. J Biol Chem. 284:8114–8126. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Brisson L, Driffort V, Benoist L, Poet M,
Counillon L, Antelmi E, Rubino R, Besson P, Labbal F, Chevalier S,
et al: NaV1.5 Na(+) channels allosterically regulate the NHE-1
exchanger and promote the activity of breast cancer cell
invadopodia. J Cell Sci. 126:4835–4842. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Besson P, Driffort V, Bon É, Gradek F,
Chevalier S and Roger S: How do voltage-gated sodium channels
enhance migration and invasiveness in cancer cells? Biochim Biophys
Acta. 1848.2493–2501. 2015.
|
|
35
|
Brackenbury WJ: Voltage-gated sodium
channels and metastatic disease. Channels (Austin). 6:352–361.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Maness PF and Schachner M: Neural
recognition molecules of the immunoglobulin superfamily: Signaling
transducers of axon guidance and neuronal migration. Nat Neurosci.
10:19–26. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Ding Y, Brackenbury WJ, Onganer PU,
Montano X, Porter LM, Bates LF and Djamgoz MB: Epidermal growth
factor upregulates motility of Mat-LyLu rat prostate cancer cells
partially via voltage-gated Na+ channel activity. J Cell
Physiol. 215:77–81. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Mantegazza M, Curia G, Biagini G, Ragsdale
DS and Avoli M: Voltage-gated sodium channels as therapeutic
targets in epilepsy and other neurological disorders. Lancet
Neurol. 9:413–424. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Hille B: Ionic channels of excitable
membranes. Cell. 69:5791992. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Crill WE: Persistent sodium current in
mammalian central neurons. Annu Rev Physiol. 58:349–362. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Ju YK, Saint DA and Gage PW: Hypoxia
increases persistent sodium current in rat ventricular myocytes. J
Physiol. 497:337–347. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kunzelmann K: Ion channels and cancer. J
Membr Biol. 205:159–173. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Turnbull DM, Rawlins MD, Weightman D and
Chadwick DW: ‘Therapeutic’ serum concentration of phenytoin: The
influence of seizure type. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry.
47:231–234. 1984. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Nelson M, Yang M, Dowle AA, Thomas JR and
Brackenbury WJ: The sodium channel-blocking antiepileptic drug
phenytoin inhibits breast tumour growth and metastasis. Mol Cancer.
14:132015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Brackenbury WJ, Chioni A-M, Diss JKJ and
Djamgoz MBA: The neonatal splice variant of Nav1.5 potentiates in
vitro invasive behaviour of MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells.
Breast Cancer Res Treat. 101:149–160. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
46
|
Zucker S, Cao J and Chen WT: Critical
appraisal of the use of matrix metalloproteinase inhibitors in
cancer treatment. Oncogene. 19:6642–6650. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
47
|
Gialeli C, Theocharis AD and Karamanos NK:
Roles of matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression and their
pharmacological targeting. FEBS J. 278:16–27. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
48
|
Sekton B: Matrix metalloproteinases - an
overview. Rev Bras Ter Intensiva. 23:222–227. 2011.
|
|
49
|
Gao R, Wang J, Shen Y, Lei M and Wang Z:
Functional expression of voltage-gated sodium channels Nav1.5 in
human breast cancer cell line MDA-MB-231. J Huazhong Univ Sci
Technolog Med Sci. 29:64–67. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Azuma T, Yamada M, Murakita H, Nishikawa
Y, Kohli Y, Yamamoto K and Hori H: Cathepsin E expressed in
pancreatic cancer. Adv Exp Med Biol. 362:363–366. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Azuma T, Hirai M, Ito S, Yamamoto K,
Taggart RT, Matsuba T, Yasukawa K, Uno K, Hayakumo T and Nakajima
M: Expression of cathepsin E in pancreas: A possible tumor marker
for pancreas, a preliminary report. Int J Cancer. 67:492–497. 1996.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Kawakubo T, Yasukochi A, Toyama T,
Takahashi S, Okamoto K, Tsukuba T, Nakamura S, Ozaki Y, Nishigaki
K, Yamashita H, et al: Repression of cathepsin E expression
increases the risk of mammary carcinogenesis and links to poor
prognosis in breast cancer. Carcinogenesis. 35:714–726. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
53
|
Hagen NA, Fisher KM, Lapointe B, du Souich
P, Chary S, Moulin D, Sellers E and Ngoc AH; Canadian Tetrodotoxin
Study Group. An open-label, multi-dose efficacy and safety study of
intramuscular tetrodotoxin in patients with severe cancer-related
pain. J Pain Symptom Manage. 34:171–182. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
Dib-Hajj SD, Black JA and Waxman SG:
Voltage-gated sodium channels: therapeutic targets for pain. Pain
Med. 10:1260–1269. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Clare JJ: Targeting voltage-gated sodium
channels for pain therapy. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 19:45–62.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
56
|
Busserolles J, Alloui A, Lazdunski M and
Eschalier A: Use of riluzole to treat or prevent the adverse
effects of antineoplastic agents. US Patent 2013/0064775 A1. Filed:
March 2, 2011; issued March 14, 2013.
|
|
57
|
Yip D, Le MN, Chan JLK, Lee JH, Mehnert
JA, Yudd A, Kempf J, Shih WJ, Chen S and Goydos JS: A phase 0 trial
of riluzole in patients with resectable stage III and IV melanoma.
Clin Cancer Res. 15:3896–3902. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Biki B, Mascha E, Moriarty DC, Fitzpatrick
JM, Sessler DI and Buggy DJ: Anesthetic technique for radical
prostatectomy surgery affects cancer recurrence: A retrospective
analysis. Anesthesiology. 109:180–187. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
59
|
Mao L, Lin S and Lin J: The effects of
anesthetics on tumor progression. Int J Physiol Pathophysiol
Pharmacol. 5:1–10. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|