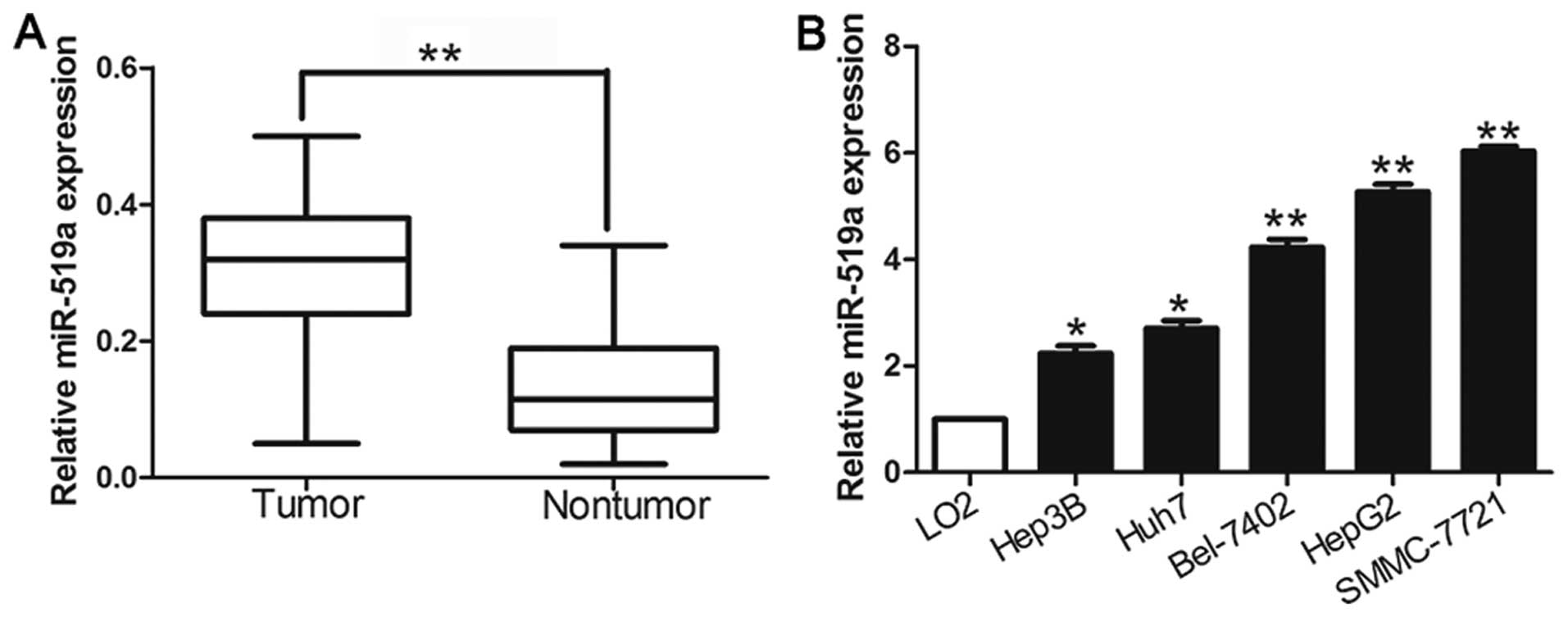
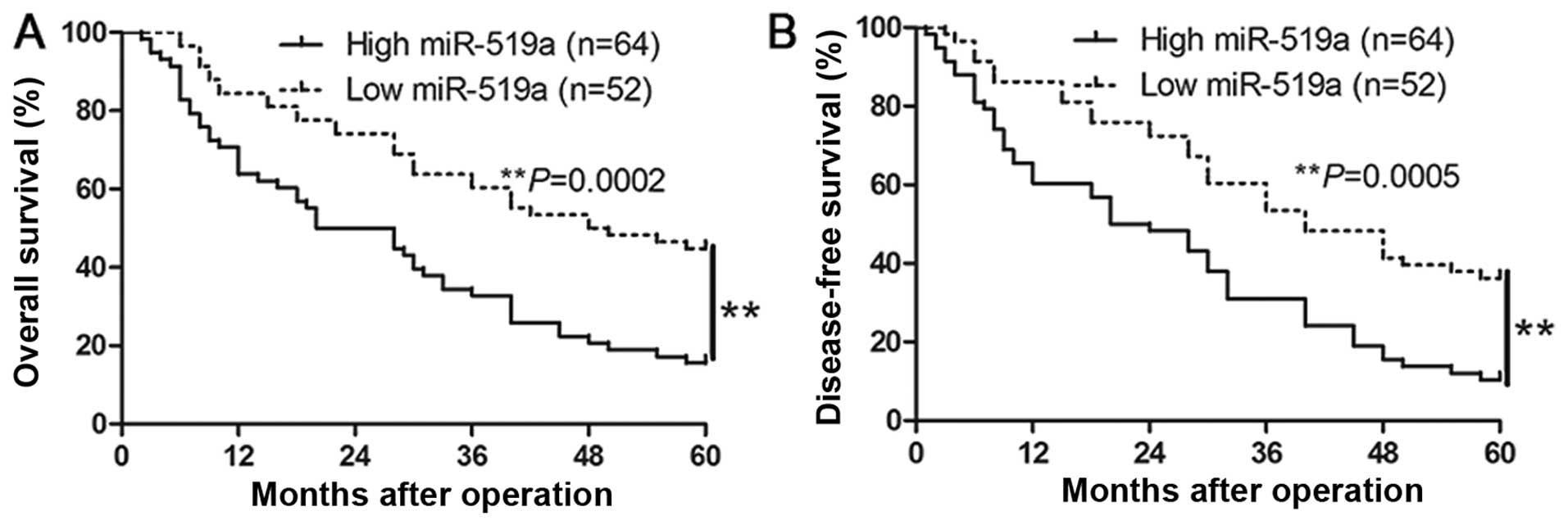
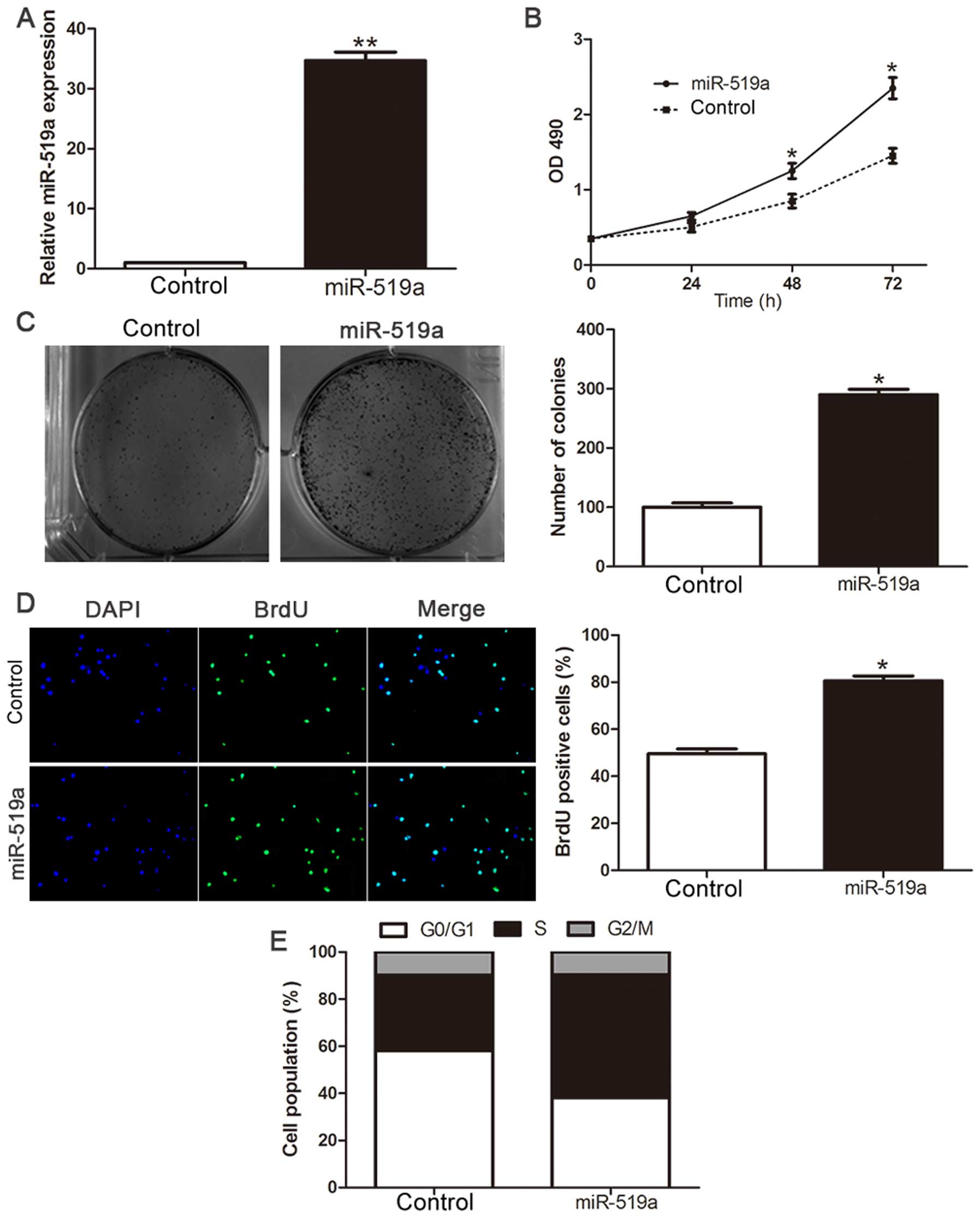
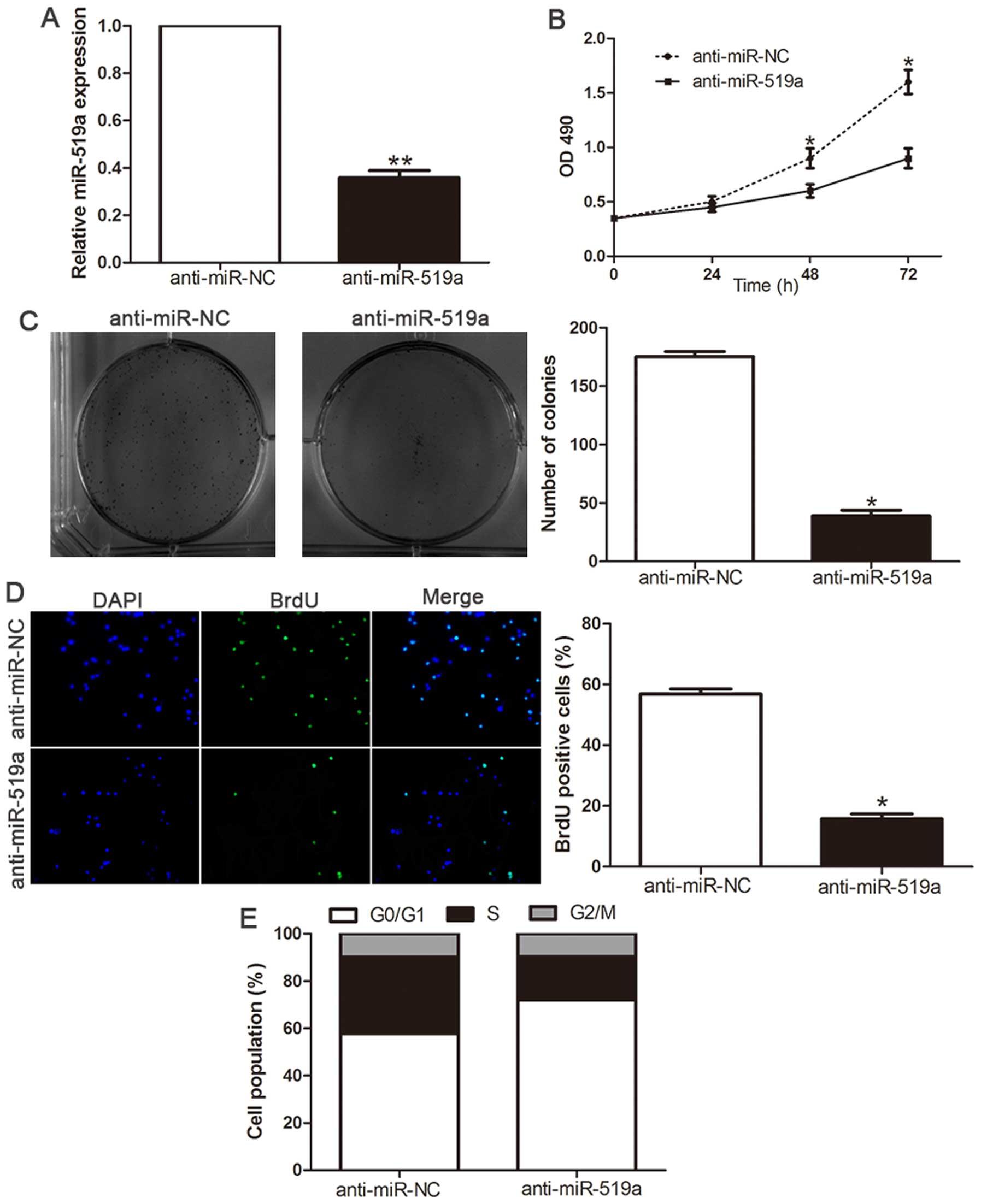
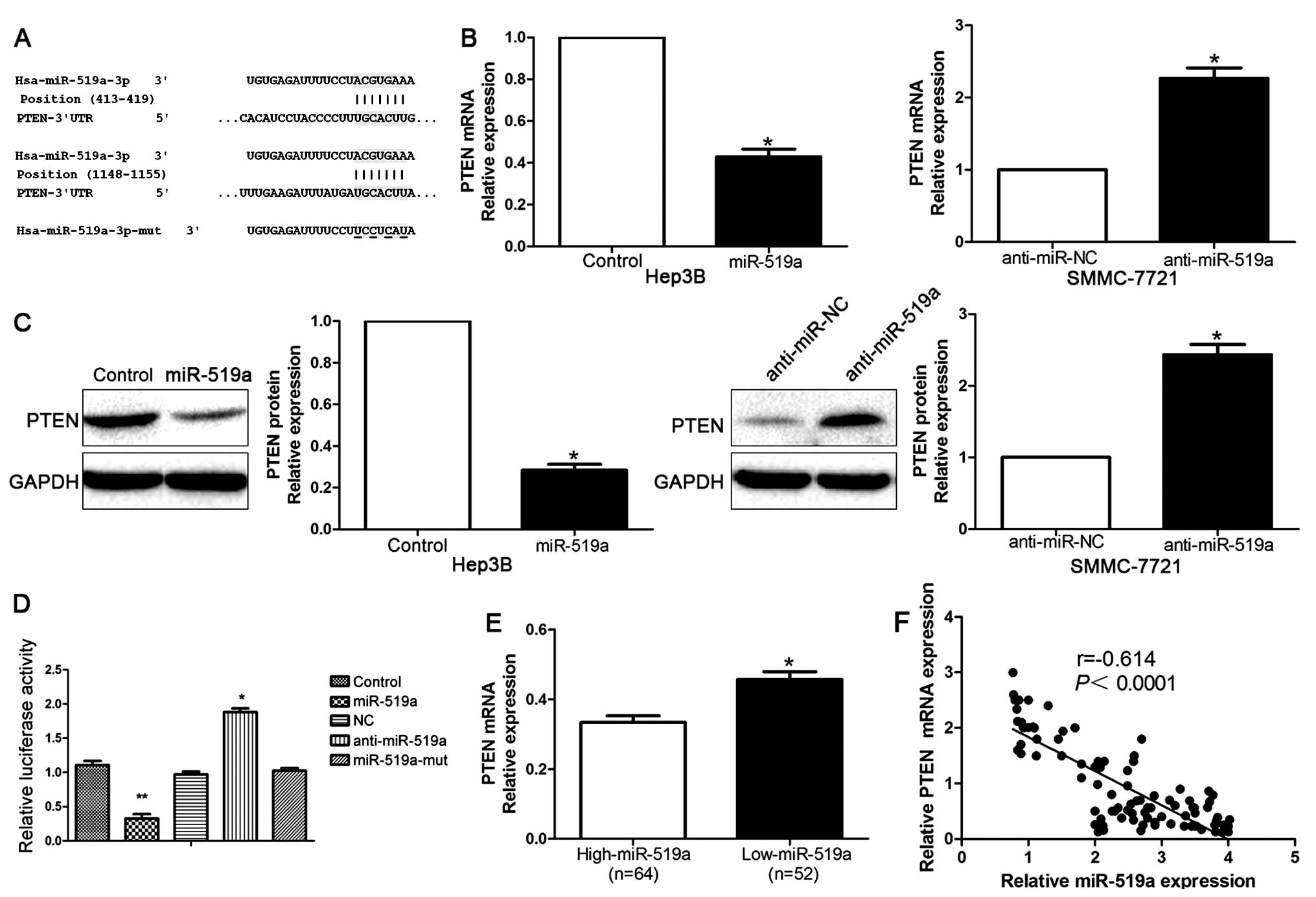
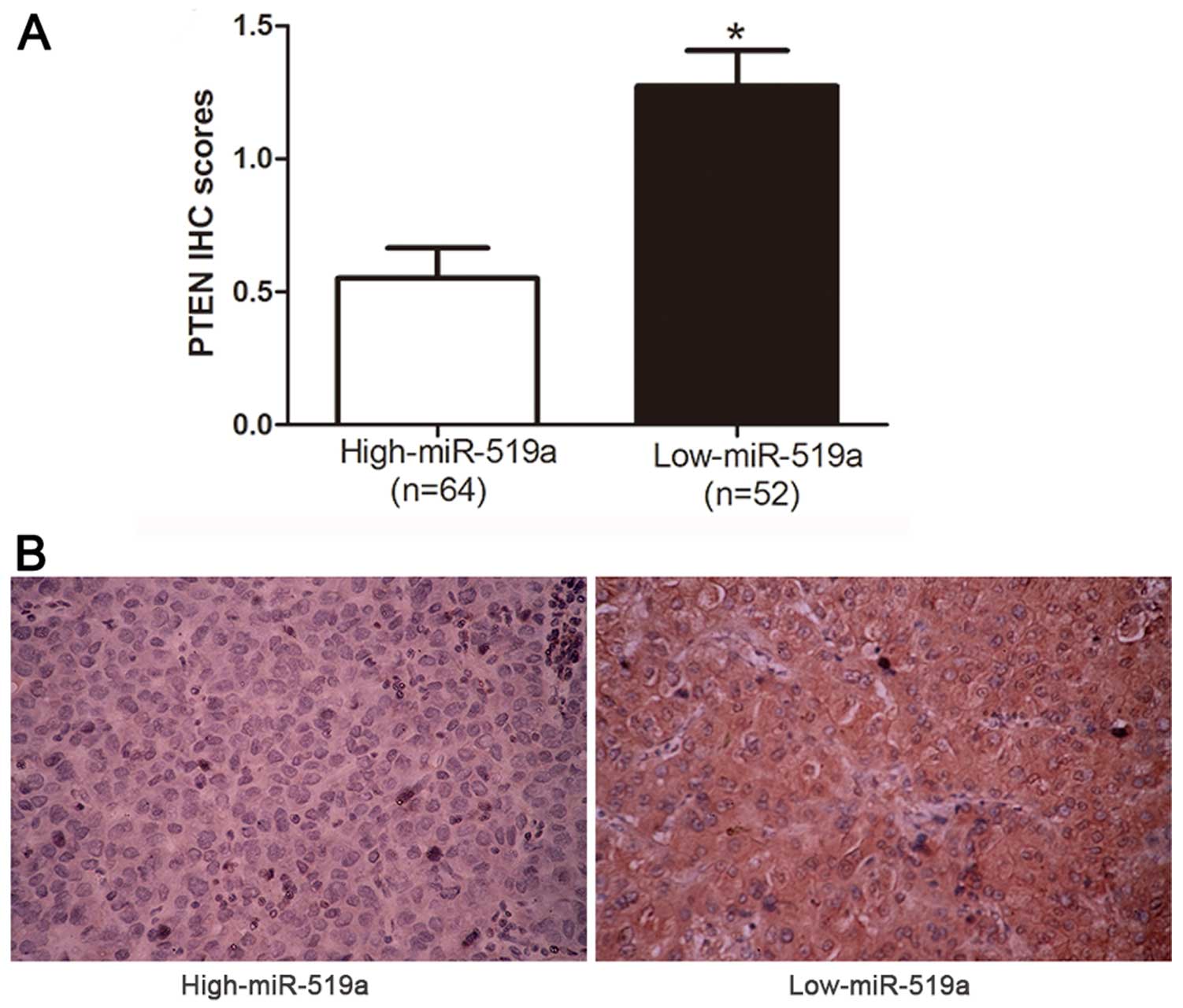
|
1
|
Bosch FX, Ribes J, Díaz M and Cléries R:
Primary liver cancer: Worldwide incidence and trends.
Gastroenterology. 127(Suppl 1): S5–S16. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: Epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Llovet JM, Di Bisceglie AM, Bruix J,
Kramer BS, Lencioni R, Zhu AX, Sherman M, Schwartz M, Lotze M,
Talwalkar J, et al: Panel of Experts in HCC-Design Clinical Trials:
Design and endpoints of clinical trials in hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst. 100:698–711. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Talwalkar JA and Gores GJ: Diagnosis and
staging of hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 127(Suppl
1): S126–S132. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: Genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Rosa A and Brivanlou AH: MicroRNAs in
early vertebrate development. Cell Cycle. 8:3513–3520. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Vasudevan S, Tong Y and Steitz JA:
Switching from repression to activation: microRNAs can up-regulate
translation. Science. 318:1931–1934. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Tu K, Zheng X, Dou C, Li C, Yang W, Yao Y
and Liu Q: MicroRNA-130b promotes cell aggressiveness by inhibiting
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Mol Sci. 15:20486–20499. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Dou C, Wang Y, Li C, Liu Z, Jia Y, Li Q,
Yang W, Yao Y, Liu Q and Tu K: MicroRNA-212 suppresses tumor growth
of human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting FOXA1. Oncotarget.
6:13216–13228. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chang RM, Yang H, Fang F, Xu JF and Yang
LY: MicroRNA-331-3p promotes proliferation and metastasis of
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting PH domain and leucine-rich
repeat protein phosphatase. Hepatology. 60:1251–1263. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Su H, Yang JR, Xu T, Huang J, Xu L, Yuan Y
and Zhuang SM: MicroRNA-101, down-regulated in hepatocellular
carcinoma, promotes apoptosis and suppresses tumorigenicity. Cancer
Res. 69:1135–1142. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yang X, Zhang XF, Lu X, Jia HL, Liang L,
Dong QZ, Ye QH and Qin LX: MicroRNA-26a suppresses angiogenesis in
human hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting hepatocyte growth
factor-cMet pathway. Hepatology. 59:1874–1885. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Santhekadur PK, Das SK, Gredler R, Chen D,
Srivastava J, Robertson C, Baldwin AS Jr, Fisher PB and Sarkar D:
Multi-function protein staphylococcal nuclease domain containing 1
(SND1) promotes tumor angiogenesis in human hepatocellular
carcinoma through novel pathway that involves nuclear factor κB and
miR-221. J Biol Chem. 287:13952–13958. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Kim TH, Kim YK, Kwon Y, Heo JH, Kang H,
Kim G and An HJ: Deregulation of miR-519a, 153, and 485-5p and its
clinicopathological relevance in ovarian epithelial tumours.
Histopathology. 57:734–743. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ward A, Shukla K, Balwierz A, Soons Z,
König R, Sahin O and Wiemann S: MicroRNA-519a is a novel oncomir
conferring tamoxifen resistance by targeting a network of
tumour-suppressor genes in ER+ breast cancer. J Pathol.
233:368–379. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Abdelmohsen K, Srikantan S, Tominaga K,
Kang MJ, Yaniv Y, Martindale JL, Yang X, Park SS, Becker KG,
Subramanian M, et al: Growth inhibition by miR-519 via multiple
p21-inducing pathways. Mol Cell Biol. 32:2530–2548. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Abdelmohsen K, Srikantan S, Kuwano Y and
Gorospe M: miR-519 reduces cell proliferation by lowering
RNA-binding protein HuR levels. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
105:20297–20302. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang W, Dou C, Wang Y, Jia Y, Li C, Zheng
X and Tu K: MicroRNA-92a contributes to tumor growth of human
hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting FBXW7. Oncol Rep.
34:2576–2584. 2015.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jiang L, Wang C, Lei F, Zhang L, Zhang X,
Liu A, Wu G, Zhu J and Song L: miR-93 promotes cell proliferation
in gliomas through activation of PI3K/Akt signaling pathway.
Oncotarget. 6:8286–8299. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in Cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Croce CM and Calin GA: miRNAs, cancer, and
stem cell division. Cell. 122:6–7. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra
E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA,
et al: MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature.
435:834–838. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Marasa BS, Srikantan S, Martindale JL, Kim
MM, Lee EK, Gorospe M and Abdelmohsen K: MicroRNA profiling in
human diploid fibroblasts uncovers miR-519 role in replicative
senescence. Aging (Albany NY). 2:333–343. 2010.
|
|
24
|
Abdelmohsen K, Kim MM, Srikantan S,
Mercken EM, Brennan SE, Wilson GM, Cabo R and Gorospe M: miR-519
suppresses tumor growth by reducing HuR levels. Cell Cycle.
9:1354–1359. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Courtney KD, Corcoran RB and Engelman JA:
The PI3K pathway as drug target in human cancer. J Clin Oncol.
28:1075–1083. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Fresno Vara JA, Casado E, de Castro J,
Cejas P, Belda-Iniesta C and González-Barón M: PI3K/Akt signalling
pathway and cancer. Cancer Treat Rev. 30:193–204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cheng GZ, Park S, Shu S, He L, Kong W,
Zhang W, Yuan Z, Wang LH and Cheng JQ: Advances of AKT pathway in
human oncogenesis and as a target for anti-cancer drug discovery.
Curr Cancer Drug Targets. 8:2–6. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cappellini A, Tabellini G, Zweyer M,
Bortul R, Tazzari PL, Billi AM, Falà F, Cocco L and Martelli AM:
The phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt pathway regulates cell cycle
progression of HL60 human leukemia cells through cytoplasmic
relocalization of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27(Kip1)
and control of cyclin D1 expression. Leukemia. 17:2157–2167. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song MS, Salmena L and Pandolfi PP: The
functions and regulation of the PTEN tumour suppressor. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 13:283–296. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cantley LC and Neel BG: New insights into
tumor suppression: PTEN suppresses tumor formation by restraining
the phosphoinositide 3-kinase/AKT pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
96:4240–4245. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Rahman MA, Kyriazanos ID, Ono T, Yamanoi
A, Kohno H, Tsuchiya M and Nagasue N: Impact of PTEN expression on
the outcome of hepatitis C virus-positive cirrhotic hepatocellular
carcinoma patients: Possible relationship with COX II and inducible
nitric oxide synthase. Int J Cancer. 100:152–157. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Tamura M, Gu J, Tran H and Yamada KM: PTEN
gene and integrin signaling in cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst.
91:1820–1828. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|